- Как копировать в терминале Linux
- Как копировать в терминале Linux
- 1. Обычный терминал
- 2. Редактор Vim
- 3. Терминальный сервер tmux
- Выводы
- How to Copy Paste in Linux Terminal [For Absolute Beginners]
- How to copy and paste text and commands in the Linux terminal
- Method 1: Using keyboard shortcuts for copy-pasting in the terminal
- Method 2: Using right-click context menu for copy-pasting in the terminal
- Method 3: Use the mouse to copy and paste into the Linux terminal
- Why Linux terminals do not use the ‘universal’ Ctrl+C and Ctrl+V for
- There are no universal key shortcuts for copy-paste in the Linux terminal. Here’s why!
- Conclusion
- Copying text from a terminal
- General approach
- Terminals without CLIPBOARD selection
- Xorg
- Wayland
- Intercepting commands output
- Accessing Linux terminal backlog
- Comparison of common emulators
- Special cases
- putty
- urxvt
- xterm
- mlterm
Как копировать в терминале Linux
Буфер обмена операционной системы и возможность копировать и вставлять текст из одного места в другое очень сильно облегчает работу в терминале. Теперь вам необязательно искать команду в истории или набирать её вручную. Вы можете скопировать текст с другого терминала, файла или браузера, а затем выполнить его. Сложно представить как передать команде длинные и сложные параметры без возможности копирования и вставки.
В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрим как копировать в терминале Linux в разных ситуациях, а также как вставить полученный текст. В целом, тут нет ничего сложного если вы работаете с графическим окружением и там поддерживается мышь.
Как копировать в терминале Linux
1. Обычный терминал
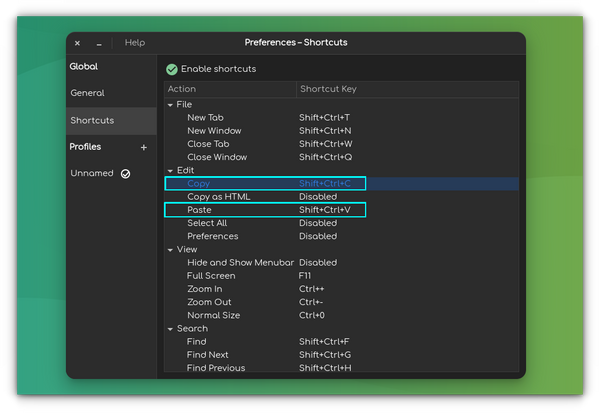
Для того чтобы скопировать текст в обычном графическом эмуляторе терминала достаточно выделить его мышкой и нажать сочетание клавиш Ctrl+Shift+C. Затем, для вставки скопированного в терминал надо нажать Ctrl+Shift+V.
Обычно для копирования и вставки текста используются сочетания клавиш Ctrl+C и Ctrl+V. Однако в терминале сочетание Ctrl+C завершает программу, которая в данный момент выполняется. Поэтому для копирования разработчикам пришлось выбрать новое сочетание. Из традиционных сочетаний клавиш можно использовать Ctrl+Insert и Shift+Insert для копирования и вставки соответственно.
Если программа выводит данные слишком быстро и вы не успеваете их отметить и скопировать, можно нажать сочетание клавиш Ctrl+S для того чтобы приостановить программу. Некоторые программы полностью останавливаются, некоторые останавливают только вывода, но теперь у вас будет достаточно времени для того чтобы скопировать нужные данные. Для того чтобы возобновить работу программы используйте сочетание Ctrl+Q. Теперь вы знаете как копировать текст в терминале linux.
