- Elcomsoft wifi password recovery
- Word attack
- Dictionary attack
- Dictionary options
- Password mutation options
- Mask attack
- Other types of changeable ranges:
- Combination attack
- Hybrid attack
- Однократное и домашнее использования
- Программы для восстановления паролей и доступа к зашифрованным документам
- Advanced Office Password Recovery
- Advanced PDF Password Recovery
- Advanced Intuit Password Recovery
- Advanced Archive Password Recovery
- Elcomsoft Internet Password Breaker
- Advanced EFS Data Recovery
- Elcomsoft System Recovery
- Дополнительно
- Решения для доступа к зашифрованной информации на мобильных устройствах
- Elcomsoft Phone Breaker
- Elcomsoft Phone Viewer
Elcomsoft wifi password recovery
In modern world strong passwords are used by most applications and services. In case of strong password the recovery process may consume a very long time. Elcomsoft offers the solutions which significantly increase password recovery speed.
First of all you have to try all possible fast attacks: Dictionary and Brute-Force with mask. If you have tried those attacks with no success, only plain Brute-Force gives you a chance to recover a password.
- Distributed computing. Use power of all available computers to get your password. We offer Elcomsoft Distributed Password Recovery, very powerful tool that supports hundreds of file formats.
- GPU acceleration. You can use modern graphic cards to accelerate password recovery. Our programs support AMD and Nvidia GPUs. Please read our GPU FAQ to get more information.
Password recovery for new file formats can be a very complicated task and may take a long time. In modern world password recovery speed becomes slower and slower, so simple Brute-force or Dictionary attack is not enough for effective password breaking. We can try to use the «human factor» for password recovery. Most of people don’t use randomly generated strong passwords because they are very hard to remember. People invent they own password creation rules and think their passwords are strong.
For example, the rule can be as follows:
[My name] [Year of birth] [Some random characters, easy to remember]
And the possible passwords are:
These passwords are very weak but cannot be recovered using simple Brute-force or Dictionary. We created our advanced attack engine to help to recover such passwords.
The following attacks are available:
Word attack
This attack tries all possible variations of the given word and applies all possible mutations to each variation.
Dictionary attack
Dictionary options
Press «Add» to add dictionary file(s) to the list, «Remove» to remove the selected one(s), and «Up/Down» to change an order.
Password mutation options
Here you select the name of the dictionary file, as well as the options that affect the speed and efficiency of the attack. All mutations are divided into a several ‘classes’ (described below). The program can set the mutation ‘level’ for every type, that allows to select between speed and efficiency. With the minimum level, the program checks only lowercase passwords, and performs basic mutations only: e.g. Border mutation uses not all special characters, but only digits, and only at the end of the password. For an intermediate level, more special characters are being used (both as prefix and as a suffix); and uppercase characters are also tested. At the maximum level, even more advanced prefixes and suffixes are added, but of course, it runs much slower (as far as more variations are checked).
- Case mutation: the program checks all variations of uppercase/lowercase characters.
- Digit mutation: adding several digits to the work (from the dictionary) as prefix and suffix.
- Border mutation: similar to the above, but adding not only digits, but also most commonly used combinations like 123, $$$, 666, qwerty, 007, ххх etc.; in addition, adding some chars at both end of the word, e.g. #password#, $password$ and more.
- Freak mutation: replacing some characters (one or more); for example, the word password will also generate p@ssword, p@$$word and p@$$w0rd. Freak mutation is based on l337 language. Check https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Leet for more info.
- Abbreviation mutation: some commonly-used abbreviations like ihateyou — ih8you, loveyou — loveu, foryou — 4u etc.
- Order mutation: reversing the order (password — drowssap), repeating the word (password — passwordpassword), adding the reversed word (password — passworddrowssap).
- Vowels mutation: playing with vowels, e.g. psswrd, PaSSWoRD, pAsswOrd etc.
- Strip mutation: removing one char, e.g. assword, pssword, pasword.
- Swap mutation: replacing some characters, e.g. apssword, psasword, password.
- Duplicate mutation: duplicating the characters, e.g. ppassword, paassword, passsword, passwword etc.
- Delimiter mutation: adding delimters between characters: p.a.s.s.w.o.r.d, p+a+s+s+w+o+r+d, p-a-s-s-w-o-r-d.
- Year mutation: adding the year (four digits) at the end of the word: password1973, password2002.
