- How to Delete a File or Directory in Linux – Command to Remove a Folder and its Contents
- How to Delete a File in Linux
- Using the GUI file manager
- Using the rm command
- Using the shred command
- Using the trash-cli command
- How to Delete a Directory in Linux
- Using the rm command
- Using the rmdir command
- Conclusion
- Как удалить папку в Linux через терминал (консоль)
- Как удалить пустую папку в Linux через терминал
- Как удалить папку с содержимым (с файлами) в Linux
- Как удалить все файлы в папке Linux
- Поиск и удаление с помощью команды find
How to Delete a File or Directory in Linux – Command to Remove a Folder and its Contents
Shittu Olumide
In Linux, deleting files or directories is a fundamental operation that every user must know. Although it may seem like a straightforward task, there are different methods to delete files or directories, each with its specific use case.
This tutorial will provide a step-by-step guide on how to delete files or directories in Linux. We will also walk through the commands you can use to remove files and folders along with their content.
How to Delete a File in Linux
Deleting a file involves removing the reference to the file from the file system. The file itself is not immediately removed from the storage device, but its space is marked as available for reuse.
There are several ways to delete a file in Linux. Here are some of the most common methods:
Using the GUI file manager
Most Linux distributions come with a GUI file manager that allows you to delete files using a graphical interface. Simply navigate to the file you want to delete, right-click it, and select «Delete» or «Move to Trash.»
Using the rm command
You can also use the rm (remove) command to delete files and directories in Linux. To delete a file using the rm command, type the following command in the terminal:
Make sure you replace filename with the name of the file you want to delete. If the file is write-protected or you don’t have sufficient permissions to delete it, you will be prompted to confirm the deletion.
Using the shred command
The shred command is a more secure way to delete files by overwriting the file’s contents multiple times before deleting it. This makes it difficult for anyone to recover the deleted file.
To use the shred command, type the following command in the terminal:
Make sure to replace filename with the name of the file you want to delete. The -u option tells shred to delete the file after overwriting it.
Using the trash-cli command
The trash-cli command provides a safer way to delete files by moving them to the trash instead of immediately deleting them. To be able to use the trash-cli command, you install it first:
sudo apt-get install trash-cli After installation, you can delete a file using the following command:
How to Delete a Directory in Linux
To delete a directory in Linux, you can use the rmdir or rm command. You use the rmdir command to remove an empty directory, while the rm command removes a directory and all its contents.
Using the rm command
Here are the steps to delete a directory in Linux using the rm command:
- Open the terminal: To delete a directory in Linux, you need to use the command line. Open the terminal by pressing «Ctrl+Alt+T» on your keyboard or by searching for «terminal» in your system’s application launcher.
- Navigate to the directory you want to delete: Use the cd command to navigate to the directory you want to delete. For example, if the directory you want to delete is called my_directory and is located in your home folder, type cd ~/my_directory and press «Enter».
- Check the contents of the directory: Before deleting the directory, it is a good idea to check its contents to make sure you are deleting the right directory. Use the ls command to list the contents of the directory. For example, type ls and press «Enter» to see the files and folders inside the my_directory folder.
- Delete the directory and its contents: To delete the directory and all its contents, use the rm command with the -r option, which stands for recursive. Type rm -r my_directory and press «Enter». You will be prompted to confirm the deletion. Type y and press «Enter» to confirm.
- Verify that the directory has been deleted: To verify that the directory has been deleted, use the ls command to list the contents of the parent directory. For example, if the my_directory folder was located in your home folder, type ls ~/ and press «Enter». The my_directory folder should no longer be listed.
Note: Be very careful when using the rm -r command, as it can delete files and directories irreversibly.
Using the rmdir command
Here are the steps to delete a directory in Linux using the rmdir command:
- Open the terminal: Open the terminal by pressing «Ctrl+Alt+T» on your keyboard or by searching for «terminal» in your system’s application launcher.
- Navigate to the directory you want to delete: Use the cd command to navigate to the directory you want to delete. For example, if the directory you want to delete is called my_directory and is located in your home folder, type cd ~/my_directory and press «Enter».
- Delete the directory: To delete the directory, use the rmdir command followed by the name of the directory. Type rmdir my_directory and press «Enter». If the directory is not empty, you will receive an error message and the directory will not be deleted.
- Verify that the directory has been deleted: To verify that the directory has been deleted, use the ls command to list the contents of the parent directory. For example, if the my_directory folder was located in your home folder, type ls ~/ and press «Enter». The my_directory folder should no longer be listed.
Conclusion
The rm command is the most commonly used command for deleting files, while the rmdir and rm commands with the -r or -R options are used for deleting directories. By following this step-by-step guide, you can now effectively delete files or directories in Linux.
- Be careful when using the rm command with the -r or -R option as it can delete files and directories irreversibly.
- Always double-check the file or directory name before deleting to avoid accidentally deleting the wrong file or directory.
- Use the shred command only when necessary, as it can take longer to delete files than other methods.
