- 4 Ways to Identify Who is Logged-In on Your Linux System
- 1. Get the running processes of logged-in user using w
- 2. Get the user name and process of logged in user using who and users command
- Users Command
- 3. Get the username you are currently logged in using whoami
- 4. Get the user login history at any time
- 12 Ways to Find User Account Info and Login Details in Linux
- 1. id Command – Show User and Group IDs
- 2. groups Command – View User Group Memberships
- 3. finger Command – Show User Information
- 4. getent Command – Fetch User Info from System Database
- 5. grep Command – Search for Patterns or Specific Text in Files
- 6. lslogins Command – Display User Information in Linux
- 7. users Command – List Current Logged-In Users on Linux
- 8. who Command – Show Information Of Currently Logged-In Users
- 9. w Command – Show Currently Logged-In User Activity
- 10. last Command – Show Most Recent Login Session
- 11. lastb Command – Show Failed Login Attempts
- 12. lastlog Command – List User Login Information
4 Ways to Identify Who is Logged-In on Your Linux System
This article is written by Hari Haran.
As a system administrator, you may want to know who is on the system at any give point in time. You may also want to know what they are doing. In this article let us review 4 different methods to identify who is on your Linux system.
1. Get the running processes of logged-in user using w
- Name of the user
- User’s machine number or tty number
- Remote machine address
- User’s Login time
- Idle time (not usable time)
- Time used by all processes attached to the tty (JCPU time)
- Time used by the current process (PCPU time)
- Command currently getting executed by the users
Following options can be used for the w command:
- -h Ignore the header information
- -u Display the load average (uptime output)
- -s Remove the JCPU, PCPU, and login time.
$ w 23:04:27 up 29 days, 7:51, 3 users, load average: 0.04, 0.06, 0.02 USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT ramesh pts/0 dev-db-server 22:57 8.00s 0.05s 0.01s sshd: ramesh [priv] jason pts/1 dev-db-server 23:01 2:53 0.01s 0.01s -bash john pts/2 dev-db-server 23:04 0.00s 0.00s 0.00s w $ w -h ramesh pts/0 dev-db-server 22:57 17:43 2.52s 0.01s sshd: ramesh [priv] jason pts/1 dev-db-server 23:01 20:28 0.01s 0.01s -bash john pts/2 dev-db-server 23:04 0.00s 0.03s 0.00s w -h $ w -u 23:22:06 up 29 days, 8:08, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00 USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT ramesh pts/0 dev-db-server 22:57 17:47 2.52s 2.49s top jason pts/1 dev-db-server 23:01 20:32 0.01s 0.01s -bash john pts/2 dev-db-server 23:04 0.00s 0.03s 0.00s w -u $ w -s 23:22:10 up 29 days, 8:08, 3 users, load average: 0.00, 0.00, 0.00 USER TTY FROM IDLE WHAT ramesh pts/0 dev-db-server 17:51 sshd: ramesh [priv] jason pts/1 dev-db-server 20:36 -bash john pts/2 dev-db-server 1.00s w -s
2. Get the user name and process of logged in user using who and users command
who command is used to get the list of the usernames who are currently logged in. Output of the who command contains the following columns: user name, tty number, date and time, machine address.
$ who ramesh pts/0 2009-03-28 22:57 (dev-db-server) jason pts/1 2009-03-28 23:01 (dev-db-server) john pts/2 2009-03-28 23:04 (dev-db-server)
To get a list of all usernames that are currently logged in, use the following:
$ who | cut -d' ' -f1 | sort | uniq john jason ramesh
Users Command
users command is used to print the user name who are all currently logged in the current host. It is one of the command don’t have any option other than help and version. If the user using, ‘n’ number of terminals, the user name will shown in ‘n’ number of time in the output.
$ users john jason ramesh
3. Get the username you are currently logged in using whoami
whoami command is used to print the loggedin user name.
$ whoami john
whoami command gives the same output as id -un as shown below:
$ id -un john
who am i command will display the logged-in user name and current tty details. The output of this command contains the following columns: logged-in user name, tty name, current time with date and ip-address from where this users initiated the connection.
$ who am i john pts/2 2009-03-28 23:04 (dev-db-server) $ who mom likes john pts/2 2009-03-28 23:04 (dev-db-server) Warning: Don't try "who mom hates" command.
