- Classic SysAdmin: How to Search for Files from the Linux Command Line
- How to use the find command
- Find by name
- Find by type
- Outputting results to a file
- Finding files by size
- Keep learning
- Find Files in Linux Using the Command Line
- Find a File in Linux by Name or Extension
- Using Common find Commands and Syntax to Find a File in Linux
- Basic Examples
- Options and Optimization for find
- Find a File in Linux by Modification Time
- Use grep to Find a File in Linux Based on Content
- How to Find and Process a File in Linux
- How to Find and Delete a File in Linux
- More Information
Classic SysAdmin: How to Search for Files from the Linux Command Line
This is a classic article written by Jack Wallen from the Linux.com archives. For more great SysAdmin tips and techniques check out our free intro to Linux course.
It goes without saying that every good Linux desktop environment offers the ability to search your file system for files and folders. If your default desktop doesn’t — because this is Linux — you can always install an app to make searching your directory hierarchy a breeze.
But what about the command line? If you happen to frequently work in the command line or you administer GUI-less Linux servers, where do you turn when you need to locate a file? Fortunately, Linux has exactly what you need to locate the files in question, built right into the system.
The command in question is find. To make the understanding of this command even more enticing, once you know it, you can start working it into your Bash scripts. That’s not only convenience, that’s power.
Let’s get up to speed with the find command so you can take control of locating files on your Linux servers and desktops, without the need of a GUI.
How to use the find command
When I first glimpsed Linux, back in 1997, I didn’t quite understand how the find command worked; therefore, it never seemed to function as I expected. It seemed simple; issue the command find FILENAME (where FILENAME is the name of the file) and the command was supposed to locate the file and report back. Little did I know there was more to the command than that. Much more.
If you issue the command man find, you’ll see the syntax of the find command is:
find [-H] [-L] [-P] [-D debugopts] [-Olevel] [starting-point. ] [expression]
Naturally, if you’re unfamiliar with how man works, you might be confused about or overwhelmed by that syntax. For ease of understanding, let’s simplify that. The most basic syntax of a basic find command would look like this:
find /path option filename
Find by name
Let’s break down that basic command to make it as clear as possible. The most simplistic structure of the find command should include a path for the file, an option, and the filename itself. You may be thinking, “If I know the path to the file, I’d already know where to find it!”. Well, the path for the file could be the root of your drive; so / would be a legitimate path. Entering that as your path would take find longer to process — because it has to start from scratch — but if you have no idea where the file is, you can start from there. In the name of efficiency, it is always best to have at least an idea where to start searching.
The next bit of the command is the option. As with most Linux commands, you have a number of available options. However, we are starting from the beginning, so let’s make it easy. Because we are attempting to find a file by name, we’ll use one of two options:
Remember, Linux is very particular about case, so if you’re looking for a file named Linux.odt, the following command will return no results.
