- How to format a usb drive with FAT32 file system on Linux
- Как отформатировать USB-устройство в Fat32 в Linux
- Отформатируйте USB-устройство в Fat32 — Gnome Disk Utility
- Ubuntu
- Debian
- Arch Linux
- Fedora
- OpenSUSE
- Отформатируйте USB-устройство в Fat32
- Отформатируйте USB-устройство в Fat32 — Mkfs
- How to Format Disk Partitions in Linux
- Checking the Partitions
- Formatting Disk Partition in Linux
- Formatting Disk Partition with ext4 File System
- Formatting Disk Partition with FAT32 File System
- Formatting Disk Partition with NTFS File System
- Mounting the Disk Partition in Linux
- Understanding the Linux File System
How to format a usb drive with FAT32 file system on Linux
For all Linux users, work with usb drives, is really easy, and share data with Windows users through it, is also easy.
At least before you need to format the usb drive for any reason, if you format it using Linux ext3 or any other Linux mode, you will not be able (at least not easily) to share data with Windows users. What you need is to format the usb drive using FAT32 file system.
Install dosfstools package
The package you need to install in your Linux PC to be able to format disk using FAT32 file system is: dosfstools
Install dosfstools in Debian / Ubuntu
apt-get install dosfstools Install dosfstools in Arch Linux
Install dosfstools in Slackware
slackpkg install dosfstools Format usb drive with FAT32
Now that you have the right tools installed, it is time to use it, so to format a usb drive using FAT32 first insert your usb drive in the usb slot of your computer, and check with
You will see something like this:
Disk /dev/sda: 80.0 GB, 80026361856 bytes 255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 9729 cylinders Units = cylinders of 16065 * 512 = 8225280 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk identifier: 0xed1f86f7 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/sda1 * 1 1135 9116856 7 HPFS/NTFS /dev/sda2 1136 9141 64308195 5 Extended Partition 2 does not end on cylinder boundary. /dev/sda3 9142 9729 4717440 12 Compaq diagnostics Partition 3 does not end on cylinder boundary. /dev/sda5 1136 3047 15358108+ 83 Linux /dev/sda6 3048 3493 3580101 7 HPFS/NTFS /dev/sda7 3494 8809 42700738+ 83 Linux /dev/sda8 8810 9141 2666758+ 82 Linux swap Disk /dev/sdc: 8075 MB, 8075120640 bytes 154 heads, 36 sectors/track, 2844 cylinders Units = cylinders of 5544 * 512 = 2838528 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk identifier: 0xb0bcd68e Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/sdc1 1 2845 7884836 83 Linux As you can see /dev/sdc is where my usb thumb drive was connected.
WARNING: Be really careful before formating a disk, you will not be able to recover your data, double check that you are applying the command to the right device before you hit ENTER
Note: You are supposed to have a partition created on the disk, before you format it.
If you enjoyed the article, please share it
You can also subscribe in different ways
Как отформатировать USB-устройство в Fat32 в Linux
Вам нужно отформатировать USB-устройство в Fat32 на вашем ПК с Linux? Не можете понять, как отформатировать файловую систему? Мы можем помочь! Мы покажем вам, как отформатировать USB-устройство в Fat32 в Linux!
Отформатируйте USB-устройство в Fat32 — Gnome Disk Utility
Приложение Gnome Disk Utility — это самый быстрый и простой способ для пользователя Linux отформатировать USB-устройство в Fat32. Причина? Он имеет простой в использовании пользовательский интерфейс, поддерживает формат Fat32 и такие вещи, как «быстрое форматирование».
Чтобы начать процесс форматирования, вам необходимо установить Gnome Disk Utility на свой компьютер. К сожалению, хотя Gnome Disk Utility поставляется со многими операционными системами Linux, она поставляется не со всеми из них.
Программы для Windows, мобильные приложения, игры — ВСЁ БЕСПЛАТНО, в нашем закрытом телеграмм канале — Подписывайтесь:)
С использованием Ctrl + Alt + T комбинацию клавиш, откройте окно терминала на рабочем столе Linux. Или откройте меню приложения, найдите «Терминал» и запустите приложение таким образом.
После открытия окна терминала следуйте инструкциям по установке Gnome Disk Utility, которые соответствуют используемой вами ОС Linux.
Ubuntu
В Ubuntu установите приложение Gnome Disk Utility со следующим Квартира команда ниже.
sudo apt install gnome-disk-utility
Debian
Те, кто использует Debian Linux, смогут установить Дисковую утилиту Gnome, используя Apt-get команда.
sudo apt-get install gnome-disk-utility
Arch Linux
Если вы являетесь пользователем Arch Linux, вы сможете установить Дисковую утилиту Gnome с Pacman команда быстро.
sudo pacman -S gnome-disk-utility
Fedora
В Fedora Linux уже может быть установлено приложение Gnome Disk Utility. Однако, если это не так, вы сможете заставить его работать со следующими Dnf команда.
sudo dnf install gnome-disk-utility
OpenSUSE
Если вы используете OpenSUSE Linux, вы сможете быстро установить приложение Gnome Disk Utility, используя следующие Zypper команда.
sudo zypper install gnome-disk-utility
Отформатируйте USB-устройство в Fat32
Теперь, когда на вашем компьютере с Linux установлена дисковая утилита Gnome, найдите «Диски» в меню приложения. Когда приложение открыто, следуйте пошаговым инструкциям ниже, чтобы узнать, как отформатировать USB-устройство в Fat32.
Шаг 1: Подключите USB-устройство к USB-порту. После подключения он должен появиться на боковой панели Gnome Disk Utility. Просмотрите боковую панель вашего устройства и щелкните по нему мышью.
Шаг 2: Обнаружив свое устройство и щелкнув по нему мышью, вы увидите обзор USB-устройства. Отсюда найдите меню Gnome Disk Utility и щелкните его.
Не можете найти меню Gnome Disk Utility? Он находится прямо слева от кнопки свертывания.
Шаг 3: В меню Gnome Disk Utility нажмите кнопку «Форматировать диск». Затем найдите меню «Стереть».
В меню «Стереть» выберите «Быстро» или «Медленно». Для достижения наилучших результатов мы рекомендуем вариант «Медленно», так как он более безопасен.
Шаг 4: После выбора опции в меню «Стереть» найдите меню «Разбиение на разделы», выберите «Совместимо со всеми системами и устройствами (MBR / DOS)» и щелкните по нему.
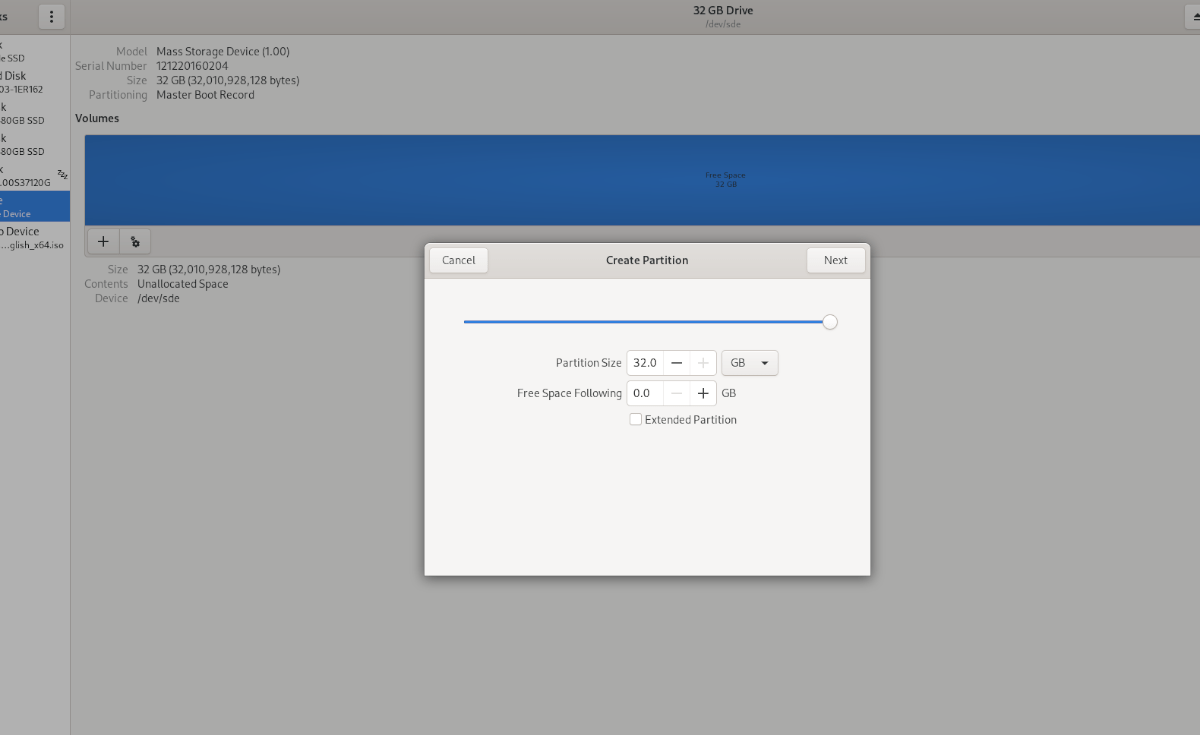
Шаг 5: В разделе «Тома» вашего устройства найдите кнопку «+» и щелкните по ней, чтобы создать новый раздел. При нажатии на эту кнопку появится окно «Создать раздел».
Во всплывающем окне выберите размер раздела, свободное место и т. Д. Нажмите «Далее», чтобы перейти на следующую страницу.
Шаг 6: На следующей странице найдите раздел «Имя тома» и назовите свой том. Или оставьте поле пустым, если хотите.
Найдите кнопку «Стереть» и нажмите на нее, если вы хотите стереть данные с устройства заранее. Затем найдите «Тип» и нажмите «Для использования со всеми системами и устройствами (FAT)».
По завершении нажмите «Создать».
Шаг 7: После нажатия кнопки «Создать» в Gnome Disk Utility ваше USB-устройство будет отформатировано в Fat32!
Отформатируйте USB-устройство в Fat32 — Mkfs
Еще один быстрый способ отформатировать USB-устройство в Fat32 — использовать mkfs команда в терминале. Чтобы начать процесс, нажмите Ctrl + Alt + T на клавиатуре, чтобы открыть терминал. Или найдите «терминал» в меню приложения и запустите его таким образом.
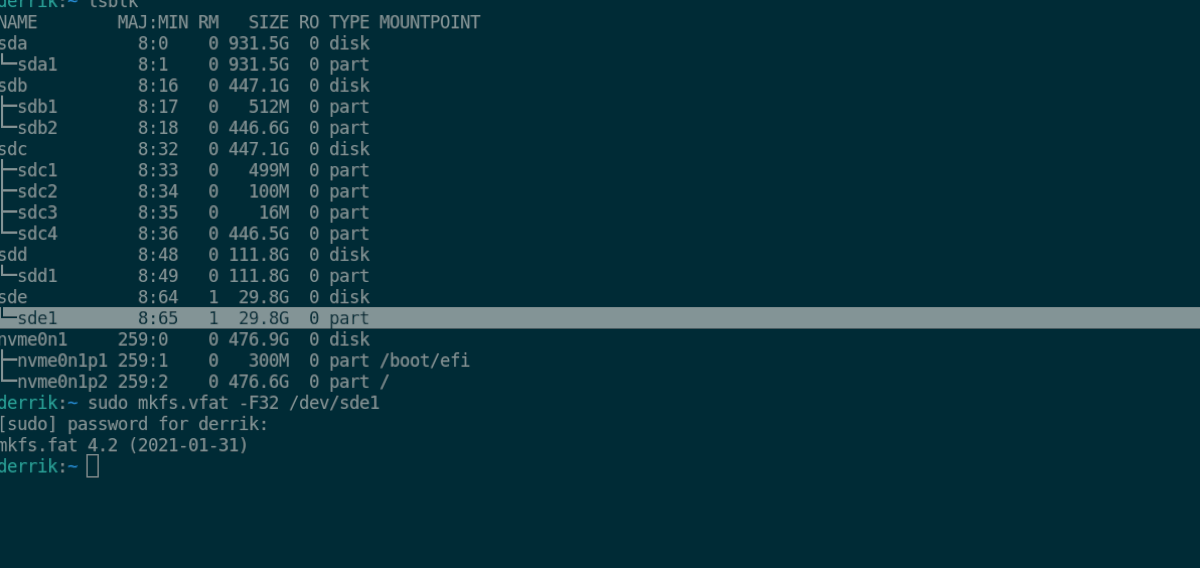
После открытия окна терминала подключите USB-устройство. Затем выполните lsblk в терминале, чтобы просмотреть все подключенные устройства хранения.
Просматривать lsblk и найдите свое USB-устройство и найдите этикетку устройства. В этом примере метка устройства /dev/sde1 . Ваш будет отличаться!
Примечание: не могу понять, как читать lsblk? Ознакомьтесь с нашим руководством о том, как найти информацию о жестком диске, чтобы получить помощь!
Обнаружив USB-устройство, отключите его, если оно еще не отключено. Вы можете сделать это, введя размонтировать команду вместе с меткой устройства.
