- How to Copy Files in Linux: A Complete Guide
- Using the Command Line
- Using the Interface
- Community Q&A
- You Might Also Like
- How to copy-paste on Ubuntu terminal
- How to copy-paste on Ubuntu terminal using right-click context menu
- How to copy-paste on Ubuntu terminal using keyboard shortcuts
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Sharqa Hameed
- How to copy and paste a file?
- 4 Answers 4
How to Copy Files in Linux: A Complete Guide
This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Jack Lloyd. Jack Lloyd is a Technology Writer and Editor for wikiHow. He has over two years of experience writing and editing technology-related articles. He is technology enthusiast and an English teacher.
The wikiHow Tech Team also followed the article’s instructions and verified that they work.
This article has been viewed 219,820 times.
This wikiHow teaches you how to copy and paste a file on a Linux computer. The command line can be used to copy and paste files, or you can use the keyboard shortcuts or your computer’s right-click function if you’re using a version of Linux that has a user interface.
- Open the Terminal by pressing Alt + Ctrl + T on most Linux versions.
- Type in cd path where «path» is the address of the folder in which the file you want to copy is located.
- Type the «copy» tag cp followed by a file’s name and extension.
Using the Command Line
- For example, to tell Terminal to look for your file in the Desktop folder, you would type cd Desktop into Terminal.
- Make sure you capitalize the folder’s name if necessary.
- If attempting to switch to a folder results in an error, you’ll need to enter the folder’s entire path (e.g., /home/name/Desktop/folder instead of just folder ) here.
- For example, if you want to copy a file named «hello», you would type cp hello into Terminal.
- If the file name has an extension on the end of it (e.g., «.desktop»), make sure you include the extension in the file’s name when typing it into Terminal.
- For example, if you want to copy «hello» into a folder named «Hi» that’s stored in the Documents folder, you would have cp hello /home/name/Documents/Hi (where «name» is your username) typed into Terminal.
Press ↵ Enter . Doing so will run your command. Your file will be pasted into the folder you specified.
Using the Interface
- Click the file you want to copy to select it, or drag your mouse across multiple files to select them all.
- Press Ctrl + C to copy the files.
- Go to the folder into which you want to copy the files.
- Press Ctrl + V to paste in the files.
- Some Linux versions will also display a menu bar at the top of the screen. If so, you can click Edit instead of right-clicking the selected file.
Community Q&A
What option will allow me to copy the contents of /dir1 to /dir2 while preserving the modification times, ownership, and permissions?
You can try «-a» for an archive to preserve as much as possible. You can also do «—preserve» followed by a comma-separated list of attributes to preserve (or «—preserve all»). Finally, try «cp —help» or «man cp» for more options.
Thanks! We’re glad this was helpful.
Thank you for your feedback.
As a small thank you, we’d like to offer you a $30 gift card (valid at GoNift.com). Use it to try out great new products and services nationwide without paying full price—wine, food delivery, clothing and more. Enjoy! Claim Your Gift If wikiHow has helped you, please consider a small contribution to support us in helping more readers like you. We’re committed to providing the world with free how-to resources, and even $1 helps us in our mission. Support wikiHow
If you want to move a file to a different folder rather than copying the file, you can type mv instead of cp when specifying the file’s name and its destination (e.g., mv hello Documents).
Holding down Ctrl while clicking individual files will select each file you click. Right-clicking one of the selected files and selecting Copy will then copy all of the selected files.
Not all versions of Linux have a user interface. If your version of Linux has only a command line, you’ll need to use the «cp» command to copy your files.
You Might Also Like
How to Transfer Files from One Linux Server to Another
Can Linux Run .exe Files? How to Run Windows Software on Linux
How to Open Linux Firewall Ports: Ubuntu, Debian, & More
How to Run an INSTALL.sh Script on Linux in 4 Easy Steps
Use Ping in Linux: Tutorial, Examples, & Interpreting Results
How to Delete Read-Only Files in Linux
How to copy-paste on Ubuntu terminal
In user-interface design and human-computer interaction, copy-paste are operations that provide an interprocess communication mechanism for moving data via the user interface of a system. The copy command duplicates the data and saves it to temporary storage (the clipboard). Then this data from the clipboard is pasted into the desired location. The copied data is accessible to any program that supports the functionality and allows itself to transfer data easily.