If, however, you were to alter the command by using the -iname option, the find command would locate your file, regardless of case. So the new command looks like:
Find by type
What if you’re not so concerned with locating a file by name but would rather locate all files of a certain type? Some of the more common file descriptors are:
- f – regular file
- d – directory
- l – symbolic link
- c – character devices
- b – block devices
Now, suppose you want to locate all block devices (a file that refers to a device) on your system. With the help of the -type option, we can do that like so:
The above command would result in quite a lot of output (much of it indicating permission denied), but would include output similar to:
/dev/hidraw6 /dev/hidraw5 /dev/vboxnetctl /dev/vboxdrvu /dev/vboxdrv /dev/dmmidi2 /dev/midi2 /dev/kvm
We can use the same option to help us look for configuration files. Say, for instance, you want to locate all regular files that end in the .conf extension. This command would look something like:
The above command would traverse the entire directory structure to locate all regular files ending in .conf. If you know most of your configuration files are housed in /etc, you could specify that like so:
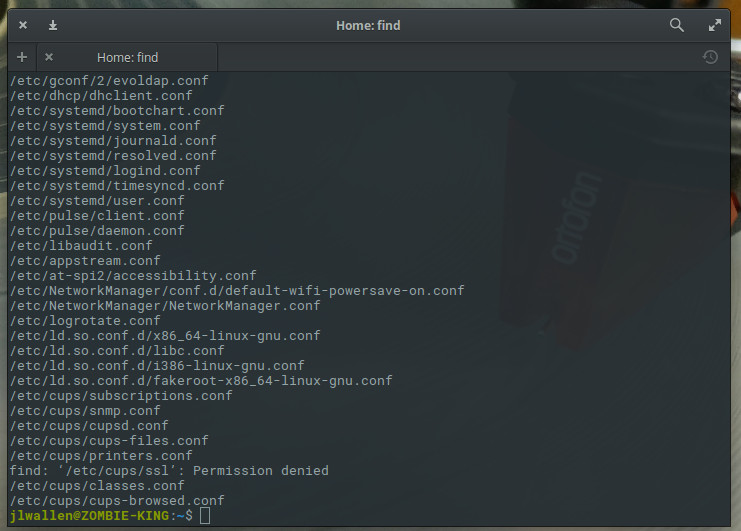
find /etc -type f -name “*.conf”
The above command would list all of your .conf files from /etc (Figure 1).
Outputting results to a file
One really handy trick is to output the results of the search into a file. When you know the output might be extensive, or if you want to comb through the results later, this can be incredibly helpful. For this, we’ll use the same example as above and pipe the results into a file called conf_search. This new command would look like:
find /etc -type f -name “*.conf” > conf_search
You will now have a file (conf_search) that contains all of the results from the find command issued.
Finding files by size
Now we get to a moment where the find command becomes incredibly helpful. I’ve had instances where desktops or servers have found their drives mysteriously filled. To quickly make space (or help locate the problem), you can use the find command to locate files of a certain size. Say, for instance, you want to go large and locate files that are over 1000MB. The find command can be issued, with the help of the -size option, like so:
You might be surprised at how many files turn up. With the output from the command, you can comb through the directory structure and free up space or troubleshoot to find out what is mysteriously filling up your drive.
You can search with the following size descriptions:
- c – bytes
- k – Kilobytes
- M – Megabytes
- G – Gigabytes
- b – 512-byte blocks
Keep learning
We’ve only scratched the surface of the find command, but you now have a fundamental understanding of how to locate files on your Linux systems. Make sure to issue the command man find to get a deeper, more complete, knowledge of how to make this powerful tool work for you.
Find Files in Linux Using the Command Line
Estamos traduciendo nuestros guías y tutoriales al Español. Es posible que usted esté viendo una traducción generada automáticamente. Estamos trabajando con traductores profesionales para verificar las traducciones de nuestro sitio web. Este proyecto es un trabajo en curso.
When you have to find a file in Linux, it’s sometimes not as easy as finding a file in another operating system. This is especially true if you are running Linux without a graphical user interface and need to rely on the command line. This article covers the basics of how to find a file in Linux using the CLI. The find command in Linux is used to find a file (or files) by recursively filtering objects in the file system based on a simple conditional mechanism. You can use the find command to search for a file or directory on your file system. By using the -exec flag ( find -exec ), matches, which can be files, directories, symbolic links, system devices, etc., can be found and immediately processed within the same command.
Find a File in Linux by Name or Extension
Use find from the command line to locate a specific file by name or extension. The following example searches for *.err files in the /home/username/ directory and all sub-directories:
find /home/username/ -name "*.err" Using Common find Commands and Syntax to Find a File in Linux
find expressions take the following form:
find options starting/path expression - The options attribute will control the find process’s behavior and optimization method.
- The starting/path attribute will define the top-level directory where find begins filtering.
- The expression attribute controls the tests that search the directory hierarchy to produce output.