2. Редактор Vim
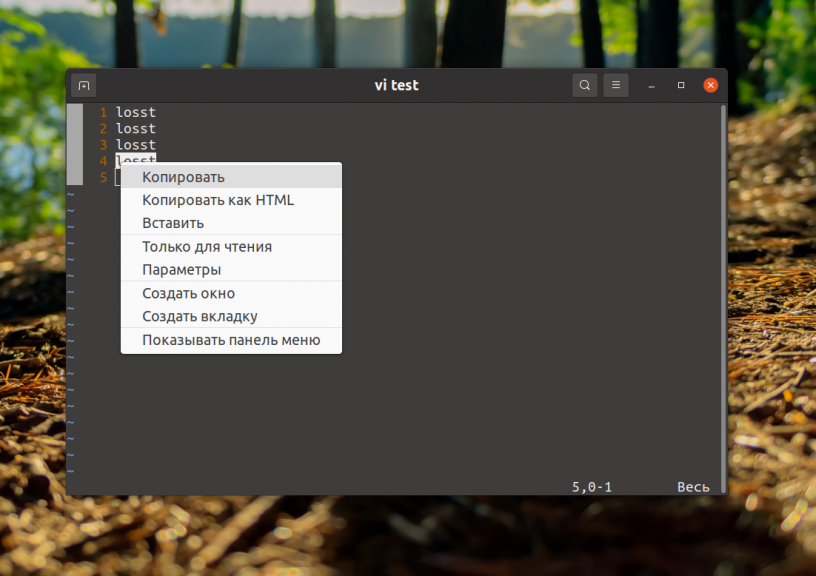
Если в редакторе включена поддержка мыши, то копировать текст, описанным выше способом у вас не получится. Для того, чтобы всё же иметь возможность скопировать текст средствами операционной системы необходимо зажать кнопку Shift во время выделения мышкой. Для копирования можно использовать то же сочетание клавиш Ctrl+Shift+C или же вызвать контекстное меню с зажатой клавишей Shift и выбрать пункт Скопировать:
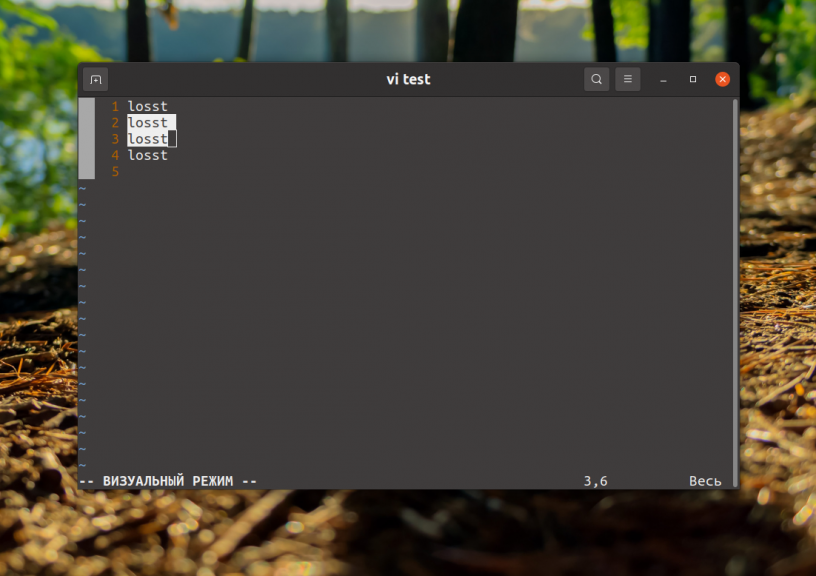
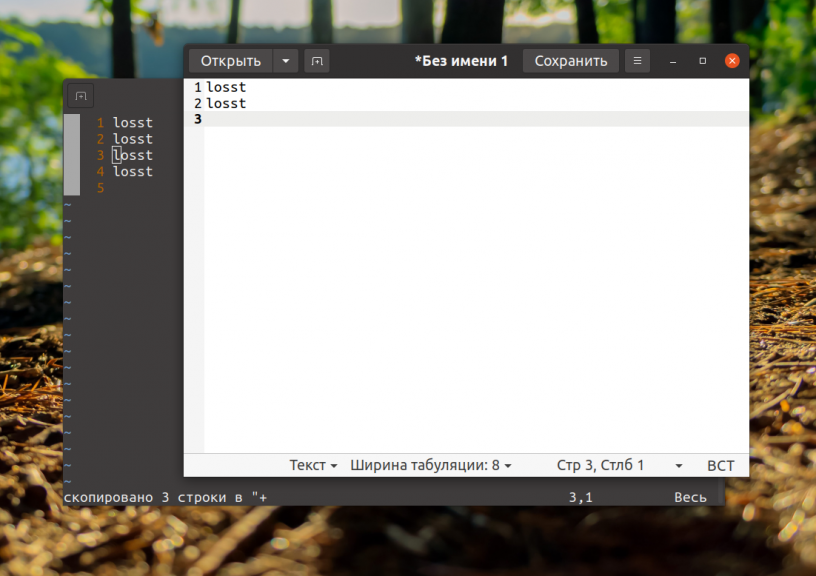
Однако при таком способе копирования может быть скопировано много лишнего, например, номера строк. В текстовом редакторе Vim есть встроенная функциональность копирования. Если включена поддержка мыши, вы можете выделить текст мышью. Если нет, для перехода в режим выделения нажмите клавишу V в командном режиме. Затем используется стрелки для выделения нужной области:
Для копирования во внутренний буфер Vim следует использовать клавишу y, а для вставки — p. Если надо выйти с режима выделения без осуществления каких-либо действий — нажмите Esc. Такой способ копирования работает только внутри программы, нигде в системе скопированный текст вставить вы не сможете.
