- Mastering Linux: How to Display Current Date and Time in Terminal
- Compatibility of Linux OS for Displaying Date and Time
- Commands for Getting Current Date and Time
- The Date Command
- The Time Command
- The Timedatectl Command
- Time in Linux
- Other helpful code examples for displaying current date and time in Linux terminal
- Conclusion
- Как узнать текущее время Linux
- Текущее время Linux
- С помощью date
- 2. С помощью hwclock
- 3. С помощью timedatectl
- Выводы
- Linux Get Current Time
- Conclusion:
- About the author
- Omar Farooq
Mastering Linux: How to Display Current Date and Time in Terminal
Learn step-by-step instructions on how to display the current date and time in the terminal using various Linux commands. Ensure accurate time settings for system logs, backups, and troubleshooting. Try it now!
As a Linux user, you may need to display the current date and time in the terminal for various reasons, such as system logs, backups, and troubleshooting. Thankfully, Linux operating systems have built-in commands that allow you to display the current date and time easily. In this article, we will provide you with step-by-step instructions on how to use various Linux commands to display the current date and time in the terminal.
Compatibility of Linux OS for Displaying Date and Time
Various Linux operating systems have built-in compatibility for displaying date and time in the terminal. However, the commands used to display date and time may vary depending on the Linux distribution being used. In general, you can use any of the following commands to display the current date and time in the terminal:
Commands for Getting Current Date and Time
The Date Command
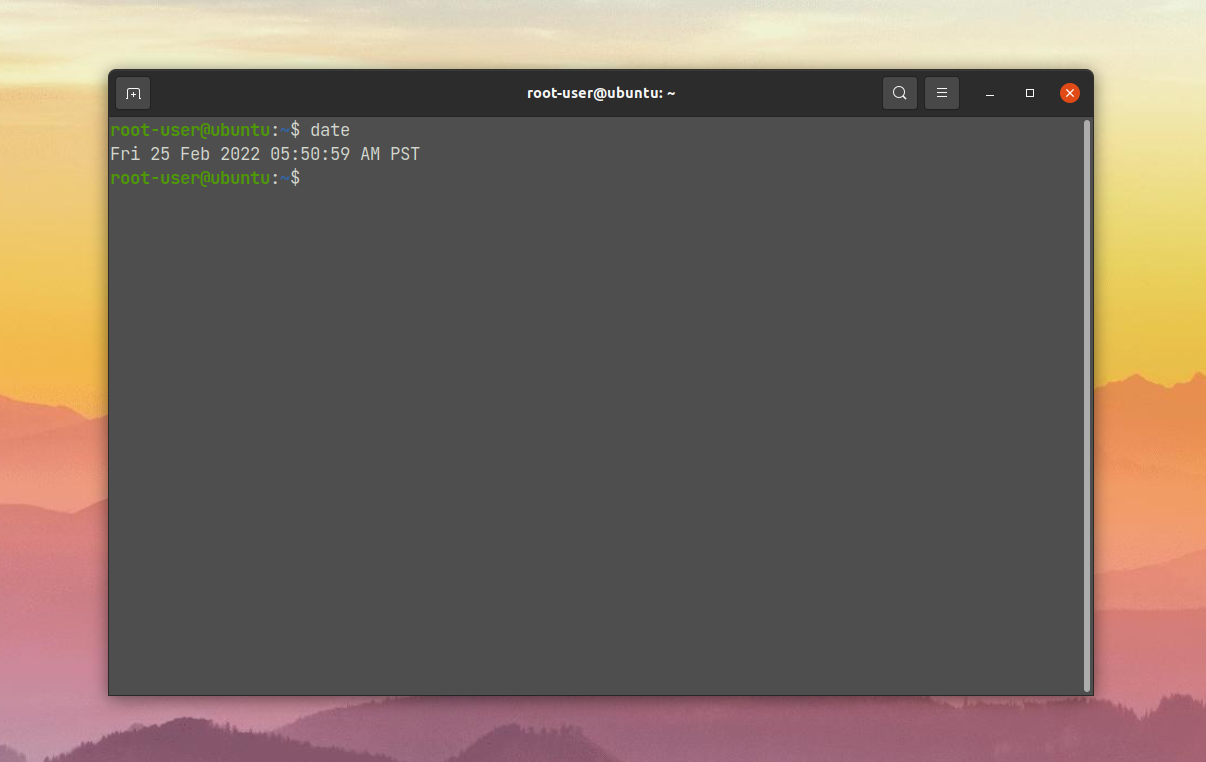
The date command is used to display and set the system time in BASH. To display the current date and time in the terminal, simply type date and press enter. The terminal will display the date and time in the default format, which is usually in the format of “Day Month Date Time Timezone Year”. For example:
$ date Thu Aug 19 20:38:00 EDT 2021 You can also use the date command to set the system time in BASH. For example, to set the system time to 8:00 PM, August 19, 2021, you can use the following command:
$ sudo date -s "2021-08-19 20:00:00" The date command can also display the date and time in different formats. To display the date and time in a specific format, you can use the following command:
$ date +"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" 2021-08-19 20:38:00 This command will display the date and time in the format of “Year-Month-Day Hour:Minute:Second”.
