- How to Create an Empty File Linux?
- Method 1: Create an Empty File Using the “touch” Command
- Method 2: Create an Empty File Using the “echo” Command
- Method 3: Create an Empty File Using Nano Editor
- Method 4: Create an Empty File Using “printf” Command
- Bonus Tip: How to Check the Status of an Empty File?
- Conclusion
- How to Create a File in Linux Using Terminal/Command Line
- Creating New Linux Files from Command Line
- Create a File with Touch Command
- Create a New File With the Redirect Operator
- Create File with cat Command
- Create File with echo Command
- Create File with printf Command
- Using Text Editors to Create a Linux File
- Vi Text Editor
- Vim Text Editor
- Nano Text Editor
- 4 Ways to Create a Text File in Linux Terminal
- Create file in Linux command line
- 1. Create an empty file using touch command
- 2. Create files using cat command
- 3. Create new file using echo command
- 4. Create a new file using a text editor like Nano or Vim
How to Create an Empty File Linux?
Creating an empty file is an important concept to manage the record before writing data in it. It occupies 0 bytes because no data is stored in it. If you are at the beginner stage of Linux user and don’t know the creation of empty files for storing data or information. This guide will demonstrate several methods to create an empty file in the Ubuntu system. The supported content is enlisted below:
- Method 1: Create an Empty File Using the “touch” Command
- Method 2: Create an Empty File Using the “echo” Command
- Method 3: Create an Empty File Using Nano Editor
- Method 4: Create an Empty File Using “printf” Command
- Bonus Tip: How to Check the Status of an Empty File?
Method 1: Create an Empty File Using the “touch” Command
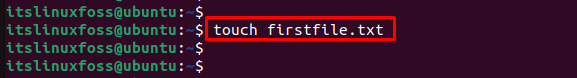
In Linux, most administrators need to create empty files to manage multiple files with the name of network users. The “touch” command helps to create an empty file by specifying the name based on needs. To create an empty file, run the below script:
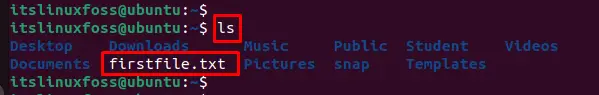
Using the “ls” command, you can verify that “firstfile.txt” has been created in the Home directory:
Method 2: Create an Empty File Using the “echo” Command
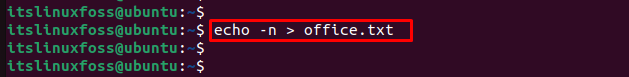
An alternative method for creating an empty file is possible through the “echo” command. This command requires the “-n” utility to create an empty file specifying the name and file type.
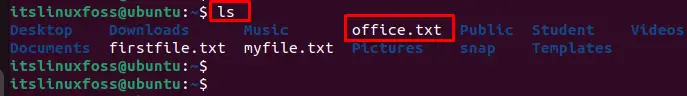
To confirm the creation of the empty file, you can utilize the “ls” command to visualize the “office.txt” has been successfully created in the directory.
Method 3: Create an Empty File Using Nano Editor
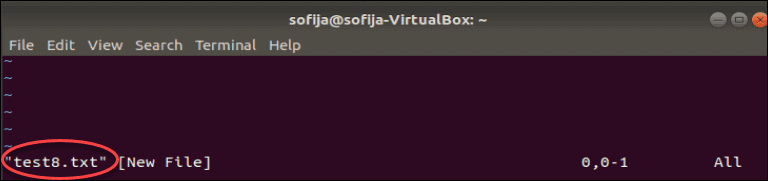
Another method can be considered to generate an empty file via Nano Editor. For instance, the “officefile.txt” file has been created through the “nano” command:
After executing the above command, it navigates to the Nano Editor by specifying the particular file name.
The empty file is ready, as visualized in the above figure.
Method 4: Create an Empty File Using “printf” Command
An interesting method can also be adapted for creating an empty file through the “printf” command. For this purpose, an “empfile.txt” will be created after executing the below script:
After executing the script, the “empfile.txt” has been created that can be visualized via the “ls” command:
That is all for creating an empty file.
Bonus Tip: How to Check the Status of an Empty File?
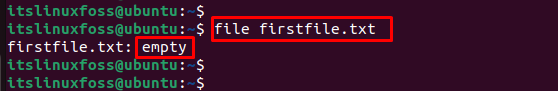
It is additional information to display the status of an empty file. In our case, an existing file, “firstfile.txt”, is stored in the home directory. To check the status of the particular file, run the below script:
The executed command verifies the status “empty” of the particular file “firstfile.txt” in the above figure.
