- Запуск скрипта sh в Linux
- Как работают скрипты
- Запуск скрипта sh в Linux
- Выводы
- How to execute/run Linux Shell scripts
- Executing a shell script with source command or . command
- Execute a script with interpreter(bash, ksh, csh, sh etc)
- Executing Linux shell script with ./ notation
- Executing script by entering complete PATH for the script
- Execute shell scripts like Linux commands
- Surendra Anne
- Latest posts by Surendra Anne (see all)
Запуск скрипта sh в Linux
Вся сила Linux в использовании терминала. Это такая командная оболочка, где вы можете выполнять различные команды, которые будут быстро и эффективно выполнять различные действия. Ну впрочем, вы наверное это уже знаете. Для Linux было создано множество скриптов, которые выполняются в различных командных оболочках. Это очень удобно, вы просто объединяете несколько команд, которые выполняют определенное действие, а затем выполняете их одной командой или даже с помощью ярлыка.
Но у новичков может возникнуть вопрос — как запустить скрипт в Linux, что для этого нужно сделать, что будет происходить и какие команды нужно выполнить. Но сначала нужно рассмотреть как работают скрипты и что такое исполняемость.
Как работают скрипты
В Linux почти не используется расширение файла для опережения его типа на системном уровне. Это могут делать файловые менеджеры и то не всегда. Вместо этого, используются сигнатуры начала файла и специальные флаги. Система считает исполняемыми только те файлы, которым присвоен атрибут исполняемости.