The Time Command
The time command can execute a program and print a summary of real-time, user CPU time, and system CPU time spent by executing a program. It can also display the current date and time in the terminal. To display the current date and time using the time command, simply type time and press enter. The terminal will display the date and time along with the statistics of the command execution. For example:
$ timereal 0m0.000s user 0m0.000s sys 0m0.000s Thu Aug 19 20:38:00 EDT 2021 The Timedatectl Command
The timedatectl command can be used to display the current time and date in the terminal. It can also be used to set or change the time, set the time zone, and enable or disable automatic synchronization with NTP servers. To display the current date and time using the timedatectl command, simply type timedatectl and press enter. The terminal will display the current time and date along with other information such as the time zone and NTP synchronization status. For example:
$ timedatectl Local time: Thu 2021-08-19 20:38:00 EDT Universal time: Fri 2021-08-20 00:38:00 UTC RTC time: Fri 2021-08-20 00:38:00 Time zone: America/New_York (EDT, -0400) NTP enabled: yes NTP synchronized: yes RTC in local TZ: no DST active: yes Last DST change: DST began at Sun 2021-03-14 01:59:59 EST Sun 2021-03-14 03:00:00 EDT Next DST change: DST ends (the clock jumps one hour backwards) at Sun 2021-11-07 01:59:59 EDT Sun 2021-11-07 01:00:00 EST To set or change the time using the timedatectl command, you can use the following command:
$ sudo timedatectl set-time "2021-08-19 20:00:00" This command will set the system time to 8:00 PM, August 19, 2021.
Time in Linux
Time concepts, commands, clocks, timers and high resolution sleep and timers are explained. Duration: 35:38
Other helpful code examples for displaying current date and time in Linux terminal
In Shell as proof, show date linux code example
In Shell , time in linux command code example
Open a terminal and type the following command:dateSat Nov 7 22:44:59 IST 2020You can format the date as follows in dd-mm-yy format: date +"%d-%m-%y"07-11-2020Conclusion
Displaying the current date and time in the terminal is a useful feature of Linux operating systems. The date , time , and timedatectl commands can be used to display the current date and time, and to set or change the system time. Incorrect time settings can cause issues with system authentication and encryption, so it is important to ensure accurate time settings. Additionally, the Unix epoch, which is the number of seconds that have elapsed since January 1, 1970 (midnight), can also be used to represent time in Linux. By mastering these commands, you can easily manage the time and date in your Linux system.
Как узнать текущее время Linux
Иногда знание текущего времени на компьютере играет большую роль, например, при отслеживании выполнения тех или иных процессов. И далеко не всегда нужную информацию можно посмотреть через системный интерфейс Linux. Поэтому существуют различные команды для терминала.
В данной статье мы расскажем про то, как узнать текущее время Linux. Заодно упомянем тему часовых поясов и синхронизацию с серверами времени.
Текущее время Linux
В системе Linux есть три удобных утилиты для определения точного времени. Наиболее продвинутой из них можно назвать date. Но и остальные имеют свои особенности.
