- Как в Linux форматировать жесткий диск в NTFS?
- Шаг 1: Проверьте наличие необходимых пакетов
- Шаг 2: Подготовьте жесткий диск
- Шаг 3: Удалите существующие разделы (если есть)
- Шаг 4: Создайте новый раздел NTFS
- Шаг 5: Примените изменения
- Шаг 6: Форматируйте новый раздел NTFS
- Шаг 7: Подключите новый раздел
- Шаг 8: Проверьте результаты
- How to Format Disk Partitions in Linux
- Checking the Partitions
- Formatting Disk Partition in Linux
- Formatting Disk Partition with ext4 File System
- Formatting Disk Partition with FAT32 File System
- Formatting Disk Partition with NTFS File System
- Mounting the Disk Partition in Linux
- Understanding the Linux File System
Как в Linux форматировать жесткий диск в NTFS?
NTFS (New Technology File System) является одним из наиболее популярных форматов файловой системы для Windows. Если вы хотите использовать жесткий диск с NTFS на Linux, вам необходимо сначала отформатировать его в соответствующем формате. В этой статье мы расскажем, как отформатировать жесткий диск в NTFS в Linux.
Шаг 1: Проверьте наличие необходимых пакетов
Прежде чем начать, убедитесь, что у вас установлены все необходимые пакеты. Вам понадобятся следующие пакеты:
ntfs-3g — пакет, который обеспечивает поддержку NTFS в Linux.
gparted — графический инструмент для управления разделами жестких дисков.
Чтобы установить эти пакеты в Ubuntu или Debian, выполните следующую команду в терминале:
sudo apt-get install ntfs-3g gparted
Шаг 2: Подготовьте жесткий диск
Прежде чем отформатировать жесткий диск, необходимо подготовить его. Подключите жесткий диск к компьютеру и запустите gparted.
В окне GParted выберите нужный жесткий диск в верхней правой части окна. Убедитесь, что вы выбрали правильный диск, чтобы не потерять данные.
Шаг 3: Удалите существующие разделы (если есть)
Если на жестком диске уже есть разделы, вы можете удалить их, чтобы создать новый NTFS раздел. Нажмите правой кнопкой мыши на разделе, который вы хотите удалить, и выберите «Delete» (Удалить).
После этого вы увидите неразмеченное пространство на жестком диске.
Шаг 4: Создайте новый раздел NTFS
Нажмите правой кнопкой мыши на неразмеченном пространстве на жестком диске и выберите «New» (Новый). Выберите файловую систему NTFS в выпадающем списке «File System».
Вы также можете выбрать метку раздела, размер раздела и положение на жестком диске. После завершения настройки параметров раздела, нажмите «Add» (Добавить).
Шаг 5: Примените изменения
После создания нового NTFS раздела, вы увидите его в GParted. Нажмите на кнопку «Apply» (Применить) в верхней частиокна, чтобы применить все изменения на жестком диске. GParted попросит вас подтвердить изменения. Щелкните «Apply» (Применить) еще раз для подтверждения.
Шаг 6: Форматируйте новый раздел NTFS
Теперь, когда у вас есть новый раздел NTFS на жестком диске, вы можете отформатировать его в этом формате. Откройте терминал и выполните следующую команду:
Замените «X» на букву диска и «n» на номер раздела, который вы создали в предыдущих шагах. Например, если вы создали раздел на втором диске с именем «sdb1», выполните следующую команду:
Шаг 7: Подключите новый раздел
После того, как вы отформатировали новый раздел NTFS, вам нужно его подключить, чтобы использовать его в Linux. Создайте папку, куда вы хотите подключить новый раздел, и выполните следующую команду:
sudo mount /dev/sdXn /path/to/mount/point
Замените «X» на букву диска и «n» на номер раздела, который вы создали. Замените «/path/to/mount/point» на путь к папке, которую вы создали для монтирования раздела.
Например, если вы создали папку «/mnt/data» для монтирования нового раздела на втором диске «sdb1», выполните следующую команду:
sudo mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt/data
Шаг 8: Проверьте результаты
Теперь вы можете проверить, что новый раздел NTFS успешно отформатирован и подключен в Linux. Откройте файловый менеджер и перейдите в папку, в которую вы монтировали раздел. Вы должны увидеть новый NTFS раздел и иметь возможность записывать и читать файлы на нем.
Отформатировать жесткий диск в NTFS в Linux довольно просто. Вы можете использовать графический инструмент GParted или терминал для создания нового раздела NTFS и отформатирования его в соответствующем формате. После отформатирования нового раздела вы можете легко подключить его и начать использовать в Linux.
