- Linux: Delete files & folders using command line terminal
- In Linux, delete a file using terminal
- Delete Linux empty folder using terminal
- Delete empty directory/folder
- Delete the Linux directory/folder that contains the files
- Command to remove file with a dash ‘-‘
- Delete everything
- List of Flags to use with the rm command
- How to Delete a File or Directory in Linux – Command to Remove a Folder and its Contents
- How to Delete a File in Linux
- Using the GUI file manager
- Using the rm command
- Using the shred command
- Using the trash-cli command
- How to Delete a Directory in Linux
- Using the rm command
- Using the rmdir command
- Conclusion
Linux: Delete files & folders using command line terminal
As we know Linux is slightly different from Windows for various tasks even in deleting files and folders. And here we will see the quick Linux commands to delete a file and directory using the terminal.
However, just like in Windows, system files or the important folders are only accessible by the admin, in Linux, they are under sudo or root users. Therefore, if want to delete any system file on Linux using GUI, then you should log in as root but that is a bit risky because you don’t want to run all your applications under an admin user.
Therefore, under the standard sudo user, we can use the command terminal to easily delete any files and folders including empty ones.
Note: If you get a permission denied error while using any command given below then use sudo with that.
In Linux, delete a file using terminal
To delete a file in Linux follow the below-given steps. Here we are using Ubuntu, however, the steps will be the same for all the available distros.
- Open the command terminal, and the shortcut key for doing that is [ Ctrl ] + [ Alt ] + [ T ].
- Switch to the directory where the files are located that you want to delete using a command cd filename. For example, a file in the /opt directory, so to switch into that type- cd /opt.
- Now, to know whether the file which we want to remove, is in the current directory, we can use ls command.
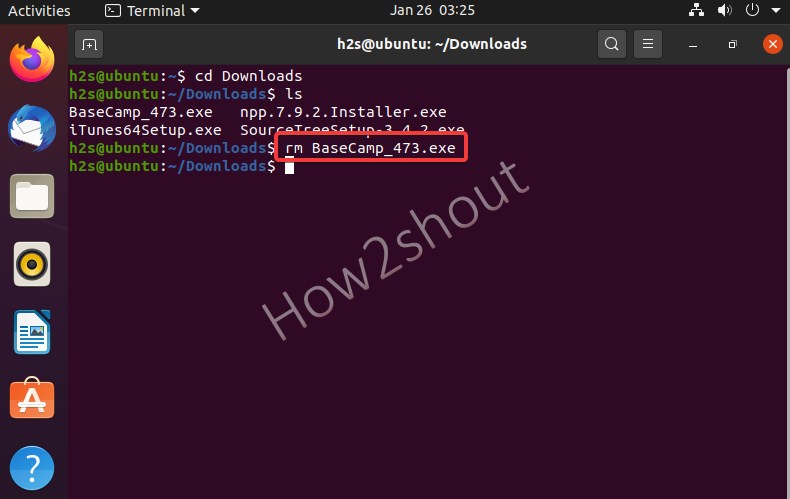
- To delete a file, you now type: rm filename .
- The command rm stands for “remove”. For example, here we have a file BaseCamp_473.exe then the command will be rm BaseCamp_473.exe. The file with this name will then be deleted if that is available in the directory.
- One thing that needs to be noted, using the command terminal and the rm command, the files will be deleted directly and not going to be moved to the recycle bin.
Delete Linux empty folder using terminal
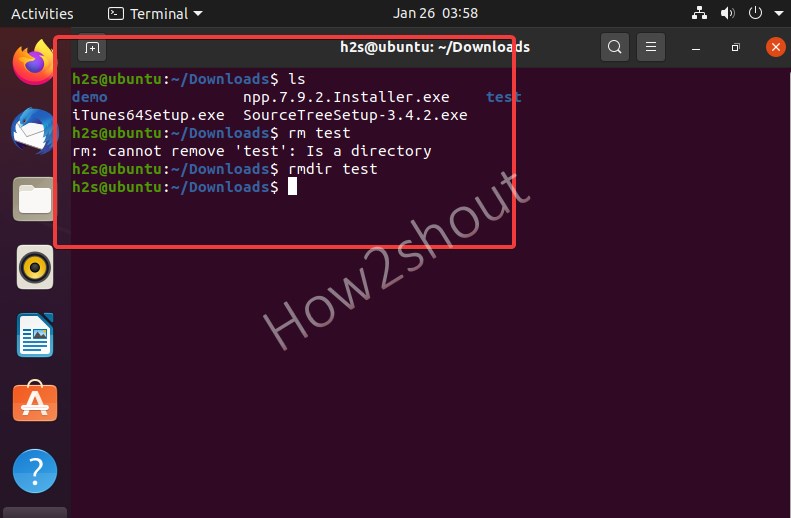
The process to remove directories is also the same as files, however, the command will slightly be different because if we use rm command then that will give an error such as “rm: cannot remove ‘test’: Is a directory“. Therefore, using it you cannot delete files in the terminal. Moreover, Linux also differentiates between empty and filled folders, and how to deal with them is given below.
