- 5 Linux Command Line Based Tools for Downloading Files and Browsing Websites
- 1. rTorrent
- Installation of rTorrent in Linux
- 2. Wget
- Installation of Wget in Linux
- Basic Usage of Wget Command
- 3. cURL
- Installation of cURL in Linux
- Basic Usage of cURL Command
- 4. w3m
- Installation of w3m in Linux
- Basic Usage of w3m Command
- 5. Elinks
- Installation of Elinks in Linux
- Basic Usage of elinks Command
- Downloading Files on Linux using the Command Line
- Downloading Files using Wget
- How to Install Wget?
- Features of Wget
- Downloading Files using Curl
- How to Install Curl?
- Features of Curl
- Best Command Line Method to Download Files
- About the author
- Zeeman Memon
5 Linux Command Line Based Tools for Downloading Files and Browsing Websites
Linux command-line, the most adventurous and fascinating part of GNU/Linux is a very cool and powerful tool. A command-line itself is very productive and the availability of various inbuilt and third-party command-line applications makes Linux robust and powerful. The Linux Shell supports a variety of web applications of various kinds be it torrent downloader, dedicated downloader, or internet surfing.
Here we are presenting 5 great command line Internet tools, which are very useful and prove to be very handy in downloading files in Linux.
1. rTorrent
rTorrent is a text-based BitTorrent client which is written in C++ aimed at high performance. It is available for most of the standard Linux distributions including FreeBSD and Mac OS X.
Installation of rTorrent in Linux
$ sudo apt install rtorrent (on Debian, Ubuntu, & Mint) $ sudo dnf install rtorrent (on Fedora, CentOS & RHEL) $ sudo pacman -S rtorrent (on Arch and Manjaro) $ sudo zypper install rtorrent (on OpenSuse)
Check if rtorrent is installed correctly by running the following command in the terminal.
Functioning of rTorrent
Some of the useful Key-bindings and their use.
- CTRL+ q – Quit rTorrent Application
- CTRL+ s – Start Download
- CTRL+ d – Stop an active Download or Remove an already stopped Download.
- CTRL+ k – Stop and Close an active Download.
- CTRL+ r – Hash Check a torrent before Upload/Download Begins.
- CTRL+ q – When this key combination is executed twice, rTorrent shutdown without sending a stop Signal.
- Left Arrow Key – Redirect to Previous screen.
- Right Arrow Key – Redirect to Next Screen
2. Wget
Wget is a part of the GNU Project, the name is derived from World Wide Web (WWW). Wget is a brilliant tool that is useful for recursive download, offline viewing of HTML from a local Server and is available for most of the platforms be it Windows, Mac, Linux.
Wget makes it possible to download files over HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP. Moreover, it can be useful in mirroring the whole website as well as support for proxy browsing, pausing/resuming Downloads.
Installation of Wget in Linux
Wget being a GNU project comes bundled with Most of the Standard Linux Distributions and there is no need to download and install it separately. If in case, it’s not installed by default, you can still install it using apt, yum, or dnf.
$ sudo apt install wget (on Debian, Ubuntu, & Mint) $ sudo dnf install wget (on Fedora, CentOS & RHEL) $ sudo pacman -S wget (on Arch and Manjaro) $ sudo zypper install wget (on OpenSuse)
Basic Usage of Wget Command
Download a single file using wget.
# wget http://www.website-name.com/file
Download a whole website, recursively.
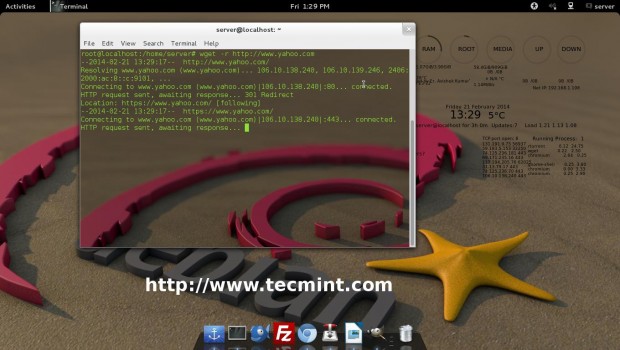
# wget -r http://www.website-name.com
Download specific types of files (say pdf and png) from a website.
