- How to Compare Two Files in Linux Terminal
- Creating Text Files in Linux
- Using diff to Compare Files in Linux
- Outputting the Differences between Two Files
- Find Out Two Files are Identical Using Diff in Linux
- Diff Command Output Alternate View
- How to Compare Two Files in Linux
- How to Use “diff” Command in Linux to Compare Files:
- How to Get Output in One Line Using the “diff” Command:
- How to Check the Difference of Files in Context Mode Using the “diff” Command:
- How to Check the Difference of Files in Unified Mode Using the “diff” Command:
- How to Ignore Case Sensitivity While Using the “diff” Command:
- How to Use Vim Editor to Compare Two Files:
- How to Compare Two Files Using “colordiff”:
- Conclusion:
- About the author
- Sam U
How to Compare Two Files in Linux Terminal
The need for file comparison on a Linux operating system is often overlooked but has an important role to play especially for Linux system administrators. Being able to flexibly compare two files on a Linux terminal sheds some light on how unique or different a set of files are perceived to be.
[ You might also like: How to Join Two Text Files in Linux ]
For example, two files can exist with the same properties and size. Instead of making the assumption that they are identical, a Linux file comparison program will clear the air on such an issue. You could be surprised to find out that the differentiating factor of the two files is some wording or spacing that matches with one file and fails to do so with the other one.
Several terminal-based Linux programs can help us achieve the objective of this article but only a few stand out in terms of dynamic functionalities.
Creating Text Files in Linux
Let us create two sample files from the Linux terminal. Ensure that you are a sudoer user or have sudo privileges on the Linux operating system you are using.
We will populate this file with some random content.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 one two three four five six seven eight nine ten This file contains some number sequences in numeric and textual form. Regards, LinuxShellTips Tutor
Let us create a second file.
We will populate this file with content slightly similar to file1.
11 2 13 4 15 6 7 8 19 10 one twice three four five six seven eight nine ten This file contains some number sequences in numeric form and some textual representation of the numbers. Regards, LinuxShellTips Tutor
Using diff to Compare Files in Linux
Since diff is a terminal-based program, using it outputs the targeted differences between two files. In other words, the diff output tells you the changes that can be implemented on file1 to make it a match or identical to file2.
Outputting the Differences between Two Files
Let us implement the first attempt into comparing these two files:
We can interpret this output in the following manner:
If you go back to the original file1 and file2 files we created earlier, you will note that the above diff command output is not displaying all the content from the two files. It has omitted all the similarities of the two files and only displayed their differences.
Find Out Two Files are Identical Using Diff in Linux
Let us create a third file called file3.
We will populate this file with content similar to file1.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 one two three four five six seven eight nine ten This file contains some number sequences in numeric and textual form. Regards, LinuxShellTips Tutor
A one-liner diff command output should be able to directly tell us if two files are identical.
The use of the extra -s command argument makes this output possible. However, implementing it with two unidentical files will still output their differences.
If you are looking for a one-liner output on two files you suspect to be different, consider the use of the diff command with the -q option.
$ diff -q file1 file2 Files file1 and file2 differ
Diff Command Output Alternate View
If you need the output comparison of your two files to be side-by-side, consider implementing the diff command with the -y option.
If you want the above command to suppress or ignore the similarities of the two files, include the —suppress-common-lines option.
$ diff -y --suppress-common-lines file1 file2
If you are dealing with two large files and want to limit the output to specific column numbers, you would implement the diff command in the following manner.
The above command assumes the two files in comparison are somewhat large and exceed 50 columns in terms of text size. The diff output will be limited to 50 columns.
How to Compare Two Files in Linux
If you want to compare two files and decipher the difference, a command called “diff” is used. This guide is focused on providing you the usage of the “diff” command with various options to get the difference between two files.
So, how does the “diff” command actually function? The “diff” command compares the two files and outputs a list of differences between both files. More precisely, it yields a list of modifications that require to be made in the first file to match the second file. The “diff” command is also used by the programmers to get the difference between two source code files to develop patches.
Before diving into the examples, note that the order of the files is very important. Because the “diff” command gives output based on the order of the files.