С помощью date
Чтобы получить общую информацию, выполните команду:
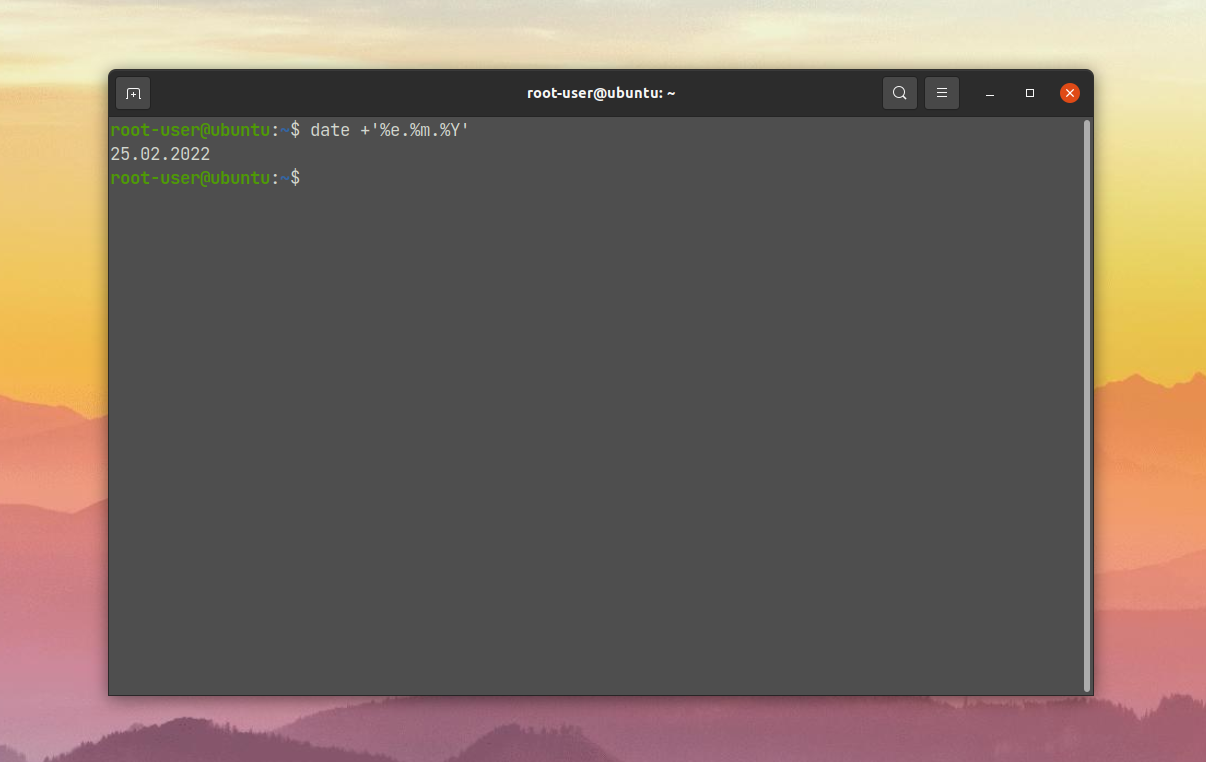
Сначала выводится дата (день-число-месяц-год), время в 12-часовом формате с пометками AM (до полудня) и PM (после полудня) и часовой пояс. Информацию можно вывести в мировом UTC-формате:
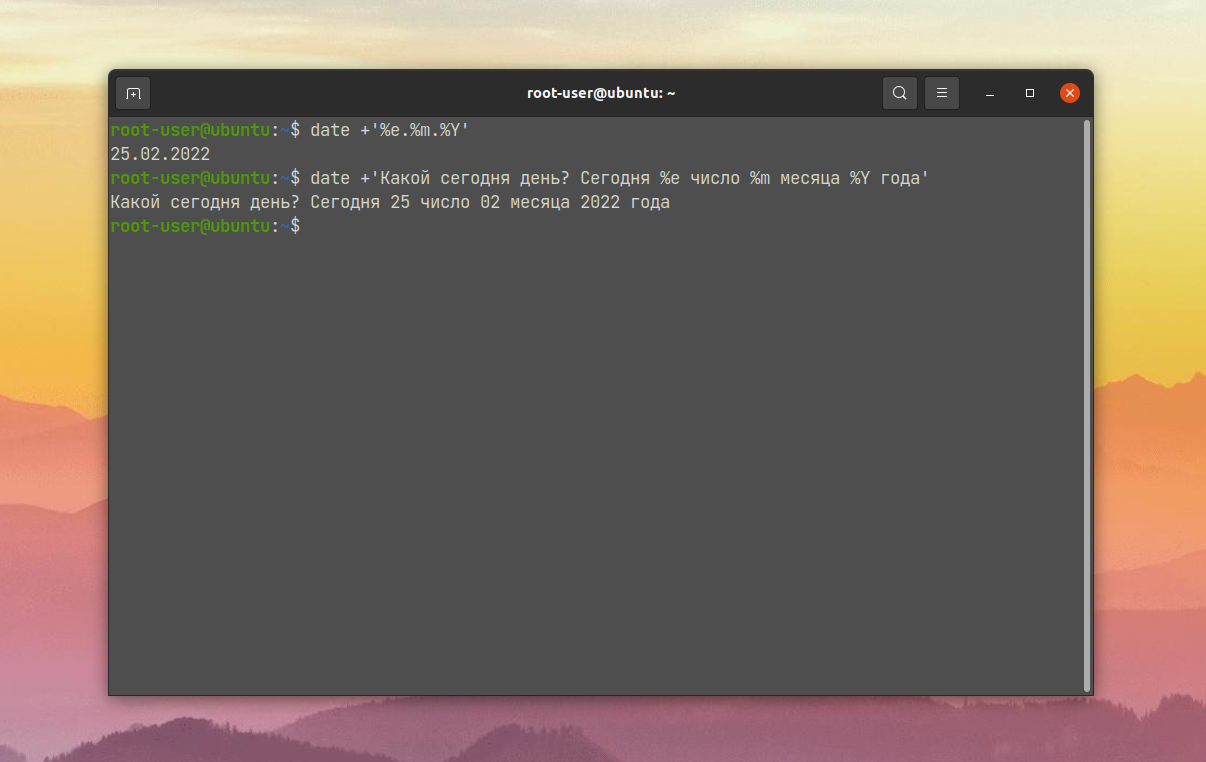
