- How to use systemctl to manage Linux services
- Restart a service
- Stop and start a service
- Training & certification
- Control whether the service starts with the system
- Mask a service
- Display all subcommands
- The challenge
- Automation advice
- Wrap up
- Управление сервисами в Linux. Команда systemctl
- Список сервисов
- Запуск сервиса
- Останов сервиса
- Перезапуск сервиса
- Автозагрузка сервисов
- Статус сервиса
- Заключение
How to use systemctl to manage Linux services
Suppose you’re making configuration changes to a Linux server. Perhaps you just fired up Vim and made edits to the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file, and it’s time to test your new settings. Now what?
Services such as SSH pull their settings from configuration files during the startup process. To let the service know about changes to the file, you need to restart the service so that it rereads the file. You can use the systemctl command to manage services and control when they start.
Restart a service
After editing the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file, use the systemctl restart command to make the service pick up the new settings:
$ sudo systemctl restart sshdYou can verify the service is running by using the status subcommand:
$ sudo systemctl status sshdStop and start a service
Perhaps while troubleshooting you need to stop a service to determine whether it is the culprit or interfering with some other process. Use the stop subcommand for this:
Once you determine if this service is associated with the issue, you can restart it:
$ sudo systemctl start sshdTraining & certification
While the restart subcommand is useful for refreshing a service’s configuration, the stop and start features give you more granular control.
Control whether the service starts with the system
One consideration with using stop and start is that the two commands apply only to the current runtime. The next time you boot the system, the service will either start or not start, depending on its default settings. You can use the enable and disable subcommands to manage those defaults.
When you disable the service, it doesn’t start the next time the system boots. You might use this setting as part of your security hardening process or for troubleshooting:
$ sudo systemctl disable sshdReboot the system with reboot sudo systemctl reboot , and the service won’t automatically start.
You may determine that you need the service to start automatically. In that case, use the enable subcommand:
$ sudo systemctl enable sshdThe enable subcommand doesn’t start a service, it only marks it to start automatically at boot. To enable and start a service at the same time, use the —now option:
$ sudo systemctl enable --now sshdMask a service
You can manually start a disabled service with the systemctl start command after the system boots. To prevent this, use the mask subcommand. Masking the service links its configuration to /dev/null . A user or process will not be able to start this service at all (whereas with a disabled service, a user or process can still start it). Use the unmask subcommand to reverse the setting:
Display all subcommands
Bash’s built-in tab-completion feature is one of my favorite tricks for systemctl (and other commands). When working with commands that support subcommands, this feature saves you a lot of time. Simply type systemctl and add a space, then tap the Tab key twice. Bash displays all available subcommands.
The challenge
Do you think you’re ready to use systemctl to manage your services? Fire up a lab virtual machine and choose a service to work with. Don’t do this on a production system! Make sure you can accomplish the following tasks:
Automation advice
Wrap up
Many management tasks involve the systemctl command, but the ones covered above represent the majority of them. Service management is critical, especially when editing configuration files and hardening a system. Plan to be confident, competent, and quick at using systemctl and its common subcommands.
Управление сервисами в Linux. Команда systemctl
Сервисы или службы — это программы, которые работают в системе Linux в фоновом режиме. Обычно они запускаются при загрузке системы. Большинство сервисов необходимы для полноценной работы системы, то есть они являются своего рода кирпичиками, из которых строится работающая система.
При запуске системы загружается целый ряд сервисов, которые включены для автозагрузки. Сервисы работают пока система запущена, и выгружаются при выключении системы.
Чаще всего в Linux дистрибутивах для инициализации сервисов используется демон Systemd. К Systemd-дистрибутивам относятся Ubuntu, Debian, Linux Mint, Fedora, openSUSE, Solus и другие.
Есть дистрибутивы, которые не используют Systemd. Вместо Systemd могут использоваться такие системы инициализации, как Upstart, SysV.
В качестве примеров сервисов можно привести: веб-сервер Apache, Network Manager, файрвол Ufw и другие.
Для управления сервисами (Systemd) используется утилита systemctl . Ниже мы рассмотрим основные команды данной утилиты.