Delete empty directory/folder
- Go to Applications and open Terminal, whereas Ubuntu, Manjaro, and other user-friendly Linux can also use the key combination [ Ctrl ] + [ Alt ] + [ T ] to open it.
- With the help of cd command switch to the directory from where you want to remove the empty folder.
- To check whether the directory is in the currently selected folder, you can ls use the command.
- Type in the command rmdir foldername , replace the foldername in the command with the directory you want to delete, and then press the [ Enter ] key.
- Example for the terminal: rmdir test
- Remember, the command rmdir stands for “remove directory” and only deletes empty directories.
Delete the Linux directory/folder that contains the files
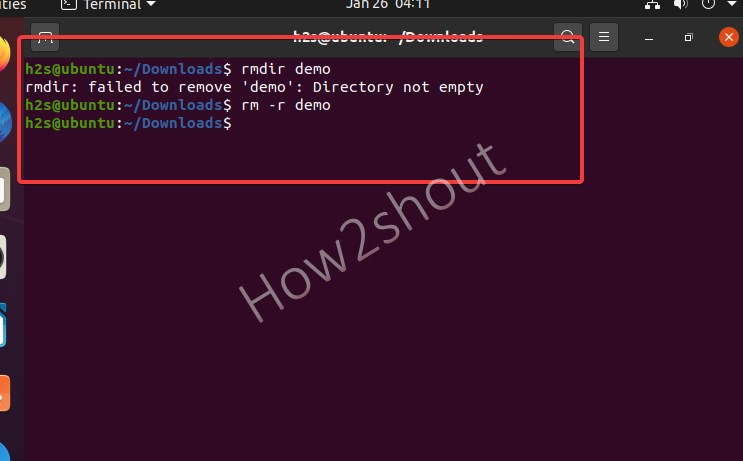
Now, if there is some folder that contains files and folder then we cannot use rmdir the command, for that simply use rm with -r flag will be in use. Moreover, we can even use this for empty directories as well.
- Press the key combination [ Ctrl ] + [ Alt ] + [ T ] to open a terminal.
- Go to the directory from where you want to remove the folder along with its file. To switch between folders we can use cd command.
- Again just like we did above, first, confirm whether the folder you want to remove is actually there or not using ls use the command.
- Type in the command rm -r , followed by the directory you want to delete, and press [ Enter ].
- For Example in the terminal: rm -r demo
- The command rm -r is the abbreviation for “remove recursive” and deletes filled directories. Sometimes, if any folder is not getting deleted, we can use the -f flag means force, as well. Example– rm -rf foldername
Command to remove file with a dash ‘-‘
To remove a file whose name starts with a ‘-‘, for example ‘-h2s’,
use one of these commands:
Delete everything
This is really a disastrous command because it will remove all essential files on your Linux system and leave nothing but an unbootable panic system, thus this is here just for knowledge, and don’t try it on the system you are working. In short, your Linux will delete all directories on all hard drives and partitions.
The above command will give a warning, that this will remove everything, thus in case you want to use it then type – sudo rm -rf / —no-preserve-root
List of Flags to use with the rm command
-f, --force ignore nonexistent files and arguments, never prompt -i prompt before every removal -I prompt once before removing more than three files, or when removing recursively; less intrusive than -i, while still giving protection against most mistakes -r, -R, --recursive remove directories and their contents recursively -d, --dir remove empty directories -v, --verbose explain what is being doneHow to Delete a File or Directory in Linux – Command to Remove a Folder and its Contents
Shittu Olumide
In Linux, deleting files or directories is a fundamental operation that every user must know. Although it may seem like a straightforward task, there are different methods to delete files or directories, each with its specific use case.
