- How to use echo command to print out content of a text file?
- 6 Answers 6
- Echo Command in Linux (With Examples)
- Echo Command Syntax
- Echo Command Options
- Examples of Echo Command
- Changing the Output Format
- Writing to a File
- Displaying Variable Values
- Displaying Command Outputs
- echo Command in Linux: 7 Practical Examples
- Examples of the echo command in Linux
- 1. Displaying the value of a variable
- 2. Don’t print the final newline character
- 3. Redirect the output to a file
- 4. Using escape characters with echo command
- 5. Display text with single or double quotes with echo command
- 6. Display files in directory
- 7. Use echo command to empty a file in Linux
- Bonus Tips
- Display echo command output in color
- See what a command will do without running it
- What else?
How to use echo command to print out content of a text file?
According to text book it should redirect a programs standards input. Now I am redirecting a.txt to echo but instead of printing the content of the file it is printing out one empty line! Appreciate if anyone display this behaviour.
@AndrewS but that’s just part of it, another part is I don’t really think it is possible. How would you distinguish echo foo to output «foo» but echo (empty variable, no value) to just wait for user input through stdin? That’ll probably break like a half of existing scripts.
6 Answers 6
echo doesn’t read stdin so in this case, the redirect is just meaningless.
To print out a file just use the command below
Here for future reference: in my case, echo «$(
In Unix, I believe all you have to do, assuming you have a file that isn’t hefty is: cat
use below command to print the file content using echo,
here you can also get benefit of all echo features, I most like the removing of trailing newline character, (to get exact same hash as that of buffer and not the file)
echo -n `cat file.txt` | sha256sum cat command will display the file with CR or return:
$ cat names.txt Homer Marge Bart Lisa Maggie you could use echo command with cat as command substitution. However, it will replace CR or return (unix: \n) with spaces:
$ echo $(cat names.txt) Homer Marge Bart Lisa Maggie Could be an interesting feature if you want to pipe to further data processing though. E.g. replacing spaces with sed command.
The echo command does not accept data from standard input ( STDIN ), but only works on the arguments passed to it.
So if we pass data to echo from standard input, e.g. with < or | , it will be ignored because echo only works with arguments.
This can be changed by using echo together with the xargs command, which is designed to call a command with arguments that are data from standard input.
Echo Command in Linux (With Examples)
The echo command is a built-in Linux feature that prints out arguments as the standard output. echo is commonly used to display text strings or command results as messages.
In this tutorial, you will learn about all the different ways you can use the echo command in Linux.
Echo Command Syntax
The echo command in Linux is used to display a string provided by the user.
For example, use the following command to print Hello, World! as the output:
Note: Using the echo command without any option returns the provided string as the output, with no changes.
Echo Command Options
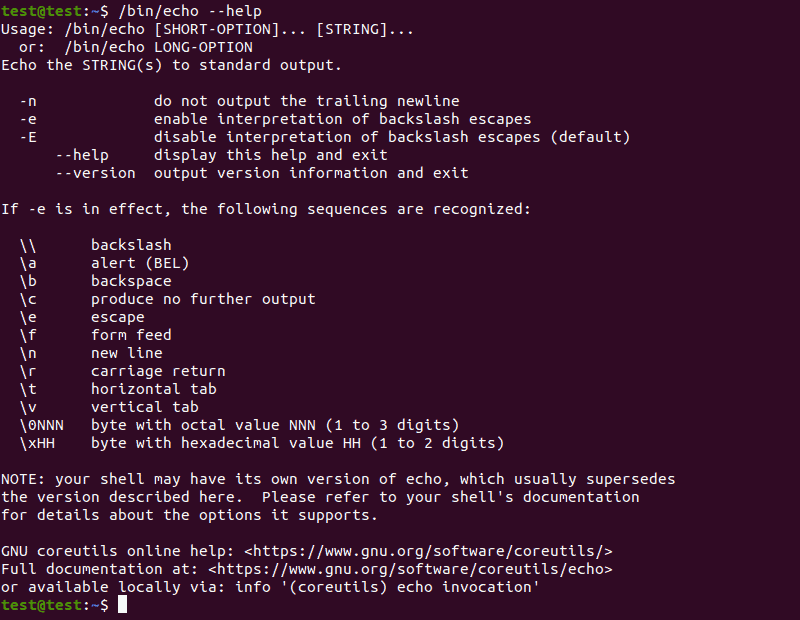
Use the —help argument to list all available echo command options:
Note: Using the echo —help command returns —help as the output.
The echo command uses the following options:
- -n : Displays the output while omitting the newline after it.
- -E : The default option, disables the interpretation of escape characters.
- -e : Enables the interpretation of the following escape characters:
- \\: Displays a backslash character (\).
- \a : Plays a sound alert when displaying the output.
- \b : Creates a backspace character, equivalent to pressing Backspace.
- \c : Omits any output following the escape character.
- \e : The escape character, equivalent to pressing Esc.