Список сервисов
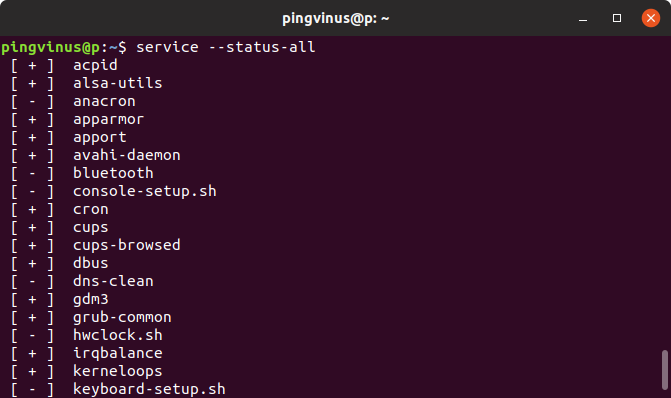
Чтобы просмотреть список всех сервисов можно воспользоваться командой:
Данная команда пробегает по алфавитному списку всех доступных сервисов и выполняет для них команду status.
В выводе команды используются следующие обозначения:
- [ + ] — запущенный сервис.
- [ — ] — остановленный сервис.
- [ ? ] — для данного сервиса отсутствует команда status.
Запуск сервиса
Для запуска сервиса используется команда systemctl start имя_сервиса
Останов сервиса
Для остановки сервиса используется команда systemctl stop имя_сервиса
Перезапуск сервиса
Перезапуск сервиса выполняется командой systemctl restart имя_сервиса
sudo systemctl restart ufwОбычно перезапуск конкретного сервиса требуется, когда были изменены настройки данного сервиса.
Некоторые сервисы поддерживают «мягкую» перезагрузку. В этом случае сервис считывает связанные с ним файлы конфигурации, но не прерывает процесс сервиса. Для выполнения «мягкой» перезагрузки используется команда systemctl reload имя_сервиса . Не все сервисы поддерживают «мягкую» перезагрузку. Если она не поддерживается, то появится сообщение вида: Failed to reload ufw.service: Job type reload is not applicable for unit ufw.service.
Автозагрузка сервисов
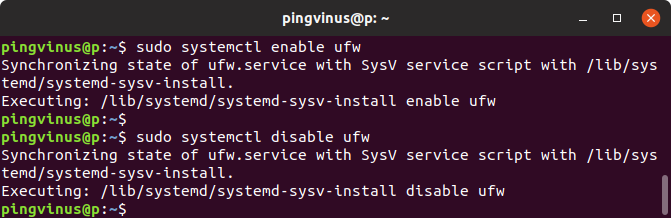
Чтобы сервис стартовал (загружался) при запуске системы, его нужно включить в список автозагрузки. Для этого используется команда systemctl enable имя_сервиса
sudo systemctl enable ufw Synchronizing state of ufw.service with SysV service script with /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install. Executing: /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install enable ufwЧтобы включить сервис в автозапуск и сразу же запустить используется команда:
Чтобы удалить сервис из автозагрузки, используется команда systemctl disable имя_сервиса
sudo systemctl disable ufwСтатус сервиса
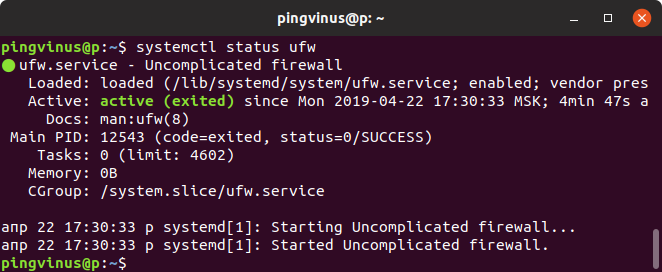
Для вывода информации (статуса) сервиса используется команда systemctl status имя_сервиса
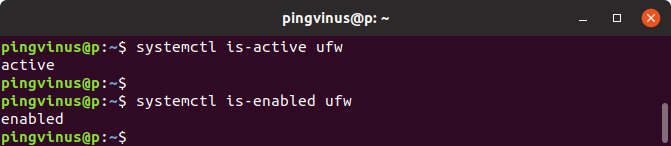
Чтобы проверить, запущен ли в данный момент сервис, используется команда systemctl is-active имя_сервиса
systemctl is-active ufw aciveЧтобы проверить, включен ли сервис для автозапуска при загрузке системы, используется команда systemctl is-enabled имя_сервиса
systemctl is-enabled ufw enabledЗаключение
Мы рассмотрели наиболее часто используемые команды утилиты systemctl. Полный список команд и опций утилиты systemctl можно получить, выполнив: