- Enabling the RPM Fusion repositories
- Third party repositories
- Mixing third party software repositories
- The purpose of RPM Fusion
- Additional resources
- Enabling the RPM Fusion repositories using command-line utilities
- Prerequisites
- Procedure
- Enabling the RPM Fusion repositories using graphical applications
- Prerequisites
- Procedure
- Enabling Appstream data from the RPM Fusion repositories
- Prerequisites
- Procedure
- Enabling the RPM Fusion repositories for ostree-based systems
- Prerequisites
- Procedure
- References
- Adding or removing software repositories in Fedora
- Adding repositories
- Enabling repositories
- Disabling repositories
- Removing repositories
- Third-Party Repositories
- How to use
- Enabling third-party repositories
- Installing from third-party repositories
- Managing third-party repositories
- Included software
- How to Configure Software Repositories in Fedora
- View Enabled Repositories in Fedora
- Adding, Enabling, and Disabling a DNF Repository
Enabling the RPM Fusion repositories
This page discusses third-party software sources not officially affiliated with or endorsed by the Fedora Project. Use them at your own discretion. Fedora recommends the use of free and open source software and avoidance of software encumbered by patents.
Third party repositories
There are a number of third-party software repositories for Fedora. They have more liberal licensing policies and provide software packages that Fedora excludes for various reasons. These software repositories are not officially affiliated or endorsed by the Fedora Project. Use them at your own discretion. For complete list, see FedoraThirdPartyRepos The following repositories are commonly used by end users and do not conflict with each other:
Mixing third party software repositories
Mixing a lot of third party repositories is not recommended since they might conflict with each other causing instability and hard to debug issues. If you are not a technical user, one way is to not enable the third-party repo by default and instead use the —enablerepo switch for dnf, or a similar method configurable in the graphical package manager.
The purpose of RPM Fusion
The RPM Fusion project is a community-maintained software repository providing additional packages that are not distributed by Fedora.
Additional resources
- RPM Fusion home page: https://rpmfusion.org/
- For more information on what packages are allowed to be distributed with Fedora, see the following wiki page: https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/Forbidden_items
- You can buy multimedia codecs from Fluendo. This is a legal solution for users from countries where software patents apply. For more information, see: https://fluendo.com/en/products/enterprise/fluendo-codec-pack/.
Enabling the RPM Fusion repositories using command-line utilities
This procedure describes how to enable the RPM Fusion software repositories without using any graphical applications.
Prerequisites
Procedure
$ sudo dnf install \ https://download1.rpmfusion.org/free/fedora/rpmfusion-free-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm
$ sudo dnf install \ https://download1.rpmfusion.org/nonfree/fedora/rpmfusion-nonfree-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm
Enabling the RPM Fusion repositories using graphical applications
This procedure describes how to enable the RPM Fusion software repositories without using any command-line utilities.
Prerequisites
Procedure
- In your web browser, open the following page: https://rpmfusion.org/Configuration.
- To enable the Free repository, click the RPM Fusion free for Fedora version link on the page, where version is the Fedora release you are using. This prompts you to save or open the repo file.
- Open the file using the Software Install application.
- The Software application opens. Click the blue Install button.
- Optionally, enable the Nonfree repository: click the RPM Fusion nonfree for Fedora version link on the page, where version is the Fedora release you are using.
- Save and install the file with the Software application again.
Enabling Appstream data from the RPM Fusion repositories
This procedure describes how to install the Appstream data provided by the RPM Fusion software repositories.
Prerequisites
- You have internet access.
- You are using the Gnome desktop environment.
- You have the RPMFusion repositories installed
Procedure
$ sudo dnf group update core
Enabling the RPM Fusion repositories for ostree-based systems
This procedure describes how to enable the RPM Fusion software repositories for systems based on ostree (i.e. Silverblue, Kinoite, Fedora IoT).
This is a two-stage process where you have to install versioned RPM Fusion repos and then you are able to replace them with unversioned RPM Fusion repos.
For more information about this process and the problem it solves, please refer to the relevant thread on the Fedora Discourse site.
Prerequisites
- You are using an ostree-based system such as Silverblue, Kinoite, or Fedora IoT.
- You have internet access.