This tutorial will provide a step-by-step guide on how to delete files or directories in Linux. We will also walk through the commands you can use to remove files and folders along with their content.
How to Delete a File in Linux
Deleting a file involves removing the reference to the file from the file system. The file itself is not immediately removed from the storage device, but its space is marked as available for reuse.
There are several ways to delete a file in Linux. Here are some of the most common methods:
Using the GUI file manager
Most Linux distributions come with a GUI file manager that allows you to delete files using a graphical interface. Simply navigate to the file you want to delete, right-click it, and select «Delete» or «Move to Trash.»
Using the rm command
You can also use the rm (remove) command to delete files and directories in Linux. To delete a file using the rm command, type the following command in the terminal:
Make sure you replace filename with the name of the file you want to delete. If the file is write-protected or you don’t have sufficient permissions to delete it, you will be prompted to confirm the deletion.
Using the shred command
The shred command is a more secure way to delete files by overwriting the file’s contents multiple times before deleting it. This makes it difficult for anyone to recover the deleted file.
To use the shred command, type the following command in the terminal:
Make sure to replace filename with the name of the file you want to delete. The -u option tells shred to delete the file after overwriting it.
Using the trash-cli command
The trash-cli command provides a safer way to delete files by moving them to the trash instead of immediately deleting them. To be able to use the trash-cli command, you install it first:
sudo apt-get install trash-cli After installation, you can delete a file using the following command:
How to Delete a Directory in Linux
To delete a directory in Linux, you can use the rmdir or rm command. You use the rmdir command to remove an empty directory, while the rm command removes a directory and all its contents.
Using the rm command
Here are the steps to delete a directory in Linux using the rm command:
- Open the terminal: To delete a directory in Linux, you need to use the command line. Open the terminal by pressing «Ctrl+Alt+T» on your keyboard or by searching for «terminal» in your system’s application launcher.
- Navigate to the directory you want to delete: Use the cd command to navigate to the directory you want to delete. For example, if the directory you want to delete is called my_directory and is located in your home folder, type cd ~/my_directory and press «Enter».
- Check the contents of the directory: Before deleting the directory, it is a good idea to check its contents to make sure you are deleting the right directory. Use the ls command to list the contents of the directory. For example, type ls and press «Enter» to see the files and folders inside the my_directory folder.
- Delete the directory and its contents: To delete the directory and all its contents, use the rm command with the -r option, which stands for recursive. Type rm -r my_directory and press «Enter». You will be prompted to confirm the deletion. Type y and press «Enter» to confirm.
- Verify that the directory has been deleted: To verify that the directory has been deleted, use the ls command to list the contents of the parent directory. For example, if the my_directory folder was located in your home folder, type ls ~/ and press «Enter». The my_directory folder should no longer be listed.
Note: Be very careful when using the rm -r command, as it can delete files and directories irreversibly.
Using the rmdir command
Here are the steps to delete a directory in Linux using the rmdir command:
- Open the terminal: Open the terminal by pressing «Ctrl+Alt+T» on your keyboard or by searching for «terminal» in your system’s application launcher.
- Navigate to the directory you want to delete: Use the cd command to navigate to the directory you want to delete. For example, if the directory you want to delete is called my_directory and is located in your home folder, type cd ~/my_directory and press «Enter».
- Delete the directory: To delete the directory, use the rmdir command followed by the name of the directory. Type rmdir my_directory and press «Enter». If the directory is not empty, you will receive an error message and the directory will not be deleted.
- Verify that the directory has been deleted: To verify that the directory has been deleted, use the ls command to list the contents of the parent directory. For example, if the my_directory folder was located in your home folder, type ls ~/ and press «Enter». The my_directory folder should no longer be listed.
Conclusion
The rm command is the most commonly used command for deleting files, while the rmdir and rm commands with the -r or -R options are used for deleting directories. By following this step-by-step guide, you can now effectively delete files or directories in Linux.
- Be careful when using the rm command with the -r or -R option as it can delete files and directories irreversibly.
- Always double-check the file or directory name before deleting to avoid accidentally deleting the wrong file or directory.
- Use the shred command only when necessary, as it can take longer to delete files than other methods.
- Be mindful of file permissions when deleting files or directories, as some files or directories may require root access to delete.
Let’s connect on Twitter and on LinkedIn. You can also subscribe to my YouTube channel.