- 3 Ways to fix ifconfig command not found in Linux
- Install ifconfig command in Linux
- Run ifconfig command with full path
- Add ifconfig binary to $PATH location
- ifconfig command alternative
- 5 Ways to Fix the ifconfig Command not Found Error on Debian
- How to Fix ifconfig Command Not Found?
- Method 1: Install net-tools
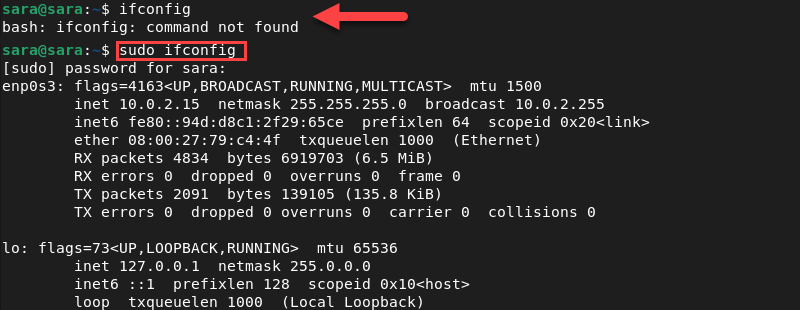
- Method 2: Run ifconfig with sudo or as root
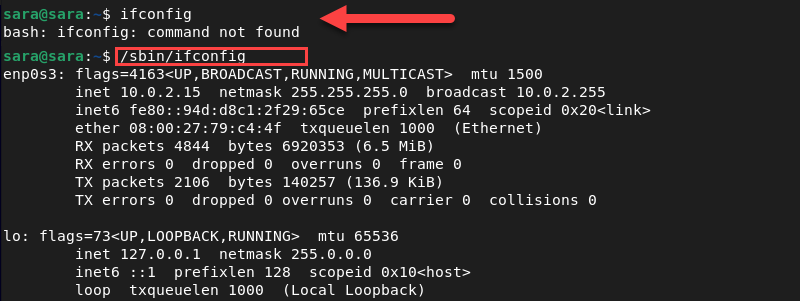
- Method 3: Use the Full Path to the Command
- Method 4: Update the System PATH Variable
- Method 5: Use an Alternative Command
- Ошибка ifconfig команда не найдена
- Ошибка ifconfig команда не найдена
- Выводы
3 Ways to fix ifconfig command not found in Linux
The “ifconfig: command not found” error typically means that the ifconfig binary is not installed or the path of the binary file is not under the $PATH.
So we can use the following 3 ways to fix this issue.
- install ifconfig command through net-tools package
- run ifconfig command with full path
- add the directory path of the ifconfig command to the $PATH
Install ifconfig command in Linux
The ifconfig command is a powerful tool used in Linux to check and configure network interfaces.
It can be used to check IP addresses, check connectivity, configure IP addresses, check packet network loss, and much more.
The ifconfig command is part of the net-tools package in Linux.
First, let’s check if you have installed net-tools package in your system.
On RedHat, Centos, and Fedora: rpm -qa|grep net-tools
On Ubuntu, Debian, and Mint: dpkg —list|grep net-tools
If you want to learn more about how to list installed package in Linux, you can refer to this article.
If the output is empty, it means that the package is not installed on your system. You will need to install it with:
On RedHat, Centos, Fedora: yum -y install net-tools
On Ubuntu, Debian, Mint: apt-get install net-tools
Check this article to get more info about how to install packages in Linux.
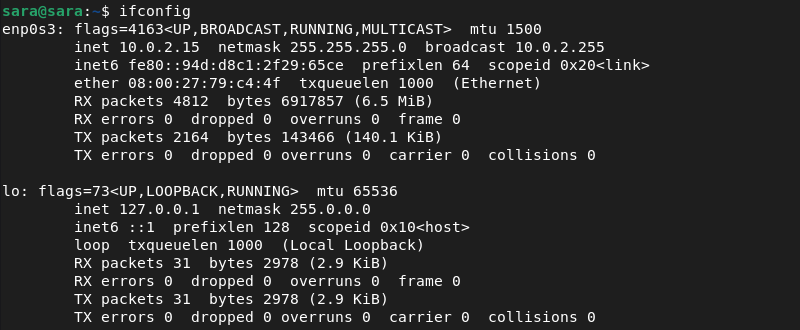
Once the installation is completed, try running ifconfig again and it should work.