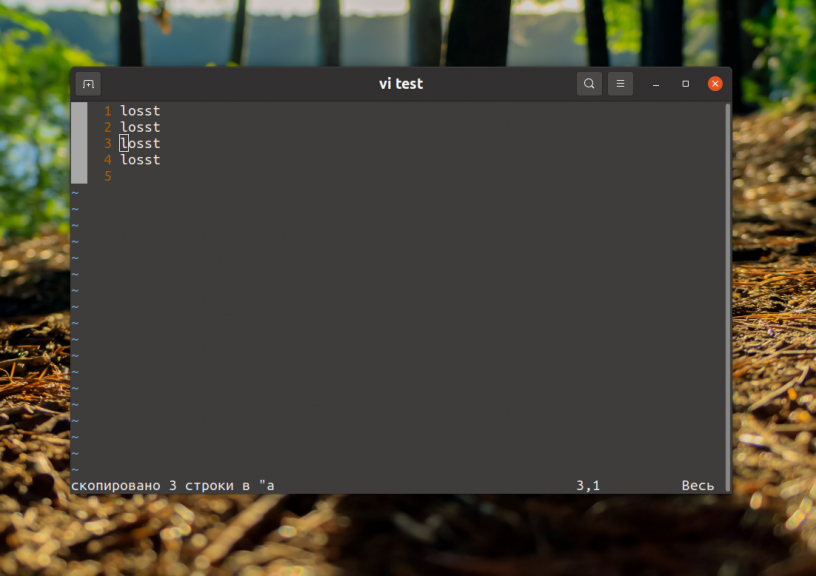
Однако Vim умеет работать и с буфером обмена операционной системы. Вообще у Vim очень широкие возможности копирования и вставки. Здесь поддерживается такая вещь как регистры, в которые можно сохранять данные и извлекать их оттуда. Всего таких регистров 26. По умолчанию используется безымянный регистр. Именно в него попадает текст при копировании с помощью клавиши y или удалении с помощью x. У большинства регистров есть своё предназначение. Однако есть именованные регистры с именами от a до z, в которые вы можете складывать произвольные данные.
Для доступа к регистрам используется символ » в командном режиме или режиме выделения. Если вы редактируете текст, то нужно нажать Esc для выхода в командный режим или выделить нужный текст, затем нажать Shift и кнопку, которая отвечает за « на клавиатуре, а затем кнопку имени регистра. Например, для того чтобы скопировать текст в регистр a используйте такую последовательность «ay.
