Команда tar в Linux
В качестве инструмента для архивации данных в Linux используются разные программы. Например архиватор Zip Linux, приобретший большую популярность из-за совместимости с ОС Windows. Но это не стандартная для системы программа. Поэтому хотелось бы осветить команду tar Linux — встроенный архиватор.
Изначально tar использовалась для архивации данных на ленточных устройствах. Но также она позволяет записывать вывод в файл, и этот способ стал широко применяться в Linux по своему назначению. Здесь будут рассмотрены самые распространенные варианты работы с этой утилитой.
Синтаксис команды tar
Синтаксис команд для создания и распаковки архива практически не отличается (в том числе с утилитами сжатия bzip2 или gzip). Так, чтобы создать новый архив, в терминале используется следующая конструкция:
tar опции архив.tar файлы_для_архивации
tar опции архив.tar
Функции, которые может выполнять команда:
| Функция | Длинный формат | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| -A | —concatenate | Присоединить существующий архив к другому |
| -c | —create | Создать новый архив |
| -d | —diff —delete | Проверить различие между архивами Удалить из существующего архива файл |
| -r | —append | Присоединить файлы к концу архива |
| -t | —list | Сформировать список содержимого архива |
| -u | —update | Обновить архив более новыми файлами с тем же именем |
| -x | —extract | Извлечь файлы из архива |
