- How to Find and Delete Empty Directories in Linux
- Find and Remove Empty Directories in Linux
- How Do I List Empty Directories in Linux?
- Using “Find” Command
- Example 01: List Empty Directories
- Example 02: List Empty Files
- Example 03: List Empty Files
- Example 04: List Empty files
- Example 05: List Empty folders
- Example 06: List Empty files Count Number
- Example 07: List Non-Empty Files Count Number
- Example 08: List Empty Files With Size
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Aqsa Yasin
- Find Empty Directories in Linux Command Line
- Find Empty Directories in Linux
- Find Empty Files in Linux
- Delete Empty Files and Directories using Find Command
- Delete Empty Files and Directories using xargs and find-exec
- Final Words
How to Find and Delete Empty Directories in Linux
Many times empty directories get cluttered in the Linux file system, and it becomes a difficult task to manually search for and delete each of them. The command rmdir (remove directory) is used in Linux to delete empty folders.
The command is quite simple to use and the basic syntax is:
Here, ‘empty folder name1‘, ‘empty folder name2‘, etc. are the names of the folders including the full path. If the folders are in the same directory then, as you might already know, there is no need to write down full paths.
You can also use wildcard expressions to remove empty directories with patterns in their names. For example, to remove empty directories with the substring ‘test‘ in their name, run:
However, to use rmdir we always need to specify the name (or full path) of each empty directory to be removed. There is no option in rmdir to recursively look for empty directories and then remove them.
We make use of the functionalities of the find command in such cases.
Find and Remove Empty Directories in Linux
The find command is used to search for files and folders in Linux based on different parameters like filename, size, type, etc. We will use find to determine empty directories recursively and then execute rmdir to delete the found directories.
Use the argument ‘-empty’ to look for empty objects and specify ‘-type d’ to only find directories.
$ find path_of_folder_to_search -type d -empty
To find empty directories recursively in the same folder, run:
Now, since we already have the recursively found list of empty directories, we use the ‘-exec’ argument of the find command to run rmdir over them.
$ find . -type d -empty -exec rmdir <> \;
The placeholder <> substitutes each entry in the list of found directories and ‘\;’ signifies the end of the command to be executed.
However, even with this, it will just do a single round of search and remove directories that are empty, but it will not remove directories that become empty after the first round of deletion.
To tackle this, we simply use the ‘-delete’ option, which will repeatedly delete all empty directories till the top-level directory.
$ find . -type d -empty -delete
This is how we can remove all empty directories recursively in Linux.
Conclusion
We learned how to use the rmdir command and find command in Linux to delete empty directories recursively. Learn more about these commands in their respective man pages:
Thanks for reading and do share your thoughts below!
How Do I List Empty Directories in Linux?
Most of the time this question arises, how will you list the empty file and folders when you are working on the Linux-based operating system? Empty files and directories are those which have no data or sub-directories within them, respectively. If you want to learn how to do it, then this tutorial is meant for you. You have to go through each step defined in this tutorial to list the empty folders or files in the terminal. First, you must have sudo privileges of a Linux-based system to use it. After logging in from the system, you have to open the command terminal from the Applications. We will have a look at some of the examples for listing empty folders.
Using “Find” Command
There are a lot of ways to use the ‘find’ command in our examples to list the empty folders and files in the command shell. We will discuss each one of them.
