- 10+ ip route command examples in Linux [Cheat Sheet]
- Types of route
- Syntax for ip route command
- Different examples to use ip route command
- 1. List current routing table using ip route command
- 2. Add a new route using ip route command
- 3. Add a new default gateway route using ip route command
- 4. Add a new route to specific device with ip route command
- 5. Delete a route using ip route command
- 6. Modify an existing route using ip route command
- 7. Clear routes with flush using ip route command
- 8. Clear all the routes using ip route command
- 9. Get a single route to a destination
- 10. Get a single route from the source
- 11. List routes with given scope only
- 12. List routes for specified device only
- Conclusion
- What’s Next
- Further Reading
- Просмотр и построение таблиц маршрутизации в Linux
- Как посмотреть таблицу маршрутизации
- Команда route
- Команда netstat
- Построение таблицы маршрутизации
- Route
- Ключи
- Основные опции (command)
- Обозначения
- Опции для указания вводных данных
- IP Route
- Основные опции (command)
- Обозначения
- Опции для указания вводных данных
- Примеры статической маршрутизации
- Составление нового маршрута
- Изменение локальной сети
- Изменение адреса тоннеля
- Изменение провайдера
10+ ip route command examples in Linux [Cheat Sheet]
In Linux, ip command is used to show or manipulate routing, devices, policy routing and tunnels. ip route is a part of ip command. It helps to manage the route entries in the kernel routing tables that keep information about paths to other networked nodes. The routes can be set for different IP addresses (destination). You can use ip route command to add, delete, change, and list the routes.
Types of route
Following are the different types of routes.
- unicast: It describes real paths to the destinations covered by the route prefix.
- unreachable: Unreachable destinations. The packets are discarded and the ICMP message host unreachable is generated.
- blackhole: Unreachable destinations. The packets are discarded silently.
- prohibi: Unreachable destinations. The packets are discarded and the ICMP message communication administratively prohibited is generated.
- local: The destinations are assigned to this host.
- broadcast: The destinations are broadcast addresses. The packets are sent as link broadcasts.
- throw: The packets are dropped and the ICMP message net unreachable is generated.
- nat: A special nat route. The destinations covered by the prefix are considered dummy (or external) addresses and require translation to real (or internal) ones before forwarding.
- anycast: The destinations are anycast addresses assigned to this host. They are not implemented.
- multicast: A special type for multicast routing. It is not present in normal routing tables.
Syntax for ip route command
The syntax for ip route command is:
Some important commands in ip route are:
Different examples to use ip route command
1. List current routing table using ip route command
You can use ip route list or ip route show command to list current routes or routing table.
Sample Output:
2. Add a new route using ip route command
The ip route add command is used to add a new route for the specified network range. You will need root privileges to execute the command.
Sample Output:
You can also use ip route only to list the routing table.
3. Add a new default gateway route using ip route command
A default gateway is the IP address of the router that connects your host to remote networks. You can use the following command to add a new default gateway route.
$ sudo ip route add default via
Sample Output:
4. Add a new route to specific device with ip route command
The below command adds a new route specifying the network interface or network device as the gateway.
Sample Output:
5. Delete a route using ip route command
You can use the ip route delete command to delete a route from the routing table.
Sample Output:
6. Modify an existing route using ip route command
You can change a route using the ip route change command.
Sample Output:
For example, to change the default gateway route, you can use the below command.
7. Clear routes with flush using ip route command
The ip route flush command clears a route from the routing table for a particular destination.
Sample Output:
8. Clear all the routes using ip route command
You can also use ip route flush command to remove all the routes from the routing table.
$ sudo ip route flush table main Sample Output:
9. Get a single route to a destination
The below command is used to get a single route to a destination address and prints its contents.
$ ip route get to destination Sample Output:
deepak@ubuntu:~$ ip route get to 192.168.0.133 192.168.0.133 dev enp0s3 src 192.168.0.103 uid 1000 cache
10. Get a single route from the source
You can run the following command to get a single route from the source address.
$ ip route get destination from source Sample Output:
deepak@ubuntu:~$ ip route get to 192.168.0.133 from 192.168.0.103 192.168.0.133 from 192.168.0.103 dev enp0s3 uid 1000 cache 11. List routes with given scope only
You can run the below command to list routes with the given scope only.
$ ip route list scope scope_value Sample Output:
12. List routes for specified device only
The following command lists the routes with the specified device only.