- Be mindful of file permissions when deleting files or directories, as some files or directories may require root access to delete.
Let’s connect on Twitter and on LinkedIn. You can also subscribe to my YouTube channel.
Как удалить папку в Linux через терминал (консоль)
Операционная система Linux позволяет выполнять практически любые действия при помощи терминала или консоли. Более того, при администрировании Linux-серверов работа с терминалом – это основной способ управления системой. Поэтому навыки работы с консолью абсолютно необходимы, если вы хотите действительно научиться работать с Linux.
В данной инструкции мы рассмотрим тему удаления папок (каталогов). Здесь вы узнаете, как удалить пустую папку или каталог с файлами через терминал или консоль. Также мы немного затронем тему создания и поиска папок.
Как удалить пустую папку в Linux через терминал
Если вам нужно удалить пустую папку в Linux через терминал, то для этого проще всего использовать команду rmdir. Данная команда используется для удаления пустых папок из файловой системы Linux. Каталоги с файлами или другими каталогами данная команда не удаляет.
Синтаксис команды rmdir выглядит следующим образом:
rmdir [-p] [-v | --verbose] [--ignore-fail-on-non-empty] directories …
Разберем доступные параметры подробней:
rmdir --help Получение справки о команде rmdir rmdir -p Удаление всех пустых папок по всему указанному пути. rmdir -v или rmdir --verbose Вывод подробной информации о всех удаляемых объектах. rmdir --ignore-fail-on-non-empty Игнорирование ошибок, которые возникают при попытке удаления не пустых папок.
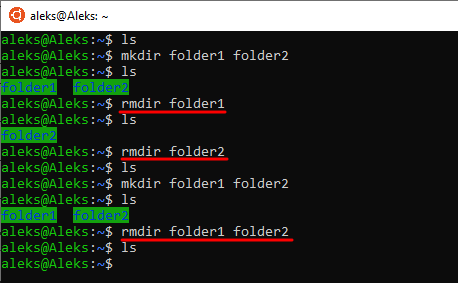
Для того чтобы просто удалить пустую папку нужно ввести « rmdir foldername ». Где « foldername » это название удаляемого объекта. При желании можно удалить сразу несколько папок, для этого достаточно перечислить их через пробел.
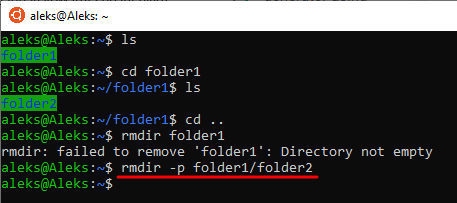
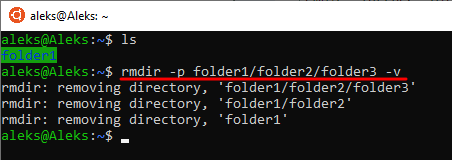
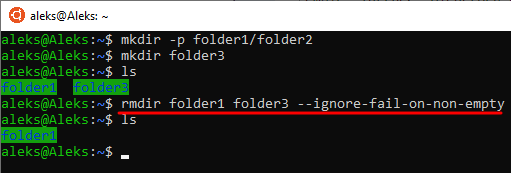
Если необходимо удалить каталог, в котором есть другие каталоги (без файлов), то можно воспользоваться параметром « -p ». Для этого нужно ввести « rmdir -p » и указать полный путь. Например, если в каталоге folder1 есть другой каталог folder2, то мы можем удалить их сразу одной командой « rmdir -p folder1/folder2 ».
При использовании параметра « -v » в консоль будет выведена подробная информация о процессе удаления каталогов.
А при использовании параметра « ignore-fail-on-non-empty » команда будет игнорировать ошибки, которые будут возникать при попытке удаления непустых каталогов.
Нужно отметить, что также существует команда « mkdir », которая предназначена для создания папок и обладает точно таким же синтаксисом.
С ее помощью вы можете создать папки по одной или целым деревом (при использовании параметра « -p »).
Как удалить папку с содержимым (с файлами) в Linux
Если нужно удалить папку с каким-то содержимым, например, с файлами, то тут уже нужно использовать команду « rm ». Данная Linux команда предназначена для удаления файлов, но с ее помощью можно удалять и каталоги, если использовать параметр «-r», который включает рекурсивное удаление.
Синтаксис команды rm выглядит следующим образом:
Разберем основные параметры команды rm:
-f, --force Игнорировать несуществующие файлы, ничего не спрашивать. -i Спрашивать перед каждым удалением. -I Спрашивать перед удалением более чем 3 файлов и при использовании рекурсивного удаления. -r, -R, --recursive Удаление каталогов и их содержимого рекурсивно. -v, --verbose Вывод информации об удаляемых каталогах. --help Вывод справочной информации о команде. --version Вывод информации о версии.