Example 01: List Empty Directories
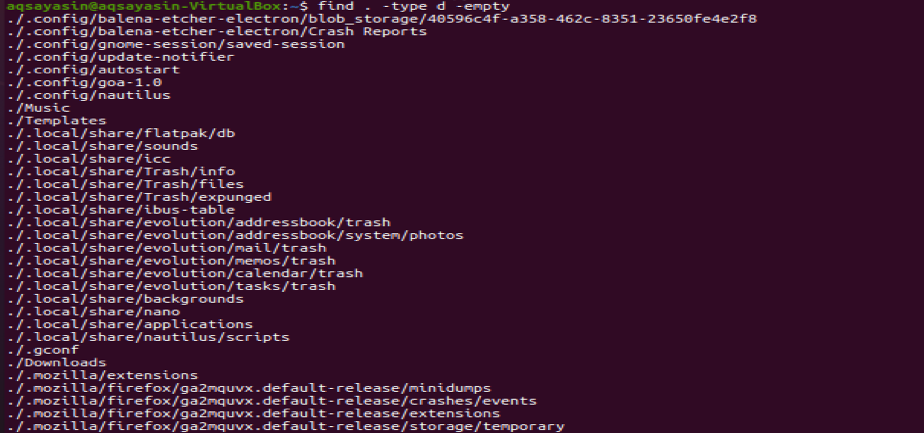
So assume you are at your home directory of the Linux system, you need to look at all the empty directories within it. Use the ‘find’ command along with the ‘-type’ flag that specifies the directory type search using the keyword ‘d’. The word ‘-empty’ has been used as a flag to search only empty directories within the home directory as stated below. The dot means the current location which is the home directory of a Linux-based system. The output shows all the empty directories within the home directory and its sub-directories.
Example 02: List Empty Files
Now, it’s time to list all the empty files within the home directory using the same above command with a slight change. We will be using the “f” flag to specify that the searched item must be the file type. Execute the below command in the shell and you will get a list of empty files residing in the home directory and its sub-directories as presented in the snapshot.
Example 03: List Empty Files
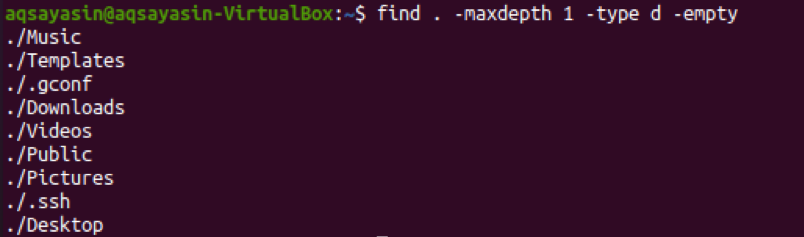
Suppose somebody wants to list the empty directories only that are residing in the home directory of the Linux system without the empty directories in the sub-directories of the home directories, then they can also use the “find” command. In this command, you have to define the depth of the tree you want to search by listing empty directories using the “-maxdepth” flag. You can specify the tree depth by a number as we have used 1 in the below command. This means it will only search for the empty directories which are directly residing in the home directory of the system. Try to execute the below-stated query in the terminal shell. The output shows the list of all the empty directories, which means all of these listed directories have no data within them.
We were listing all the empty directories or files in the home directory. Now, it’s time to have a slight change. We will be looking at the empty files and folders within some other directories.
Example 04: List Empty files
For that purpose, we have to define a path of that particular directory within the instruction. The remaining command will be as it is. Try the below command to search the empty files within the folder ‘Documents’. The output is elaborating that the directory ‘Documents’ have only two in it which are currently empty e.g., one.txt and scnd.txt.
Example 05: List Empty folders
Now let’s alter this command to see empty directories within the directory “Documents”. To do this, we have to write “d” instead of “f” as displayed below. Try executing the below query to show empty folders. The output shows that we have currently no empty files in the directory “Documents”.
Example 06: List Empty files Count Number
You have seen how to list the empty files and folders. Now, we will be looking at the count number of empty files and folders located in a certain folder. For that, we will be using the same “find” command. All the old parameters will remain the same in the query with a slight change. We are using the “wc –l” parameter in the command to count the empty files residing in the current location. Execution of the stated command gives us the output of 18. This means that the home directory has only a total of 18 empty files in it.
