- Files being used by a unix process
- Update
- 6 Answers 6
- How to Check Open Files in Linux
- Pre-Requisites
- LSOF Utility
- How to Install lsof on Debian/Ubuntu
- How to Install on REHL/CentOS
- How to Install on Arch
- How to Install on Fedora
- Basic lsof Usage
- How to Show Processes that Opened a File
- How Show files Opened by a Specific User
- How to Show Files Opened by a Specific Process
- How to Show Files Opened in a Directory
- How to Show Network Connection
- How to Continuously Show Files
- Conclusion
- About the author
- John Otieno
Files being used by a unix process
The fuser command lets me know which processes are using a file or directory. I’m looking for command that does the opposite: lets me know which files are being used by a process.
Update
6 Answers 6
lsof stands for “LiSt Open Files”. This shell command seems deceptively simple: It lists information about files opened by processes on a UNIX box.
Despite its (apparent) modest mission statement, lsof is actually one of the most powerful and useful UNIX commands. Its raw power comes from one of UNIX’s design principle often described as ”in UNIX everything is a file”. What this means is that the lsof concept of an open file not only covers regular files but also the following:
- Directories
- Streams or network files (for example, Internet or UNIX domain sockets and NFS files)
- Native libraries (for example, .soor .dylibdynamic libraries linked to a process)
- Block and character special files (for example, disk volume, external hard drive, console, or mouse)
- Pipes
Wait, I Cannot Find lsof on My System!
lsof is such a popular tool that it has been ported to pretty much all UNIX dialects (Linux, Mac OS X, BSD, Solaris, and so on). If it is unavailable on your box, use your usual package management system to install it. You can find lsof packages for Solaris on Sun Freeware.
While I wouldn’t begrudge anyone learning Dtrace or gaining experience installing software, in Solaris there is a command to see the files a process has open: /usr/bin/pfiles
% tail -f /etc/motd & [1] 6033 % pfiles 6033 6033: tail -f /etc/motd Current rlimit: 256 file descriptors 0: S_IFREG mode:0644 dev:182,65538 ino:163065 uid:0 gid:3 size:54 O_RDONLY|O_LARGEFILE /etc/motd 1: S_IFCHR mode:0620 dev:299,0 ino:718837882 uid:101 gid:7 rdev:24,3 O_RDWR|O_NOCTTY|O_LARGEFILE /dev/pts/3 2: S_IFCHR mode:0620 dev:299,0 ino:718837882 uid:101 gid:7 rdev:24,3 O_RDWR|O_NOCTTY|O_LARGEFILE /dev/pts/3 - you can use ls command and grep to find out the files used by chrome
$ ls -l /proc/*/fd | grep «chrome»
lrwx—— 1 ba abc 64 Jul 16 22:19 104 -> /home/abc/.config/google-chrome/Default/Cookies
lr-x—— 1 abc abc 64 Jul 16 22:19 113 -> /opt/google/chrome/nacl_irt_x86_64.nexe
lrwx—— 1 abc abc 64 Jul 16 22:19 121 -> /home/abc/.cache/google-chrome/Default/Cache/data_0
lrwx—— 1 abc abc 64 Jul 16 22:19 122 -> /home/abc/.cache/google-chrome/Default/Cache/data_1
lrwx—— 1 abc abc 64 Jul 16 22:19 123 -> /home/abc/.cache/google-chrome/Default/Cache/data_2
lr-x—— 1 abc abc 64 Jul 16 22:19 125 -> /home/abc/.config/google-chrome/Dictionaries/en-US-3-0.bdic
Another command to find out the result using lsof and grep
$ lsof | grep «chrome»
chrome 2204 abc cwd DIR 8,5 4096 1441794 /home/abc
chrome 2204 abc rtd DIR 8,5 4096 2 /
chrome 2204 abc txt REG 8,5 87345336 5111885 /opt/google/chrome/chrome
chrome 2204 abc mem REG 8,5 4202496 1443927 /home/abc/.cache/google-chrome/Default/Media Cache/data_3
chrome 2204 abc mem REG 8,5 1056768 1443926 /home/abc/.cache/google-chrome/Default/Media Cache/data_2
chrome 2204 abc mem REG 8,5 270336 1443925 /home/abc/.cache/google-chrome/Default/Media Cache/data_1
chrome 2204 abc mem REG 8,5 45056 1443924 /home/abc/.cache/google-chrome/Default/Media Cache/data_0
This is a classic application for dtrace.
I can’t remember the syntax exactly, but you can have a trace fire every time a file is opened by any process on the system. It can be done on a running system without anywhere near as much overhead as I expected it would have. If you’re running solaris as an administrator, dtrace is your best friend. Even if you’re not a programmer, it is quite simple to learn and a VERY powerful system query tool.