You may need to write long commands or sentences obtained in a file or on the internet while working on the Ubuntu terminal. You can save your precious time by utilizing copy-pasting techniques rather than entering them word by word. Using the standard keyboard commands Ctrl+c and Ctrl+v, you may have copied and pasted text multiple times in your Ubuntu Graphical User Applications such as LibreOffice, Gedit, OpenOffice. However, you may be surprised to learn that many common keyboard shortcuts do not work in Ubuntu Terminal.
This article will show you how to copy-paste in the Ubuntu terminal using two different methods. The examples below are executed on Ubuntu 20.04; other Linux distributions can also use the same copy-paste approach. Now, let’s get started!
How to copy-paste on Ubuntu terminal using right-click context menu
You need to utilize the mouse to highlight the text; why not use it to copy and paste? You can use the mouse right-click for copy-paste as you do in other Ubuntu applications. For this, select the text you want to copy, then right-click on it, and from the context menu, click on the “Copy” option. You can paste this copied command to the terminal window, any script, or any other document.
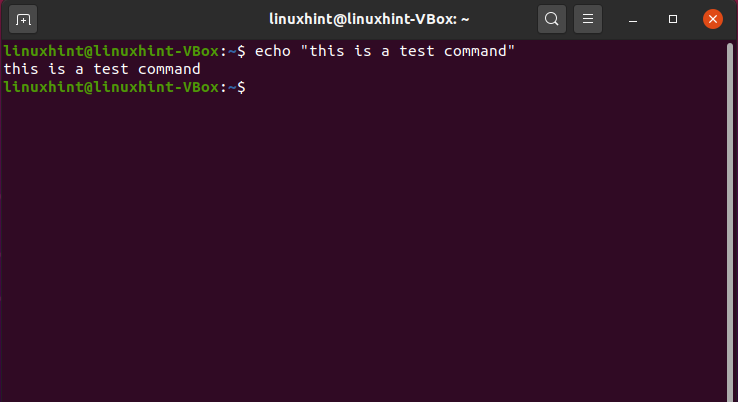
Example 1: In the below-given example, we will copy-paste the command executed in the Ubuntu terminal to a document named “testscript”:
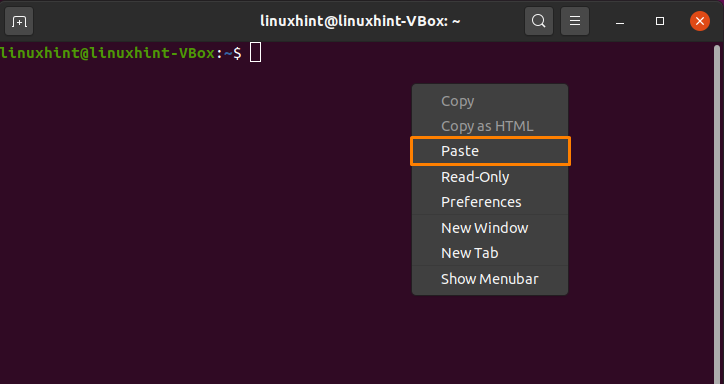
Firstly, we have selected the command. After that, utilizing the right-click context menu, we will click on the “Copy” option:
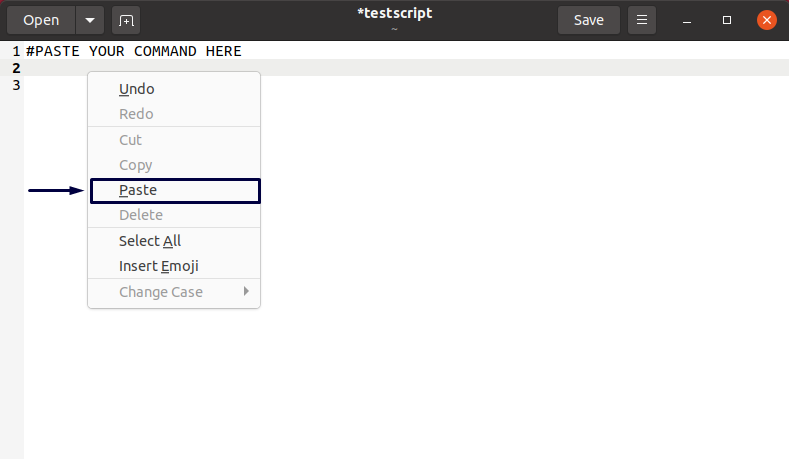
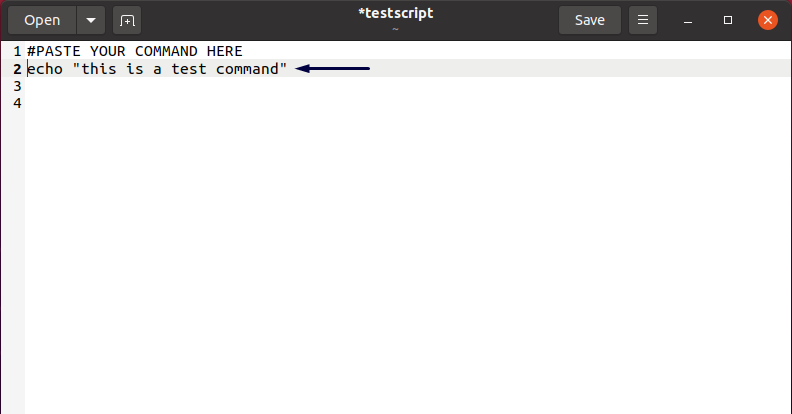
Now, we will paste the copied command in our “testscript” document. Click on the document position, where you want to place the copied command, and then from the right-click context menu, click on the “Paste” option:
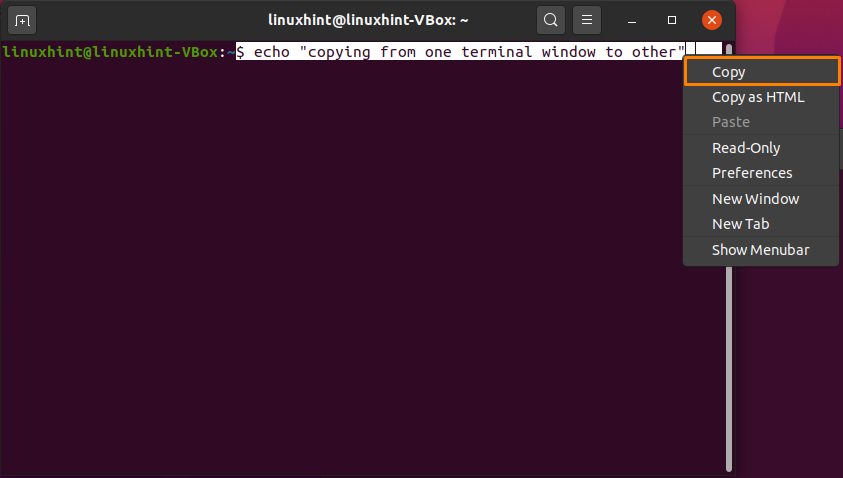
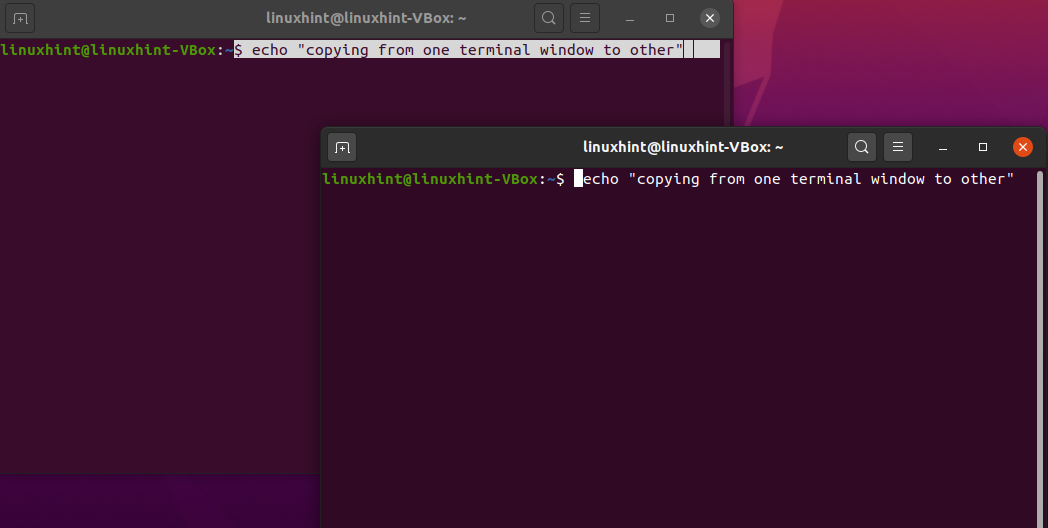
Example 2: In Ubuntu, you can also use your mouse’s context menu right-click to copy-paste from a terminal to the other terminal window. For this, select the command and click on the “Copy” option:
Move into the other terminal and paste the selected command in the following way:
How to copy-paste on Ubuntu terminal using keyboard shortcuts
Most computer users are accustomed to using “CTRL+c” and “CTRL+v” for copy-pasting text. These shortcuts also work on Ubuntu Desktop, but not in the terminal. To copy or paste commands from or to the Ubuntu terminal, you must add the “Shift” key in these keyboard shortcuts.