Run ifconfig command with full path
If the net-tools package is installed but the ifconfig command still won’t work, you can try running it with full path.
The full path of a command is the complete file system directory path that leads to the command’s executable file.
It is used to specify the exact location of the command when executing it in a terminal or command prompt.
For example, on a Linux system, the full path of the “ls” command might be “/bin/ls” and on a Windows system, the full path of the “cmd” command might be “C:\Windows\System32\cmd.exe”.
In Linux, type “which ifconfig” to find out the location of ifconfig command. Then run “/path/to/ifconfig” and it should work as expected.
You can run these commands:
On RedHat, Centos, Fedora: /usr/sbin/ifconfig
On Ubuntu, Debian, Mint: /sbin/ifconfig
Alternatively, you can also use the find command if you are not sure about the path of ifconfig command.
The find command can help locate the ifconfig command on a system, especially if the command’s path is not included in the system’s $PATH environment variable.
Here’s an example command you can use to search for the ifconfig command:
find / -name ifconfig 2>/dev/null
This command will search the entire file system starting from the root directory (/) for files with the name ifconfig, and redirect any error messages to /dev/null to suppress them. Once the command has finished running, it will output the path to the ifconfig command.
Note that depending on the size of your system, this search could take some time to complete
By using the full path of the command, you are specifying the exact location of the command to the system, which ensures that the correct version of the command is run, even if there are multiple versions of the command available on the system.
Add ifconfig binary to $PATH location
The third option to fix this problem is to add your ifconfig binary to the $PATH location.
The $PATH variable is an environment variable that contains the list of directories where your system looks for executables.
You can use echo $PATH command to check the current value of this variable.
If the directory of ifconfig binary is not listed, you will get “ifconfig command not found” error.
In this case, you can add the ifconfig directory path to the $PATH variable.
On RedHat, Centos, Fedora: export PATH=$PATH:/usr/sbin/
On Ubuntu, Debian, Mint: export PATH=$PATH:/sbin/
Once you have updated the $PATH variable, try running ifconfig again and it should work.
Tips: different users use different $PATH configuration. You can try to switch to root user to try ifconfig command.
That might work because the $PATH for root user has more directories.
ifconfig command alternative
The ifconfig command has been deprecated and is no longer being actively maintained. It may not be installed by default on some systems. We can use ip command instead.
The ip command can perform all the functions of the ifconfig command, but it can also do much more. It allows you to manage routing tables, tunnels, and more.
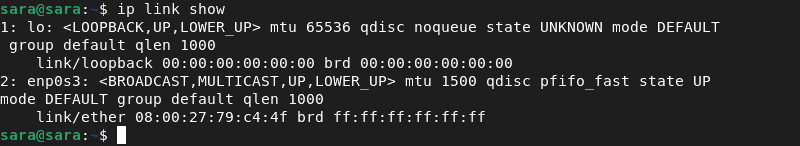
The ip command is available in most modern Linux distributions. For example, if we need to show ip addr, we can run ip addr command.
The ip route show command is used to display the routing table on a Linux system. The routing table contains information about how packets should be routed between different networks, and it is used by the system to determine how to forward network traffic.
If you want to get more info about ip command, check out this post.
We hope you found this blog post helpful and that it helped you solve your problem. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to leave them in the comment section below. Thanks for reading!
David is a Cloud & DevOps Enthusiast. He has years of experience as a Linux engineer. He had working experience in AMD, EMC. He likes Linux, Python, bash, and more. He is a technical blogger and a Software Engineer. He enjoys sharing his learning and contributing to open-source.
howtouselinux.com is dedicated to providing comprehensive information on using Linux.