- Shift mutation: shifting character in a word: password -> asswordp
- Substitution mutation: substitute a character: password -> paddword. In this mutation, the changes depend on the qwerty keyboard, taking into account that the user can skip the key when creating a password and press the key next to it. For example, “oassword” instead of “password”. Or “fog” instead of “dog”. Therefore, not all possible characters fall into the search, but only those located nearby on the keyboard
- Length mutation: password -> passwor ..
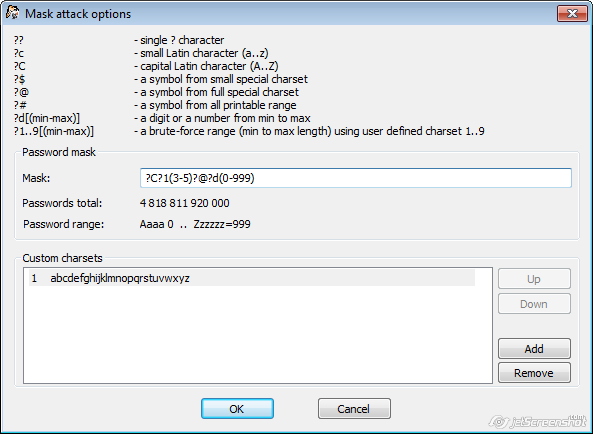
Mask attack
With the mask attack, you can check for passwords with the known/complex structure.
The syntax of the mask attack.
The mask consists of immutable characters and changeable (iterable) ranges.
«admin» characters will not change Instead of each ?d — a digit is substituted (character range from 0 to 9),
Thus, such passwords will be checked:
admin000, admin001 .. admin999
Other types of changeable ranges:
?d(1980-2020) — number from 1980 to 2020
admin1980, admin1981 .. admin2020
?1(1-3) — custom (charset) from 1 to 3 characters. So, if you use 1 set of lowercase letters, for each?1 a lowercase letter from a to zzz will be used
You can combine ranges and set up to 10 different ranges.
If the brackets are omitted, it will be counted as one character, i.e.
With the mask attack, you can check for passwords with the known/complex structure. In the Mask field, you can select the mask using the following options:
- ?? — the ‘?’ symbol itself
- ?c — small Latin character (from ‘a’ to ‘z’)
- ?C — large Latin character (from ‘A’ to ‘Z’)
- ?$ — one of the special characters (small set): !@#$%^&*()-_+= and space
- ?@ — one of the special characters (large/complete set): !\»#$%&'()*+,-./:;?@[\]^_`<|>~ and space
- ?# — any printable character with the code from 0x20 to 0x7F
- ?d — one digit (from 0 to 9)
- ?d(min-max) — a number from min to max.
- ?w[dictionary_name.udic] — a word from dictionary_name.udic.
- ?W[dictionary_name.udic] — a word from a given dictionary with an additional check for the first character to be either uppercase or lowercase. F.e. ?W[english.dic]?d
- ?0..9(min-max) — min..max characters from custom set. min >= 0
In order to use the last option, you should also create your (custom) own character set (below); each set has its own number. For example, assume that you password is formed as follows:
- one capital letter
- from 3 to 5 small letters
- special character (from large set)
- from one to three digits
In that case, the mask is going to be (assuming that the custom charset containing all small letters is created; if it is the only one, it will have the number 1):
Once the mask is properly set, you will see the Password total (the total number of passwords that fits into this mask), and Password range (first and last passwords to be checked):
Combination attack
This attack allows to test passwords that consist of two words, each of them taken from the dictionary (word list). Select the dictionaries in Dictionary 1 and Dictionary 2 fields (you can use the same file or different ones); and the additional options are:
- Check upper- and lower-case combination
- Use word delimiters
- Use extra mutations
With the first option, the program will try to capitalize the first letter of each word, i.e. testing all four combinations. The second option (Use word delimiters) allows to set the different characters (like dash and underline, though you can set any other ones as well) to be used between words. Finally, you can apply extra mutations to all resulting passwords (Dictionary mutations options will be used). The program tries to estimate the total number of passwords instantly, but mutations will not be counted (it is virtually impossible to do that).
Hybrid attack
In Dictionary attack, If several mutations are specified, then passwords are formed sequentially, first with some mutations, then with others, etc. Mutations do NOT overlap each other
For Examle:
The Digits and Strip mutations are set. First, a list of Digits mutations (such as password1, password2 . ) is formed, then Strip mutations (pssword, paword ..) are added to this list. But password1, password2 (as well as pssword, paword) are no longer transformed.