How to Use “diff” Command in Linux to Compare Files:
The syntax of the “diff” command is mentioned below:
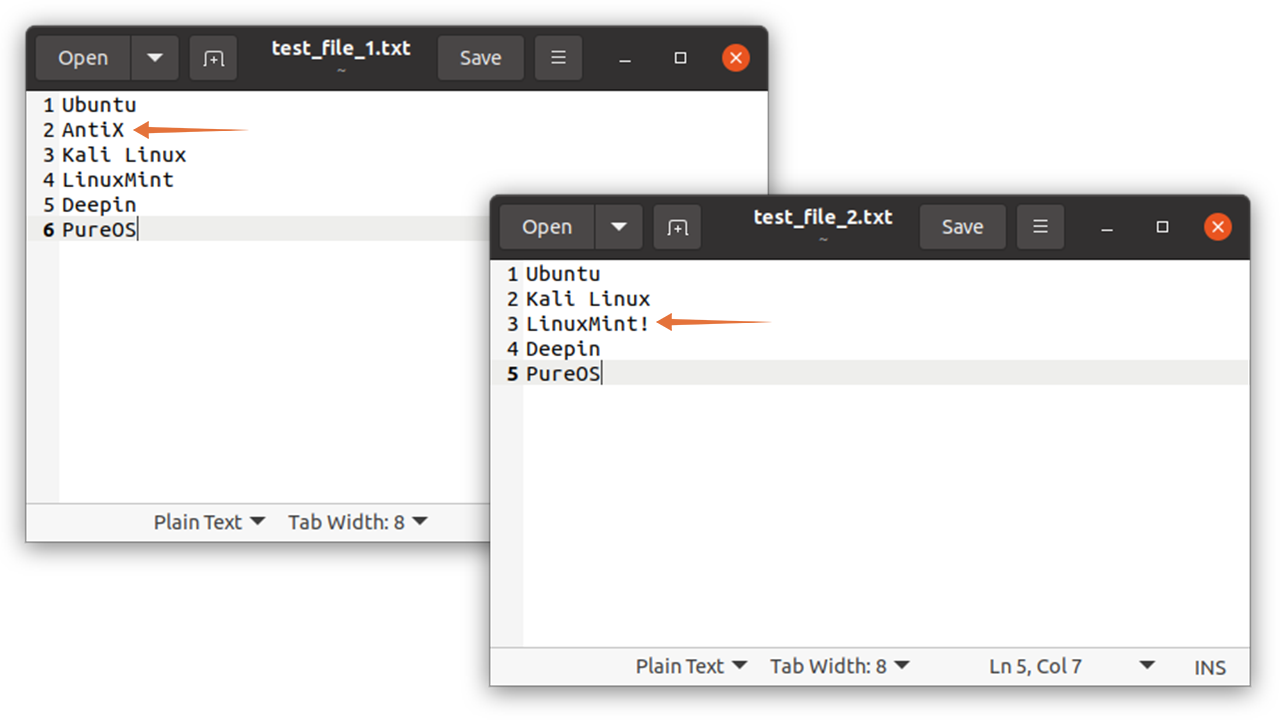
First, create two files. I am creating text files by the name of “test_file_1.txt” and “test_file_2.txt”. These files contain content with a slight difference:
Now use the following command to get the difference:
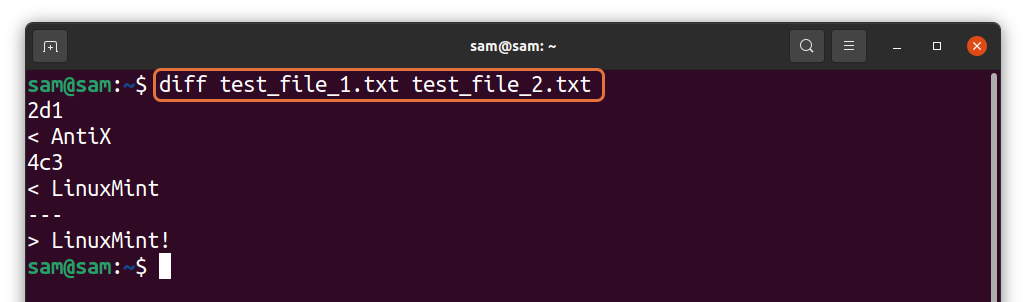
The standard output displayed the lines that match according to the order of the files mentioned in the command. So, let’s decode the output:
The comparison of the files is labeled, and each label has a number on either side. The format is as follows:
[Line number of file 1][Label(a,c,d)][Line number of file 2]
- a – Add: Add content in the first file to synch with the second file.