Also, if you do su to some other user, this command will give the information about the logged in user name details.
4. Get the user login history at any time
last command will give login history for a specific username. If we don’t give any argument for this command, it will list login history for all users. By default this information will read from /var/log/wtmp file. The output of this command contains the following columns:
- User name
- Tty device number
- Login date and time
- Logout time
- Total working time
$ last jason jason pts/0 dev-db-server Fri Mar 27 22:57 still logged in jason pts/0 dev-db-server Fri Mar 27 22:09 - 22:54 (00:45) jason pts/0 dev-db-server Wed Mar 25 19:58 - 22:26 (02:28) jason pts/1 dev-db-server Mon Mar 16 20:10 - 21:44 (01:33) jason pts/0 192.168.201.11 Fri Mar 13 08:35 - 16:46 (08:11) jason pts/1 192.168.201.12 Thu Mar 12 09:03 - 09:19 (00:15) jason pts/0 dev-db-server Wed Mar 11 20:11 - 20:50 (00:39
This article is written by Hari Haran. He is working in bk Systems (p) Ltd, and interested in contributing to the open source. The Geek Stuff welcomes your tips and guest articles.
12 Ways to Find User Account Info and Login Details in Linux
This article will show you useful ways to find information about users on a Linux system. Here we’ll describe commands to get a user’s account details, show login details as well what users are doing on the system.
If you want to add or create users in Linux, use the useradd command, and to modify or change any attributes of an already created user account, use the usermod command via the command line.
You might also like:
We’ll start by looking at 12 useful commands to find a user’s account information, then proceed to explain commands to view login details in the Linux system.
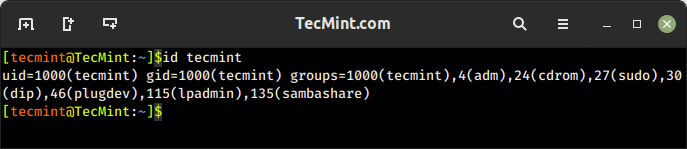
1. id Command – Show User and Group IDs
The id is a simple command line utility for displaying a real and effective user and group IDs identity information for the current user or specified user.
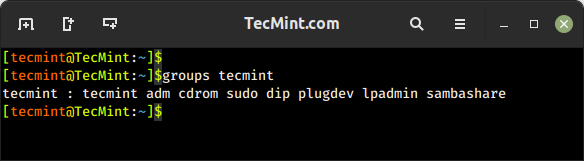
2. groups Command – View User Group Memberships
The groups command is used to display the group memberships for a user. It lists all the groups that a user belongs to, including both primary and supplementary groups.
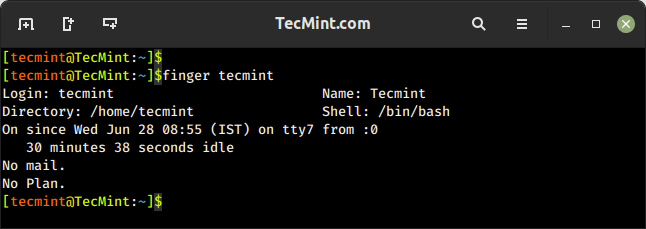
3. finger Command – Show User Information
The finger command is used to search for information about a user on Linux, which includes detailed information about a specific user or a list of users, including their login name, real name, terminal, idle time, login time, and other relevant details.
The finger command doesn’t come pre-installed on many Linux distributions, you need to install it using your default package manager as shown.
$ sudo apt install finger [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum install finger [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emerge -a sys-apps/finger [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo apk add finger [On Alpine Linux] $ sudo pacman -S finger [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install finger [On OpenSUSE]
It shows a user’s real name; home directory; shell; login: name, time; and so much more as shown below.
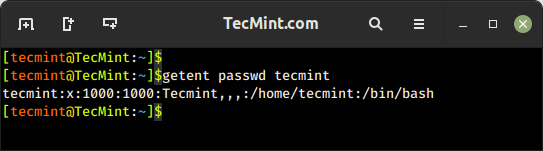
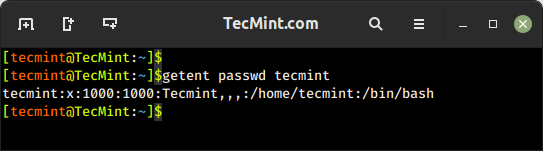
4. getent Command – Fetch User Info from System Database
The getent command is used to retrieve information from various databases, including the system user and group databases. It can be used to retrieve information about users, groups, hosts, networks, protocols, and other system entities that are stored in database files like /etc/passwd, /etc/group, /etc/hosts, etc.