# wget -r -A png,pdf http://www.website-name.com
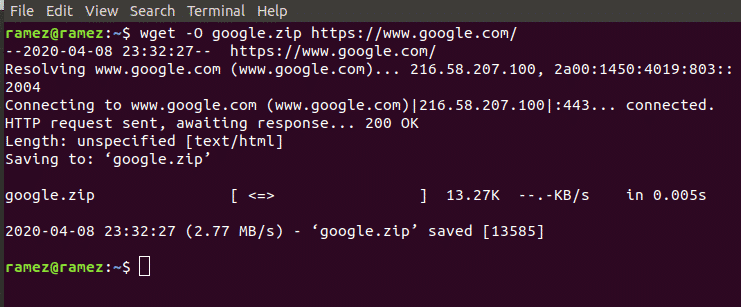
Wget is a wonderful tool that enables custom and filtered download even on a limited resource Machine. A screenshot of wget download, where we are mirroring a website (Yahoo.com).
For more such wget download examples, read our article that shows 10 Wget Download Command Examples.
3. cURL
a cURL is a command-line tool for transferring data over a number of protocols. cURL is a client-side application that supports protocols like FTP, HTTP, FTPS, TFTP, TELNET, IMAP, POP3, etc.
cURL is a simple downloader that is different from wget in supporting LDAP, POP3 as compared to others. Moreover, Proxy Downloading, pausing download, resuming download are well supported in cURL.
Installation of cURL in Linux
By default, cURL is available in most of the distribution either in the repository or installed. if it’s not installed, just do an apt or yum to get a required package from the repository.
$ sudo apt install curl (on Debian, Ubuntu, & Mint) $ sudo dnf install curl (on Fedora, CentOS & RHEL) $ sudo pacman -S curl (on Arch and Manjaro) $ sudo zypper install curl (on OpenSuse)
Basic Usage of cURL Command
For more such curl command examples, read our article that shows 15 Tips On How to Use ‘Curl’ Command in Linux.
4. w3m
The w3m is a text-based web browser released under GPL. W3m support tables, frames, color, SSL connection, and inline images. W3m is known for fast browsing.
Installation of w3m in Linux
Again w3m is available by default in most of the Linux Distribution. If in case, it is not available you can always apt or yum the required package.
$ sudo apt install w3m (on Debian, Ubuntu, & Mint) $ sudo dnf install w3m (on Fedora, CentOS & RHEL) $ sudo pacman -S w3m (on Arch and Manjaro) $ sudo zypper install w3m (on OpenSuse)
Basic Usage of w3m Command
5. Elinks
Elinks is a free text-based web browser for Unix and Unix-based systems. Elinks support HTTP, HTTP Cookies and also support browsing scripts in Perl and Ruby.
Tab-based browsing is well supported. The best thing is that it supports Mouse, Display Colours, and supports a number of protocols like HTTP, FTP, SMB, Ipv4, and Ipv6.
Installation of Elinks in Linux
By default elinks also available in most Linux distributions. If not, install it via apt or yum.
$ sudo apt install elinks (on Debian, Ubuntu, & Mint) $ sudo dnf install elinks (on Fedora, CentOS & RHEL) $ sudo pacman -S elinks (on Arch and Manjaro) $ sudo zypper install elinks (on OpenSuse)
Basic Usage of elinks Command
That’s all for now. I’ll be here again with an interesting article which you people will love to read. Till then stay tuned and connected to Tecmint and don’t forget to give your valuable feedback in the comment section.
Downloading Files on Linux using the Command Line
In recent years, technology has evolved and grown significantly, highlighting the changes taking place in the digital world. These technological advancements have led to the creation of so many extraordinary tools and softwares that have significantly aided in making our lives easier.
Linux, a Unix based open-source operating system, is one example of such a software that only a few years back, didn’t have the specs to be used in desktops and as a result, was mainly considered for server development. However, with time, it has rapidly evolved, becoming a reliable and powerful operating system, which in turn has led to it gaining the attention of a large number of users.