- \f : The form feed character, causes the printer to automatically advance to the start of the next page.
- \n : Adds a new line to the output.
- \r : Performs a carriage return.
- \t : Creates horizontal tab spaces.
- \v : Creates vertical tab spaces.
- \NNN : Byte with the octal value of NNN .
- \xHH : Byte with the hexadecimal value of HH .
Examples of Echo Command
Here are some ways you can use the echo command in Linux:
Changing the Output Format
Using the -e option allows you to use escape characters. These special characters make it easy to customize the output of the echo command.
For instance, using \c let you shorten the output by omitting the part of the string that follows the escape character:
echo -e 'Hello, World! \c This is PNAP!'Note: If you are using the -e option, enter your string enclosed in single quotation marks. This ensures that any escape characters are interpreted correctly.
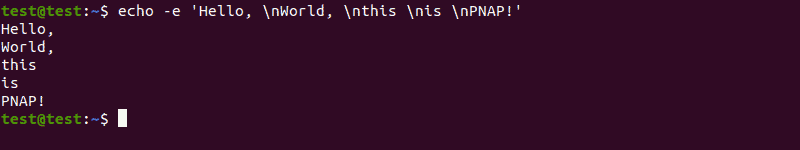
Use \n any time you want to move the output to a new line:
echo -e 'Hello, \nWorld, \nthis \nis \nPNAP!'Add horizontal tab spaces by using \t :
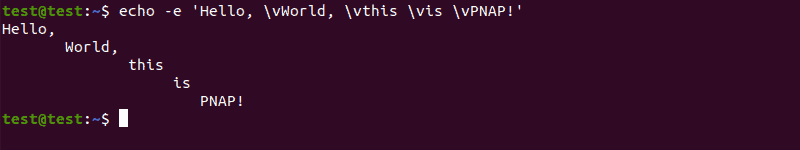
Use \v to create vertical tab spaces:
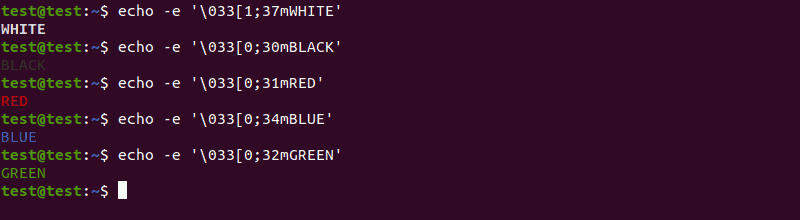
echo -e 'Hello, \vWorld, \vthis \vis \vPNAP!'Using ANSI escape sequences lets you change the color of the output text:
echo -e '\033[1;37mWHITE' echo -e '\033[0;30mBLACK' echo -e '\033[0;31mRED' echo -e '\033[0;34mBLUE' echo -e '\033[0;32mGREEN'Writing to a File
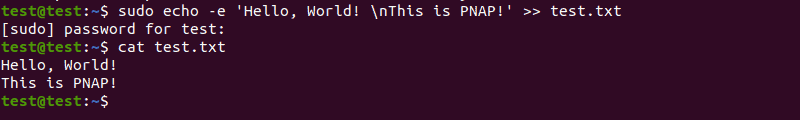
Use > or >> to include the string in an echo command in a file, instead of displaying it as output:
sudo echo -e 'Hello, World! \nThis is PNAP!' >> test.txtIf the specified text file doesn’t already exist, this command will create it. Use the cat command to display the content of the file:
Note: Using > overwrites the content of the text file with the new string, while >> adds the new string to the existing content.
Displaying Variable Values
The echo command is also used to display variable values as output. For instance, to display the name of the current user, use:
Displaying Command Outputs
The echo command allows you to include the result of other commands in the output:
- [string] : The string you want to include with echo
- [command] : The command you want to combine with the echo command to display the result.
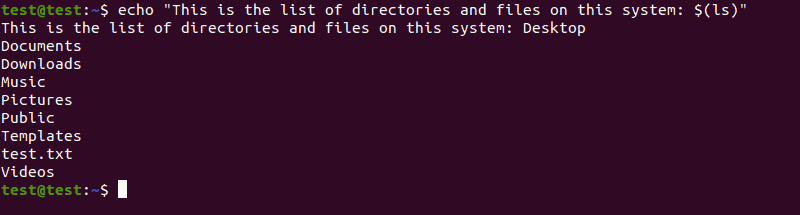
For instance, list all the files and directories in the Home directory by using:
echo "This is the list of directories and files on this system: $(ls)"After reading this tutorial, you should know how to use the echo command in Linux.
For more Linux commands, check out our Linux Command Cheat Sheet
echo Command in Linux: 7 Practical Examples
Learn to use the echo command in Linux with these simple but useful examples. The echo command is useful for displaying information in bash shell scripts.
The echo command is perhaps one of the first few commands you see when you start learning Linux commands or bash shell scripting.