- To copy text or command from Ubuntu terminal, press “CTRL+Shift+c”
- To paste text or command in Ubuntu terminal, press “CTRL+Shift+v”
- To copy text or command from outside of the Ubuntu terminal, press “CTRL+c”
- To paste text or command in any document or script, press: “CTRL+v”
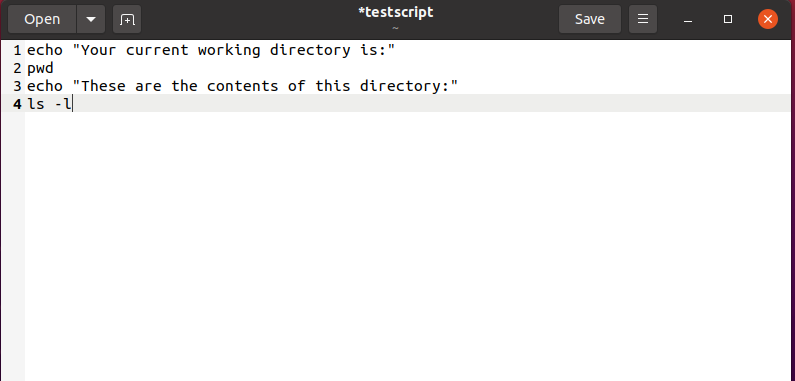
Example 1: In the below-given example, we will try to copy commands from the document “testscript” to our Ubuntu terminal:
First of all, we will select all of the required commands for copying and then press “CTRL+c”:
After that, we will move towards our terminal window and paste the commands in it by pressing “CTRL+SHIFT+v”:
This operation will paste and execute the copied commands in the terminal simultaneously:
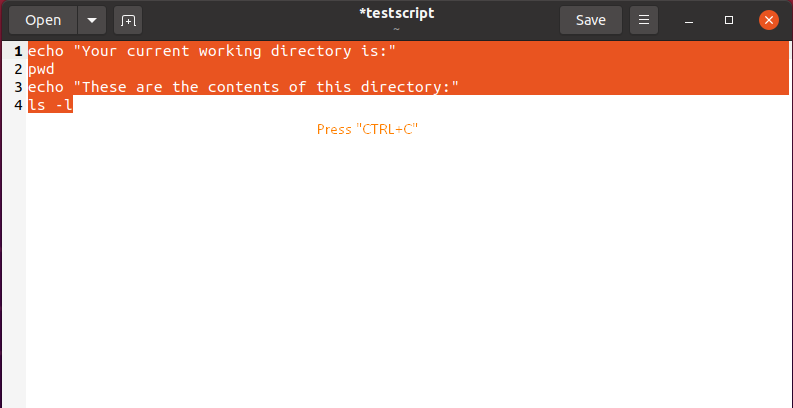
If you paste a command into the Ubuntu terminal with a trailing newline, the command will be executed right away. I have discovered that selecting a command by clicking at the end and dragging it to the beginning is the easiest way to avoid this. We will be able to paste commands in the Ubuntu terminal through this selection method without executing it instantly.