- c – Change: Indicates that a modification needed in the content of first file to match the second file.
- d – Delete: Remove content from the first file to match with the second.
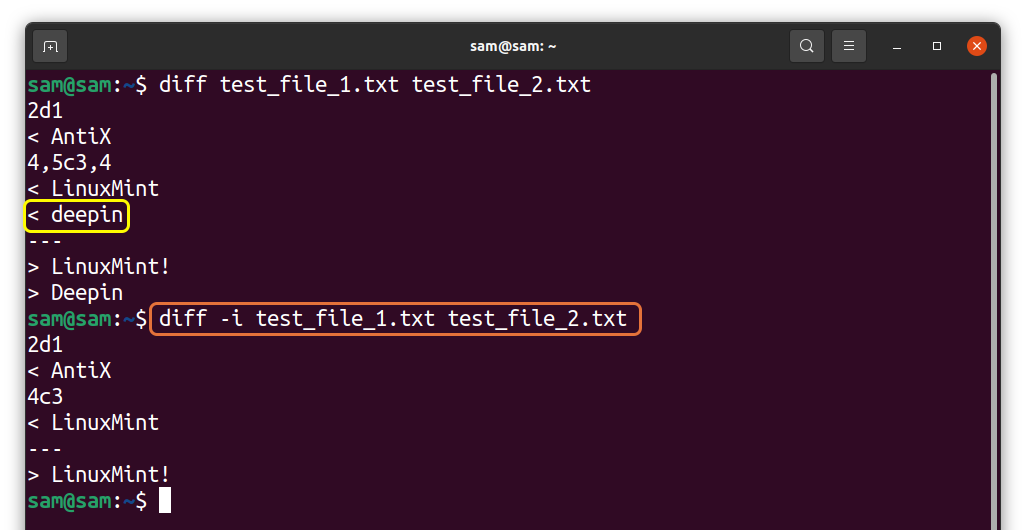
“2d1” indicates to delete line number 2 of the first file to match the second file from line number 1.
Similarly, “4c3” means making a change in the fourth line of the first file to match line number 3 of the second file as both lines are slightly different.
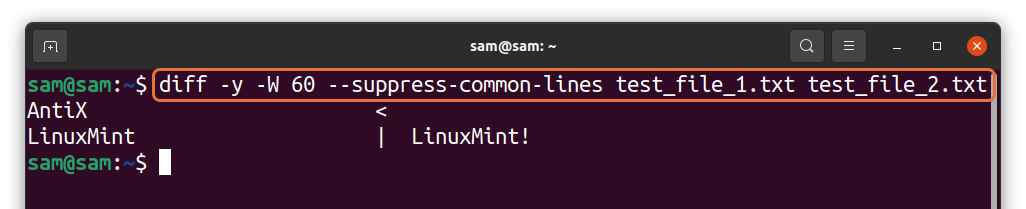
There is another method to view the difference, use the “diff” command with the “-y” option:
In the above output, the content of “test_file_1.txt” is displayed on the left side, while the content of “text_file_2.txt” is displayed on the right side. The difference is indicated by the symbols:
The “-W” indicates the width between the content of two files. To get separately and view the difference, use the following:
How to Get Output in One Line Using the “diff” Command:
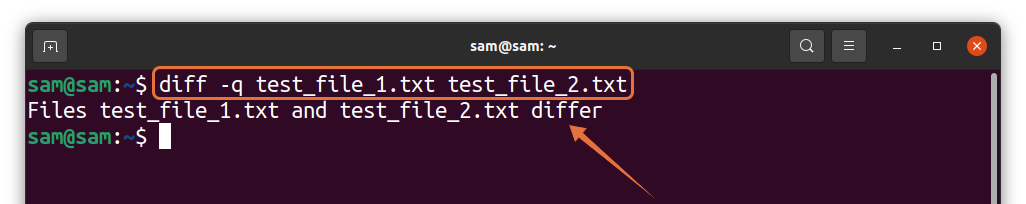