При определении каждой функции используются параметры, которые регламентируют выполнение конкретных операций с tar-архивом:
| Параметр | Длиннный формат | Описание |
|---|---|---|
| -C dir | —directory=DIR | Сменить директорию перед выполнением операции на dir |
| -f file | —file | Вывести результат в файл (или на устройство) file |
| -j | —bzip2 | Перенаправить вывод в команду bzip2 |
| -p | —same-permissions | Сохранить все права доступа к файлу |
| -v | —verbose | Выводить подробную информацию процесса |
| —totals | Выводить итоговую информацию завершенного процесса | |
| -z | —gzip | Перенаправить вывод в команду gzip |
А дальше рассмотрим примеры того, как может применяться команда tar Linux.
Как пользоваться tar
1. Создание архива tar
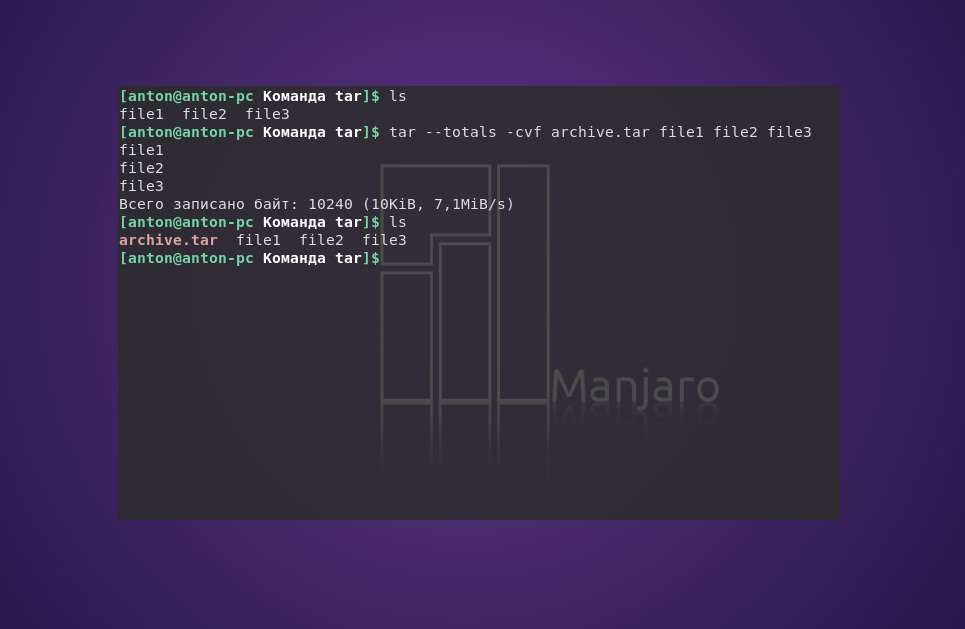
С помощью следующей команды создается архив archive.tar с подробным выводом информации, включающий файлы file1, file2 и file3:
tar —totals —create —verbose —file archive.tar file1 file2 file3
Но длинные опции и параметры можно заменить (при возможности) однобуквенными значениями:
tar —totals -cvf archive.tar file1 file2 file3
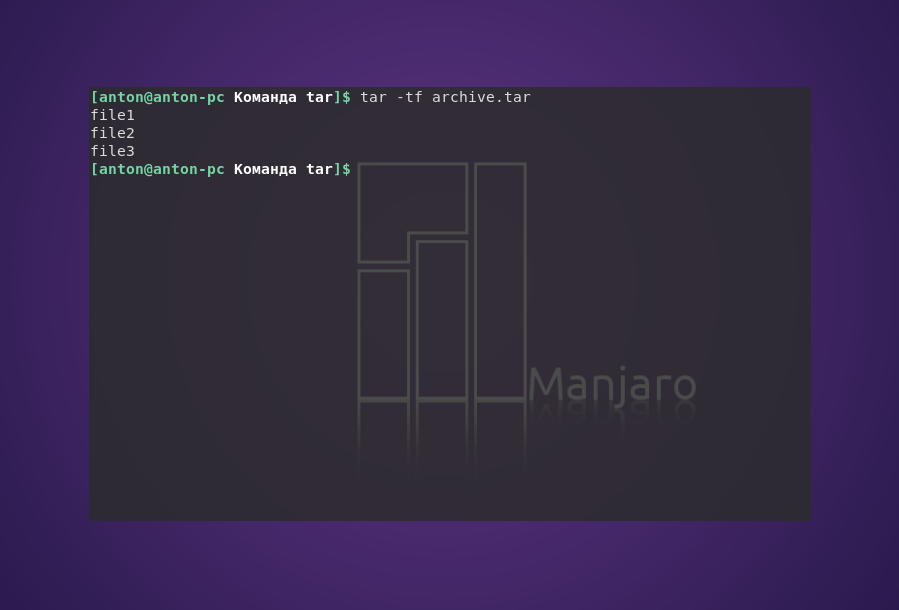
2. Просмотр содержимого архива
Следующая команда выводит содержимое архива, не распаковывая его:
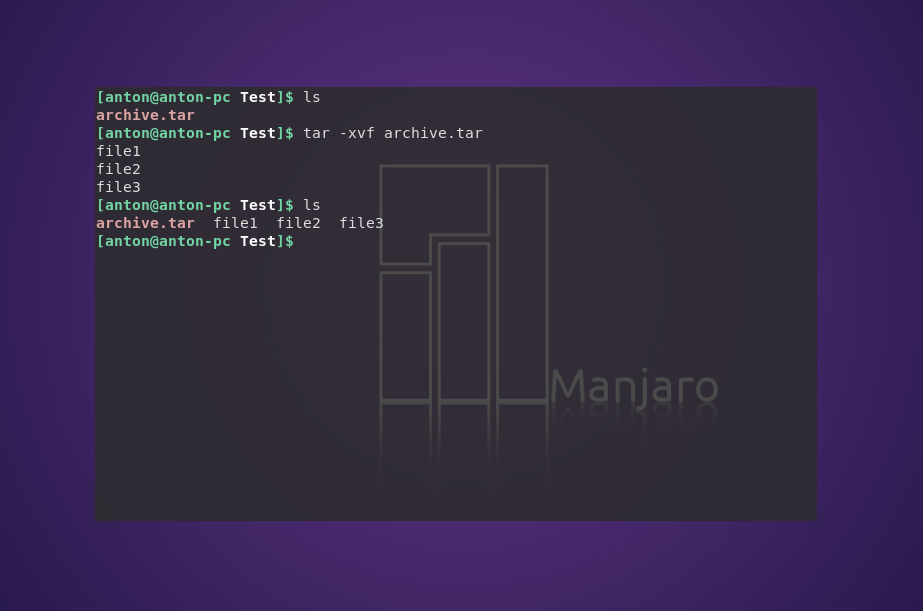
3. Распаковка архива tar Linux
Распаковывает архив test.tar с выводом файлов на экран:
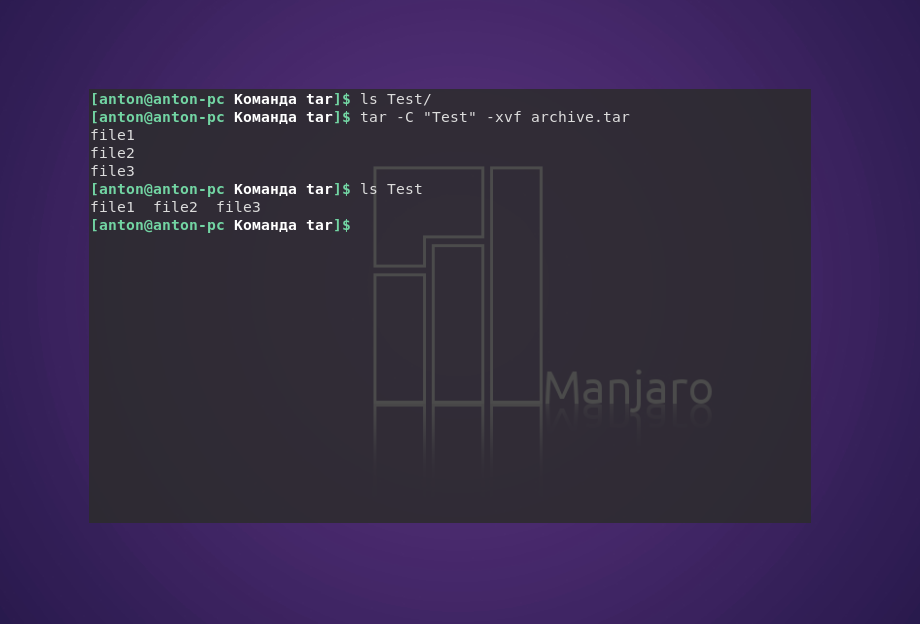
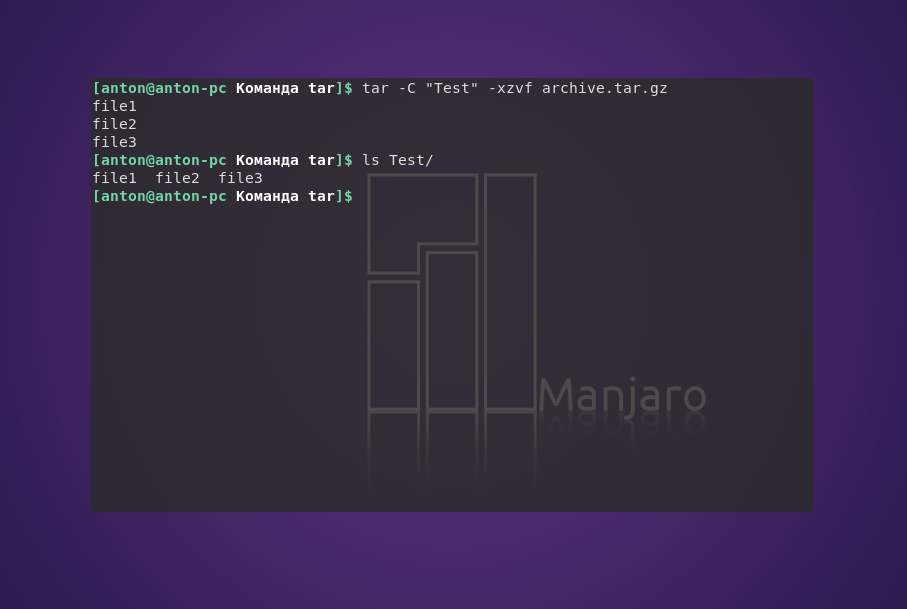
Чтобы сделать это в другой каталог, можно воспользоваться параметром -C:
tar -C «Test» -xvf archive.tar
3. Работа со сжатыми архивами
Следует помнить, что tar только создаёт архив, но не сжимает. Для этого используются упомянутые компрессорные утилиты bzip2 и gzip. Файлы, сжатые с их помощью, имеют соответствующие расширения .tar.bz2 и .tar.gz. Чтобы создать сжатый архив с помощью bzip2, введите:
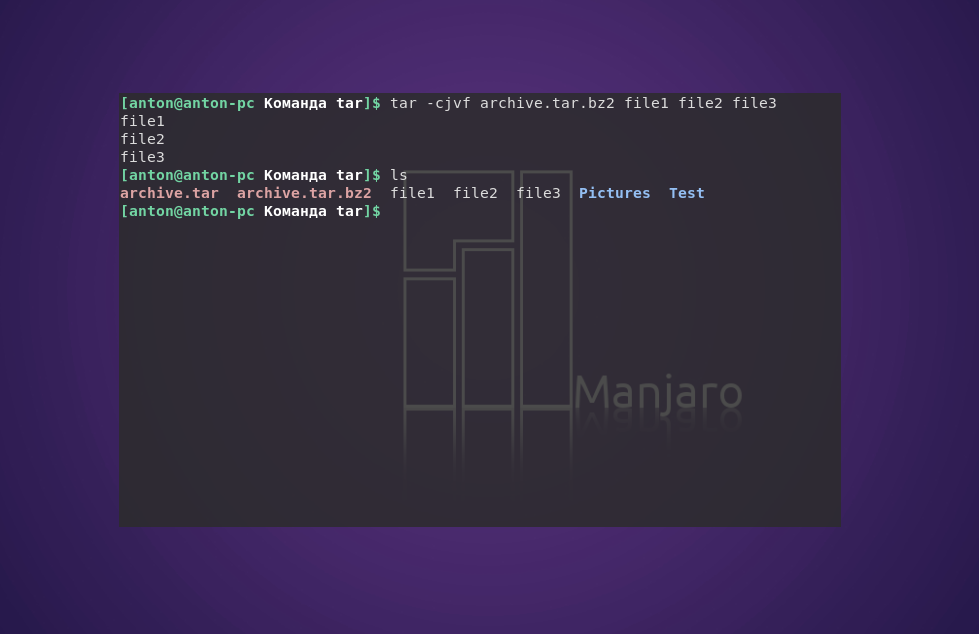
tar -cjvf archive.tar.bz2 file1 file2 file3
Синтаксис для gzip отличается одной буквой в параметрах, и меняется окончание расширения архива:
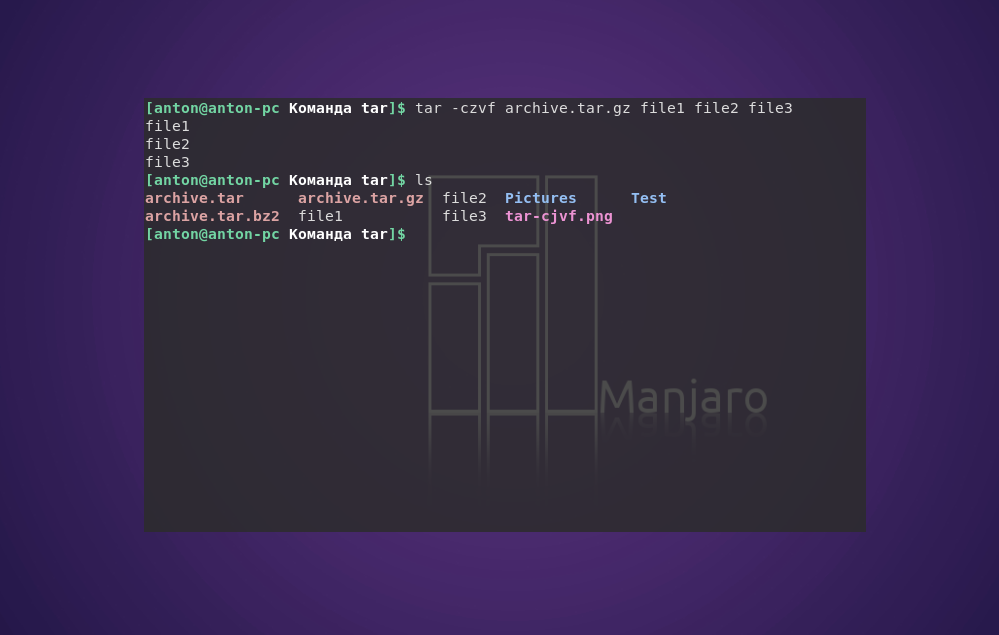
tar -czvf archive.tar.gz file1 file2 file3
При распаковке tar-архивов с таким расширением следует указывать соответствующую опцию:
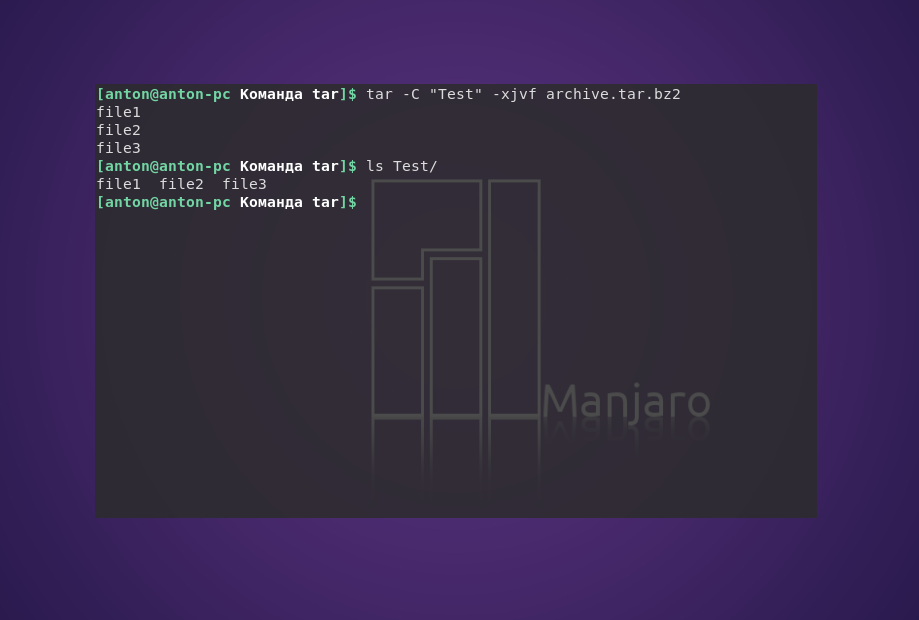
tar -C «Test» -xjvf arhive.tar.bz2
На заметку: архиватор tar — одна из немногих утилит в GNU/Linux, в которой перед использованием однобуквенных параметров, стоящих вместе, можно не ставить знак дефиса.
Выводы
В этой статье была рассмотрена команда tar Linux, которая используется для архивации файлов и поставляется по умолчанию во всех дистрибутивах. В её возможности входит создание и распаковка архива файлов без их сжатия. Для сжатия утилита применяется в связке с популярными компрессорами bzip2 и gzip.