Теперь о том, как работают скрипты. Это обычные файлы, которые содержат текст. Но если для них установлен атрибут исполняемости, то для их открытия используется специальная программа — интерпретатор, например, оболочка bash. А уже интерпретатор читает последовательно строку за строкой и выполняет все команды, которые содержатся в файле. У нас есть несколько способов выполнить запуск скрипта linux. Мы можем запустить его как любую другую программу через терминал или же запустить оболочку и сообщить ей какой файл нужно выполнять. В этом случае не нужно даже флага исполняемости.
Запуск скрипта sh в Linux
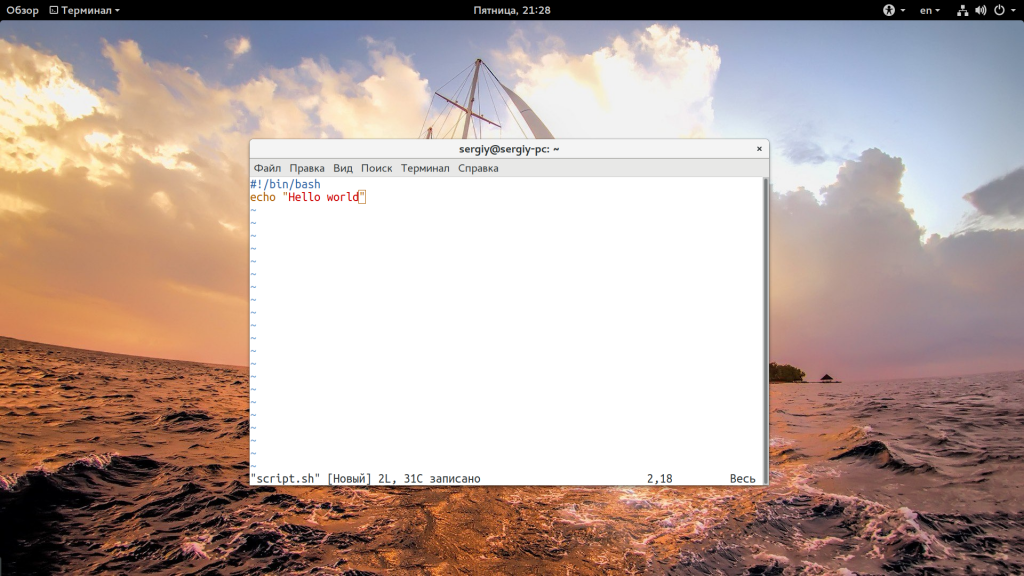
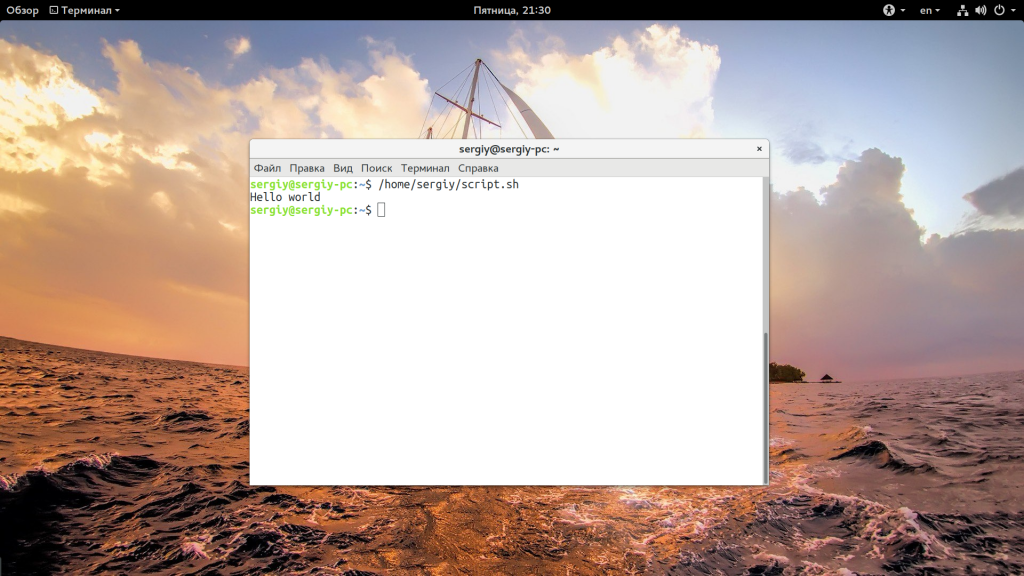
Сначала рассмотрим пример небольшого sh скрипта:
Вторая строка — это действие, которое выполняет скрипт, но нас больше всего интересует первая — это оболочка, с помощью которого его нужно выполнить. Это может быть не только /bin/bash, но и /bin/sh, и даже /usr/bin/python или /usr/bin/php. Также часто встречается ситуация, что путь к исполняемому файлу оболочки получают с помощью утилиты env: /usr/bin/env php и так далее. Чтобы выполнить скрипт в указанной оболочке, нужно установить для него флаг исполняемости:
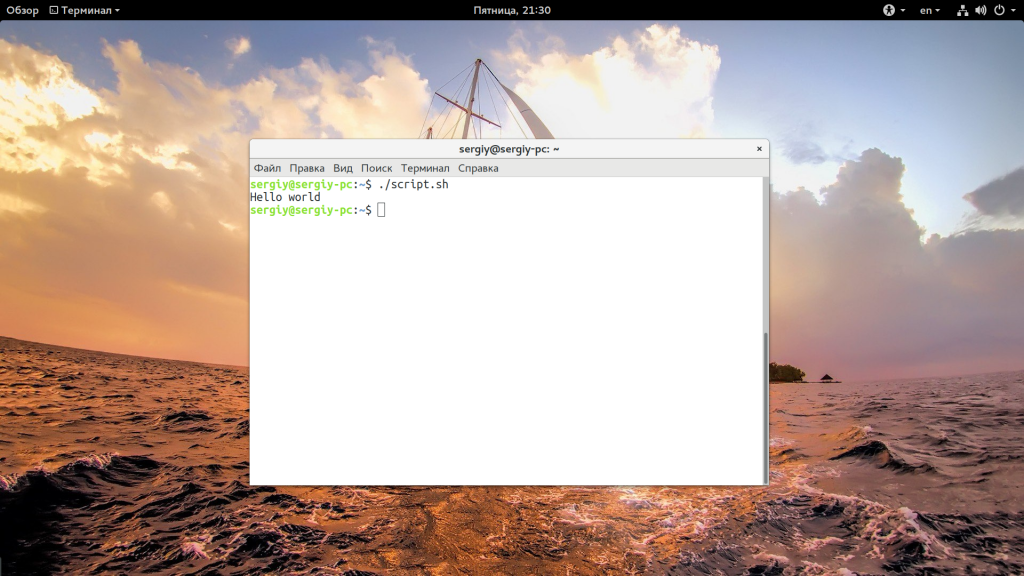
Мы разрешаем выполнять запуск sh linux всем категориям пользователей — владельцу, группе файла и остальным. Следующий важный момент — это то место где находится скрипт, если вы просто наберете script.sh, то поиск будет выполнен только глобально, в каталогах, которые записаны в переменную PATH и даже если вы находитесь сейчас в той папке где находится скрипт, то он не будет найден. К нему нужно указывать полный путь, например, для той же текущей папки. Запуск скрипта sh в linux:
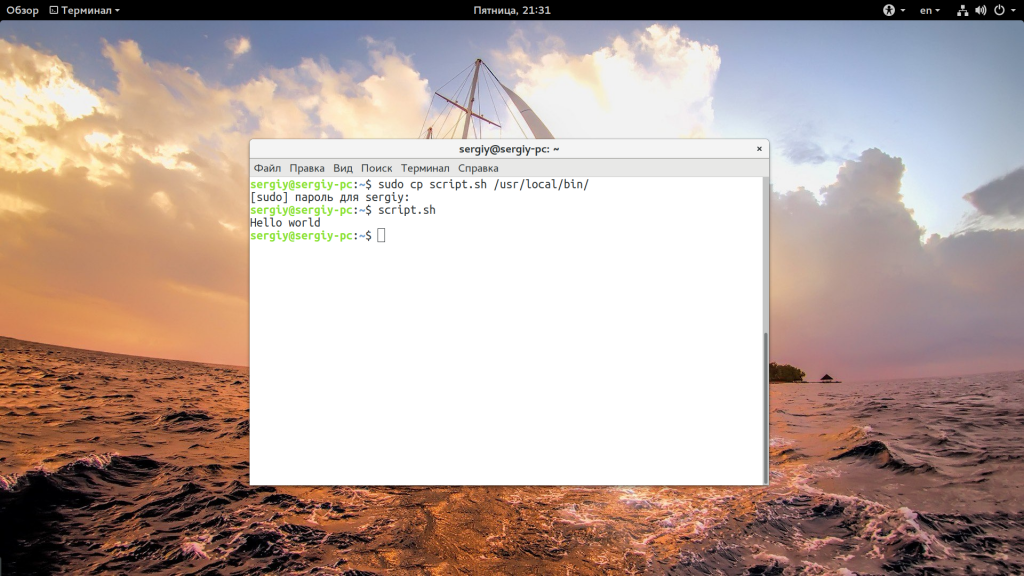
Если вы не хотите писать полный путь к скрипту, это можно сделать, достаточно переместить скрипт в одну из папок, которые указаны в переменной PATH. Одна из них, которая предназначена для ручной установки программ — /usr/local/bin.
cp script.sh /usr/local/bin/script.sh
Теперь вы можете выполнить:
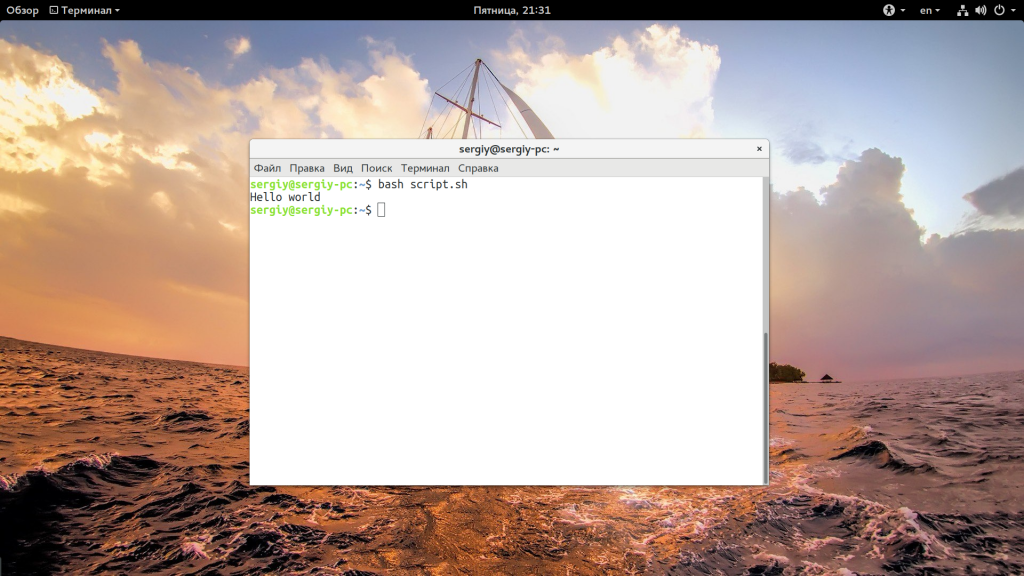
Это был первый способ вызвать скрипт, но есть еще один — мы можем запустить оболочку и сразу же передать ей скрипт, который нужно выполнить. Вы могли редко видеть такой способ с bash, но он довольно часто используется для скриптов php или python. Запустим так наш скрипт:
А если нам нужно запустить скрипт на php, то выполните:
Вот так все просто здесь работает. Так можно запустить скрипт как фоновый процесс, используйте символ &:
Даже запустить процесс linux не так сложно.