To get a user’s account details, use the passwd database and the username as follows.
5. grep Command – Search for Patterns or Specific Text in Files
The grep command is a powerful command used to search for patterns or specific text in files. It allows you to filter and extract lines from text based on matching patterns. The name “grep” stands for “Global Regular Expression Print“.
You might also like:
You can use grep to find information about a specific user from the system accounts file: /etc/passwd as shown below.
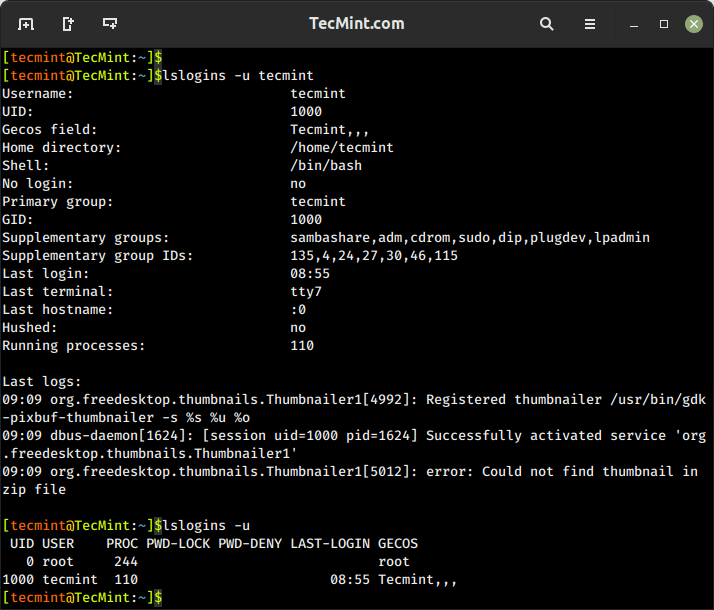
6. lslogins Command – Display User Information in Linux
The lslogins command shows information about known users in the system, which typically includes details such as the username, UID (User ID), GID (Group ID), home directory, shell, last login time, and more, depending on the options used and the system configuration.
$ lslogins -u tecmint $ lslogins -u
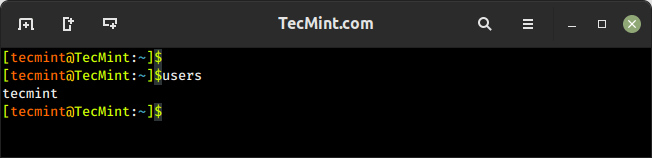
7. users Command – List Current Logged-In Users on Linux
The users command is used to display the list of currently logged-in users on the Linux system.
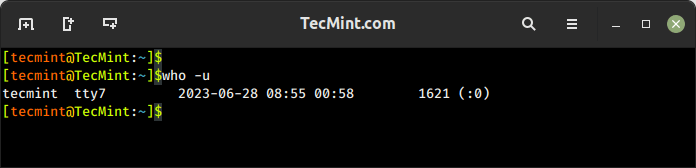
8. who Command – Show Information Of Currently Logged-In Users
The who command is used to display users who are logged on to the system, including the username, terminal, login time, and remote host from which the user is logged in.
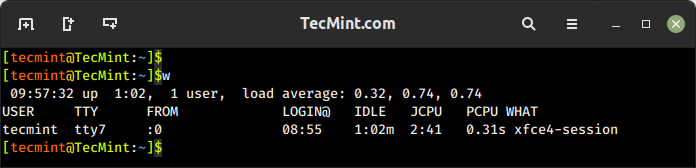
9. w Command – Show Currently Logged-In User Activity
The w command shows a summary of the currently logged-in users and their activity, which displays the login session, including the username, terminal, login time, idle time, JCPU (total CPU time used by all processes), PCPU (CPU time used by the current process), and the command or process running on the terminal.