Для вставки надо будет использовать подобный синтаксис «ap. Аналогично всему этому есть регистр, связанный с буфером обмена операционной системы. Его имя +. Но для того чтобы он работал, необходимо чтобы в системе был установлен пакет vim-gtk3 или gvim. В Ubuntu команда установки будет выглядеть вот так:
Затем вы сможете скопировать текст в системный буфер с помощью такой последовательности: «+y. После чего его можно будет вставить в любой программе вне Vim. Если надо вставить такой текст в Vim, используйте последовательность «+p.
3. Терминальный сервер tmux
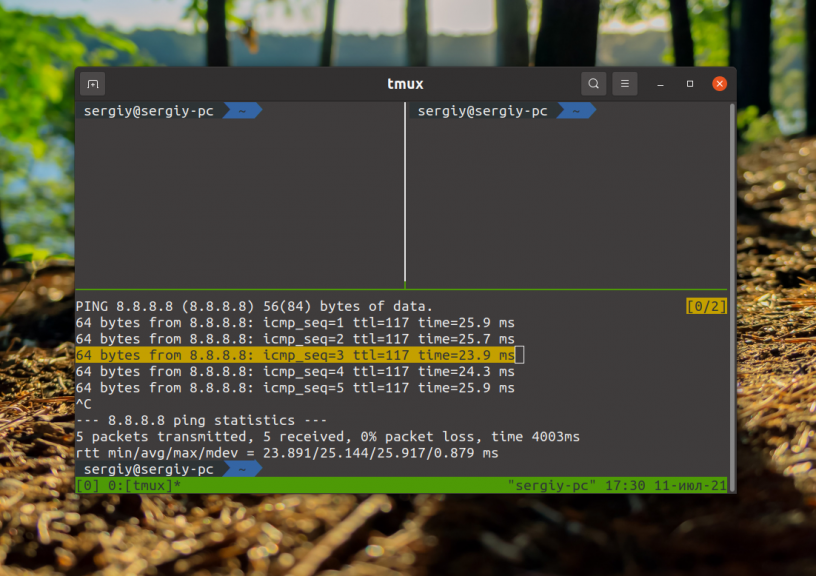
Если вы используете tmux для разделения одного окна терминала на несколько, то копировать с помощью зажатой кнопки Shift будет не очень удобно. Вы не сможете выделить текст в рамках одного виртуального окна, будет выделяться всё окно терминала и в выделение попадёт много ненужных данных. Для выделения и вставки следует использовать встроенные средства. Если у вас включена поддержка мыши в tmux, то скопировать текст можно просто выделив его мышью.
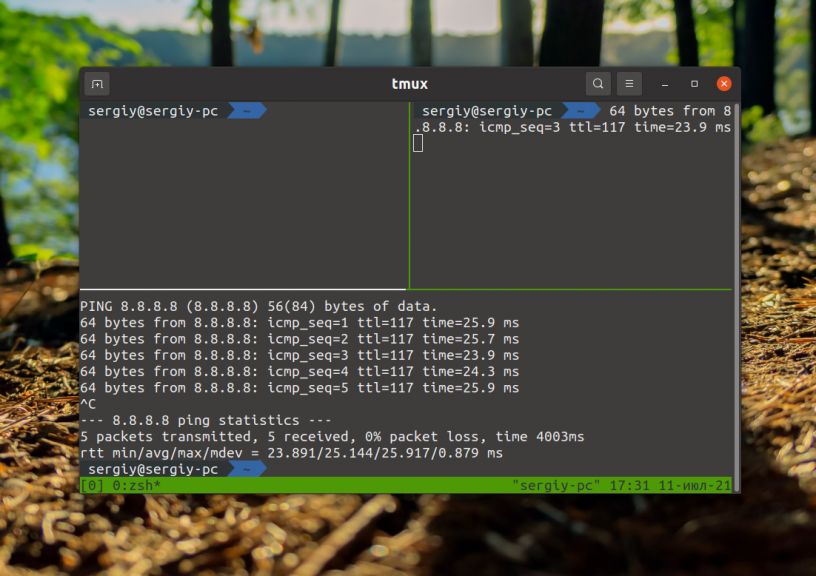
Если поддержки мыши нет, нажмите управляющее сочетание клавиш, по умолчанию Ctrl+b, а затем символ [ для того чтобы войти в режим выделения. Используйте стрелки для перемещения по тексту. Переместите курсор к началу текста для копирования и нажмите Ctrl+Пробел. Затем переместите курсор к концу фрагмента. Выделенный текст будет подсвечен:
Затем нажмите сочетание клавиш Alt+W для того чтобы скопировать текст в буфер. Для вставки скопированного текста используйте сочетание клавиш Ctrl+b затем ].