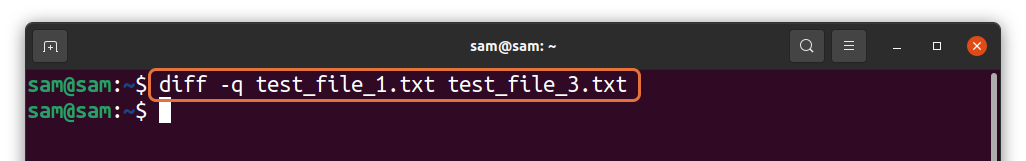
If the labeled method is hard for you to decode, then there is a simpler approach. Using the “-q” option with the “diff” command gives you output in one line. Well, without any additional information, though:
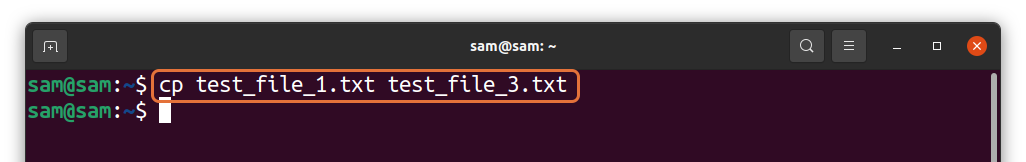
If the files differ, then the above command will give an output. If the files are identical, then there will be no output. To demonstrate it, I am creating a copy of “test_file_1.txt” using:
A new file will be created by the name of “test_file_3.txt” containing the same content that “test_file_1.txt” has. Now, use:
Since both the files have similar content, therefore, there would be no output.
How to Check the Difference of Files in Context Mode Using the “diff” Command:
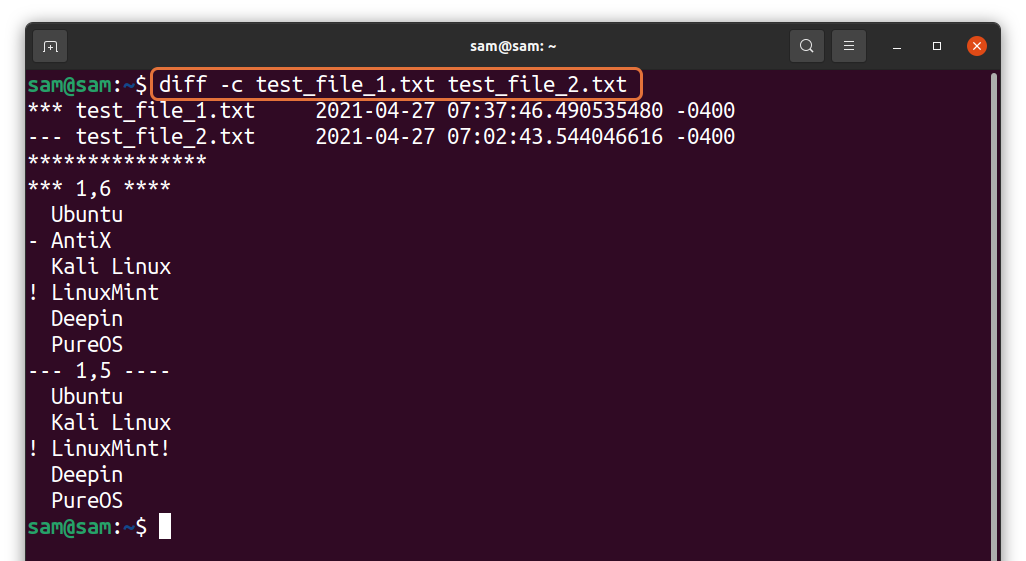
To get the comparison in context mode, the “-c” option will be used with the “diff” command:
To maintain the difference, the first file is indicated by “***” along with the date and time of the creation, while the second file is indicated by “—”.