Example 07: List Non-Empty Files Count Number
As we learned how to count the number of empty files within a particular directory. It’s time to count the number of non-empty directories of files within some directory. For this particular purpose, we will be using the “-not” flag parameter in a query. The remaining query will be the same from start to end. So, let’s run the below ‘find’ command in the terminal shell as shown in the snapshot. The output shows the count of non-empty files within the home directory and its sub-directories which is “6474”.
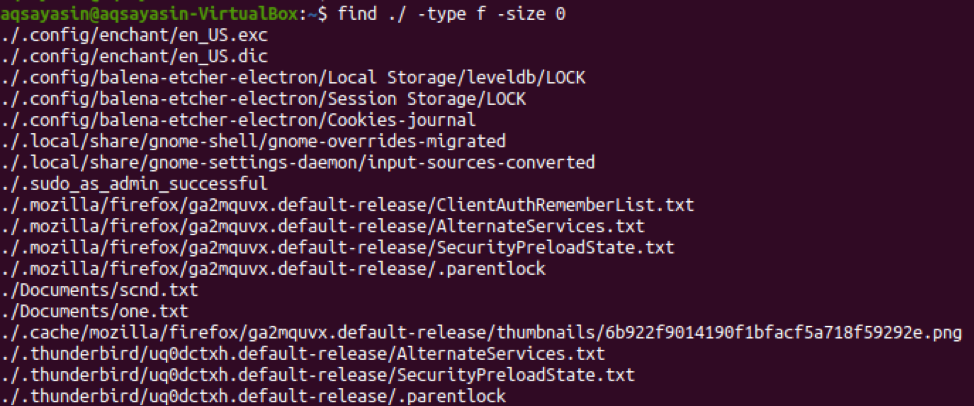
Example 08: List Empty Files With Size
Last but not least, we will be using the “find” command along with the keyword “size” to search the files according to the size specified. Now, we will be listing the files from the home directory that have zero data within them. We have defined the value of keyword size as “0”. The output is shown below with the list of files having the size “0”.
Conclusion
Finally! We have done all the necessary commands to list or show the empty files within some directory.
About the author
Aqsa Yasin
I am a self-motivated information technology professional with a passion for writing. I am a technical writer and love to write for all Linux flavors and Windows.
Find Empty Directories in Linux Command Line
Here are a few examples of finding and deleting empty directories in the Linux command line.
Linux users are bound to have multiple empty directories and it’s quite easy to find them.
But wait, just listing empty directories won’t do the job so I’ll also show you how to delete them!
