- Command line option to check which filesystem I am using?
- 9 Answers 9
- 7 Ways to Determine the File System Type in Linux (Ext2, Ext3 or Ext4)
- 1. Using df Command
- 2. Using fsck Command
- 3. Using lsblk Command
- 4. Using mount Command
- 5. Using blkid Command
- 6. Using file Command
- 7. Using fstab File
- Related Posts
- 15 thoughts on “7 Ways to Determine the File System Type in Linux (Ext2, Ext3 or Ext4)”
- Linux — узнать файловую систему диска или раздела
- How to Show File System Type in Linux
- 1. Using df — T Command
- 2. Using lsblk -fs Command
Command line option to check which filesystem I am using?
Is there a command that will show which file system (ext3, ext4, FAT32, . ) the various partitions and disks are using? Similar to how sudo fdisk -l lists information about disks and partitions?
What do you mean by «similar to» sudo fdisk -l ? . Even when the drive is not mounted, fisk gives you the file system type, and it is a command line tool. I unmounted two of my drives (a USB, and an Internal) and this worked fine: sudo fdisk -l|grep «^/dev»
@fred fdisk says things like «Linux» and «Linux swap», can’t see that it tells me whether it’s ext3 or ext4.
Don’t go by the name;; go by the filesystem Id . if its 83 , fdisk reports it as «Linux , **gpart** as mentioned by Luke Maurer) reports it as **ext2** ,, same thing.. The drives I tested are Ext4 (but were reported as ‘ext2’ and ‘Linux’ by the two apps), but it seems that this identity is a higher abstraction. Whether you really need to go further is up to you. but the **Id** certainly gives you a pretty closes idea. (if you need to know specifically, perhaps ‘gpart in full scan mode will do it. (I havent tried its full scan, but I suspect it won’t say much more (??)..
9 Answers 9
me@hostname:/$ mount /dev/sda1 on / type ext4 (rw,errors=remount-ro) proc on /proc type proc (rw,noexec,nosuid,nodev) none on /sys type sysfs (rw,noexec,nosuid,nodev) none on /sys/fs/fuse/connections type fusectl (rw) Except that the disks aren’t mounted — I’m trying to figure out which FS to put in /etc/fstab for a USB external disk
@frabjous Why use Nautilus? Could also just mount it on the command line and then check; this usually works even if you don’t specify the filesystem.
Found a solution in ubuntuforums: blkid
sudo blkid /dev/sda1 /dev/sda1: UUID=". " TYPE="ext4" sudo blkid /dev/sdf1 /dev/sdf1: LABEL="backup" UUID=". " TYPE="ext3" sudo blkid /dev/md0 /dev/md0: LABEL="raid" UUID=". " TYPE="ext4" Mount without specifying filesystem (commenting out any entries in fstab) works as well:
sudo mount /dev/sdf1 /mnt/tmp mount | grep /mnt/tmp /dev/sdf1 on /mnt/tmp type ext3 (rw) df -h -T will list all disks used with filesystem type.
This command will also let you query which filesystem is in use for an arbitrary given directory.
For example, the following output shows that the /usr/local/lib directory is on the /dev/xvdb device, and it’s formatted with the ext4 filesystem.
user@disp556:~$ sudo df -h -T /usr/local/lib Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/xvdb ext4 2.0G 135M 1.8G 7% /usr/local user@disp556:~$ Will give you the filesystem of any attached devices, whether they are mounted or not.
It also gives you other useful information for creating the needed line for your fstab file such as the UUID.
All of the solutions suggested here are valid, but don’t allow to see if for instance a partition is FAT16 or FAT32. For this level of detail, the best command is
/dev/sdc: DOS/MBR boot sector, code offset 0x58+2, OEM-ID "MSWIN4.1", sectors/cluster 32, Media descriptor 0xf8, sectors/track 63, heads 255, sectors 15794176 (volumes > 32 MB) , FAT (32 bit), sectors/FAT 3856, reserved 0x1, serial number 0x4c437f55, unlabeled It’s somewhat overkill, but there’s always gpart . It’s meant for when the partition table is broken, but it does tell you what type all the filesystems it can find are.