How to Format Disk Partitions in Linux
A disk partition must be formatted and mounted before use. The formatting process can also be done for several other reasons, such as changing the file system, fixing errors, or deleting all data.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to format and mount disk partitions in Linux using ext4, FAT32, or NTFS file system.
- A system running Linux
- A user account with sudo or root privileges
- Access to a terminal window / command line (Activities >Search >Terminal)
Checking the Partitions
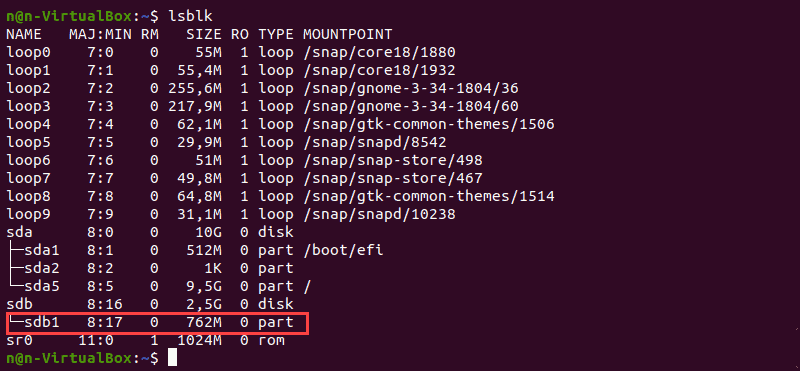
Before formatting, locate a partition you wish to format. To do so, run the lsblk command that displays block devices. Block devices are files that represent devices such as hard drives, RAM disks, USB drives, and CD/ROM drives.
The terminal prints out a list of all block devices as well as information about them:
- NAME – Device names
- MAJ:MIN – Major or minor device numbers
- RM – Whether the device is removable (1 if yes, 0 if no)
- SIZE – The size of the device
- RO – Whether the device is read-only
- TYPE – The type of the device
- MOUNTPOINT – Device’s mount point
We will use the /dev/sdb1 partition as an example.
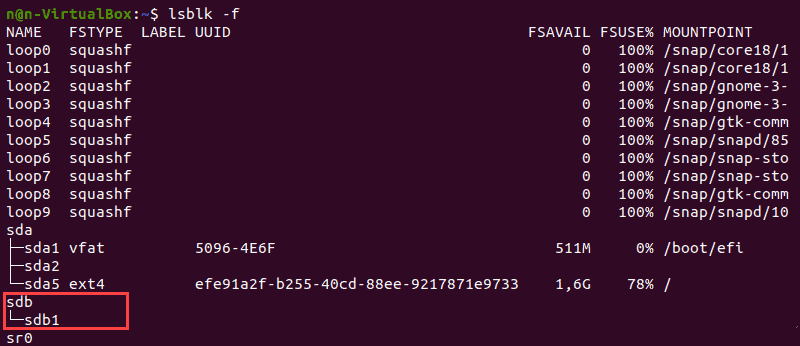
The lsblk command without additional options does not display information about the devices’ file systems.
To display a list containing file system information, add the -f option:
The terminal prints out the list of all block devices. The partitions that do not contain information on the file system in use are non-formatted partitions.
Note: Consider learning how to create partitions in Linux.
Formatting Disk Partition in Linux
There are three ways to format disk partitions using the mkfs command, depending on the file system type:
The general syntax for formatting disk partitions in Linux is:
mkfs [options] [-t type fs-options] device [size]Formatting Disk Partition with ext4 File System
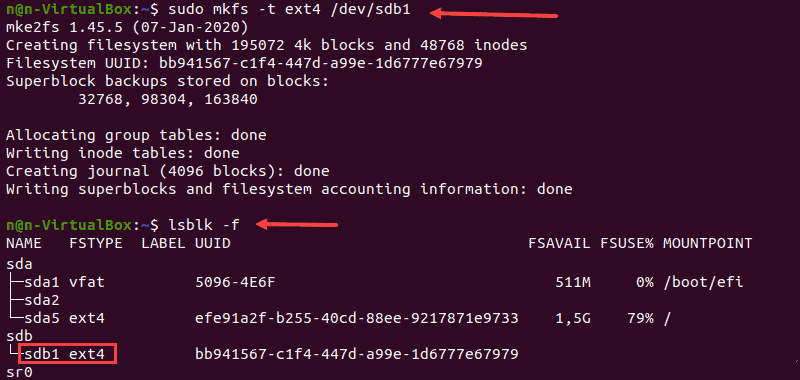
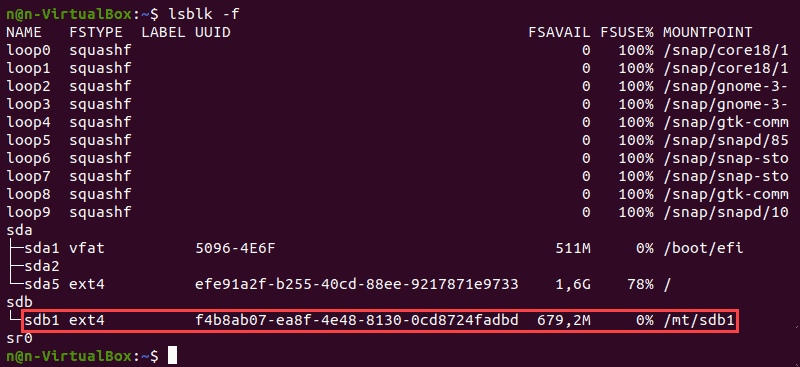
1. Format a disk partition with the ext4 file system using the following command:
2. Next, verify the file system change using the command:
The terminal prints out a list of block devices.
3. Locate the preferred partition and confirm that it uses the ext4 file system.
Formatting Disk Partition with FAT32 File System
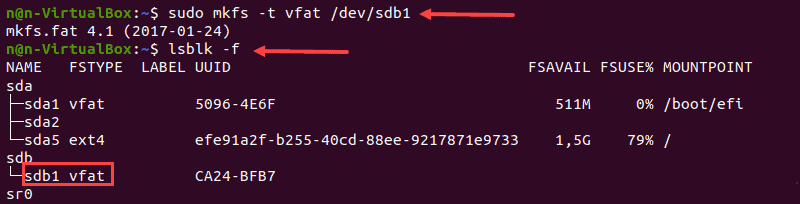
1. To format a disk with a FAT32 file system, use:
2. Again, run the lsblk command to verify the file system change and locate the preferred partition from the list.
Formatting Disk Partition with NTFS File System
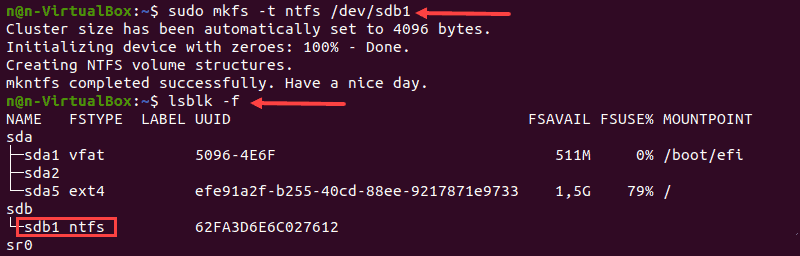
1. Run the mkfs command and specify the NTFS file system to format a disk:
The terminal prints a confirmation message when the formatting process completes.
2. Next, verify the file system change using:
3. Locate the preferred partition and confirm that it uses the NFTS file system.
Mounting the Disk Partition in Linux
Before using the disk, create a mount point and mount the partition to it. A mount point is a directory used to access data stored in disks.
1. Create a mount point by entering:
2. After that, mount the partition by using the following command:
sudo mount -t auto /dev/sdb1 [mountpoint]Note: Replace [mountpoint] with the preferred mount point (example: /usr/media ).
There is no output if the process completes successfully.
3. Verify if the partition is mounted using the following command:
Understanding the Linux File System
Choosing the right file system before formatting a storage disk is crucial. Each type of file system has different file size limitations or different operating system compatibility.
The most commonly used file systems are:
Their main features and differences are:
| File System | Supported File Size | Compatibility | Ideal Usage |
| FAT32 | up to 4 GB | Windows, Mac, Linux | For maximum compatibility |
| NTFS | 16 EiB – 1 KB | Windows, Mac (read-only), most Linux distributions | For internal drives and Windows system file |
| Ext4 | 16 GiB – 16 TiB | Windows, Mac, Linux (requires extra drivers to access) | For files larger than 4 GB |
Note: Refer to our Introduction to Linux File System article to learn more about the evolution and features of different Linux file systems.
After following this tutorial, you should be able to format and mount a partition in Linux in various file systems. Partition manipulation is essential for efficient data management, and next, we recommend learning how to delete a partition in Linux.