Sample Output:
To view the routes with device name enp0s3, you can use:
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have learned how we can manage the routing table using the ip route command in the Linux system. You can add, delete, change, and list the routes in the routing table. If you still have any confusion, feel free to ask us in the comment section.
What’s Next
Further Reading
Didn’t find what you were looking for? Perform a quick search across GoLinuxCloud
If my articles on GoLinuxCloud has helped you, kindly consider buying me a coffee as a token of appreciation.

For any other feedbacks or questions you can either use the comments section or contact me form.
Thank You for your support!!
Просмотр и построение таблиц маршрутизации в Linux
Вся цифровая информация передаётся по сети в виде пакетов данных. По пути от отправителя к адресату они проходят через цепочку промежуточных устройств – маршрутизаторов (роутеров) и/или соответственно настроенных компьютеров.
Маршрутизация – это процесс определения пути (сетевого маршрута) для установки соединения между хост-устройствами. Этот путь настраивается как внутри локального устройства, так и на маршрутизаторе.
Построение сетевого маршрута происходит на основе информации из таблиц маршрутизации. Для их формирования применяются протоколы маршрутизации или инструкции сетевого администратора.
Каждая таблица содержит ряд параметров, позволяющих правильно идентифицировать и читать сетевой маршрут. Таблица содержит минимум 5 разделов:
- Destination (Target). IP-адрес сети назначения – конечной цели для передаваемых данных.
- Netmask (Genmask). Маска сети.
- Gateway. IP-адрес шлюза, через который можно добраться до цели.
- Interface. Адрес сетевого интерфейса, по которому доступен шлюз.
- Metric. Числовой показатель, задающий предпочтительность маршрута.
Опционально в таблице также может содержаться следующая информация:
- адрес отправителя (source);
- размер TCP-окна (window);
- максимальная величина пакета (MSS) и типы записей.
Как посмотреть таблицу маршрутизации
Таблицу маршрутизации в Linux (например, в популярных серверных ОС типа Ubuntu или CentOS) можно посмотреть с помощью нескольких команд.
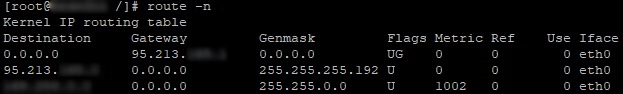
Команда route
Программа используется для настройки параметров статической маршрутизации. Просмотр таблицы можно осуществить с помощью команды:
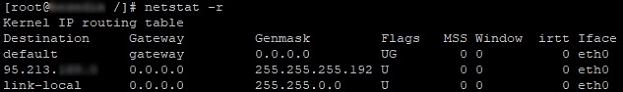
Команда netstat
Утилита используется для сбора информации о состоянии сетевых соединений. Вывести таблицу можно с помощью команды:
Построение таблицы маршрутизации
Существует несколько основных утилит для настройки таблицы маршрутизации (добавления, обновления, удаления старых и новых маршрутов):
- Route. Устаревшая утилита, входящая в состав пакета net-tools. Служит для отображения таблицы маршрутизации и построения статических маршрутов.
- IP Route. Обновленный инструмент, призванный заменить Route. Имеет большую функциональность, по сравнению со своим предшественником.
Оба инструмента могут использоваться для выполнения аналогичных задач. Далее будет рассмотрен синтаксис каждого в пределе основных возможностей.
Route
Команда имеет следующий вид:
route [-f] [-p] command -net [destination] netmask [MASK netmask] gw [gateway] metric [METRIC metric] dev [IF interface]
Ключи
- -f – очистка таблиц от записей всех шлюзов.
- -p – сохранение маршрута в качестве постоянного при использовании ADD. По умолчанию все маршруты временные и после перезагрузки системы сбрасываются.
Основные опции (command)
- add – добавление маршрута.
- del – удаление маршрута.
- replace – замена маршрута.
- change – изменение или настройка параметров маршрута.
Обозначения
- [destination] – адрес сети назначения.
- [MASKnetmask] – маска подсети.
- [gateway] – адрес шлюза.
- [METRICmetric] – числовой показатель, задающий предпочтительность маршрута (используется в том случае, если устройство является маршрутизатором).
- [IFinterface] – сетевой интерфейс.
Опции для указания вводных данных
IP Route
Команда имеет следующий вид:
ip route command [destination] netmask [MASK netmask] via [gateway] metric [METRIC metric] dev [IF interface]
Основные опции (command)
- add – добавление маршрута.
- del – удаление маршрута.
