- Как скопировать файл Linux на USB?
- Как скопировать файлы из Ubuntu на внешний жесткий диск?
- Как скопировать электронные письма на USB-накопитель?
- Как мне найти USB-накопитель на моем компьютере?
- Как скопировать файл в Unix?
- Как скопировать файл в Терминал?
- Какая команда используется для копирования?
- Каков самый быстрый способ скопировать большие файлы в Linux?
- Как скопировать файлы с одного диска Linux на другой?
- Как копировать файлы постепенно?
- How to Copy Files to a USB Flash Drive Using the Terminal [TTY]
- How to Use Terminal to Copy Files to a USB Flash Drive
- Step 01: Attach and Mount USB Flash Drive
- Step 02: Copy files from USB to your Linux machine
- Change your current directory
- List all the files from the USB drive
- How to properly copy files from hard drive to USB flash drive in tty4 terminal?
- 2 Answers 2
- How to Copy Files to USB Using Terminal
- 1. Know Where USB Mounted
- 2. Change to USB Mounted directory
- 3. List Content Inside USB
- 4. Copy files to USB
- 6. Verify
- Conclusion
Как скопировать файл Linux на USB?
В Команда Linux cp используется для копирования файлов и каталогов в другое место. Чтобы скопировать файл, укажите «cp», а затем имя файла для копирования. Затем укажите место, в котором должен появиться новый файл. Новый файл не обязательно должен иметь то же имя, что и тот, который вы копируете.
Как скопировать файлы из Ubuntu на внешний жесткий диск?
Сначала вам нужно открыть Терминал (Ctrl + Alt + T) и запустите команду fdisk -l . После этого вы увидите списки разделов в вашей системе, например / dev / sda1-2-3-4. Идентифицировать нужно по размеру или системной информации.
Как скопировать электронные письма на USB-накопитель?
- Вставьте USB-накопитель в USB-порт, затем перейдите в почтовый ящик и откройте письмо, которое вы хотите сохранить.
- Нажмите и скопируйте часть, которую хотите сохранить, или, если вы хотите сохранить всю электронную почту, адреса и все остальное, выделите электронное письмо сверху вниз.
Как мне найти USB-накопитель на моем компьютере?
Вставьте USB-накопитель в USB-порт компьютера, расположенный на передней или задней панели компьютера. Щелкните «Пуск» и выберите «Мой компьютер». Имя вашего USB-накопителя должно появиться под «Устройства со съемным Хранение ».
Как скопировать файл в Unix?
cp — это команда оболочки Linux для копирования файлов и каталогов.
.
Параметры команды cp.
| вариант | описание |
|---|---|
| cp -n | нет перезаписи файла |
| cp -R | рекурсивная копия (включая скрытые файлы) |
| Процессор | update — копировать, когда источник новее, чем dest |
Как скопировать файл в Терминал?
В приложении Терминал на вашем Mac, используйте команду cp, чтобы создать копия файла. Флаг -R заставляет cp копировать папку и ее содержимое. Обратите внимание, что имя папки не заканчивается косой чертой, что изменит способ копирования папки cp.
Какая команда используется для копирования?
Команда копирует файлы компьютера из одного каталога в другой.
.
копировать (команда)
| В Команда копирования ReactOS | |
|---|---|
| Разработчики) | DEC, Intel, MetaComCo, Heath Company, Zilog, Microware, HP, Microsoft, IBM, DR, TSL, Datalight, Novell, Toshiba |
| Тип | Командование |
Каков самый быстрый способ скопировать большие файлы в Linux?
- Отслеживание прогресса копирования и скопированных файлов.
- Переход к следующему файлу перед ошибкой (gcp)
- Синхронизация каталогов (rsync)
- Копирование файлов по сети (rsync)
Как скопировать файлы с одного диска Linux на другой?
- Убедитесь, что размер второго жесткого диска не меньше размера первого.
- Запускаем живую систему.
- Скопируйте жесткий диск, например: dd if = / dev / nvme0n1p of = / dev / sda bs = 32M. или с помощью cat (через): cat / dev / nvme0n1p> / dev / sda.
Как копировать файлы постепенно?
- Откройте Панель управления из меню «Пуск».
- Щелкните Резервное копирование компьютера в разделе «Система и безопасность».
- Нажмите Настроить резервное копирование, чтобы начать.
- Выберите, что для резервного копирования, щелкнув «Разрешить выбор Windows» или «Разрешить выбор».
- Выберите данные для резервного копирования.