Find Empty Directories in Linux
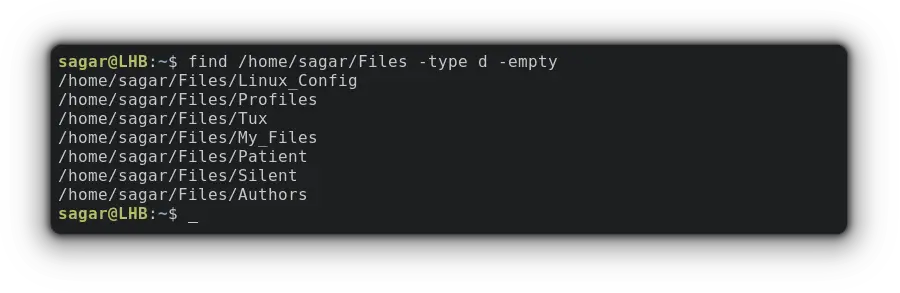
To Find an empty directory, you’ll just have to pair the -empty option with the find command. Let me show you how:
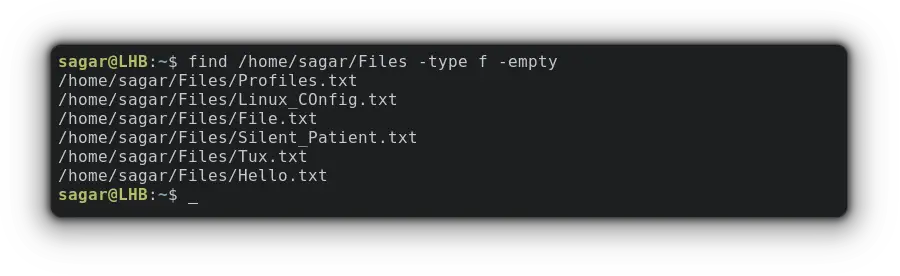
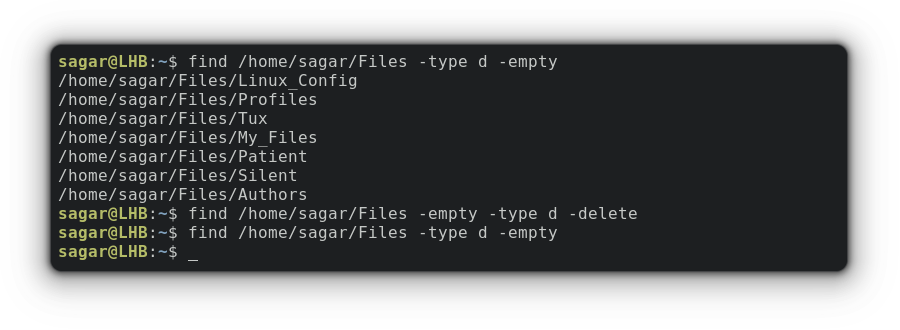
find /home/sagar/Files -type d -emptyWhen you use the find command with the -type d option, it will search for directories only.
Find Empty Files in Linux
As I mentioned just above that -type d was used to search for directories, you can change this behavior to search for files by using type f .
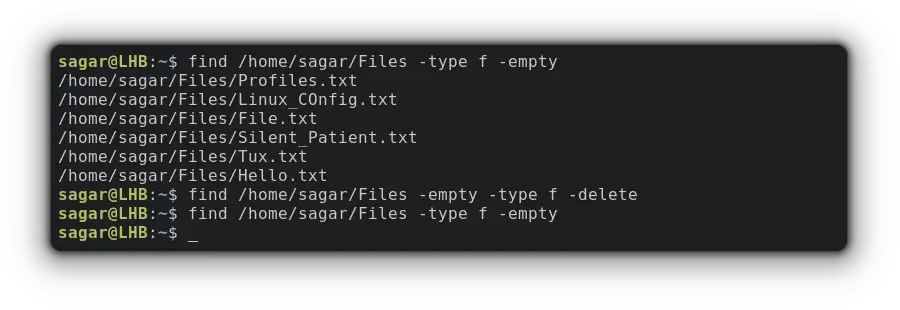
find /home/sagar/Files -type f -emptyFind is an excellent command. If you are interested in learning more, here are a few more examples 👇
Delete Empty Files and Directories using Find Command
To delete the files and directories given by the find command, you just have to use the -delete option.
So let’s start with deleting empty directories:
find /home/sagar/Files -empty -type d -deleteYou can do the same with files by interchanging -type d with -type f :
find /home/sagar/Files -empty -type f -deleteDelete Empty Files and Directories using xargs and find-exec
The find exec is nothing but allows you to execute custom operations such as running scripts and executing programs on search results.
While xargs can take input from the standard input or even consider the output of another command as input and can use it as a command.
So let’s start with removing empty files and directories using the find with the exec command.