I can not test it: it does not seem installed on my Solaris servers. If you can post an example, that would help.
Under some unix systems, ( IE: Linux ), all files opened by a process have a FD id.
ls -la /proc/2055/fd total 0 dr-x------ 2 kent kent 0 Nov 19 21:44 . dr-xr-xr-x 7 kent kent 0 Nov 19 21:42 .. lr-x------ 1 kent kent 64 Nov 19 21:44 0 -> /dev/null l-wx------ 1 kent kent 64 Nov 19 21:44 1 -> /home/kent/.xsession-errors lrwx------ 1 kent kent 64 Nov 19 21:44 10 -> socket:[3977613] lrwx------ 1 kent kent 64 Nov 19 21:44 11 -> /home/kent/.googleearth/Cache/dbCache.dat lrwx------ 1 kent kent 64 Nov 19 21:44 12 -> /home/kent/.googleearth/Cache/dbCache.dat.index lrwx------ 1 kent kent 64 Nov 19 21:44 13 -> socket:[3978765] lrwx------ 1 kent kent 64 Nov 19 21:44 14 -> socket:[3978763] lrwx------ 1 kent kent 64 Nov 19 21:44 15 -> socket:[3978766] lrwx------ 1 kent kent 64 Nov 19 21:44 17 -> socket:[3978764] l-wx------ 1 kent kent 64 Nov 19 21:44 2 -> /home/kent/.xsession-errors lr-x------ 1 kent kent 64 Nov 19 21:44 3 -> pipe:[3977583] l-wx------ 1 kent kent 64 Nov 19 21:44 4 -> pipe:[3977583] lr-x------ 1 kent kent 64 Nov 19 21:44 5 -> pipe:[3977584] l-wx------ 1 kent kent 64 Nov 19 21:44 6 -> pipe:[3977584] lr-x------ 1 kent kent 64 Nov 19 21:44 7 -> pipe:[3977587] l-wx------ 1 kent kent 64 Nov 19 21:44 8 -> pipe:[3977587] lrwx------ 1 kent kent 64 Nov 19 21:44 9 -> socket:[3977588] Additionally, sometimes you even get «FDINFO» ( I think this is a kernel flag on linux )
cat /proc/2055/fdinfo/11 pos: 232741818 flags: 02 How to Check Open Files in Linux
You may have come across the saying, “Everything is a file in Linux.” Although this is not entirely true, it does hold a set of truths to it.
In Linux and Unix-like systems, everything is like a file. That means the resources in the Unix system get assigned a file descriptor, including storage devices, network sockets, processes, etc.
A file descriptor is a unique number that identifies a file and other input/output devices. It describes resources and how the kernel accesses them. Think of it as a gateway to the Kernel abstraction hardware resources.
Unfortunately, the concept of file descriptors is beyond the scope of this tutorial; consider the link provided below to get started on learning more:
That means that Unix and Unix-like systems such as Linux use such files heavily. As a Linux power user, seeing the open files and the process and users using them is incredibly useful.
This tutorial will focus on ways to view the files open and which process or user is responsible.
Pre-Requisites
Before we begin, ensure that you have:
If you have these, let us get started:
LSOF Utility
Created by Victor A Abell, List open files, or lsof for short, is a command-line utility that allows us to view the open files and the processes or users who opened them.
The lsof utility is available in major Linux distributions; however, you may find it not installed and thus may need to install manually.
How to Install lsof on Debian/Ubuntu
To install it on Debian, use the command:
sudo apt-get install lsof -y
How to Install on REHL/CentOS
To install on REHL and CentOS, use the command:
How to Install on Arch
On Arch, call the package manager using the command:
How to Install on Fedora
On Fedora, use the command:
Once you have the lsof utility installed and updated, we can begin using it.