- replace – замена маршрута.
- change – изменение или настройка параметров маршрута.
Обозначения
- [destination] – адрес сети назначения.
- [MASKnetmask] – маска подсети.
- [gateway] – адрес шлюза.
- [METRICmetric] – числовой показатель, задающий предпочтительность маршрута (используется в том случае, если устройство является маршрутизатором).
- [IFinterface] – сетевой интерфейс.
Опции для указания вводных данных
- via – используется в значении «через» для указания шлюза.
- dev – сетевой интерфейс.
- netmask – маска подсети.
- metric – метрика.
Примеры статической маршрутизации
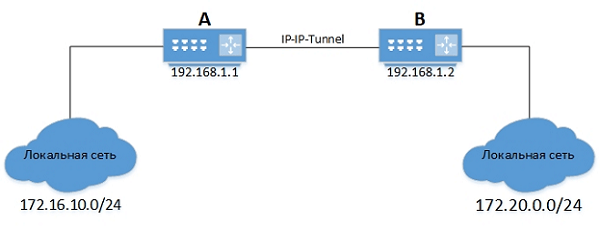
Составление нового маршрута
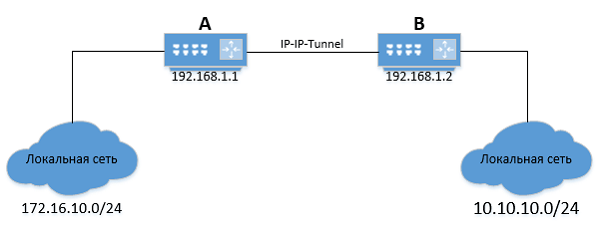
Можно представить два офиса: A и B. В каждом стоят маршрутизаторы на Linux, которые соединены между собой IP-IP туннелем.
Маршрутизатор A имеет IP-адрес — 192.168.1.1, а маршрутизатор B — 192.168.1.2.
Чтобы подключение к локальной сеть маршрутизатора A стало возможным из локальной сети маршрутизатора B и наоборот, нужно прописать на маршрутизаторе B:
route add -net 172.16.10.0/24 gw 192.168.1.1
Будет произведена установка шлюза «192.168.1.1» для сети «172.16.10.0/24».
Также необходимо прописать на маршрутизаторе A обратный маршрут в локальную сеть маршрутизатора B:
route add -net 172.20.0.0/24 gw 192.168.1.2
Изменение локальной сети
В случае изменения локальной сети маршрутизатора B, необходимо удалить старую запись:
route del -net 172.20.0.0/24 gw 192.168.1.2
А после добавить новый маршрут на маршрутизаторе А:
route add -net 172.20.0.0/24 gw 192.168.1.2
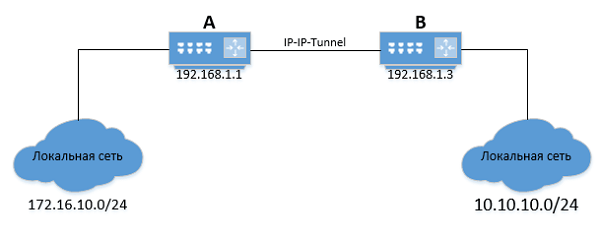
Изменение адреса тоннеля
Если на маршрутизаторе B изменится IP-адрес туннеля, то следует также актуализировать адрес шлюза на маршрутизаторе А:
ip route replace 172.16.10.0/24 via 192.168.1.3
После выполнения команды адрес шлюза для подсети «172.16.10.0/24» будет изменён.
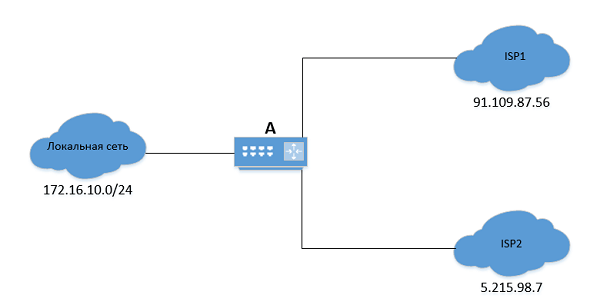
Изменение провайдера
Чтобы перенаправить трафик через другого провайдера («ISP2»), следует изменить маршрут «по умолчанию» («default»):
ip route replace default via 5.215.98.7
Надежный хостинг для сайта. 14 дней — бесплатно!
Мы всегда на связи в соцсетях
Поддержка в привычной среде