We hope you find our site helpful and informative.
5 Ways to Fix the ifconfig Command not Found Error on Debian
The ifconfig command is a legacy tool used to configure network interfaces in Linux. Even though the utility was deprecated and replaced with the ip command, ifconfig is still used and often comes preinstalled on modern Linux distributions. However, installing ifconfig on Debian can be problematic.
This guide explains how to install ifconfig on Debian and fix the «command not found» error.
- Debian system (this tutorial uses Debian 11. The instructions also apply to Debian 10 and 9).
- Access to the terminal.
- Sudo privileges.
How to Fix ifconfig Command Not Found?
The ifconfig command is part of the net-tools package, a Linux network utility deprecated because of a lack of maintenance and IPv6 support.
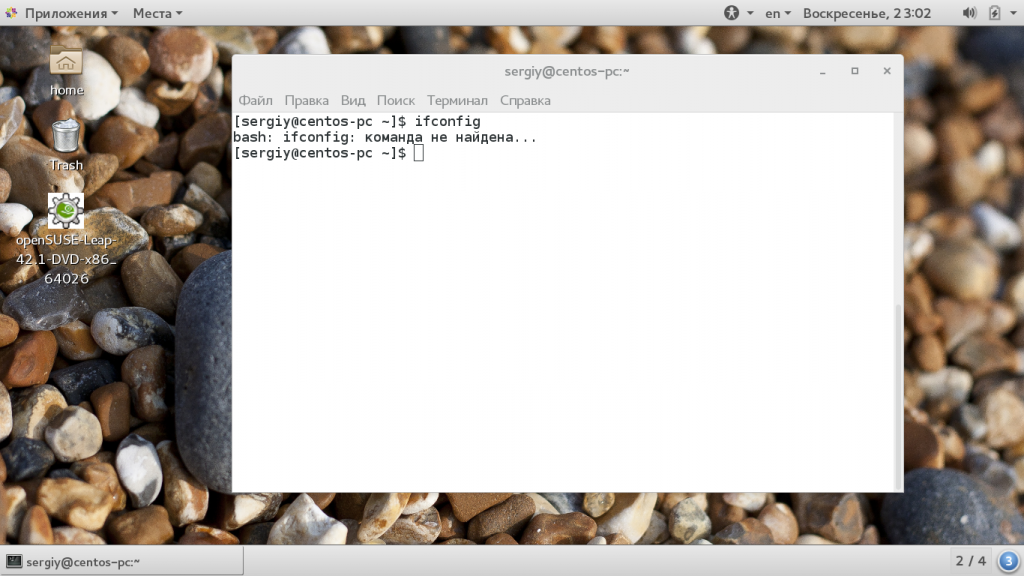
While certain distributions still have net-tools preinstalled, others, like Debian, don’t. Therefore, when Debian users try to run ifconfig , the output prints an error.
The error occurs either because the system does not have net-tools or because the ifconfig directory is not added to the standard PATH variable.
The following sections explain how to fix the ifconfig «command not found» issue.
Method 1: Install net-tools
The first step to fixing the «command not found» error is to install net-tools. Do the following:
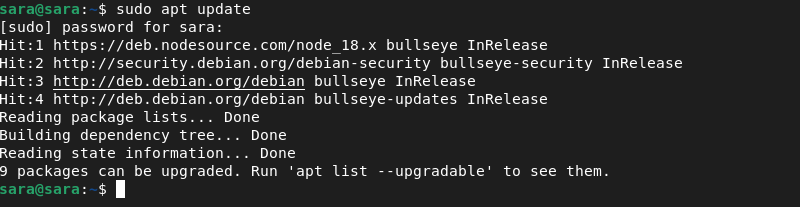
1. Update Debian repositories.
2. Install net-tools with apt.
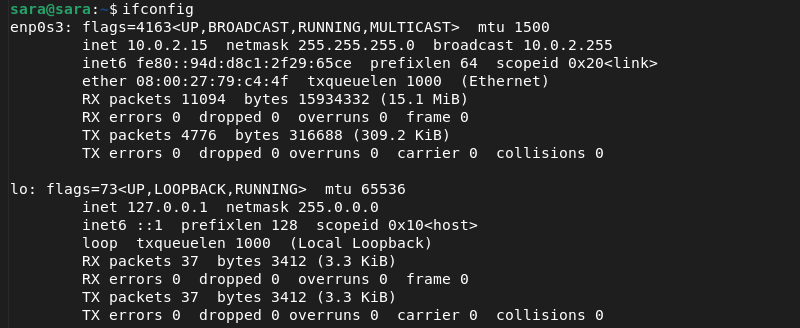
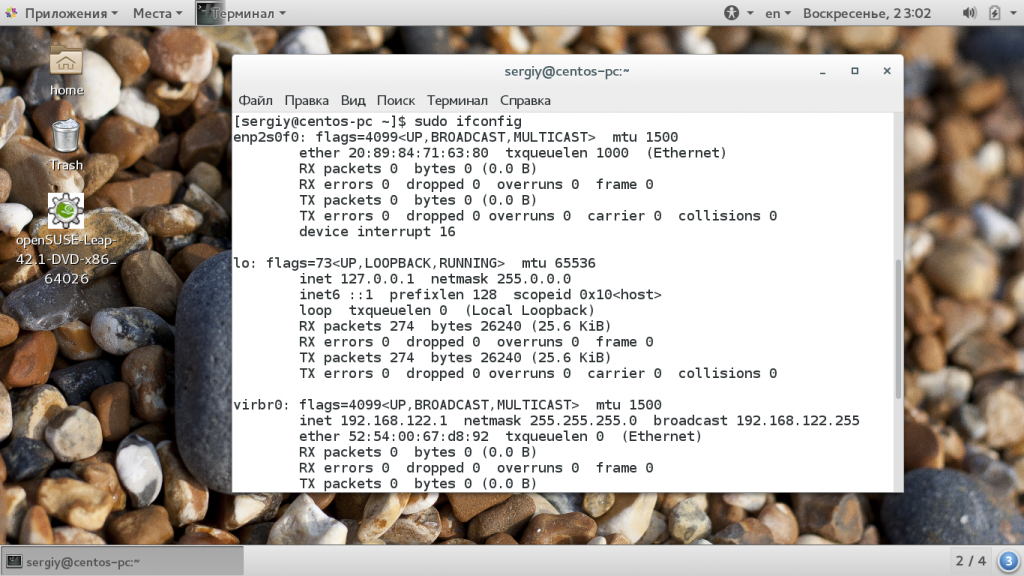
sudo apt install net-tools3. Run ifconfig to confirm the installation.
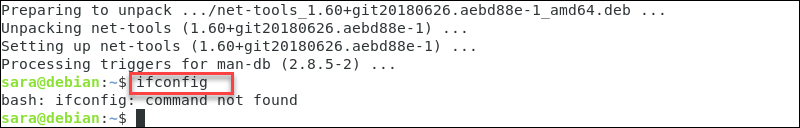
The output above verifies the installation. However, in some cases, Debian won’t execute ifconfig even after the user installs net-tools . The command prints the same error as before the installation:
This happens because the system installs ifconfig in /sbin/, which is not a part of the standard user PATH variable. By default, regular users cannot invoke ifconfig unless they add the command to PATH. However, workaround methods exist.
Method 2: Run ifconfig with sudo or as root
One way to run ifconfig without adding the command to PATH is to use sudo or switch to root with su. If you only need to execute ifconfig once, use sudo instead of su since the former is a safer option:
Method 3: Use the Full Path to the Command
Another option is to run the command as a regular user but to type in the full path to ifconfig :
The method works but requires users to remember the path, which is not practical if ifconfig is used often.
Method 4: Update the System PATH Variable
Using sudo or the entire path to the command works but is not practical in the long term. When a user needs to run ifconfig multiple times, it’s best to add the /sbin/ directory to the PATH variable permanently.