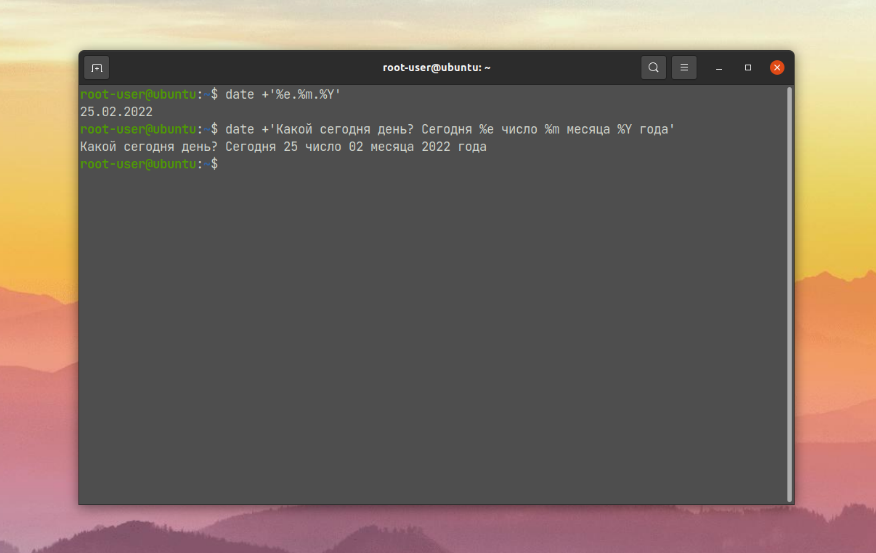
Форматирование задается после знака +. Первый символ после знака % интерпретируется как один из модификаторов. А остальные символы выводятся как обычный текст. Этим можно пользоваться:
date +’Какой сегодня день? Сегодня %e число %m месяца %Y года’
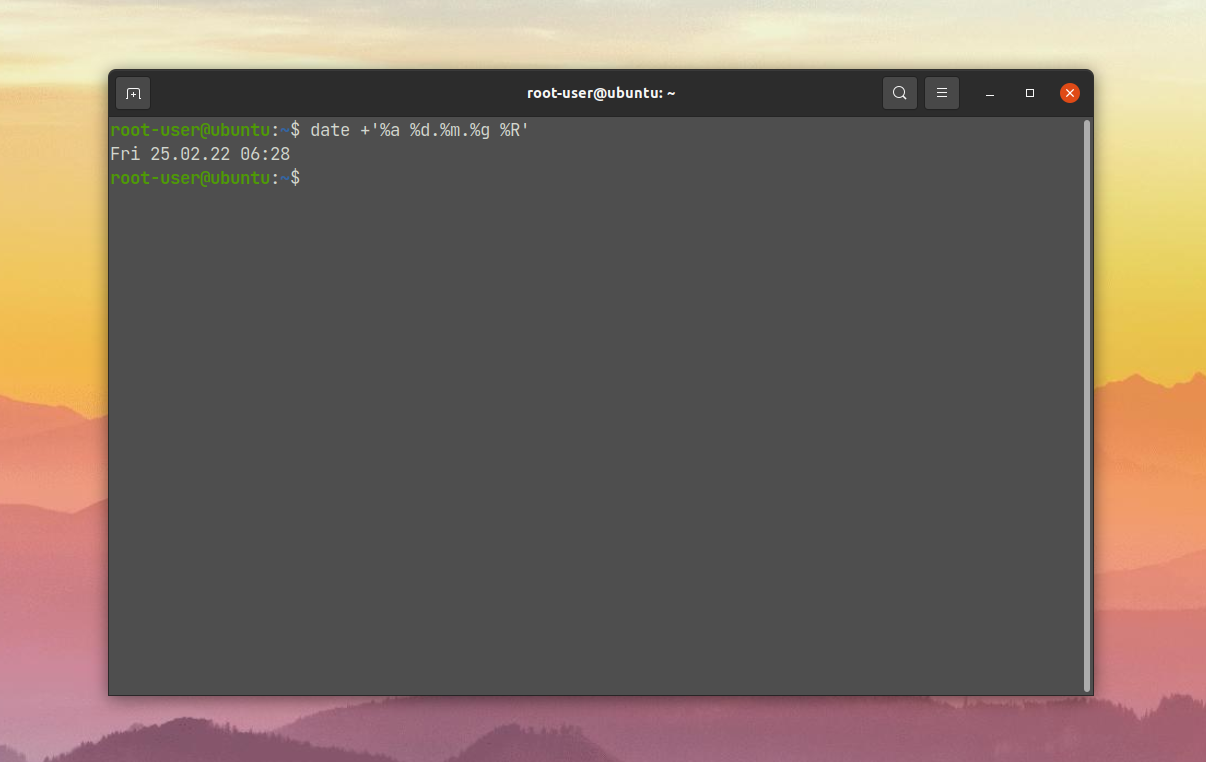
Еще один пример – вывод даты в кратком виде и времени в 24-часовом формате:
Ну и не совсем стандартный вариант – вывести, какой это по счету день в году, и сам год:
date +’Сегодня %j день %Y года’
данной статьей. В ней детально описан синтаксис, опции, форматирование вывода и конкретные примеры использования. А мы переходим к следующему способу.