EDIT: This doesn’t seem to work if something on the disk is mounted already, though (I just tried it on my running system).
Theoretically, if you just want it to print the partition table, you can use a command like this (from the man page):
But again I can’t try it right now; not sure if it’ll tell you the filesystems if it’s not doing a scan.
I just tried it. I unmounted my «sdb» data drive via Nautilus.. It’s mounpoint directory showed as «Total 0» via «ls -l» and anothe File Browser (PCMan) prompted me to mount it. but even though it wasn’t mounted gpart did return basic partiton information; in particuar, it did show the filesystem
It works, but a bit slower than the other answers — it takes a while to scan a 1TB disk. Still thanks for the pointer to a useful tool, I’m sure gpart will come in handy.
A nice simple tool to find out information about attached devices. and to do backups is the fsarchiver program.
You probably have to install it to use it.
The command I usually use to find out what is on the system is :
sudo fsarchiver probe simple and that comes back with something like :
[======DISK======] [=============NAME==============] [====SIZE====] [MAJ] [MIN] [sda ] [WDC WD1001FALS-0 ] [ 931.51 GB] [ 8] [ 0] [sdb ] [ST31000524AS ] [ 931.51 GB] [ 8] [ 16] [sdg ] [DataTraveler 3.0 ] [ 29.31 GB] [ 8] [ 96] [=====DEVICE=====] [==FILESYS==] [======LABEL======] [====SIZE====] [MAJ] [MIN] [sda1 ] [xfs ] [ ] [ 500.00 MB] [ 8] [ 1] [sda2 ] [LVM2_member] [ ] [ 931.02 GB] [ 8] [ 2] [sdb5 ] [ext4 ] [mydisk_data_01 ] [ 931.51 GB] [ 8] [ 21] [sdg1 ] [vfat ] [KINGSTON ] [ 29.30 GB] [ 8] [ 97] [dm-0 ] [xfs ] [ ] [ 100.00 GB] [253] [ 0] [dm-1 ] [swap ] [ ] [ 34.00 GB] [253] [ 1] [dm-2 ] [xfs ] [ ] [ 797.02 GB] [253] [ 2]
7 Ways to Determine the File System Type in Linux (Ext2, Ext3 or Ext4)
A file system is the way in which files are named, stored, retrieved as well as updated on a storage disk or partition; the way files are organized on the disk.
A file system is divided in two segments called: User Data and Metadata (file name, time it was created, modified time, it’s size and location in the directory hierarchy etc).
In this guide, we will explain seven ways to identify your Linux file system type such as Ext2, Ext3, Ext4, BtrFS, GlusterFS plus many more.
1. Using df Command
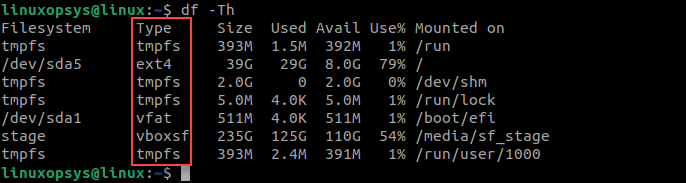
df command reports file system disk space usage, to include the file system type on a particular disk partition, use the -T flag as below:
$ df -Th OR $ df -Th | grep "^/dev"
For a comprehensive guide for df command usage go through our articles:
2. Using fsck Command
fsck is used to check and optionally repair Linux file systems, it can also print the file system type on specified disk partitions.
The flag -N disables checking of file system for errors, it just shows what would be done (but all we need is the file system type):
$ fsck -N /dev/sda3 $ fsck -N /dev/sdb1
3. Using lsblk Command
lsblk displays block devices, when used with the -f option, it prints file system type on partitions as well:
4. Using mount Command
mount command is used to mount a file system in Linux, it can also be used to mount an ISO image, mount remote Linux filesystem and so much more.