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
tar command in Linux with examples
The Linux ‘tar’ stands for tape archive, is used to create Archive and extract the Archive files. tar command in Linux is one of the important command which provides archiving functionality in Linux. We can use Linux tar command to create compressed or uncompressed Archive files and also maintain and modify them.
tar [options] [archive-file] [file or directory to be archived]
Options:
-c : Creates Archive
-x : Extract the archive
-f : creates archive with given filename
-t : displays or lists files in archived file
-u : archives and adds to an existing archive file
-v : Displays Verbose Information
-A : Concatenates the archive files
-z : zip, tells tar command that creates tar file using gzip
-j : filter archive tar file using tbzip
-W : Verify a archive file
-r : update or add file or directory in already existed .tar file
What is an Archive file?
An Archive file is a file that is composed of one or more files along with metadata. Archive files are used to collect multiple data files together into a single file for easier portability and storage, or simply to compress files to use less storage space.
Examples:
1. Creating an uncompressed tar Archive using option -cvf : This command creates a tar file called file.tar which is the Archive of all .c files in current directory.
2. Extracting files from Archive using option -xvf : This command extracts files from Archives.
3. gzip compression on the tar Archive, using option -z : This command creates a tar file called file.tar.gz which is the Archive of .c files.
4. Extracting a gzip tar Archive *.tar.gz using option -xvzf : This command extracts files from tar archived file.tar.gz files.
5. Creating compressed tar archive file in Linux using option -j : This command compresses and creates archive file less than the size of the gzip. Both compress and decompress takes more time then gzip.
$ tar cvfj file.tar.tbz example.cpp
$tar cvfj file.tar.tbz example.cpp example.cpp $tar tvf file.tar.tbz -rwxrwxrwx root/root 94 2017-09-17 02:47 example.cpp
6. Untar single tar file or specified directory in Linux : This command will Untar a file in current directory or in a specified directory using -C option.
$ tar xvfj file.tar or $ tar xvfj file.tar -C path of file in directory
7. Untar multiple .tar, .tar.gz, .tar.tbz file in Linux : This command will extract or untar multiple files from the tar, tar.gz and tar.bz2 archive file. For example the above command will extract “fileA” “fileB” from the archive files.
$ tar xvf file.tar "fileA" "fileB" or $ tar zxvf file1.tar.gz "fileA" "fileB" or $ tar jxvf file2.tar.tbz "fileA" "fileB"
8. Check size of existing tar, tar.gz, tar.tbz file in Linux : The above command will display the size of archive file in Kilobytes(KB).