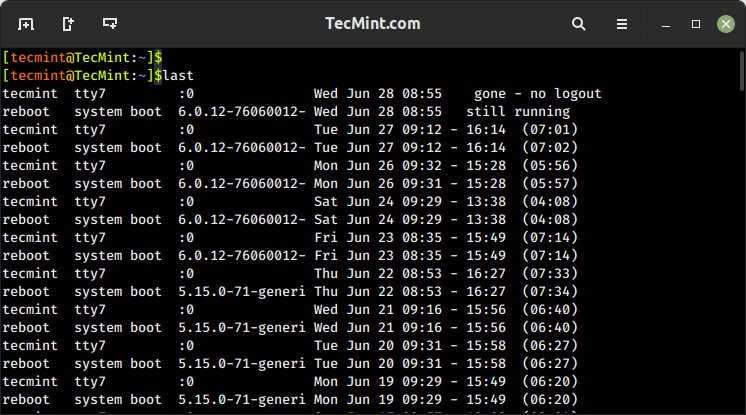
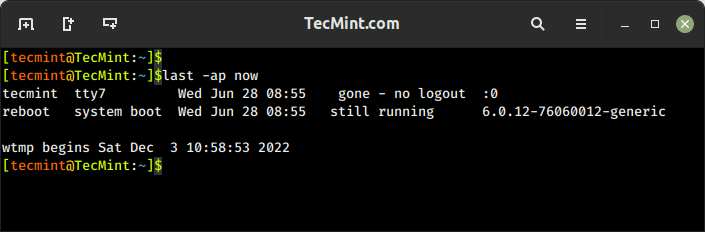
10. last Command – Show Most Recent Login Session
The last command displays a list of the most recent login sessions, which includes information about the users who have logged in, their login times, and the terminals or remote hosts they used for login.
To show all the users who were present at a specified time, use the -p option as follows.
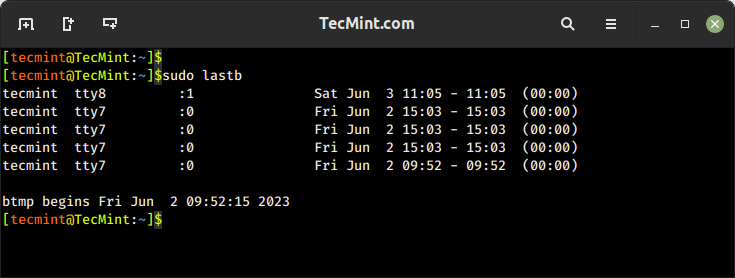
11. lastb Command – Show Failed Login Attempts
The lastb command is used to display a list of the last failed login attempts on the system. It reads from the system log file that records failed login attempts, typically stored in /var/log/btmp.
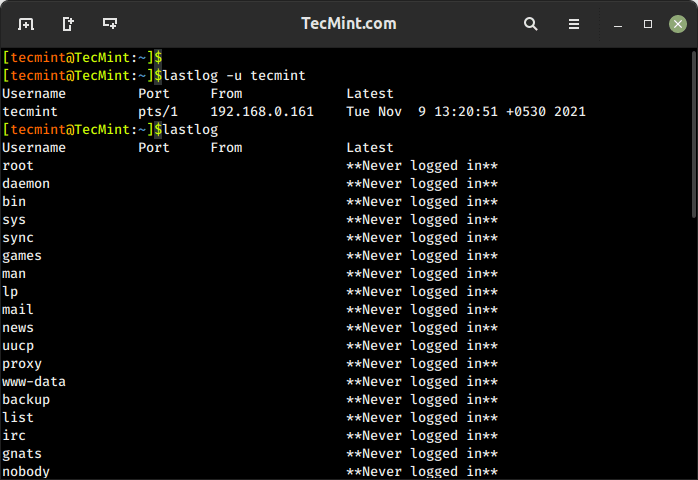
12. lastlog Command – List User Login Information
lastlog command is used to find the details of the most recent login information for all users or a specific user on the system, which provides details about the last login time and location for each user.
$ lastlog OR $ lastlog -u tecmint
That’s it! If you know any other command-line trick or command to view user account details do share with us.
You might also like:
In this article, we’ve explained various ways to find information about users and login details on a Linux system. You can ask any questions or share your thoughts via the feedback form below.