When run without any arguments, it prints info about disk partitions including the file system type as below:
5. Using blkid Command
blkid command is used to find or print block device properties, simply specify the disk partition as an argument like so:
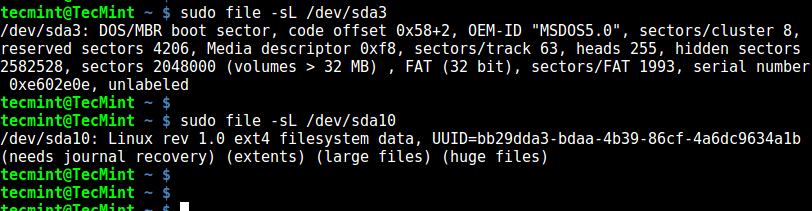
6. Using file Command
file command identifies file type, the -s flag enables reading of block or character files and -L enables following of symlinks:
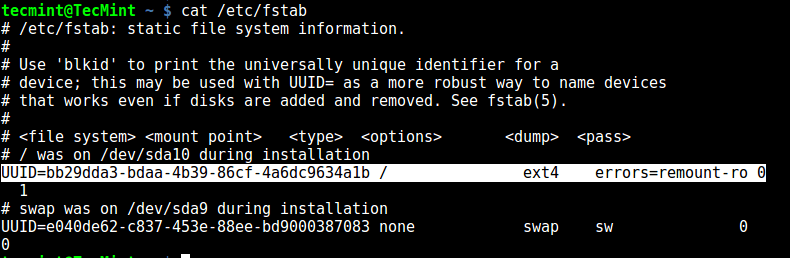
7. Using fstab File
The /etc/fstab is a static file system info (such as mount point, file system type, mount options etc) file:
That’s it! In this guide, we explained seven ways to identify your Linux file system type. Do you know of any method not mentioned here? Share it with us in the comments.
Aaron Kili is a Linux and F.O.S.S enthusiast, an upcoming Linux SysAdmin, web developer, and currently a content creator for TecMint who loves working with computers and strongly believes in sharing knowledge.
Each tutorial at TecMint is created by a team of experienced Linux system administrators so that it meets our high-quality standards.
Related Posts
15 thoughts on “7 Ways to Determine the File System Type in Linux (Ext2, Ext3 or Ext4)”
will create a ext2 filesystem on image1, if its not big enough (warning “Filesystem too small for a journal” means a filesystem without a journal, a.k.a. ext2, is created) If you don’t realize this and nevertheless mount it as ext4. The df and mount methods above will mirror back ext4:
$ df -Th /tmp/mnt* Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/loop4 ext4 1003K 24K 908K 3% /tmp/mnt1 /dev/loop5 ext4 987K 33K 812K 4% /tmp/mnt2 $ mount | grep mnt . /home/mallikab/image1 on /tmp/mnt1 type ext4 (rw,relatime,seclabel) /home/mallikab/image2 on /tmp/mnt2 type ext4 (rw,relatime,seclabel,data=ordered)
$ fsck -N /tmp/mnt1 fsck from util-linux 2.23.2 [/sbin/fsck.ext2 (1) -- /tmp/mnt1] fsck.ext2 /tmp/mnt1 $ fsck -N /tmp/mnt2 fsck from util-linux 2.23.2 [/sbin/fsck.ext4 (1) -- /tmp/mnt2] fsck.ext4 /home/mallikab/image2 $ file -sL /home/mallikab/image2 /home/mallikab/image2: Linux rev 1.0 ext4 filesystem data, UUID=b4e8e086-54ca-4d9d-9f38-32bbed211e6b (needs journal recovery) (extents) (64bit) (huge files) $ file -sL /home/mallikab/image1 /home/mallikab/image1: Linux rev 1.0 ext2 filesystem data (mounted or unclean), UUID=09b3a8c9-0b6d-43c5-b195-c45f6c091765 (extents) (64bit) (huge files) hm, although fsck doesn't indicate ext2 unless the images are mounted, i.e. $ fsck -N ~/image1 fsck from util-linux 2.23.2 [/sbin/fsck.ext4 (1) -- /home/mallikab/image1] fsck.ext4 /home/mallikab/image1
The only working method for me was ‘ lsblk -f ‘; the other replied “fuseblk“, “HPFS/NTFS/exFAT” or nothing. Reply
Linux — узнать файловую систему диска или раздела
Список команд с помощью которых можно узнать файловую систему.