$ tar czf file.tar | wc -c or $ tar czf file1.tar.gz | wc -c or $ tar czf file2.tar.tbz | wc -c
9. Update existing tar file in Linux
10. list the contents and specify the tarfile using option -tf : This command will list the entire list of archived file. We can also list for specific content in a tarfile
11. Applying pipe to through ‘grep command’ to find what we are looking for : This command will list only for the mentioned text or image in grep from archived file.
$ tar tvf file.tar | grep "text to find" or $ tar tvf file.tar | grep "filename.file extension"
12. We can pass a file name as an argument to search a tarfile : This command views the archived files along with their details.
13. Viewing the Archive using option -tvf
-rwxrwxrwx root/root 191 2017-09-17 02:20 os2.c -rwxrwxrwx root/root 218 2017-09-17 02:20 os3.c -rwxrwxrwx root/root 493 2017-09-17 02:20 os4.c
What are wildcards in Linux
Alternatively referred to as a ‘wild character’ or ‘wildcard character’, a wildcard is a symbol used to replace or represent one or more characters. Wildcards are typically either an asterisk (*), which represents one or more characters or question mark (?),which represents a single character.
14. To search for an image in .png format : This will extract only files with the extension .png from the archive file.tar. The –wildcards option tells tar to interpret wildcards in the name of the files
to be extracted; the filename (*.png) is enclosed in single-quotes to protect the wildcard (*) from being expanded incorrectly by the shell.
$ tar tvf file.tar --wildcards '*.png'
Note: In above commands ” * ” is used in place of file name to take all the files present in that particular directory.

?list=PLqM7alHXFySFc4KtwEZTANgmyJm3NqS_L
This article is contributed by Akansh Gupta. If you like GeeksforGeeks and would like to contribute, you can also write an article using write.geeksforgeeks.org or mail your article to review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. See your article appearing on the GeeksforGeeks main page and help other Geeks.
Please write comments if you find anything incorrect, or you want to share more information about the topic discussed above.
How to Extract Tar Files in Linux
wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 11 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time.
This article has been viewed 350,011 times.
Extract files from TAR archives with and without compression (GZip).
Community Q&A
When I try to extract the Tar file I get the message, «No such file or directory.» What does this mean?
You’re probably referencing the file incorrectly. Check the location that the terminal is open in, and the relevancy of the file’s location to it.
Thanks! We’re glad this was helpful.
Thank you for your feedback.
As a small thank you, we’d like to offer you a $30 gift card (valid at GoNift.com). Use it to try out great new products and services nationwide without paying full price—wine, food delivery, clothing and more. Enjoy! Claim Your Gift If wikiHow has helped you, please consider a small contribution to support us in helping more readers like you. We’re committed to providing the world with free how-to resources, and even $1 helps us in our mission. Support wikiHow
Thanks! We’re glad this was helpful.
Thank you for your feedback.
As a small thank you, we’d like to offer you a $30 gift card (valid at GoNift.com). Use it to try out great new products and services nationwide without paying full price—wine, food delivery, clothing and more. Enjoy! Claim Your Gift If wikiHow has helped you, please consider a small contribution to support us in helping more readers like you. We’re committed to providing the world with free how-to resources, and even $1 helps us in our mission. Support wikiHow
It does not matter where the file is located. As long as you change your terminal’s working directory to the directory that contains the TAR file, the extraction will work just fine.
Thanks! We’re glad this was helpful.
Thank you for your feedback.
As a small thank you, we’d like to offer you a $30 gift card (valid at GoNift.com). Use it to try out great new products and services nationwide without paying full price—wine, food delivery, clothing and more. Enjoy! Claim Your Gift If wikiHow has helped you, please consider a small contribution to support us in helping more readers like you. We’re committed to providing the world with free how-to resources, and even $1 helps us in our mission. Support wikiHow

Extracting an archive may overwrite files in some locations if the archive has a file of the same name.
You Might Also Like
How to Extract a GZ File on Windows, Linux, Mac, & Mobile
Can Linux Run .exe Files? How to Run Windows Software on Linux
How to Open Linux Firewall Ports: Ubuntu, Debian, & More
How to Run an INSTALL.sh Script on Linux in 4 Easy Steps
Use Ping in Linux: Tutorial, Examples, & Interpreting Results
How to Delete Read-Only Files in Linux
How to Install Linux on Your Computer