Conclusion
In Ubuntu, the “touch”, “echo”, “nano”, and “printf” commands are used to create an empty file in the home directory. These above commands require the file name and type users want to create. These empty files can be modified through the Nano Editor. Also, users can find out the file status by executing the “ ” script. This guide has explained all possible methods for creating an empty file via the Ubuntu terminal.
How to Create a File in Linux Using Terminal/Command Line
Creating a new file in Linux is straightforward, but there are also some surprising and clever techniques.
In this tutorial learn how to to create a file from a Linux terminal.
- Access to a command line/terminal window (Ctrl–Alt–F2 or Ctrl–Alt–T)
- A user account with sudo privileges (optional for some files/directories)
Creating New Linux Files from Command Line
Linux is designed to create any file you specify, even if it doesn’t already exist. One smart feature is that you can create a file directly, without needing to open an application first.
Here are a few commands for creating a file directly from the command line.
Create a File with Touch Command
The easiest way to create a new file in Linux is by using the touch command.
In a terminal window, enter the following:
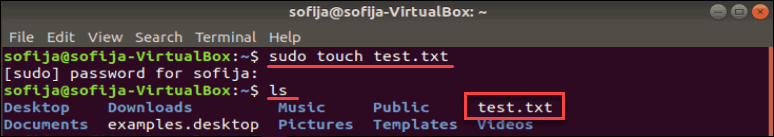
This creates a new empty file named test.txt. You can see it by entering:
The ls command lists the contents of the current directory. Since no other directory was specified, the touch command created the file in the current directory.
If there’s already a file with the name you chose, the touch command will update the timestamp.
Create a New File With the Redirect Operator
A redirection operator is a name for a character that changes the destination where the results are displayed.
Right angle bracket >
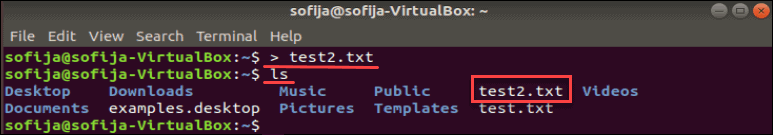
This symbol tells the system to output results into whatever you specify next. The target is usually a filename. You can use this symbol by itself to create a new file:
This creates a new empty file.
Use the ls command to list the contents of the current directory and find the file test2.txt.
Create File with cat Command
The cat command is short for concatenate. It can be used to output the contents of several files, one file, or even part of a file. If the file doesn’t exist, the Linux cat command will create it.
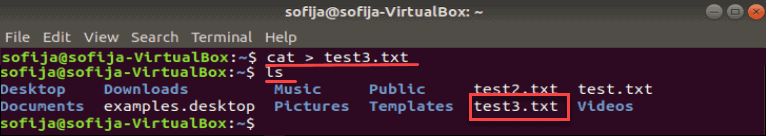
To create an empty file using cat , enter the following:
Note the redirection operator. Typically, the command displays the contents of test2.txt on the screen. The redirection operator > tells the system to place it in the test2.txt file.
Verify that the file was created:
The system should now have test.txt, test2.txt, and test3.txt in the list.
Create File with echo Command
The echo command will duplicate whatever you specify in the command, and put the copy into a file.
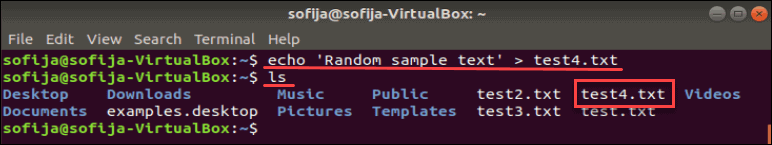
echo 'Random sample text' > test4.txtVerify that the file was created:
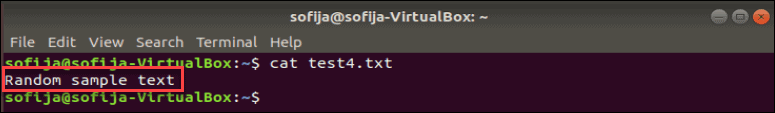
You should see the test4.txt file added to the list. Use the cat command to display the contents of the new file:
The system should display Random sample text (or whatever you entered with the echo command.)
Create File with printf Command
The printf command works like the echo command, and it adds some formatting functionality. To add a single line of text, enter:
printf 'First line of text\n' test5.txtTo add two lines of text, separate each line with the \n option:
printf 'First line of text\n Second line of text' test6.txtYou can use the cat command on either of these files to display their contents.
Note: To use several terminal instances in a single window manager, consider using Linux screen. It enables additional features and an enhanced command line for working with Linux files.