The next line signifies a range of lines considered during comparison. For the first file, it is “***1,6****” and for the second file, it is “—1,5—-”:
The difference is indicated by the symbols:
- + : Line is not present in the first file. Insert it in the first file or remove it from the second file to match both files.
- – : The line exists in the first file but not in the second file. Try to insert it in the second file or remove it from the first to match both files.
- ! : Line needs modification in order to match.
How to Check the Difference of Files in Unified Mode Using the “diff” Command:
The unified mode is quite similar to the context mode but without redundant information. The flag we use is “-u”:
In the output, the first file is indicated by “—” and the second by “+++”. The second line shows the number of lines considered for comparison in both files, then the content to be deleted, added, or modified with the symbols with them. There will be no symbol with similar lines in both files.
How to Ignore Case Sensitivity While Using the “diff” Command:
If you want to compare the files while ignoring the case sensitivity, then use the “-i” flag:
For demonstration, I have made the “D” of “Deepin” in the first file small:
As seen in the first command, the difference is indicated; while using “-i” that difference has been removed.
Some other useful options of the “diff” command are listed below:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -a | This option treats all the files as text files |
| -B | It ignores modification where lines are all blank |
| -E | This option ignores tab expansion |
| -I | It ignores the changes where all lines match |
| -s | Gives output when two files are identical |
| -w | It ignores all white space |
| -Z | It ignores white space at line end |
How to Use Vim Editor to Compare Two Files:
Another method to compare two files is using the “vimdiff” command. For that, you need to have vim installed:
Now, to compare two files use:
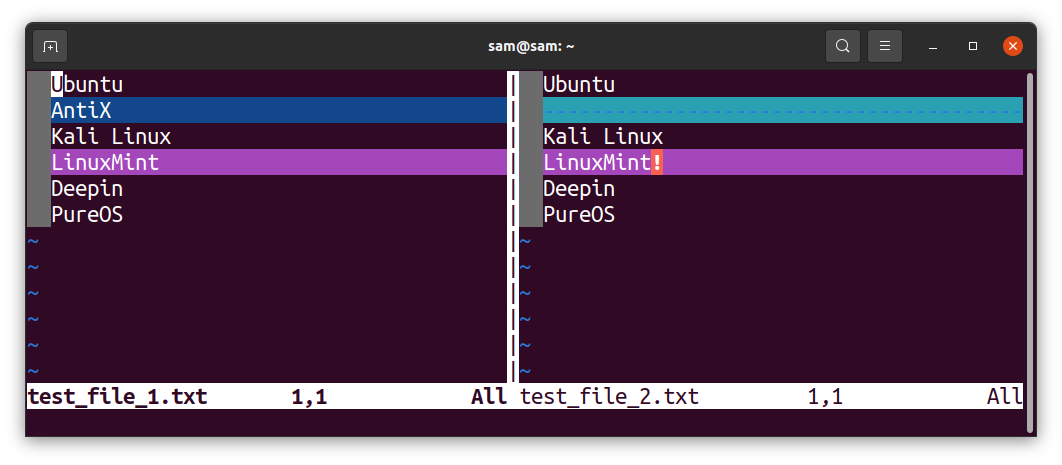
Both files will be opened side by side. The portion that does not match will be highlighted:
How to Compare Two Files Using “colordiff”:
Another approach is a sort of extension of the “diff” command. You can make the comparison more identifiable by adding colors to it. To install use:
You can replace “diff” with “colordiff” to get the standard output of the “diff” command in colored format.
Conclusion:
To compare files in Linux and even in macOS, a utility used is called the “diff”. The “diff” utility compares two files and gives information about the differences between the two files. The developers primarily use the “diff” command to create patch files.
In this guide, we thoroughly discussed the “diff” command and how to use it to compare two files with different options. We also learned how to use “colordiff” to make the file differences more recognizable. But if you find terminal-based utility hard to use, there are some GUI-based tools as well, such as Kompare, DiffMerge, Meld — Diff Tool and Diffuse — GUI Giff Tool.
About the author
Sam U
I am a professional graphics designer with over 6 years of experience. Currently doing research in virtual reality, augmented reality and mixed reality.
I hardly watch movies but love to read tech related books and articles.