2. С помощью hwclock
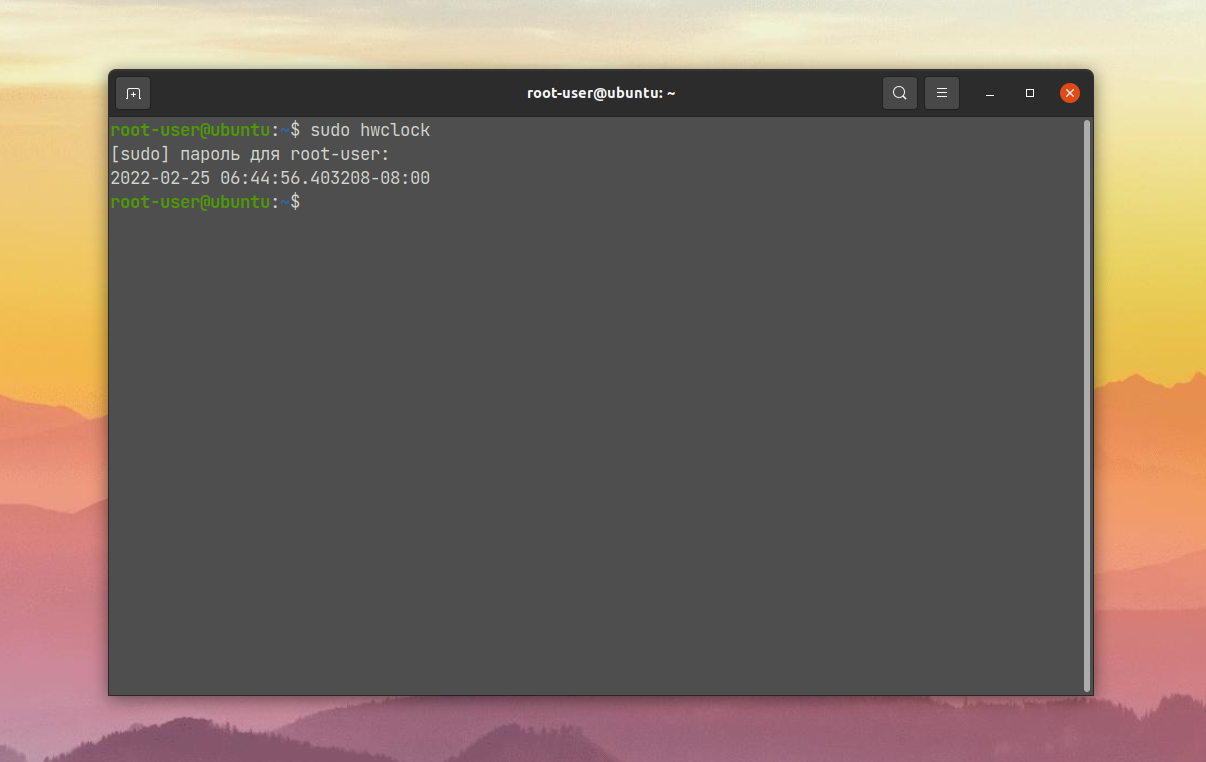
Вообще утилита hwclock используется для настройки даты и времени в системе Linux. Но еще она подходит для простого вывода этой информации. Запускать ее следует с правами супер-пользователя:
Обратите внимание на формат вывода времени. Он включает в себя еще и миллисекунды. И через дефис указывается часовой пояс. По умолчанию это UTC. Ну а для вывода локального времени нужно добавить к команде опцию —localtime:
3. С помощью timedatectl
Еще один вариант просмотра текущего времени – использование утилиты timedatectl. Достаточно ввести команду в терминале:
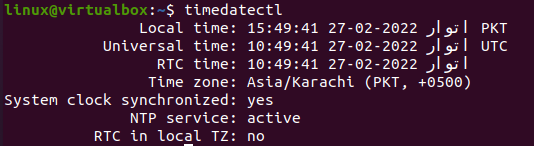
Помимо даты и времени, здесь есть следующие интересующие нас поля:
- Time zone – часовой пояс.
- System clock synchronized – синхронизация часов с сервером.
- NTP service – подключение к серверу точного времени.
Выводы
Каждый из упомянутых в статье способов Как узнать текущее время Linux имеет свои особенности. Для утилиты date можно детально настроить форматирование вывода. hwclock подходит для беглого просмотра информации, ведь в основном используется для настройки. А через timedatectl получится узнать еще и статус синхронизации часов.
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Linux Get Current Time
The time function is utilized within all operating systems like Windows, Linux, Unix, etc. You may see the current date and time at the desktop screens of your operating system within standard formats. But what about the exact current time displayed on the Linux operating system. If you are looking for a guide toward using date and time functions to display the current date and time in the Linux shell, then this article is for you. So let’s start this guide by logging in to your Ubuntu 20.04 system, as we will be performing each command on the Ubuntu 20.04 Linux shell.