Basic lsof Usage
To use the lsof tool, enter the command:
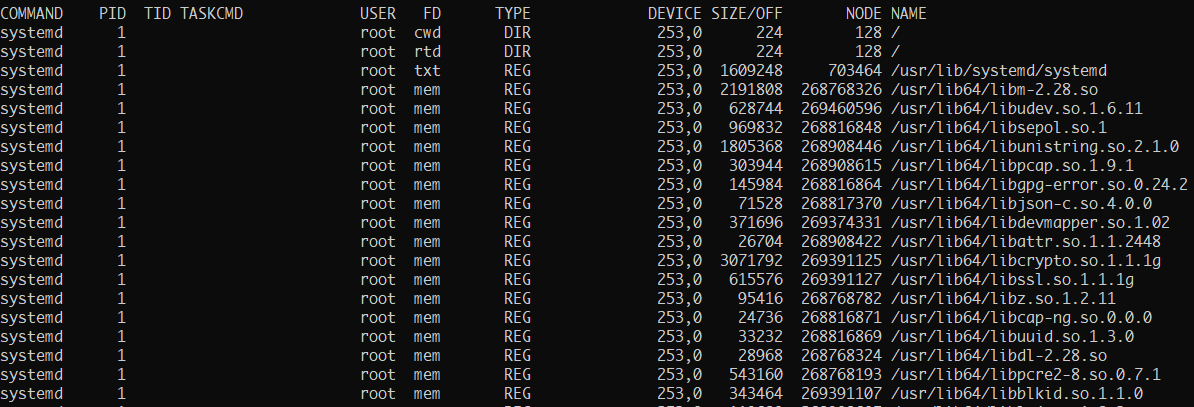
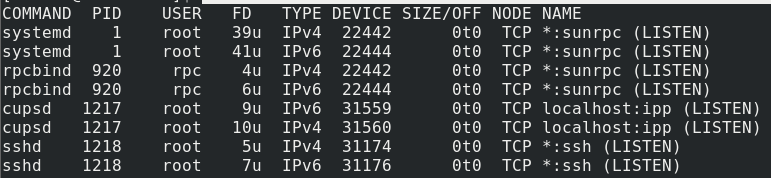
Once you execute the above command, lsof will dump a lot of information as shown below:
The above output shows all the files opened by the processes. The output has various columns, each representing specific information about the file.
- The COMMAND column – shows the name of the process that is using the file.
- PID – shows the Process Identifier of the process using the file.
- The TID – Shows the task ID (threads) of the process.
- TASKCMD – Represent the name of the task command.
- USER – The owner of the process.
- FD – Shows the file descriptor number. This is how processes use the file; the options available in this column output include:
- cwd – current working directory.
- mem – memory-mapped file
- pd – parent directory
- jld – jail directory
- ltx – shared library text
- rtd – root directory.
- txt – program code and data
- tr – kernel trace file.
- err – File descriptor information error
- mmp – Memory-mapped device.
- TYPE – Shows the type of node associated with the file, such as:
- Unix – for Unix domain socket.
- DIR – represents the directory
- REG – representing the regular file
- CHR – represents the special character file.
- LINK – symbolic link file
- BLK – Block special file
- INET – Internet domain socket
- FIFO – a named pipe (First In First Out file)
- PIPE – for pipes
- DEVICES – Shows the device numbers separated by commas in the order of special character file, block special, regular, directory, and NFS file.
- SIZE/OFF – shows the size of the file pr file offset in bytes.
- NODE – shows the node number of the local file, type for internet protocol type, etc.
- NAME – shows the name of the mount point and fs on which the file is located.
Note: Please Refer to the lsof Manual for detailed information on the columns.
How to Show Processes that Opened a File
Lsof provides us with options that help us filter the output to show only the processes that opened a specific file.
For example, to see the file that opened the file /bin/bash, use the command as:
This will give you an output as shown below:
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE / OFF NODE NAME
ksmtuned 1025 root txt REG 253 , 0 1150704 428303 / usr / bin / bash
bash 2968 centos txt REG 253 , 0 1150704 428303 / usr / bin / bash
bash 3075 centos txt REG 253 , 0 1150704 428303 / usr / bin / bash
How Show files Opened by a Specific User
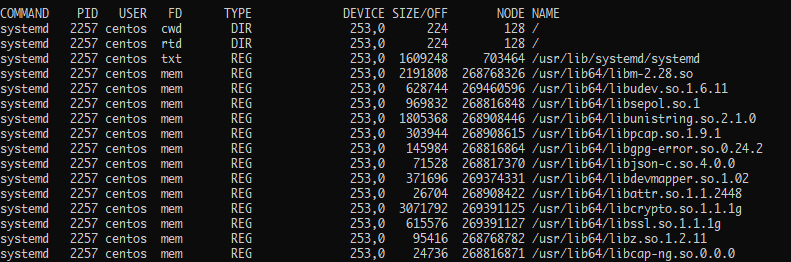
We can also filter the output to show the files opened by a specific user. We do this by using the -u flag followed by the username as:
This will give you an output as shown below:
How to Show Files Opened by a Specific Process
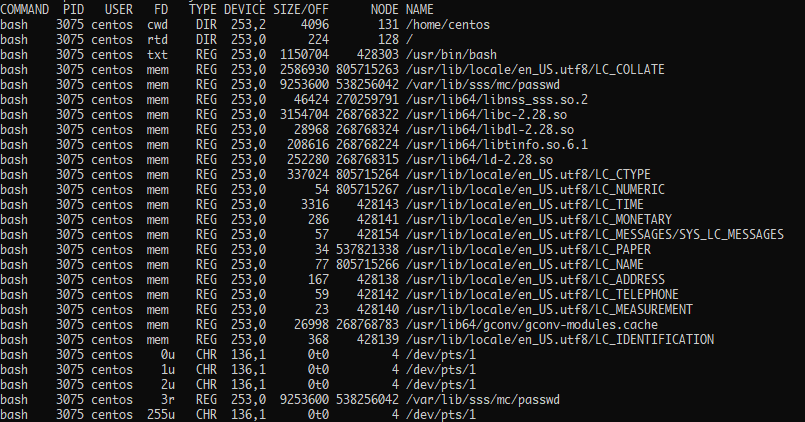
Suppose we want to view all the files opened by a specific process? For this, we can use the PID of the process to filter the output.