How to Copy Files to a USB Flash Drive Using the Terminal [TTY]
When you connect a USB drive to your computer, it automatically mounts so that you can move or copy files using a file manager such as Dolphin or Nautilus. However, when your system is booted into tty mode due to minimal distribution or a system error, the USB drive will not automatically mount.
which means you have to manually mount your flash drive, then use the cp command to move files from the source directory to the destination directory.
For a new user who has recently started using Linux, it can be overwhelming, but once you understand the basic commands, you can easily transfer files between your system and the USB drive.
How to Use Terminal to Copy Files to a USB Flash Drive
A USB flash drive must be connected to a computer before it can be mounted, and then the cp command can be used to copy files from the computer to the flash drive, so first connect the pendrive and follow the below guide:
Step 01: Attach and Mount USB Flash Drive
When you connect the thumb drive, you may hear a sound from the system, which means the system has detected and mounted the thumb drive and is ready for the operation. So you just need to know about the USB drive’s location, like where it is mounted.
This alert sound won’t be available when you are in tty mode, so at that time you need to manually mount the drive by specifying the device path like shown below:
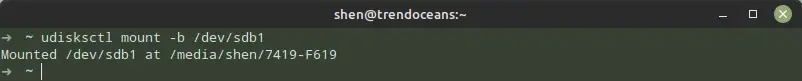
$ udisksctl mount -b /dev/sdb1If you are not sure about the drive path, then run the following command, which will list all the block devices that are available to your system.
$ lsblk $ sudo fdisk -lHere is the result of the lsblk command, which I used to list block devices:
AME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINTS sda 8:0 0 465.8G 0 disk ├─sda1 8:1 0 529M 0 part /media/shen/Recovery ├─sda2 8:2 0 100M 0 part /boot/efi ***************** ├─sda11 8:11 0 7G 0 part [SWAP] └─sda12 8:12 0 30.9G 0 part / sdb 8:16 1 14.3G 0 disk └─sdb1 8:17 1 14.3G 0 part Since “sda” is your physical drive, you can safely ignore anything on it. Instead, search for something on “sdb” or “sdc” and append it to the command below.
$ udisksctl mount -b /dev/sdb1As soon as the aforementioned command mounts the drive, a message similar to the one in the image below will appear on your screen, letting you know the path to which it has been mounted.
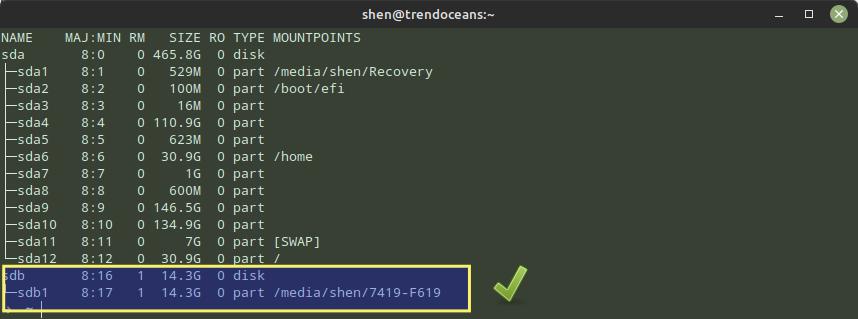
Similarly, you can verify the same by running the lsblk command in the terminal window.
You’re all done with the mounting part, so let’s move on to the next section to learn how to copy files from USB to your Linux system and vice versa.
Step 02: Copy files from USB to your Linux machine
First, you will see how to copy files from the USB drive to the Linux machine, and then we will proceed to the next section, where you will learn how to move files from your system to the USB drive by running commands.
Change your current directory
From the above section, you will be aware of the mount point where the USB drive is mounted, right? If yes, then change your current directory to the thumb drive location by using the cd command.
$ cd /media/shen/7419-F619 $ pwdand pwd commands will verify the location has been updated.
List all the files from the USB drive
After that, run the ls -l command to list all the files that are available on your pen drive, as shown in the below image:
How to properly copy files from hard drive to USB flash drive in tty4 terminal?
How to properly copy files from hard drive to USB flash drive in tty4 terminal?(mount, copy, unmount, exit, etc) P.S.Can no exit from tty4 terminal via Ctrl+Alt+F7 command, only with Alt+SysRq+B (kernel restart).
2 Answers 2
- Plug in the device
- lsblk to find the device name of your usb device. Naming is /dev/sdXY . Where X is any english letter and Y is integer, typically 1.