Procedure
$ sudo rpm-ostree install \ https://mirrors.rpmfusion.org/free/fedora/rpmfusion-free-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm \ https://mirrors.rpmfusion.org/nonfree/fedora/rpmfusion-nonfree-release-$(rpm -E %fedora).noarch.rpm $ reboot
$ sudo rpm-ostree update \ --uninstall rpmfusion-free-release \ --uninstall rpmfusion-nonfree-release \ --install rpmfusion-free-release \ --install rpmfusion-nonfree-release $ reboot
References
Adding or removing software repositories in Fedora
This section describes how to add, enable, or disable a software repository with the DNF application.
Adding repositories
This section describes how to add software repositories with the dnf config-manager command.
- Define a new repository by adding a new file with the .repo suffix to the /etc/yum.repos.d/ directory. For details about various options to use in the .repo file, see the Setting [repository] Options section in the System Administrator’s Guide
- Add the newly created repository.
dnf config-manager --add-repo repository dnf config-manager --add-repo /etc/yum.repos.d/fedora_extras.repo
Enabling repositories
This section shows how to enable a particular software repository by using the dnf config-manager command.
dnf config-manager --set-enabled repository
dnf config-manager --set-enabled fedora-extras
Disabling repositories
This section shows how to disable a particular software repository by using the dnf config-manager command.
dnf config-manager --set-disabled repository
dnf config-manager --set-disabled fedora-extras
Removing repositories
This section shows how to remove a Yum repository (or .repo file).
If you know the ID of a repository, but you’re not sure what .repo it belongs to, you can run the following command grep -E «^\[.*]» /etc/yum.repos.d/* . This will print a list of the repository IDs that are associated with each Yum repository.
rm /etc/yum.repos.d/file_name.repo
All Fedora Documentation content available under CC BY-SA 4.0 or, when specifically noted, under another accepted free and open content license.
Last build: 2023-07-14 05:50:21 UTC | Last content update: 2022-11-23
Third-Party Repositories
The Fedora Workstation Third Party repositories provide access to additional desktop software that is not included in Fedora’s own repos. The repositories are selected and managed by the Fedora Workstation Working Group, in accordance with FESCo’s third party repository policy.
The third-party repositories exist to provide access to additional software that may be necessary or important for users to have access to. This includes some proprietary software.
While facilitating the use of some proprietary software, the Fedora project continues to strongly believe in and promote free and open source software. As a result, third party repositories must be enabled by the user in order to be used, and open source alternatives are recommended wherever possible.
How to use
The following are basic instructions for how to use the third-party repositories.
Enabling third-party repositories
To install software from the third-party repositories, they must first be enabled. The easiest way to do this is in the Third-Party Repositories page of initial setup.
Alternative methods to enable the third-party repositories include:
- Through the dialog that is shown in the Software app when third-party repositories are not enabled.
- Enabling Third-Party Repositories in the Software app’s Software Repository settings.
Installing from third-party repositories
Once the repos are enabled, the software they contain can be installed in the usual way. The repos can also be searched and installed using the dnf or flatpak commands, depending on the packaging format used.
Managing third-party repositories
The Software Repository settings in the Software app can be used to see which third-party repositories are enabled, or to enable and disable individual repositories.
Included software
The following software is included in the third-party repositories:
Bitwarden, Discord, Microsoft Teams, Minecraft, Postman, Skype
How to Configure Software Repositories in Fedora
Your Fedora distribution obtains its software from repositories and each of these repositories comes with number of free and proprietary software applications available for you to install. The official Fedora repositories have thousands of free and open source applications.
In this article, we will show how to configure software repositories in Fedora distribution using the DNF package manager tool from the command line.
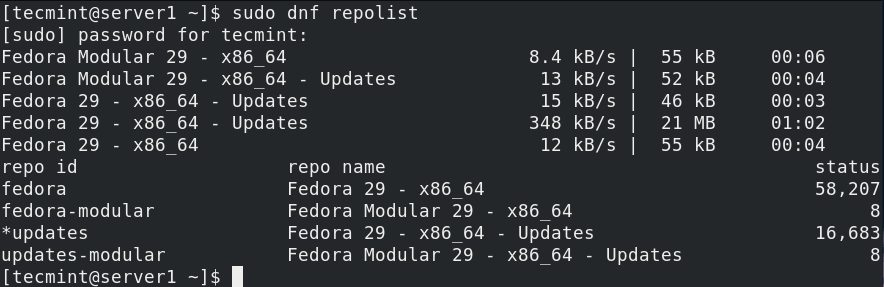
View Enabled Repositories in Fedora
To list all enabled repositories on your Fedora system, in the format repository ID, name, and status (number of packages it provides), run the following command.