Правда этот способ работает только с внутренним буфером обмена tmux. Получить скопированный таким образом текст в системе не получится.
Выводы
В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрели как копировать в терминале Linux, а также в нескольких популярных программах, таких как Vim и Tmux. А какие ещё способы копирования текста в терминале знаете вы? Напишите в комментариях!
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
How to Copy Paste in Linux Terminal [For Absolute Beginners]
Here are various ways to copy paste text and commands in Linux terminal along with explanation on why Ctrl+C and Ctrl+V doesn’t work in the terminal.
I have been using Linux for a decade now and this is why sometimes I take things for granted. Copy-pasting in the Linux terminal is one such thing. I thought everyone already knew this until one of the It’s FOSS readers asked me this question. I gave the following suggestion to the Ubuntu user:
Use Ctrl+Insert or Ctrl+Shift+C for copying and Shift+Insert or Ctrl+Shift+V for pasting text in the terminal in Ubuntu. Right-click and select the copy/paste option from the context menu is also an option.
I thought of elaborating on this topic especially when there is no single universal way of copying and pasting in the Linux terminal.
How to copy and paste text and commands in the Linux terminal
Method 1: Using keyboard shortcuts for copy-pasting in the terminal
On Ubuntu and many other Linux distributions, you can use Ctrl+Insert or Ctrl+shift+C for copying text and Shift+Insert or Ctrl+shift+V for pasting text in the terminal. The copy-pasting also works for external sources. If you copy a command example from It’s FOSS website (using the generic Ctrl+C keys), you can paste this command into the terminal using the Ctrl+Shift+V into the terminal. Similarly, you can use Ctrl+shift+C to copy text from the terminal and then use it to paste in a text editor or web browser using the regular Ctrl+V shortcut. Basically, when you are interacting with the Linux terminal, you use the Ctrl+Shift+C/V for copy-pasting.
Method 2: Using right-click context menu for copy-pasting in the terminal
Another way of copying and pasting in the terminal is by using the right-click context menu. Select the text in the terminal, right click and select Copy. Similarly, to paste the selected text, right-click and select Paste.
Method 3: Use the mouse to copy and paste into the Linux terminal
Another way to copy-paste in a Linux terminal is by using only the mouse. You can select the text you want to copy and then press the middle mouse button (scrolling wheel) to paste the copied text. Please keep in mind that these methods may not work in all the Linux distributions for a specific reason that I explain in the next section.
Why Linux terminals do not use the ‘universal’ Ctrl+C and Ctrl+V for
No Linux terminal will give you Ctrl+C for copying the text. This is because by default Ctrl+C keybinding is used for sending an interrupt signal to the command running in the foreground. This usually stops the running command. This behaviour has been existing long before Ctrl+C and Ctrl+V started being used for copy-pasting text. Since the Ctrl+C keys are ‘reserved’ for stopping a command, they cannot be used for copying.
Used Ctrl+S and hanged the terminal?
The keyboard shortcut CTRL + S in the Linux terminal is used to send a «stop» signal to the terminal, which results in a frozen terminal. Just use Ctrl+Q and you can use the terminal again.