The Command Line tool provided by Linux is one of its most powerful features that it offers to users and is also what makes it so fascinating and amazing to use. A command line is simply a text-based interface that takes in commands and forwards them to the OS which runs them. It is due to this flexible nature of it that it has gained an edge over the Graphical User Interface (GUI) and as a result, many users have switched to the Command Line for doing various tasks, one of which is the downloading of files.
Hence today we’ll be looking at two different ways on how to download files on Linux using the Command Line tool.
Downloading Files using Wget
One of the most popular command line tools for downloading files from the internet is Wget. Wget is a pretty versatile tool that supports multiple protocols such as HTTP, HTTPS and FTP and allows one to download multiple files and directories. It also provides users with a variety of features ranging from recursive downloading to playing and pausing the downloads as well as limiting its bandwidth.
Moreover, it is cross-platform which gives it quite the edge over many other command line downloaders as well as graphical downloaders.
How to Install Wget?
Wget usually comes pre-installed with most of the Linux Distributions. However, if a user is in possession of a system without Wget being installed, then the user needs to open the command line through either Ubuntu Dash or Ctrl+Alt+T shortcut and enter the following command:
It is to be noted that the command given above is for only Debian based Linux systems such as Ubuntu. If a user has a Red Hat Linux system such as Fedora, then the user needs to enter the following command into the command line:
Features of Wget
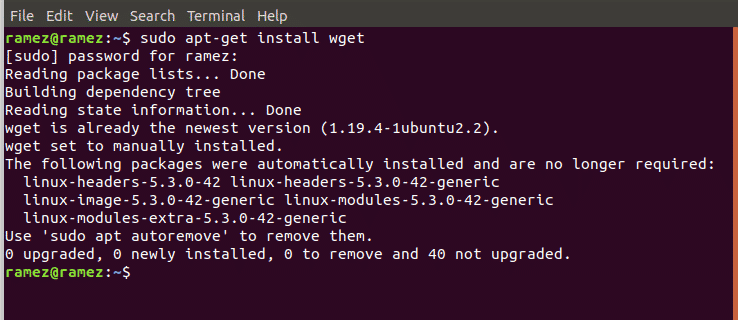
As mentioned before, Wget has multiple features incorporated inside of it. The most basic operation that Wget offers to users is downloading files by simply using its URL. This can be done by inputting the following command into the terminal:
Let us show an example to further clarify this. We will be downloading a simple image in the png format from the internet. See the image below for better understanding:
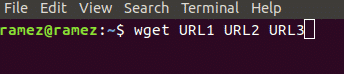
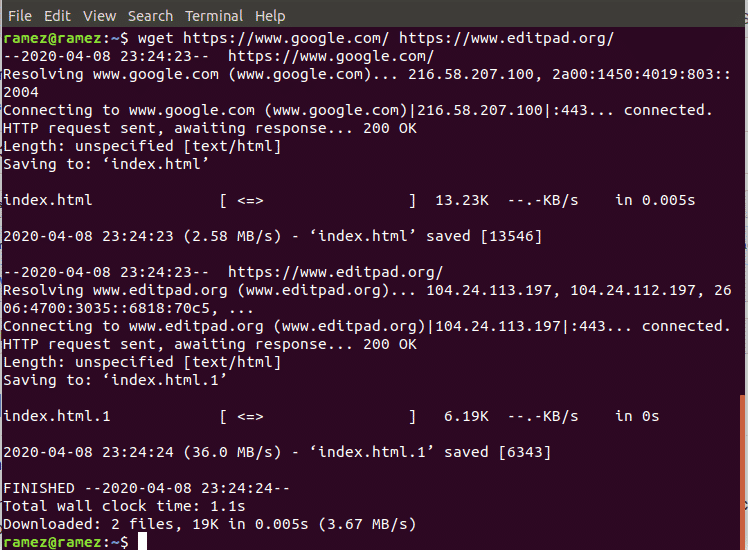
Wget also allows users to download multiple files from different URLs. This can easily be done by the following command:
Once again, we can show this using an example. We will be downloading two HTML files from two different websites. For better understanding, please look at the image below:
We can also change the name of the file from its original using the following command:
Here filename refers to the name that you want to address the file as. Using this, we can also change the type of the file. This is shown in the image below:
Wget also allows users to recursively download their files which is basically downloading all the files from the website under a single directory. This can easily be done by the following command:
For more information regarding Wget, users can input the following command into the terminal to get access to all the Wget commands that appear to be available:
Downloading Files using Curl
Curl is another command line tool that can be used to download files from the internet. Unlike Wget, which is command line only, features of Curl are powered by libcurl which is a cross-platform URL transfer library. Curl not only allows downloading of files but can also be used for uploading and exchanging of requests with servers. Curl also has a much larger support range for protocols including the important ones such as HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, SFTP etc. However, Curl does not support recursive downloads which Wget offers.