Next, we will select the command from the document by using the method mentioned above. After that, press “CTRL+c” to copy it:
Move into your Ubuntu terminal and press “CTRL+Shift+v” to paste the copied command:
The below-given shows that we have successfully pasted the command from our document to the terminal without executing it instantly:
Example 2: How to copy-paste from Ubuntu terminal to a document using keyboard shortcuts
To copy and paste any command from your terminal window; select it by pointing the cursor at the end of it. After that, utilize the mouse right-click button and drag it towards the start of the command. Once you have selected the command, press “CTRL+Shift+c” to copy it:
Next, open up your document where you want to paste the command and press “CTRL+v”. Now the “testscript” document will look like this:
Conclusion
There are always options to copy-paste in the Ubuntu terminal whenever you find yourself reusing any text. In Ubuntu, copy-paste enables you to copy and paste text or commands without retyping them repeatedly. This process also saves your time, which you can invest in other things. In this article, you have learned how to copy-paste in the Ubuntu terminal using two different methods. According to our experience, using keyboard shortcuts for copy-paste is easier than utilizing the mouse right-click menu.
About the author
Sharqa Hameed
I am a Linux enthusiast, I love to read Every Linux blog on the internet. I hold masters degree in computer science and am passionate about learning and teaching.
How to copy and paste a file?
I want copy and paste a file. The name of the file is mkoctfile.m .
The path of this file is: /usr/share/octave/3.2.4/m/miscellaneous/mkoctfile.m I want to paste it to the following path /usr/bin/mkoctfile-3.2.4 I have made the directory by using following commands: sudo su mkdir -p /usr/bin/mkoctfile-3.2.4 but I don’t know how to copy and paste mkoctfile.m in this path. Please tell me what command I have to use.
4 Answers 4
Use the cp command to copy a file, the syntax goes cp sourcefile destinationfile . Use the mv command to move the file, basically cut and paste it somewhere else.
The exact syntax you would use for your example is:
sudo cp /usr/bin/octave/3.2.4/m/miscellaneous/mkoctfile.m /usr/bin/mkoctfile-3.2.4 For more information on the cp or mv commands you can run:
To @BKSurgeon, I would suggest to use the tab key to see the paths/directories available, or type ls to see them all at once printed.
I think it is better to use cp -a than just cp , if you want to have the same affect as when copy-pasting in desktop GUI.
You can cut, copy, and paste in CLI intuitively like the way you usually did in the GUI, like so:
- cd to the folder containing files you want to copy or cut.
- copy file1 file2 folder1 folder2 or cut file1 folder1
- close the current terminal.
- open another terminal.
- cd to the folder where you want to paste them.
- paste
To be able to do so, make sure you have installed xclip and realpath . Then, append these functions to the end of your ~/.bashrc file:
copy() < # if the number of arguments equals 0 if [ $# -eq 0 ] then # if there are no arguments, save the folder you are currently in to the clipboard pwd | xclip else # save the number of argument/path to `~/.numToCopy` file. echo $# >~/.numToCopy # save all paths to clipboard # https://stackoverflow.com/q/5265702/9157799#comment128297633_5265775 realpath -s "$@" | xclip fi # mark that you want to do a copy operation echo "copy" > ~/.copyOrCut > cut() < # use the previous function to save the paths to clipboard copy "$@" # but mark it as a cut operation echo "cut" >~/.copyOrCut > paste() < # for every path for ((i=1; i If you don't know what .bashrc file is and never modify it before, just open the file explorer, go to Home, press Ctrl+H (show hidden files), search for .bashrc and open it with a text editor like gedit.
By using the above script, you are overriding the default functionality of these commands:
If you use one of those commands default functionality, just modify the script function names accordingly. For example, use p instead of paste .