You can list packages from a specified repository, for instance fedora, by running the following command. It will list all packages available and installed from the repository specified.
$ sudo dnf repository-packages fedora list
To display only a list of those packages available or installed from the specified repository, add the available or installed option respectively.
$ sudo dnf repository-packages fedora list available OR $ sudo dnf repository-packages fedora list installed
Adding, Enabling, and Disabling a DNF Repository
Before you add a new repository to your Fedora system, you need to define it by either adding a [repository] section to the /etc/dnf/dnf.conf file, or to a .repo file in the /etc/yum.repos.d/ directory. Most developers or package maintainers provide DNF repositories with their own .repo file.
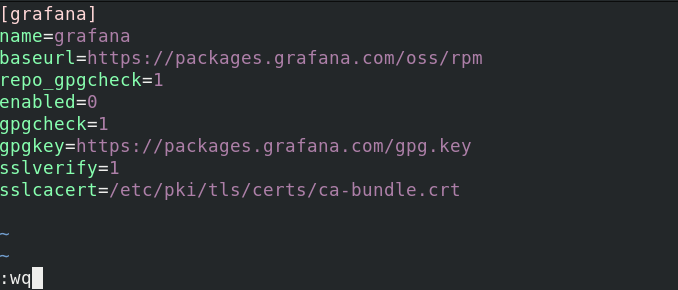
For example to define the repository for Grafana in a .repo file, create it as shown.
$ sudo vim /etc/yum.repos.d/grafana.repo
Then add the [repository] section in the file and save it. If you observe carefully, in the repository configuration shown in the image, it is not enabled as indicated by the parameter (enabled=0) ; we changed this for demonstration purposes.
Next, to add and enable new repository, run the following command.
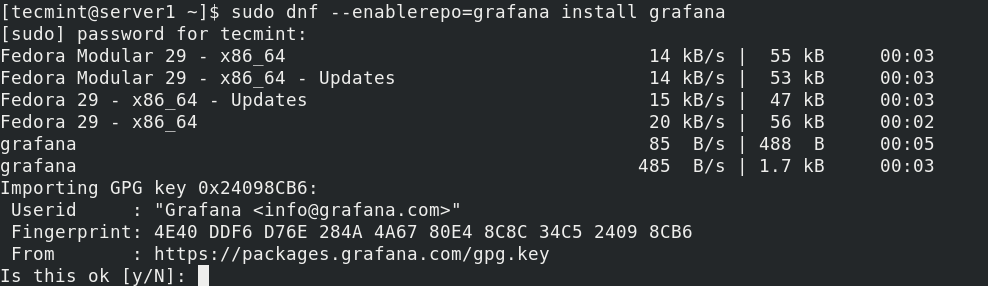
$ sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo /etc/yum.repos.d/grafana.repo
To enable or disable a DNF repository, for instance while trying to install a package from it, use the —enablerepo or —disablerepo option.
$ sudo dnf --enablerepo=grafana install grafana OR $ sudo dnf --disablerepo=fedora-extras install grafana
You can also enable or disable more than one repositories with a single command.
$ sudo dnf --enablerepo=grafana, repo2, repo3 install grafana package2 package3 OR $ sudo dnf --disablerepo=fedora, fedora-extras, remi install grafana
You can also enable and disable repositories at the same time, for example.
$ sudo dnf --enablerepo=grafana --disablerepo=fedora, fedora_extra, remi, elrepo install grafana
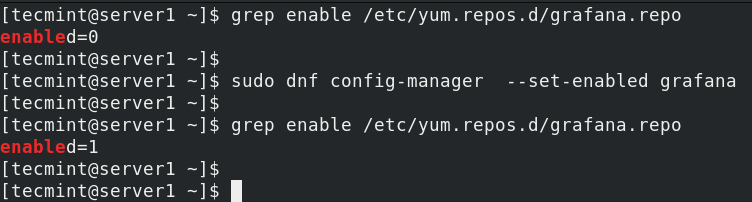
To permanently enable a particular repository, use the —set-enabled option.
$ sudo grep enable /etc/yum.repos.d/grafana.repo $ sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled grafana $ sudo grep enable /etc/yum.repos.d/grafana.repo
To permanently disable a particular repository, use the —set-disabled switch.
$ sudo dnf config-manager --set-disabled grafana
That’s all for now! In this article, we have explained how to configure software repositories in Fedora. Share your comments or ask questions via the feedback form below.