Выводы
Как видите, запуск скрипта sh в linux — это довольно простая задача, даже если вы еще плохо знакомы с терминалом. Существует действительно много скриптов и некоторые из них вам возможно придется выполнять. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
How to execute/run Linux Shell scripts
In this post we will see how to run a shell script you just received or created. There are many ways we can execute a shell script and some of the ways you don’t require execute permissions as well on that script. There is a perception that to execute a shell script we require execute permissions. This is not true. Let us see how can we execute a shell script and know other methods to do the same. We will explain each and every method and what happens internally.
Below are some ways(Which I know and you can add more if you know other ways) we can execute a shell script in Linux.
Executing shell script in Linux (7 ways)
- source scriptname
- . scriptname
- interpreter scriptname(Ex: bash scriptname or sh scriptname or ksh script)
- ./scriptname (Execute permissions required)
- /path/to/scriptname (Execute permissions required)
- Linux command by setting the PATH (Execute permissions required)
- move to /bin or /sbin (Execute permissions required)
Executing a shell script with source command or . command
Source is a Linux/Unix built-in command which do not require execute permissions on a shell script to execute it. What actually a source command do is it just read the file and execute the commands one after the other by using present shell where user logged in.
For our understanding we use following simple shell script.
As said earlier running shell scripts do not require execute permissions for at least first three ways in the above list.
Running a shell scripting through source or . command
source scriptname
. scriptname
[ surendra@linuxnix:~/scripts/sh ]$ source firstscript.sh
This is my first line
Bye in third line
[ surendra@linuxnix:~/scripts/sh ]$
With . command which is equalent to source command
[ surendra@linuxnix:~/scripts/sh] $ . firstscript.sh
This is my first line
Bye in third line
[ surendra@linuxnix:~/scripts/sh ]$
Make a note that executing . scriptname is different from ./scriptname which require execute permissions. We will see what ./scriptname below.
If you observe we do not get “Permission denied” errors.
Execute a script with interpreter(bash, ksh, csh, sh etc)
We can execute a shell script with different shell interpreater such as bash, ksh, dash, csh, tcsh, sh etc and again these do not require any execute permissions.
[ surendra@linuxnix:~/scripts/sh ]$ bash firstscript.sh
This is my first line
Bye in third line
[ surendra@linuxnix:~/scripts/sh ]$ sh firstscript.sh
This is my first line
Bye in third line
[ surendra@linuxnix:~/scripts/sh ]$ dash firstscript.sh
This is my first line
Bye in third line
[ surendra@linuxnix:~/scripts/sh ]$
O.K what happens when you are executing with different interpreter? The Shebang/Hashbang statement is not consider when executing with different interpreter. Suppose you write a script in KSH and running it with bash interpreter then script is treated as bash script instead ksh script and you may face syntax issues as well when you try to execute a script written in one shell and executing with other shell.
Executing Linux shell script with ./ notation
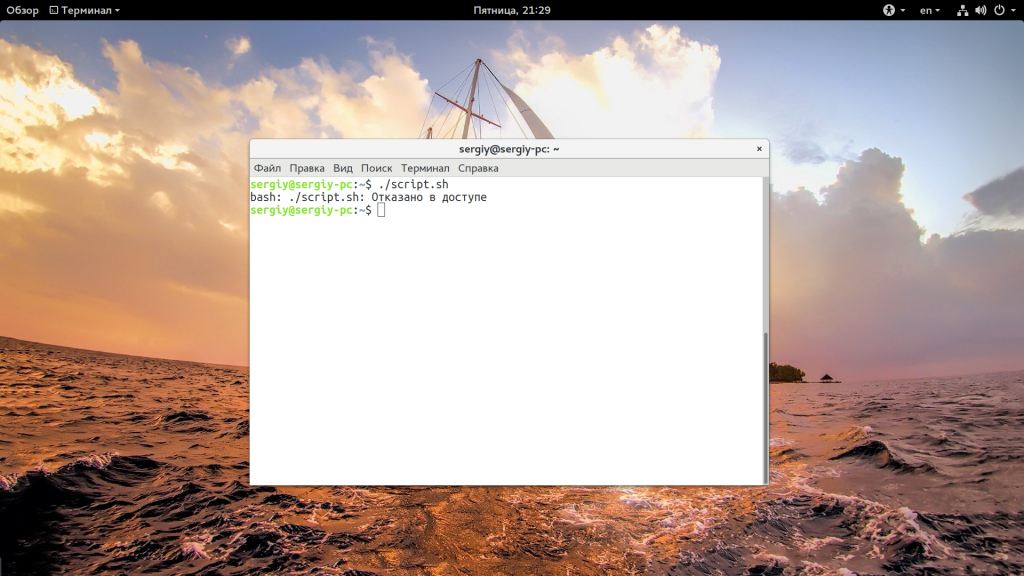
Now let’s try to execute a script without setting executable permissions to the shell script file and see what happens?.
bash: ./firstscript.sh: Permission denied
So before executing a shell script with ./ notation it is advisable to change the permissions to executable. Here are the steps to execute your shell script through ./ notation.