If the device was mounted, you will see the mountpoint, for example:
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT sdb 8:0 1 15.2G 0 disk └─sdb1 8:1 1 15.2G 0 part /media/me/4C45-110F If not, mount it. Follow to the step #3
- udisksctl mount -b /dev/sdXY , device name same as in previous step. ( /dev/sdb1 in my example) The mount folder will be reported back to you to use in the next step. For example, suppose lsblk tells me this: sdc 8:32 1 7.5G 0 disk └─sdc1 8:33 1 7.5G 0 part
Then I will do the following:
$ udisksctl mount -b /dev/sdc1 Mounted /dev/sdc1 at /media/xieerqi/A669-34EF. You can see it automatically created /media/xieerqi/A669-34EF folder and mounted my pen drive there. Also , big advantage is that you do not need sudo .
- Use rsync or cp or mv to get your files to the folder reported in step 3. Consult manual pages on usage of these commands. cp and mv are simplest. mv FILE DESTINATION — in my example (where FILE is the thing you want to move to the drive)
rsync is the best for backup however.
For example, to backup TESTDIR to my usb drive, I can do this:
$ rsync -av /home/xieerqi/TESTDIR/ /media/xieerqi/A669-34EF/~ sending incremental file list created directory /media/xieerqi/A669-34EF/~ ./ file1 file2 file3 sent 228 bytes received 125 bytes 706.00 bytes/sec total size is 0 speedup is 0.00 $ udisksctl unmount -b /dev/sdc1 Unmounted /dev/sdc1. NOTE: some drives mount to directories that have names with spaces. If you run rsync or mv with not quoted names like that, your data will not be copied to correct destination. Always quote pathnames that have spaces in them.
How to Copy Files to USB Using Terminal
Linux users feel empowered while performing tasks using the terminal application. So why leave the terminal when you can copy files to USB from the terminal app instead of a file explorer. This guide shows how to copy files and directories from a Linux system to a USB stick.
1. Know Where USB Mounted
Just before we begin, I am using Ubuntu 22.04 but the approach will mostly remain the same for any version and distribution.
Before we copy files, the USB stick needs to be mounted to your machine (laptop, PC, etc). Most Linux distributions mount the USB flash drive automatically to the system under the /media directory.
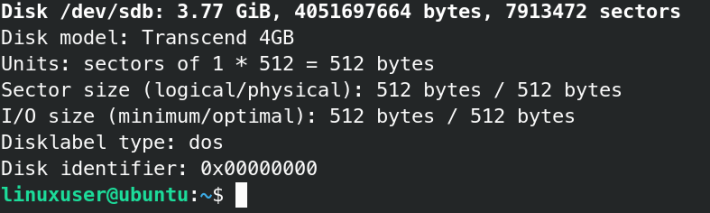
Insert the USB flash drive into your system. And let us find out the name of your USB drive using the fdisk command. Fdisk is used to manage hard drive and partitions in Linux.
It will display many disks but at the last, you will find the external disks. In the above image, you can see I have a 4 GB pen drive attached to my laptop. The /dev/sdb is the name of your USB. For you, the name may be different but mostly always named as sdc, sda, etc
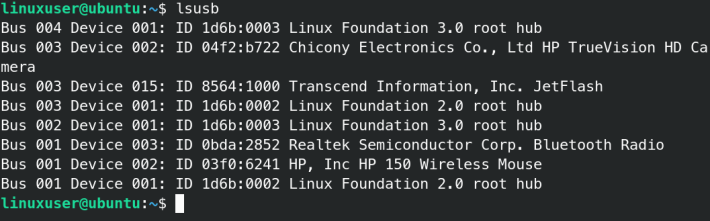
If there is no output of your USB flash drive try using the following command :
lusb is used to display all the connected and new devices on usb buses. As you can see in the above example I have a Transcend company’s pen drive connected to the available USB port. If you see the output here and not in fdisk try reattaching or formatting your USB device using tools like Gparted.