Echo is a simple command that simply prints its arguments on display.
[email protected]:~$ echo Hello World Hello WorldYou can guess why this command is called ‘echo’. Like the sound echo, the command also simply prints what it receives in the input.
Examples of the echo command in Linux
Echo is often used in shell scripts to display information, such as asking for the user to provide input or displaying the error or warning for a certain action in the script.
The echo command has a simple syntax with a few options:
echo [options] [input string]Let’s see some examples of the echo command.
1. Displaying the value of a variable
Let’s say you declared a variable var = 100. You can display the value of this variable using the echo command:
echo The value of variable var is $varIts output would be displayed as this:
The value of variable var is 1002. Don’t print the final newline character
By default, the output of the echo command adds a new line to the output so that you have the output displayed in one entire line.
[email protected]:~$ echo Hello World Hello WorldYou can suppress this new line character using the option -n:
[email protected]:~$ echo -n Hello World Hello [email protected]:~$3. Redirect the output to a file
You can use echo command to create a new file in Linux or append new text to an existing file by redirecting the output to a file:
echo "This text goes to a file" >> file.txt4. Using escape characters with echo command
The option -e with echo allows you to interpret the escape characters. With escape characters, you can display your text on the screen in a different manner of your choice.
The following escape characters are available with escape:
- \a – alert (plays a beep sound)
- \b – backspace
- \c – don’t print the final newline (same as -n option)
- \f – from feed
- \n – newline
- \r – carriage return
- \t – horizontal tab
- \v – vertical tab
- \\ – backslash
- \’ – single quote
- \” – double quote
While -e option asks the echo command to interpret the escape characters, the -E option does the opposite and ignores the escape characters.
Now let’s see how to use some of these escape characters with echo command.
echo -e "An eye for an eye leaves the whole world blind\n\t- Gandhi"Can you guess what would be the output of the above command? Here it is:
An eye for an eye leaves the whole world blind – GandhiLet’s see some other examples of escape characters. The carriage return character prints only the text after that character.
If you use the backspace character, it will remove one character before it:
[email protected]:~$ echo -e “Hello \bWorld” HelloWorldYou can play with other escape characters in the similar way.
5. Display text with single or double quotes with echo command
Dealing with single quotes and double quotes is often a headache.
If you have a single quote in the text that you want to display, you should wrap the entire input within double quotes:
[email protected]:~$ echo “It’s My World” It’s My WorldIf you want to display the double quotes, you have to ‘escape’ it:
[email protected]:~$ echo “It’s \”My\” World” It’s “My” World6. Display files in directory
You probably use the ls command to display the files in a directory. You can also use echo command for this purpose.
To display the contents of the present directory, you can use this command:
You can also use echo command to display only a certain type of files:
If you want to list only the directories, use it like this:
You cannot view the file content with echo, unfortunately.
7. Use echo command to empty a file in Linux
I have already shown this tip for emptying log files in Linux. If you have a text file and you want to clear its content without deleting the file itself, you can use the echo command in the following fashion:
Bonus Tips
Here are a few bonus tip to use the echo command in unusual or colorful manner.
Display echo command output in color
You probably would have come across some bash script that displays the text output in different color. Have you ever wondered how it is done? Let me quickly show you how to change the color of echo output.
You can use the ANSI escape sequence and change the appearance of the output like background color, underscore, bold etc.
To change the color of the output text, you can use these:
echo -e “\033[30mThis is Black”
echo -e “\033[31mThis is Red”
echo -e “\033[32mThis is Green”
echo -e “\033[33mThis is Yellow”
echo -e “\033[34mThis is Blue”
echo -e “\033[35mThis is Magenta”
echo -e “\033[36mThis is Cyan”
echo -e “\033[37mThis is White”Sample colored output for your understanding:
\033[ represents ESC[ in the above commands.
See what a command will do without running it
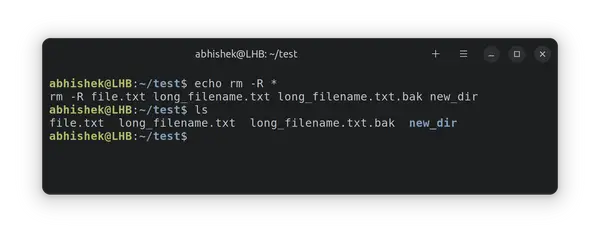
In many cases, the echo command saves you the trouble of accidentally doing something you didn’t expect.
It allows you to expand the wildcards to understand what will happen before you actually run the command.
This will output what will be passed to the rm command (and therefore what would be deleted), putting echo before a command renders it harmless (it just expands wildcards so you know what it will do).
What else?
The echo command is good for quickly printing desired output on the screen. If you want a more complicated formatted output, use the C-styled printf command in bash.
Well, that’s it. I think you have seen a good number of examples of the echo command in Linux. If you use echo for some specific purpose that could be useful to others, please share it with us in the comment section.