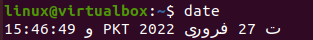
After a successful login, you first need to open the Ubuntu’s terminal shell via the activity area at the desktop taskbar. Tap on it and write “terminal” in the search bar shown on your screen. The pop-up terminal screen will be shown, and you have to tap on it to open it quickly. If this process is lengthy, try using the “CTRL+Alt+T” to launch it faster. Now, your terminal will be opened within no more than 10 seconds on your screen. Let’s start with the most basic command to display the date and time of our current time zone on the shell. On executing the following command, the time has been displayed in the “hour: minute: second” format along with the time zone, i.e., PKT. It also shows the current date according to the time zone. Upon execution, you will get the output, as shown below:
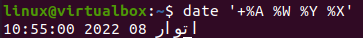
If you want to only display the date on your shell with the specific format, you need to specify the format in the date command. Use the inverted commas to add the format in “%d” for day, %m for month, %y for year separated by “-” signs. This command execution shows us the date in standard “day-month-year” format. Upon execution, you will get the following output:
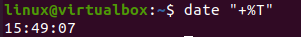
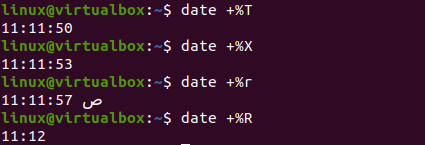
If you only want to display the current time on your shell using the “date” command, you must use the “+%T” character flag. On execution of this command, the current time for a specific time zone will be displayed in a standard format, i.e., “hour: minute: second”. Upon execution, you will get the output, as shown below:
If you want to display both the current and time in a single line with the time and date specification, you can also do that with the date command. So, to display the title “Date” and “Time”, we need to add “+DATE: %D” for date and “TIME: “%T” for time. The output of this instruction shows the date and time in standard format with titles of date/time on the shell. Upon execution, you will get the following output:
For example, we want to get the exact date and time of the same time zone and same time for some past year. We need to utilize the “—date” flag with the “=” sign to get the value to be searched. For example, we want to get a date and time exactly three years back for the same moment. On execution, the following instruction shows the date and time for the exact three years back, i.e., February 27, 2019:
Upon execution, you will get the affixed output.
If we want to take an exact date and time for the very next day on the shell, we will use the same “date” command with the “—date” flag. Use the value “tomorrow” in the inverted commas and execute the command. This will show the next exact date from the current exact date and time, i.e., February 28, 2022.
Upon execution, you will get the following output:
Upon execution, you will get the following output:
Upon execution, you will get the following output:
Upon execution, you will get the following output:
Upon execution, you will get the following output:
Another command is also known to get the current date and time for the current time zone of Linux. This command is the “timedatectl” instruction of Bash. It will not only show you the current local time but also the universal time, RTC time, your current time zone, and if the NTP services is enabled on your system. The execution of this command shows all the mentioned specifications on the shell, i.e., time and date. Upon execution, you will get the output, as shown below:
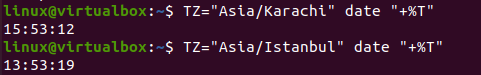
Let’s use the time zone date command to get the current time of our choice of time zone. So, we have to use the “TZ” variable with the “=” sign to get the time zone value. We want to get the current time for “Asia/Karachi” this time. The use of the “date” keyword with the “+%T” is necessary for fetching time for this time zone. We have the time displayed for the “Asia/Karachi” time zone upon execution. If you want to get the value for another time zone, use the specific time zone as a value to TZ. Let’s say we have been using the time zone “Asia/Istanbul” to get the current time for Istanbul, Turkey. The instruction shows the time for “Istanbul, Turkey” on the shell. Upon execution, you will get the following output:
$ TZ = “Asia / Karachi” date “+ % T”
$ TZ = “Asia / Istanbul” date “+ % T”
Conclusion:
In this article, we have tried to implement almost all the commands to get the current date and time for our current time zone. We have also tried to get the current time for other time zones, the past time and date, the coming date and time, and many more. You can also use %r and %R to get the current time. We hope you found this article helpful. Check the other Linux Hint articles for more tips and tutorials.
About the author
Omar Farooq
Hello Readers, I am Omar and I have been writing technical articles from last decade. You can check out my writing pieces.