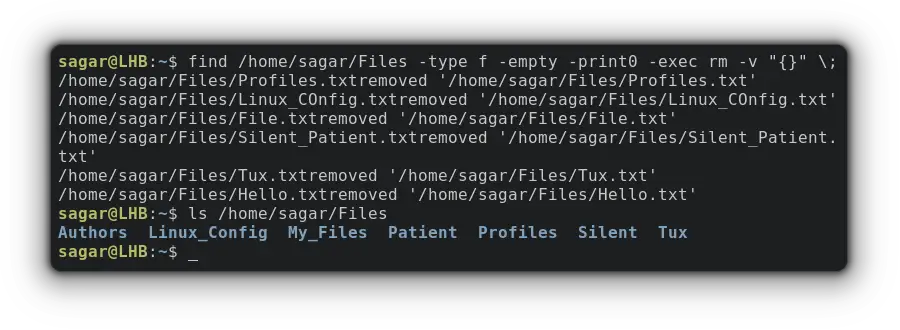
To remove empty files, you just have to utilize the given command:
find /home/sagar/Files -type f -empty -print0 -exec rm -v "<>" \;And if you want to remove directories, the given command should work just fine:
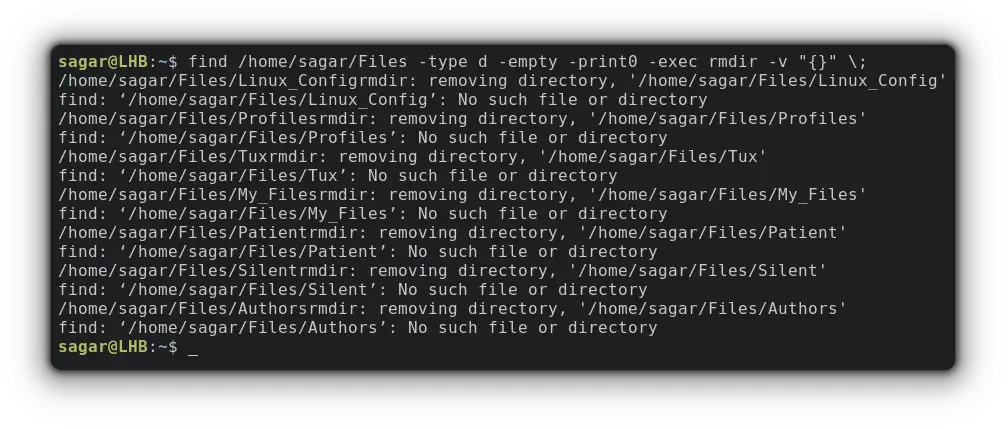
find /home/sagar/Files -type d -empty -print0 -exec rmdir -v "<>" \;Now, let’s use xargs with find to remove empty directories:
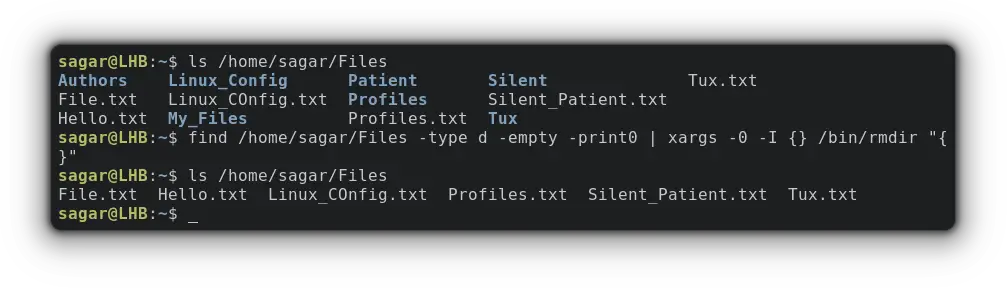
find /home/sagar/Files -type d -empty -print0 | xargs -0 -I <> /bin/rmdir "<>"Similarly, with a few tweaks to the above command and you can remove empty files:
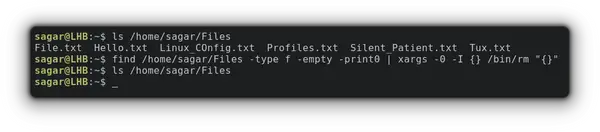
find /home/sagar/Files -type f -empty -print0 | xargs -0 -I <> /bin/rm "<>"And if you’re curious to learn more about xargs, we already have a detailed guide on that topic:
Final Words
Well, this was a short guide on how you can remove empty files and folders and I’ve tried my best to make it beginner friendly.
But still, if you encounter any doubts, I’d be happy to help!