For example, the below command shows the files opened by bash.
This will give you only the files opened by systemd as shown:
How to Show Files Opened in a Directory
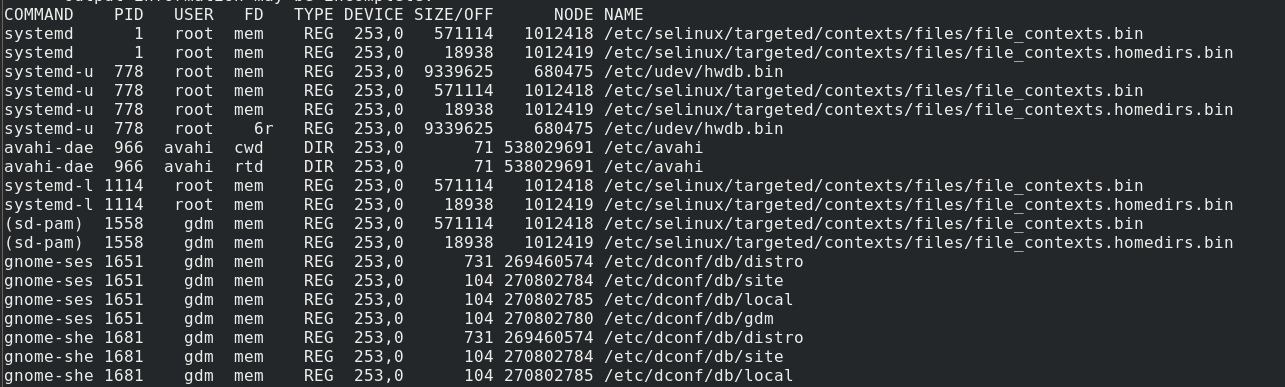
To get the files opened in a specific directory, we can pass the +D option followed by the directory path.
For example, list open files in the /etc directory.
Below is the output for this:
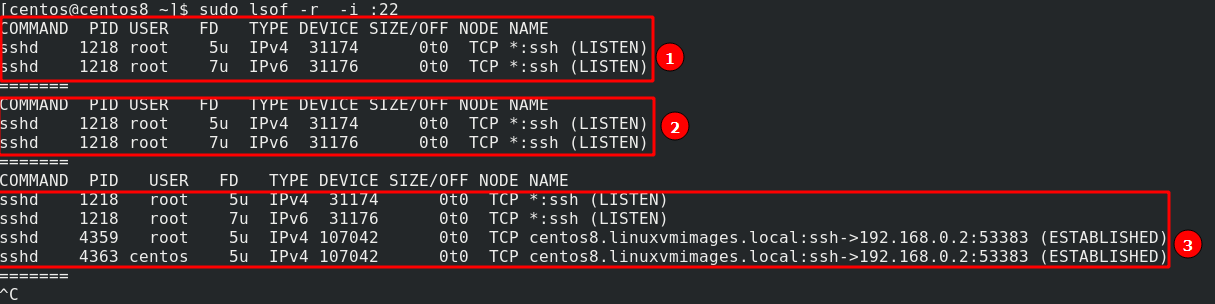
How to Show Network Connection
Since everything in Linux is a file, we can get the network files such as TCP files or connections.
This will give you the TCP connections in the system.
You can also filter by the specific port using the command shown below:
This will give you the output as shown below:
How to Continuously Show Files
Lsof provides us with a mode to loop the output every few seconds. This allows you to monitor the files opened by a process or user continuously.
This option, however, requires you to terminate the process manually.
For example, the command below continuously monitors the files opened on port 22:
As you can see, in the third loop, lsof catches the established connection to the server on SSH.
Conclusion
Lsof is an incredibly useful utility. It allows you to monitor for critical files as well as monitor users and processes opening files. This can be incredibly useful when troubleshooting or looking for malicious attempts to the system.
As shown in this tutorial, using various examples and methods, you can combine the functionality provided by the lsof tool for custom monitoring.
Thank you for reading and sharing! I hope you learned something new!
About the author
John Otieno
My name is John and am a fellow geek like you. I am passionate about all things computers from Hardware, Operating systems to Programming. My dream is to share my knowledge with the world and help out fellow geeks. Follow my content by subscribing to LinuxHint mailing list