Любой выбранный раздел с помощью file:
/dev/sda1: Linux/i386 swap file (new style), version 1 (4K pages), size 975743 pages, no label, UUID=xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx Все смонтированные разделы с помощью df:
df -T df -Th | grep "^/dev" df -Th | grep "^/dev/nvme"Файл.система Тип 1K-блоков Использовано Доступно Использовано% Cмонтировано в udev devtmpfs 16395728 12 16395716 1% /dev tmpfs tmpfs 3281384 13476 3267908 1% /run /dev/sda3 ext4 38318740 27121492 11180864 71% / none tmpfs 4 0 4 0% /sys/fs/cgroup none tmpfs 5120 0 5120 0% /run/lock none tmpfs 16406916 12 16406904 1% /run/shm none tmpfs 102400 0 102400 0% /run/user /dev/sda2 vfat 975228 3456 971772 1% /boot/efi /dev/sda4 xfs 64419347968 54767602848 9651745120 86% /u01 /dev/sdb1 xfs 58602802688 27835955672 30766847016 48% /u02 Смонтированные разделы с помощью mount:
/dev/sda3 on / type ext4 (rw,errors=remount-ro) /dev/sda2 on /boot/efi type vfat (rw) /dev/sda4 on /u01 type xfs (rw) /dev/sdb1 on /u02 type xfs (rw)В виде дерева с помощью lsblk:
NAME FSTYPE LABEL MOUNTPOINT sda ├─sda1 swap [SWAP] ├─sda2 vfat /boot/efi ├─sda3 ext4 / └─sda4 xfs /u01 sdb └─sdb1 xfs /u02Выбранный раздел с помощью blkid:
/dev/sdb1: UUID="xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx" TYPE="xfs"How to Show File System Type in Linux
Every object in a Linux computer is considered a file. A Linux file system is an organization that is used to store and manage files on a storage device. The storage device is logically divided using the file system to keep different types of files arranged for effective search, access, deletion, and modification. Linux supports various file systems, including ext2, ext3, and ext4.
In this tutorial, we will learn how to show file system type in Linux. We can determine it using different methods.
1. Using df — T Command
The df command, also known as disk file system type, in Linux is used to check the disk usage on a storage device. This command-line utility is pre-installed on most of the major Linux operating system distributions. By default, the df command displays only the available and used disk space, but you can use the -T flag to display the file system of all the storage devices that are mounted:
The df command in this output shows the following information:
- Filesystem – name of the currently mounted partition or the storage device.
- Type – storage device or partition file system types.
- Size – total size of the mounted partition or storage device.
- Used – consumed disk space of the mounted partition or storage device.
- Avail – amount of available disk space of the mounted partition or storage device.
- Use% – percentage of used disk space in the mounted partition or storage device.
- Mounted on – name of the directory where the partition or storage device is mounted.
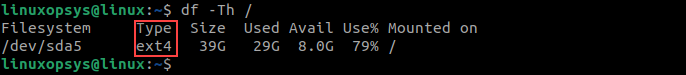
To display the metadata of a specific storage device or partition, specify the partition name with the df command. For example, to check the FS of the root partition, type:
2. Using lsblk -fs Command
To identify the filesystem type -fs option with lsblk: