- Circuits4you.com
- Arduino interfacing, circuits tutorials with code and ebooks, Step by step guides for all sensor modules used for arduino. Programming tips and tricks.
- ESP32 Access point (AP) and Station web server with HTML using Arduino IDE
- What you will Learn?
- Web Server Step by Step
- Step 1: Creating web server on ESP32
- Program to connect to Access point and Make web server
- ESP as Access Point
- Web Server Handling
- Complete Program for HTML web Server from esp32 as Access Point
- index.h
- circuits4you.com
- Simple Snake Game
- Results
- Piranha ESP32 как точка доступа WiFi
- Видео:
- Нам понадобится:
- Подключение:
- Скетч проекта:
- Нажмите " "сюда " "для включения светодиода." ); client.print( "Нажмите " "сюда " "для выключения светодиода." ); client.print("
- Нажмите " "сюда " "для выключения светодиода." ); client.print("
- Ссылки
Circuits4you.com
Arduino interfacing, circuits tutorials with code and ebooks, Step by step guides for all sensor modules used for arduino. Programming tips and tricks.
ESP32 Access point (AP) and Station web server with HTML using Arduino IDE
In this tutorial we are making ESP32 as both Station and Access point and web server. We have seen how to connect to WiFi Router and make web server in previous post.
What you will Learn?
- Making ESP32 as Access Point
- ESP32 as Station
- ESP32 as both Station and Access Point at the same time
- ESP32 as web server with HTML web page
- Using Java Scripts in ESP32
- Using CSS in ESP32
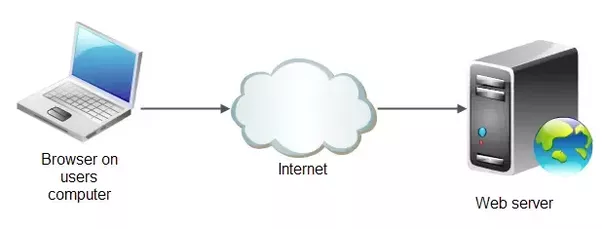
A Web server is a program that uses HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) to serve the files that form Web pages to users, in response to their requests, which are forwarded by their computers’ HTTP clients.
To implement web server on ESP32, there are two ways to make your first web server first connect to your WiFi router or make ESP32 as access point.
Web Server Step by Step
As we know that all web servers have a HTML web page to be served.
Step 1: Creating web server on ESP32
ESP can acts as access point and it can connect to access point or both.
First we make program to connect to WiFi hot spot (Access Point)
Program to connect to Access point and Make web server
We need these libraries to make web server.
WiFi.h is required for doing all WiFi related functionalities such as connection, AP, etc.
WiFiClient.h this file is required to send request to web browser
WebServer.h it handles all HTTP protocols
Define your SSID and Password of your WiFi router, where the ESP32 connects
//SSID and Password for ESP32 const char* ssid = "your_ssid"; const char* password = "password";
Web server is on port 80, you can use other ports also, default HTTP port is 80, to open web page with different port number you have to enter port number after IP address. Ex. For port number 81 you have to type 192.168.2.2:81 in browser.
ESP8266WebServer server(80); //Server on port 80
There are two ways to make web server one is to connect to WiFi hot spot or make ESP as hot spot (Access Point). In this tutorial we are making ESP as AP.
ESP as Access Point
You may find that ESP is also visible as hot spot in previous example; you can hide its AP (Access point) using this command at the beginning of setup.
WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA); //This line hides the viewing of ESP as wifi network
In some application you may find that both AP and connection to WiFi router are useful for making configuration you use ESP8266 AP and for data sending to cloud use WiFi connectivity in that case use this command and both connections. This way you can access ESP web page with two different IP address.
WiFi.mode(WIFI_AP_STA); //Both hotspot and client are enabled
Third way is only access point, default is all AP and STA are enabled, to get only AP use this command.
WiFi.mode(WIFI_AP); //Only Access point
To start ESP as Access point you have to use this simple command
WiFi.softAP(ssid, password); //Start HOTspot removing password will disable security
To get IP address i.e. assigned to ESP32 by your WiFi router use this command
IPAddress myIP = WiFi.softAPIP(); //Get IP address
Web Server Handling
When client request a web page by entering ESP32 IP address which data to be sent is handled by subroutine and that subroutine name is defined in server.on(path,subroutine_name).
server.on("/", handleRoot); //Which routine to handle at root location Example: If you have two pages you can define like this
Server.on(“/”,root); //192.168.2.2 (IP of ESP) this is root location
Server.on(“/page1”,First_page); //”192.168.2.2/page1” this is first page location
Server.on(“/page2”,Second_page); //”192.168.2.2/page2” this is second page location
You have three subroutines that handle client requests.
To start the server use this command
In main loop we handle client request
server.handleClient(); //Handle client requests
This subroutine is called when you enter IP address in web browser and hit enter. This routine sends the test “hello from esp32” to web browser.
Complete Program for HTML web Server from esp32 as Access Point
index.h
Make separate header file for storing HTML code. keep this index.h file near to ino file
const char MAIN_page[] PROGMEM = R»=====( body < text-align:center; font-family: helvetica; >canvas
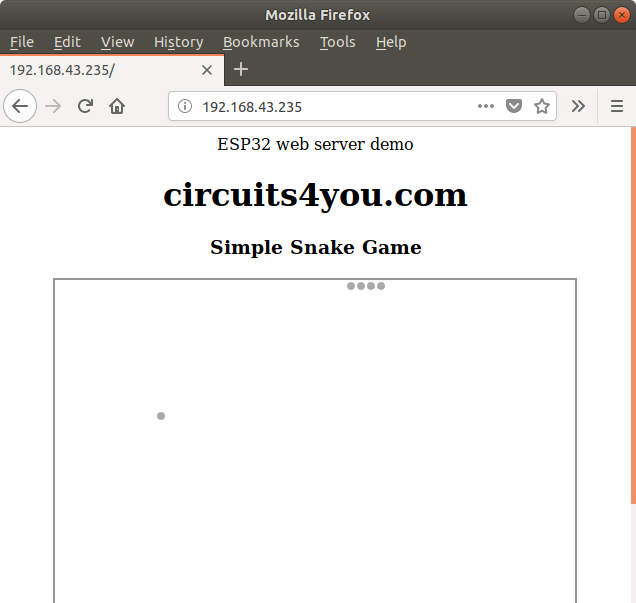
ESP32 web server democircuits4you.com
Simple Snake Game
use arraow keys to play )==== lang:arduino decode:true» title=»ESP8266 Web Server with AP Program»>/* * ESP32 Web Server Demo using Accesspoint * https://circuits4you.com * 21-11-2018 */ #include #include #include #include «index.h» //Web page header file WebServer server(80); //Enter your WiFi SSID and PASSWORD const char* ssid = «. «; const char* password = «. «; //=============================================================== // This routine is executed when you open its IP in browser //=============================================================== void handleRoot() < String s = MAIN_page; //Read HTML contents server.send(200, "text/html", s); //Send web page >//=============================================================== // Setup //=============================================================== void setup(void) < Serial.begin(115200); Serial.println(); Serial.println("Booting Sketch. "); //ESP32 As access point IP: 192.168.4.1 WiFi.mode(WIFI_AP); //Access Point mode WiFi.softAP("ESPWebServer", "12345678"); //Password length minimum 8 char //Comment below code if you are using Access point only //ESP32 connects to your wifi ----------------------------------- WiFi.mode(WIFI_STA); //Connectto your wifi WiFi.begin(ssid, password); Serial.println("Connecting to "); Serial.print(ssid); //Wait for WiFi to connect while(WiFi.waitForConnectResult() != WL_CONNECTED)< Serial.print("."); delay(1000); >//If connection successful show IP address in serial monitor Serial.println(«»); Serial.print(«Connected to «); Serial.println(ssid); Serial.print(«IP address: «); Serial.println(WiFi.localIP()); //IP address assigned to your ESP //—————————————————————- server.on(«/», handleRoot); //This is display page server.begin(); //Start server Serial.println(«HTTP server started»); > //=============================================================== // This routine is executed when you open its IP in browser //=============================================================== void loop(void)
Results
After uploading program take your mobile turn on WiFi and in WiFi setting Scan for hot spot you will find “ESPWebServer” hot spot connect to it with password “12345678” as we have given in program. After connecting to ESP hot spot, Open web browser in mobile phone and enter IP 192.168.4.1 you will see “HTML snake game”. IP address can be found in serial monitor.