Using Text Editors to Create a Linux File
All Linux distributions have at least one text editor. Some have multiple editors. Each editor has different strengths and features. This will show you three of the most popular.
Vi Text Editor
Vi is the oldest text editor in Linux. It was created alongside the Linux operating system for directly editing text files. Since it’s unlikely you’ll see a Linux distribution without it, it’s a safe editor to know.
To create a file using Vi, enter the following:
Your screen will change. Now you’re in the text editor. Press the letter i to switch to insert mode, then type a few words to try it out.
To save and exit press Esc 😡 and hit Enter .
Vim Text Editor
You may have noticed that the Vi editor wasn’t very user-friendly. Vim is a newer version, which stands for Vi editor, Modified.
Use vim to create a new text file:
This screen will look similar to the Vi editor screen. Press i to insert text, and type a few words. Save file and exit by entering:
(Escape, colon wq, then Enter.)
Nano Text Editor
Nano is a newer and much easier text editor to navigate.
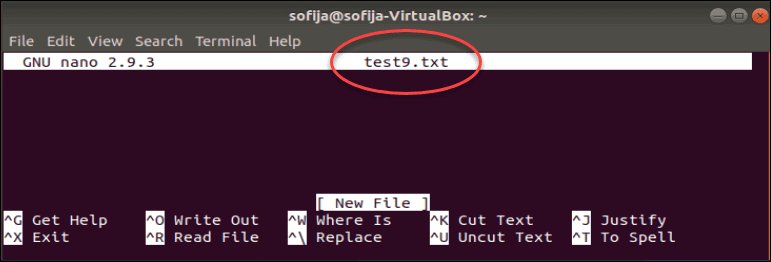
Create a new file by entering the command:
By default, Nano puts you directly into editing mode. It also displays a helpful list of commands at the bottom of the screen.
Enter some text, then press Ctrl+O to save the changes.
Press Ctrl+X to exit the editor.
Note: Learn all you need about Nano in the Install and Use Nano in Linux article.
Now you have several options to create new files in Linux from the command line. Next, learn how to copy files and directories in Linux to manage your files more efficiently.
4 Ways to Create a Text File in Linux Terminal
In this Linux beginner series, you’ll learn various methods to create a file in Linux terminal.
In this Linux beginner series, you’ll learn various methods to create a text file in Linux terminal.
If you have used the desktop oriented operating system such as Windows, creating file is a piece of cake. You right click in the file explorer and you would find the option of creating new file.
Things won’t look the same when you are in a command line environment. There is no right click option here. So how do you create a file in Linux then? Let me show you that.
Create file in Linux command line
There are various ways of creating a new file in Linux terminal. I’ll show you the commands one by one. I am using Ubuntu here but creating files in Ubuntu terminal is the same as any other Linux distribution.
1. Create an empty file using touch command
One of the biggest usages of the touch command in Linux is to create a new empty file. The syntax is super simple.
If the file doesn’t exist already, it will create a new empty file. If a file with the same name exists already, it will update the timestamps of the file.
2. Create files using cat command
Another popular way of creating new file is by using the cat command in Linux. The cat command is mostly used for viewing the content of a file but you can use it to create new file as well.
You can write some new text at this time if you want but that’s not necessary. To save and exit, use Ctrl+D terminal shortcut.
If the file with that name already exists and you write new text in it using the cat command, the new lines will be appended at the end of the file.
3. Create new file using echo command
The main use of the echo command is to simply repeat (echo) what you type on the screen. But if you use the redirection with echo, you can create a new file.
To create a new file using echo you can use something like this:
echo "This is a sample text" > filename.txtThe newly created filename.txt file will have the following text: This is a sample text. You can view the file in Linux using cat or other viewing commands.
You are not obliged to put a sample text with echo. You can create an (almost) empty file using the echo command like this:
This will create a new file with just one empty line. You can check the number of lines with wc command.
4. Create a new file using a text editor like Nano or Vim
The last method in this series is the use of a text editor. A terminal-based text editor such as Emacs, Vim or Nano can surely be used for creating a new file in Linux.
Before you use these text editors, you should make sure that you know the basics such as saving an existing from the editor. Unlike the GUI tools, using Ctrl+S in the terminal won’t save the file. It could, in fact, send your terminal into a seemingly frozen state from which you recover using Ctrl+Q.
Let’s say you are going to use Vim editor. Make sure that you are aware of the basic vim commands, and then open a new file with it like this:
What’s your favorite command?
So, I just shared 4 different ways of creating a file in Linux. Personally, I prefer using touch for creating empty file and Vim if I have to edit the file. On a related note, you may want to learn about the file command in Linux that is helpful in determining the actual type of the file.
Which command do you prefer here? Please share your views in the comment section below.