There are no universal key shortcuts for copy-paste in the Linux terminal. Here’s why!
The keybindings for copy-pasting are dependent on the terminal emulator (commonly known as terminal) you are using. If you didn’t know that already, a terminal is just an application, and you can install other terminals like Guake or Terminator. Different terminal applications may have their own keybindings for copying and pasting like Alt+C/V or Ctrl+Alt+C/V. Most Linux terminals use the Ctrl+Shift+C/V keys but if it doesn’t work for you, you may try other key combinations or configure the keys from the preferences of the terminal emulator.
Conclusion
I know this is elementary for the Sherlock Holmes of the Linux world but it could still be useful to the Watsons. If you are absolutely new to the terminal, this is going to help you a great deal. New or not, you may always use shortcuts in the Linux terminal to make your life easier. If you really care about increasing productivity through the Linux terminal, these handy Linux command tips and tricks will be a good starting point. 💬 Do you still have questions? The comment section is all yours.
Copying text from a terminal
Most mature terminal emulators permit users to copy or save their contents.
General approach
In graphical terminal emulators, contents are typically selectable by mouse, and can then be copied using the context menu, Edit menu or a key combination such as Ctrl+Shift+c .
Terminals without CLIPBOARD selection
Xorg
Some emulators do not support the CLIPBOARD selection natively, and copy data to the PRIMARY selection. For them xclip may be used:
$ xclip -o | xclip -selection clipboard -i
The above command reads data from the PRIMARY selection and writes it to CLIPBOARD selection.
Other clipboard managers such as autocutsel provide automatic synchronization between selection buffers.
Wayland
Utilities like wl-clipboard and clipboard AUR can copy data to the Wayland clipboard:
Intercepting commands output
Use tee to intercept the output of a command.
$ command 2>&1 | tee output-file
After the command is executed, output-file will contain its output, while having displayed the output at the same time.
Accessing Linux terminal backlog
The backlog of a native terminal named /dev/ttyN may be accessed via /dev/vcsN . Hence, if one is working in /dev/tty1 , the following snippet will let store the backlog in a file output-file :
Comparison of common emulators
The factual accuracy of this article or section is disputed.
Unless the «Key combination» column states otherwise, the key combination is Ctrl+Shift+c .
| Emulator | Select to PRIMARY | CLIPBOARD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Key combination | Context menu | Window menu | Select | |||
| Alacritty | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | |
| aterm AUR | Yes | No | No | No | No | |
| eterm AUR | Yes | No | No | No | No | |
| foot | Yes | Yes | No | No | Optional | |
| germinal AUR | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| Guake | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| Konsole | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Optional | |
| lilyterm-git AUR | Yes | Yes Ctrl+Delete | Yes | No | No | |
| lxterminal | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | |
| mate-terminal | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | |
| mlterm AUR | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | |
| pantheon-terminal | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| PuTTY | Yes | No | No | No | No | |
| qterminal | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | |
| roxterm AUR | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | |
| rxvt AUR | Yes | No | No | No | No | |
| sakura AUR | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | |
| st | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | |
| Terminator | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| terminology | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| Termite | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | |
| Tilda | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | |
| urxvt | Yes | Yes Ctrl+Alt+c | No | No | Optional | |
| xfce4-terminal | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | |
| xterm | Yes | Optional[1] | No | No | Yes | |
| Yakuake | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Optional | |
Special cases
putty
The xclip approach works for putty: one just has to remember that the xclip invocation should be done on the local computer (in another terminal), not on the remote machine to which putty is connected.
urxvt
Selecting text to CLIPBOARD requires the selection-to-clipboard perl extension. See rxvt-unicode#Cut and paste for details.
xterm
Access to the CLIPBOARD selection in xterm requires additional steps.
mlterm
In addition to Ctrl+Shift+c , you can use Ctrl+Insert if you do not want to kill processes accidentally.