But if you need to find password “pawod9”, first you need to make a Strip, and then put digits mutations on the passwords RECEIVED after the Strip once again. For this case you need Hybrid attack
This attack is similar to Dictionary attack described above, but all mutations are set by the user. Here you can select one or more dictionaries (wordlists), as well as several mutation rules. The rules are set in *.rul files; here are the ones coming with the program:
- all.rul — all rules (~82000)
- cases.rul — all possible case combinations (up to 15 character words)
- common.rul – common mutation rules
- custom.rul – default rules for custom attacks
- dups.rul – rules to search for passwords based on various duplicated words or characters
- dates.rul – date mutations
- keyboard.rul – rules to search for passwords based on all possible keyboard combinations
- l33t.rul – l33t ‘language’
- numbers.rul – manipulations with numbers
- rockyou.rul – top rules based on various leaked passwords
The actual contents of *.rul file starts with [Rules] section (all text before this tag is considered a comment). Maximum length of one rule is 256 bytes. Maximum length of the output word (generated by the rule) should not exceed 256 characters, too. One line can contain several rules (any ones but aN); they are processed from left to right.
Do nothing, use the original input word
Однократное и домашнее использования
Продукция Элкомсофт прекрасно подходит для однократного использования и использования в домашних условиях. Отсутствие необходимости в специальном обучении и удобный пользовательский интерфейс с пошаговым решением типичных задач делают продукты Элкомсофт максимально дружелюбными, а доступные цены «домашних» редакций – вполне доступными обычному пользователю.
Программы для восстановления паролей и доступа к зашифрованным документам
Advanced Office Password Recovery
Инструмент для восстановления, удаления и замены паролей к документам Microsoft Office, OpenOffice, WordPerfect Office, Lotus SmartSuite, Apple iWork и Hangul Office с поддержкой аппаратного ускорения с помощью видеокарт.
Скачать бесплатную пробную версию
Advanced PDF Password Recovery
Гарантированное снятие ограничений на редактирование, печать и копирование файлов PDF. Восстановление пароля на открытие документа с поддержкой аппаратного ускорения. Запатентованная технология Thunder Tables® гарантирует восстановление ключей длиной 40 бит в течение минуты.
Скачать бесплатную пробную версию
Advanced Intuit Password Recovery
Гарантированное восстановление доступа к защищённым паролями документам Intuit Quicken и QuickBooks.
Скачать бесплатную пробную версию
Advanced Archive Password Recovery
Расшифровка защищённых архивов ZIP и RAR и восстановление оригинальных паролей. Максимальная производительность при восстановлении сложных паролей. Некоторые виды архивов гарантированно расшифровываются в течение часа.
Скачать бесплатную пробную версию
Elcomsoft Internet Password Breaker
Мгновенное извлечение доступных паролей для веб-сайтов, учётных записей и почтовых ящиков из множества приложений. Поддержка сохранённых полей и паролей в Internet Explorer, Edge, Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Opera, Яндекc.Браузер, Tor, QQ Browser, UC Browser, 360 Safe Browser, Outlook и Outlook Express, Windows Mail и Windows Live Mail.
Скачать бесплатную пробную версию
Advanced EFS Data Recovery
Расшифровка файлов, зашифрованных средствами NTFS с помощью Encrypting File System (EFS).
Скачать бесплатную пробную версию
Elcomsoft System Recovery
Восстановление доступа к учётным записям Windows, включая локальные, сетевые и учётные записи Microsoft Account и создание образов дисков. Поддерживается сброс и восстановление оригинальных паролей. Поставляется с лицензированным образом Windows PE для загрузки системы с внешнего накопителя.
Дополнительно
Решения для доступа к зашифрованной информации на мобильных устройствах
Elcomsoft Phone Breaker
Извлечение информации из устройств под управлением iOS, Windows Phone, Windows 10 Mobile и BlackBerry 10, расшифровка резервных копий и подбор неизвестных паролей с использованием аппаратного ускорения.
Скачать бесплатную пробную версию
Elcomsoft Phone Viewer
Простой, удобный и компактный инструмент для просмотра информации, извлечённой из устройств под управлением iOS, облачных сервисов iCloud и Microsoft. Продукт поддерживает выходные форматы Elcomsoft Phone Breaker и стандартные форматы резервных копий iTunes.
Скачать бесплатную пробную версию