Consider the following example command:
find -O3 -L /var/www/ -name "*.html" This command enables the maximum optimization level (-O3) and allows find to follow symbolic links ( -L ). find searches the entire directory tree beneath /var/www/ for files that end with .html .
Basic Examples
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| find . -name testfile.txt | Find a file called testfile.txt in current and sub-directories. |
| find /home -name *.jpg | Find all .jpg files in the /home and sub-directories. |
| find . -type f -empty | Find an empty file within the current directory. |
| find /home -user exampleuser -mtime -7 -iname «.db» | Find all .db files (ignoring text case) modified in the last 7 days by a user named exampleuser. |
Options and Optimization for find
The default configuration for find will ignore symbolic links (shortcut files). If you want find to follow and return symbolic links, you can add the -L option to the command, as shown in the example above.
find optimizes its filtering strategy to increase performance. Three user-selectable optimization levels are specified as -O1 , -O2 , and -O3 . The -O1 optimization is the default and forces find to filter based on filename before running all other tests.
Optimization at the -O2 level prioritizes file name filters, as in -O1 , and then runs all file-type filtering before proceeding with other more resource-intensive conditions. Level -O3 optimization allows find to perform the most severe optimization and reorders all tests based on their relative expense and the likelihood of their success.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| -O1 | (Default) filter based on file name first. |
| -O2 | File name first, then file type. |
| -O3 | Allow find to automatically re-order the search based on efficient use of resources and likelihood of success. |
| -maxdepth X | Search current directory as well as all sub-directories X levels deep. |
| -iname | Search without regard for text case. |
| -not | Return only results that do not match the test case. |
| -type f | Search for files. |
| -type d | Search for directories. |
Find a File in Linux by Modification Time
The find command contains the ability to filter a directory hierarchy based on when the file was last modified:
find / -name "*conf" -mtime -7 find /home/exampleuser/ -name "*conf" -mtime -3 The first command returns a list of all files in the entire file system that end with the characters conf and modified in the last seven days. The second command filters exampleuser user’s home directory for files with names that end with the characters conf and modified in the previous three days.
Use grep to Find a File in Linux Based on Content
The find command can only filter the directory hierarchy based on a file’s name and metadata. If you need to search based on the file’s content, use a tool like grep . Consider the following example:
find . -type f -exec grep "example" '<>' \; -print This searches every object in the current directory hierarchy ( . ) that is a file ( -type f ) and then runs the command grep «example» for every file that satisfies the conditions. The files that match are printed on the screen ( -print ). The curly braces ( <> ) are a placeholder for the find match results. The <> are enclosed in single quotes ( ‘ ) to avoid handing grep a malformed file name. The -exec command is terminated with a semicolon ( ; ), which should be escaped ( \; ) to avoid interpretation by the shell.
How to Find and Process a File in Linux
The -exec option runs commands against every object that matches the find expression. Consider the following example:
find . -name "rc.conf" -exec chmod o+r '<>' \; This filters every object in the current hierarchy ( . ) for files named rc.conf and runs the chmod o+r command to modify the find results’ file permissions.
The commands run with the -exec are executed in the find process’s root directory. Use -execdir to perform the specified command in the directory where the match resides. This may alleviate security concerns and produce a more desirable performance for some operations.
The -exec or -execdir options run without further prompts. If you prefer to be prompted before action is taken, replace -exec with -ok or -execdir with -okdir .
How to Find and Delete a File in Linux
To delete the files that end up matching your search, you can add -delete at the end of the expression. Do this only when you are positive the results will only match the files you wish to delete.
In the following example, find locates all files in the hierarchy starting at the current directory and fully recursing into the directory tree. In this example, find will delete all files that end with the characters .err :
More Information
You may wish to consult the following resources for additional information on this topic. While these are provided in the hope that they will be useful, please note that we cannot vouch for the accuracy or timeliness of externally hosted materials.
This page was originally published on Monday, October 25, 2010.