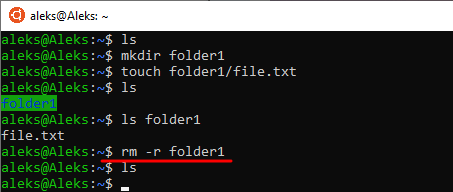
Для удаления папок с файлами нам нужно использовать параметр « -r ». Введите « rm -r » и укажите название папки, которую нужно удалить. Например, если у нас есть каталог folder1 с какими-то файлами, то мы можем ее удалить, введя команду « rm -r folder1 »
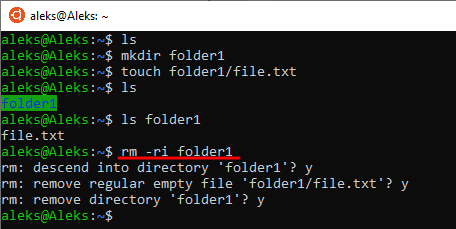
Если необходимо, чтобы удаление папок сопровождалось запросом, то вместе с параметром « -r » можно использовать параметр « -i ». В этом случае каждая операция, которую будет выполнять команда, будет требовать разрешения пользователя. При этом команда для удаления папки folder1 будет выглядеть как «rm -ri folder1 ».
Обратите внимание, во всех примерах предполагается, что удаляемый объект находится в текущей папке. Но, при необходимости вы можете удалять каталоги используя полный путь.
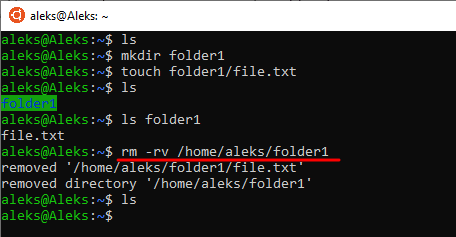
Например, вы можете указать « rm -rv /home/aleks/folder1 » для того, чтобы удалить папку folder1 с выводом подробной информации.
Как удалить все файлы в папке Linux
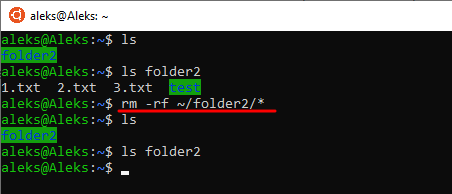
В некоторых случаях может возникнуть необходимость удалить все файлы в папке при этом не удаляя саму папку. Для решения такой задачи можно использовать вот такую команду « rm -rf /path/to/directory/* ». Данная команда удалит все файлы и папки (рекурсивно удалит все содержимое) по указанному пути.
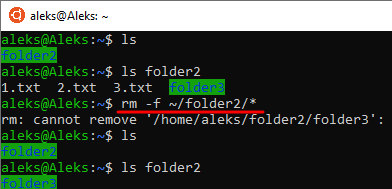
Если же нужно удалить все файлы в папке, но оставить вложенные папки, то это можно сделать командой « rm -f /path/to/directory/* ».
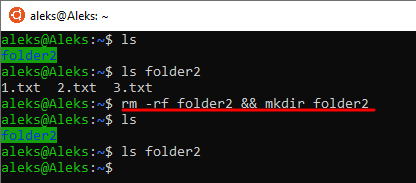
Альтернативный вариант — это удаление самой папки со всем содержимым (включая скрытые файлы и каталоги) и повторное ее создание.
Для этого подойдет команда « rm -rf foldername && mkdir foldername ».
Поиск и удаление с помощью команды find
Если нужно не просто удалить какую-то определенную папку с файлами, а сначала найти ее, то тут поможет Linux-команда find. Данная команда является мощным инструментом для поиска файлов и выполнения с ними определенных операций. Среди прочего ее можно использовать для поиска и удаления файлов.
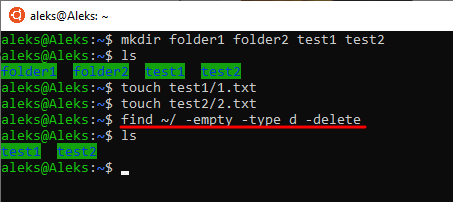
Например, чтобы найти и удалить пустые папки в домашнем каталоге можно выполнить команду:
find ~/ -empty -type d -delete
Данная команда использует следующие параметры:
-empty Поиск пустых объектов. -type d Поиск каталогов. -delete Удаление найденных объектов.
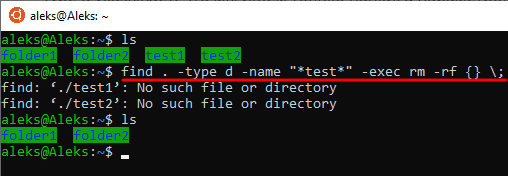
Другой пример – поиск и удаление папок с определенным названием. Так, чтобы удалить папки, содержащие в названии слово « test » можно выполнить следующую команду:
find . -type d -name "*test*" -exec rm -rf <> \;
Данная команда содержит следующие параметры:
-type d Поиск каталогов. -name Поиск объектов с определенным именем. -exec Выполнение команды.
Указанные выше примеры использования Linux-команды find – лишь часть ее возможностей. Рассмотреть все варианты ее использования в рамках этой статьи будет невозможно.