Open web browser and enter the IP
Web Server results In next post we will see how to make ESP8266 Web Server and Load HTML Web Page.
Piranha ESP32 как точка доступа WiFi
В этом проекте мы настроим Piranha ESP32 на работу в качестве точки доступа WiFi и будем управлять встроенным светодиодом через веб-сайт, размещённый на веб-сервере внутри ESP32. При подключении к серверу (через браузер с телефона или ПК), который запущен на Piranha ESP32, в браузере будет отображена страница с ссылками для управления встроенным в плату светодиодом.
Помимо библиотек WiFi и WiFiClient нам понадобиться библиотека WiFiAP для создания точки доступа.
Для управления встроенным в плату светодиодом необходимо подключиться с телефона, планшета или любого другого устройства с технологией WiFi и браузером к точке доступа esp32asAP с паролем password12345 , затем в адресной строке браузера ввести адрес точки доступа (по умолчанию 192.168.4.1 ).
Видео:
Нам понадобится:
Подключение:
Скетч проекта:
// Подключаем библиотеки #include #include #include // Определяем название и пароль точки доступа const char *ssid = "esp32asAP"; const char *password = "password12345"; // Создаём объект Веб-сервера WiFiServer server(80); void setup() < // Устанавливаем режим работы вывода светодиода pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT); Serial.begin(115200); Serial.println(); Serial.println("Инициируем точку доступа WiFi"); // Инициируем точку доступа WiFi WiFi.softAP(ssid, password); IPAddress myIP = WiFi.softAPIP(); // Выводим IP-адрес Веб-сервера Serial.print("IP-адрес точки доступа: "); Serial.println(myIP); // Инициируем сервер server.begin(); Serial.println("Сервер запущен."); >// Функция ответа клиенту inline bool respToClient(WiFiClient& client, String& currentLine) < // Читаем байт и выводим его в последовательный порт char c = client.read(); Serial.write(c); // Если байт - символ новой строки if (c == '\n') < // Если текущая строка пуста, значит был получен // символ новой строки два раза подряд // Это означает конец клиентского HTTP-запроса. if (currentLine.length() == 0) < // Посылаем HTTP заголовок client.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK"); client.println("Content-type:text/html"); client.println(); // Посылаем текст страницы client.print(""); client.print( "Нажмите " "сюда " "для включения светодиода." ); client.print( "Нажмите " "сюда " "для выключения светодиода." ); client.print(""); // посылаем пустую строку client.println(); // необходимые данные клиенту переданы - // выходим из функции с флагом true return true; > // иначе (строка не пуста) else < // стираем текущую строку currentLine = ""; >> // иначе (байт не символ новой строки), // если байт - не символ возврата каретки else if (c != '\r') < // добавляем его в текущую строку currentLine += c; >// Проверяем какой запрос сделал клиент. // Если GET /H if (currentLine.endsWith("GET /H")) < // Включаем светодиод digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH); >// Если GET /L if (currentLine.endsWith("GET /L")) < // Выключаем светодиод digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW); >return false; > // Функция обработки клиента inline void handleClient(WiFiClient& client) < // выводим сообщение в последовательный порт Serial.println("Новый клиент."); //Создаём строковый объект для хранения входных данных String currentLine = ""; // Входим в цикл пока клиент подсоединён while (client.connected()) < // Если есть данные для чтения if (client.available()) < // Вызываем функцию ответа клиенту bool resp = respToClient(client, currentLine); // Если функция передала все данные клиенту if (resp == true) // прерываем цикл break; >> // Закрываем соединение client.stop(); Serial.println("Клиент отключён."); > void loop() < // Создаём объект клиента и проверяем, есть ли подключённые клиенты WiFiClient client = server.available(); // Если клиенты есть if (client) < // Вызываем функцию обработки клиента handleClient(client); >>