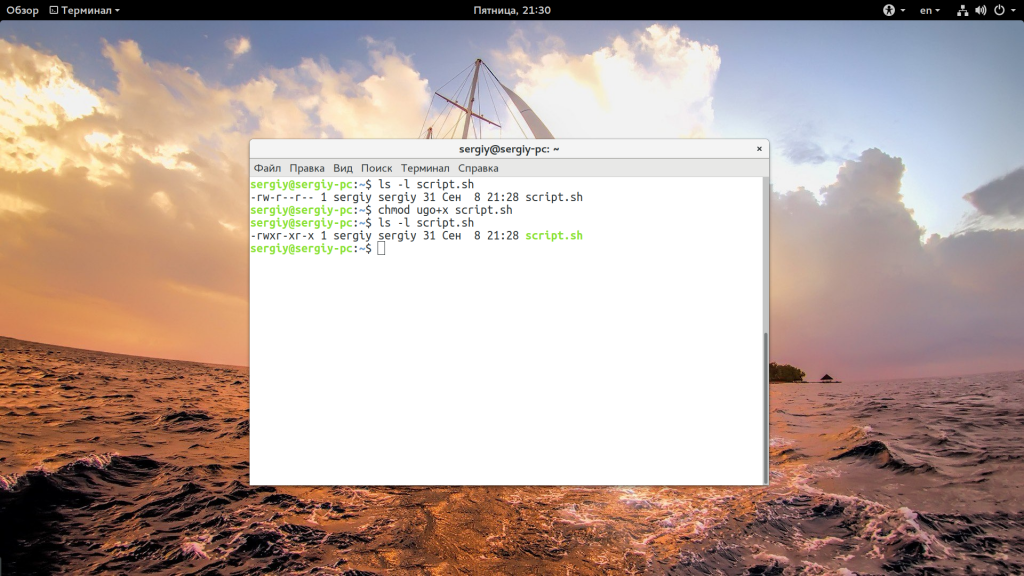
Step1: Change the permissions of shell script to executable.
Note1: The above command will give execute permissions to everyone. If you don’t want to give execute permissions to all and want to give execute permission to owner you can use below command
Note2: There is no need to have .sh as extension, just execute permissions are required to execute a script.
Note3: It’s not advisable to give 777 permissions to a script to execute it.
Go to script location and execute as blow
Executing script by entering complete PATH for the script
Execute shell scripts like Linux commands
We can execute shell scripts like normal Linux/Unix commands by setting PATH variable to your scripts location. Suppose our scripts are located in /home/surendra/scripts/sh then if we add this path to our PATH variable then we no need to use ./ or complete path or any other sort to execute a script we just have to run our script with it’s name from any location
PATH=$PATH:/home/surendra/scripts/sh
surendra@linuxnix:~/scripts/sh$ echo $PATH
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games
surendra@linuxnix:~/scripts/sh$ PATH=$PATH:/home/surendra/scripts/sh
surendra@linuxnix:~/scripts/sh$ cd
surendra@linuxnix:~$ firstscript.sh
This is my first line
Bye in third line
surendra@linuxnix:~$ cd /var
surendra@linuxnix:/var$ firstscript.sh
This is my first line
Bye in third line
Executing scripts by moving them to /bin or /sbin folder
This can be done only by root user. We can move all your scripts to one of these folders so that we can exeuct them without pointing to any interpreter.
Stay tuned to our next post on how to debug your shell scripts.
Surendra Anne
Mr Surendra Anne is from Vijayawada, Andhra Pradesh, India. He is a Linux/Open source supporter who believes in Hard work, A down to earth person, Likes to share knowledge with others, Loves dogs, Likes photography. He works as Devops Engineer with Taggle systems, an IOT automatic water metering company, Sydney . You can contact him at surendra (@) linuxnix dot com.
Latest posts by Surendra Anne (see all)
- Docker: How to copy files to/from docker container — June 30, 2020
- Anisble: ERROR! unexpected parameter type in action: Fix — June 29, 2020
- FREE: JOIN OUR DEVOPS TELEGRAM GROUPS — August 2, 2019
- Review: Whizlabs Practice Tests for AWS Certified Solutions Architect Professional (CSAP) — August 27, 2018
- How to use ohai/chef-shell to get node attributes — July 19, 2018