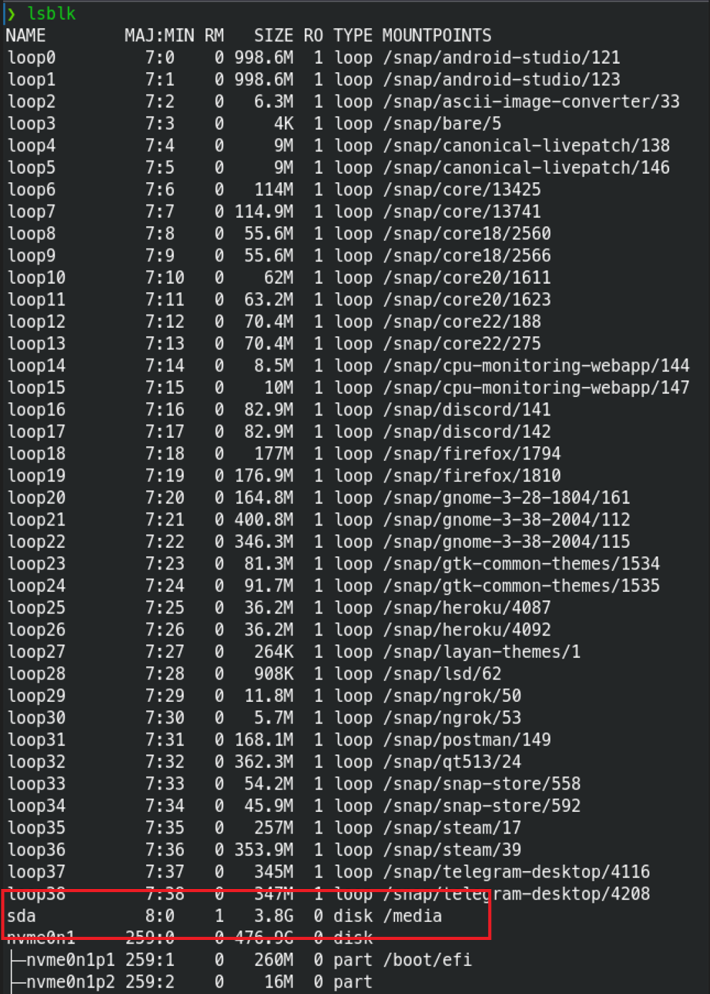
Using lsblk command you can check the device name and its mount points. Here you can see sda mounted to /media folder.
2. Change to USB Mounted directory
Change the directory with the following command
3. List Content Inside USB
Let’s see what we have inside our Pendrive. Using the list directory command :
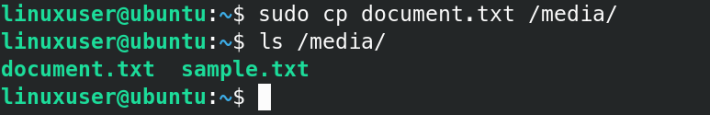
4. Copy files to USB
Now launch a new Linux terminal and navigate to the folder you to copy files from. Linux cp command is used to transfer files from one folder to another.
I want to copy files from my home directory to the USB flash drive.
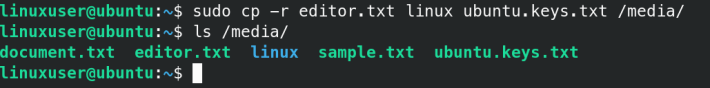
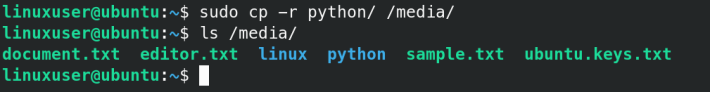
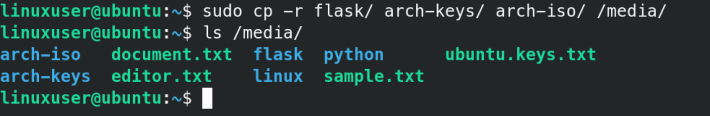
sudo cp -r filename1 filename2 filename /media-r parameter is used to recursively copy content.
sudo cp -r foldername /mediasudo cp -r folder1 folder2 foldern /media6. Verify
You can always verify that the files/folders have been copied using the ls command :
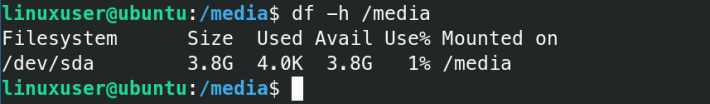
You may also verify by its size as follows:
I have a 4 GB USB flash drive.
Conclusion
Unlike graphical mode where you can copy and paste files, using a terminal we need to use the copy command to transfer files to a mounted USB device. Once we identified the mounted USB directory, we can easily copy the files. As mentioned all modern Linux automatically mounts the USB devices that part is also easy.
Thanks for reading, please leave your suggestions and feedback in the below comment section.
If this resource helped you, let us know your care by a Thanks Tweet. Tweet a thanks