To update the PATH variable, follow these steps:
1. Access .profile in Vim or another text editor.
3. Paste the following line:
5. Reboot the system to make the changes live.
6. Run ifconfig .
The output shows that the command is working.
Note: To install ifconfig for the current user only, change the $HOME/.profile file. To make changes system-wide, edit /etc/profile.
Method 5: Use an Alternative Command
While effective, ifconfig is a challenge to install and run on Debian. In modern distributions, ip is the go-to utility for network configuration.
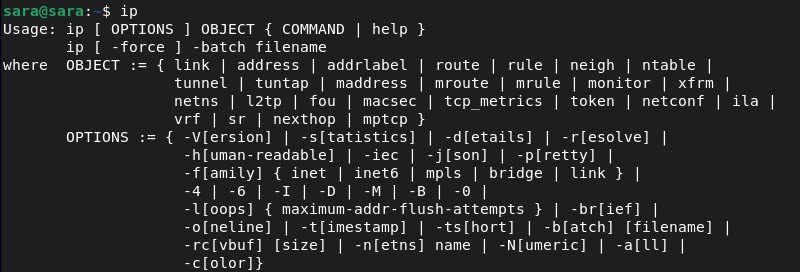
The ip tool is installed by default on Debian. Run the command without any options to see the basic functions:
The ip command prints the list of network interfaces with the link show arguments:
After reading this tutorial, you know how to install ifconfig on Debian. Next, learn how to change the hostname in Debian 10.
Ошибка ifconfig команда не найдена
В очень многих инструкциях из интернета советуется использовать команду ifconfig для настройки сети или просмотра информации о ней. Это очень давняя, но удобная утилита, которая имеет простой синтаксис и выводит информацию в простом и правильном виде.
Но когда вы попытаетесь использовать эту команду, то иногда можете получить ошибку ifconfig команда не найдена. Здесь все понятно, команда не найдена, но это довольно популярная утилита, и странно, что она не поставляется по умолчанию. В этой статье мы рассмотрим что делать если вы сталкиваетесь с такой ошибкой и почему так происходит.
Ошибка ifconfig команда не найдена
Первая причина почему вы можете получать эту ошибку, очень проста. Скорее всего, утилита установлена в вашей системе, но интерпретатор bash не может ее найти. Дело в том, что в Linux существует несколько папок для хранения исполняемых файлов. Все утилиты, которые может выполнять только суперпользователь расположены в каталоге /sbin или /usr/sbin.
Соответственно, обычному пользователю не нужно давать доступ к этим файлам, поэтому эти каталоги доступны только root, а в переменную среды PATH, из которой bash берет каталоги для поиска программ для пользователя они даже не добавлены. Проще говоря, вам достаточно только запустить программу от имени суперпользователя:
Если даже после этого вы получаете эту ошибку, то это означает, что программа таки не установлена. Дело в том, что утилита довольно давняя, и некоторым разработчикам показалось, что нужно разработать что-то более совершенное, поэтому была разработана утилита ip. Она имеет больше возможностей и лучше. Но она непривычна и имеет сложный синтаксис. Теперь команда ip используется по умолчанию во многих дистрибутивах, а ifconfig удалена.
Таким образом, чтобы исправить ошибку ifconfig команда не найдена вам понадобиться установить пакет ней. Утилита находится в пакете net-tools. Для установки в Ubuntu выполните:
sudo apt install net-tools
sudo dnf install net-tools
sudo yum install net-tools
После завершения установки пакета, а это будет выполнено очень быстро, вы можете пользоваться утилитой и ошибки ifconfig command not found больше не будет. Только запускайте ее с помощью sudo. Если вы решили больше не использовать ifconfig смотрите статью про утилиту ip linux.
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели что делать если вы встречаете ошибку bash ifconfig команда не найдена, а также почему она возникает. Это одна из самых простых ошибок, исправить ее очень просто. Надеюсь, эта информация была вам полезной.
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.