How to Install Curl?
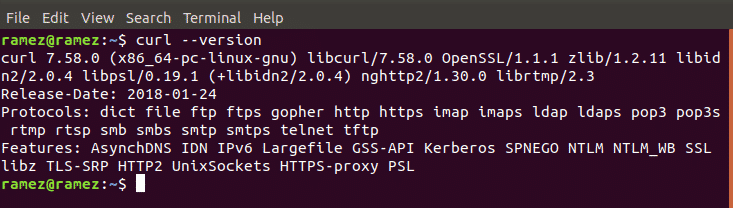
Similarly, like Wget, Curl comes pre-installed with most of the Linux Distributions. This can simply be checked by running the following command:
However, if a user is in possession of a system without Curl being installed, then the user needs to open the command line through either Ubuntu Dash or Ctrl+Alt+T shortcut and enter the following command:
It is to be noted that the command given above is for only Debian based Linux systems such as Ubuntu. If a user has a Red Hat Linux system such as Fedora, then the user needs to enter the following command into the command line:
Features of Curl
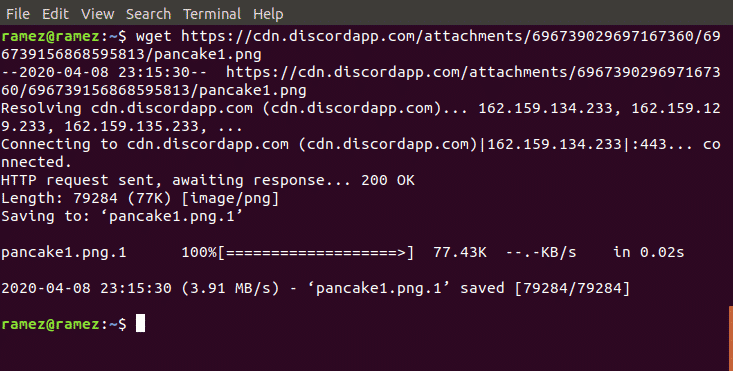
Just like Wget, Curl has multiple features incorporated inside of it. The most basic is its ability to allow users to download files from a single URL from the internet. This can be done by inputting the following command into the terminal:
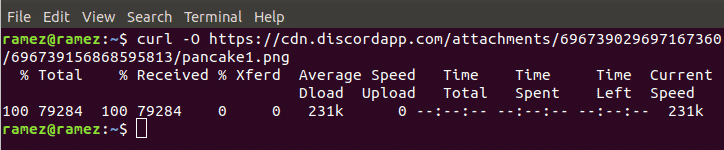
For better understanding, we will be downloading a simple image in the png format from the internet just like in the case of Wget.
Curl also allows users to change the filename and the type of the file. This can be done by the following command:
In the image above, we took a png file originally named pancake1.png and converted it to a zip file with the new name p.zip.
Just like in the case of Wget, Curl allows users to download multiple files using a number of URLs from the internet. This can easily be done by the following command:
For our example, we will use curl to download a jpg file and a png file from the internet. Results are shown in the image below:
A pretty amazing feature that Curl provides to its users is its ability to monitor the progress of the download of the file. This can be done by the following command:
For more information regarding Curl, users can input the following command into the terminal to get access to all the Curl commands that appear to be available:
Best Command Line Method to Download Files
Wget and Curl are among the wide range of command line tools that Linux offers for the downloading of files. Both offer a huge set of features that cater to different needs of the users. If users simply want to download files recursively, then Wget would be a good choice. If users are looking to interact with the server or download a file built under a protocol that Wget doesn’t support, then Curl would be a better alternative.
About the author
Zeeman Memon
Hi there! I’m a Software Engineer who loves to write about tech. You can reach out to me on LinkedIn.