После размонтирования устройства используйте mkfs.vfat -F32 команда, чтобы отформатировать его в Fat32.
sudo mkfs.vfat -F32 /dev/sde1
Программы для Windows, мобильные приложения, игры — ВСЁ БЕСПЛАТНО, в нашем закрытом телеграмм канале — Подписывайтесь:)
How to Format Disk Partitions in Linux
A disk partition must be formatted and mounted before use. The formatting process can also be done for several other reasons, such as changing the file system, fixing errors, or deleting all data.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to format and mount disk partitions in Linux using ext4, FAT32, or NTFS file system.
- A system running Linux
- A user account with sudo or root privileges
- Access to a terminal window / command line (Activities >Search >Terminal)
Checking the Partitions
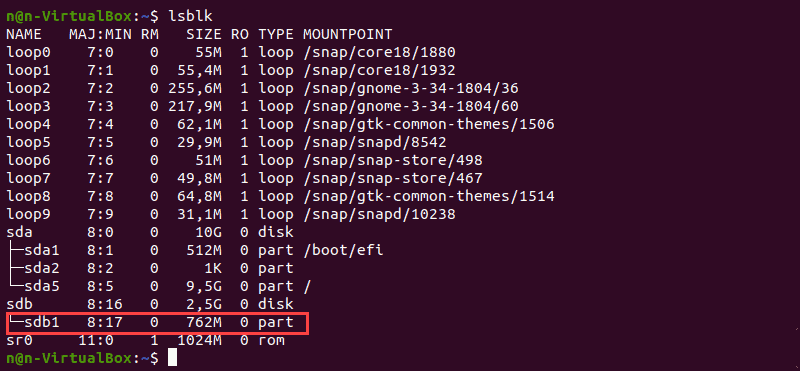
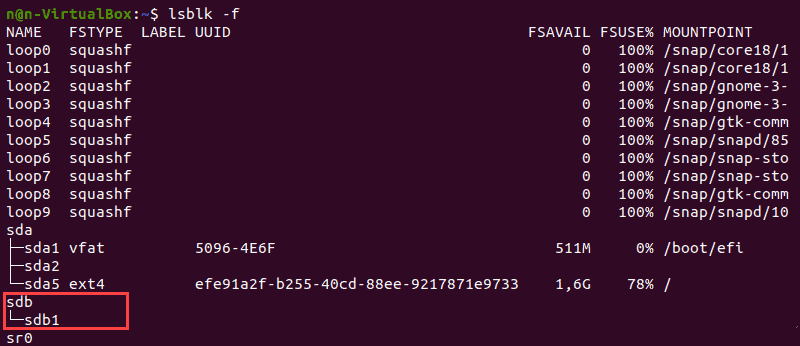
Before formatting, locate a partition you wish to format. To do so, run the lsblk command that displays block devices. Block devices are files that represent devices such as hard drives, RAM disks, USB drives, and CD/ROM drives.
The terminal prints out a list of all block devices as well as information about them:
- NAME – Device names
- MAJ:MIN – Major or minor device numbers
- RM – Whether the device is removable (1 if yes, 0 if no)
- SIZE – The size of the device
- RO – Whether the device is read-only
- TYPE – The type of the device
- MOUNTPOINT – Device’s mount point
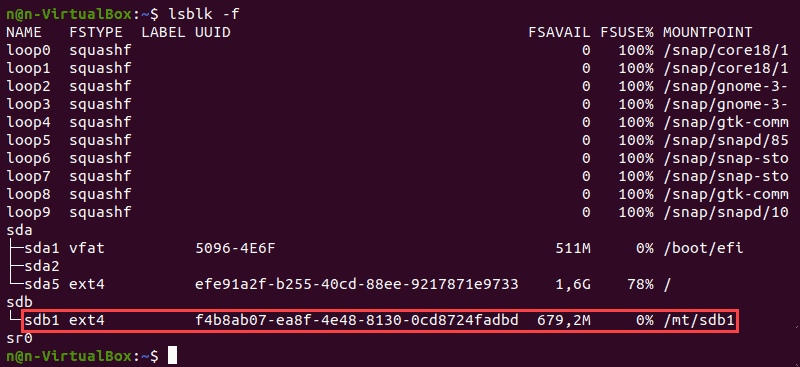
We will use the /dev/sdb1 partition as an example.
The lsblk command without additional options does not display information about the devices’ file systems.
To display a list containing file system information, add the -f option:
The terminal prints out the list of all block devices. The partitions that do not contain information on the file system in use are non-formatted partitions.
Note: Consider learning how to create partitions in Linux.
Formatting Disk Partition in Linux
There are three ways to format disk partitions using the mkfs command, depending on the file system type:
The general syntax for formatting disk partitions in Linux is:
mkfs [options] [-t type fs-options] device [size]Formatting Disk Partition with ext4 File System
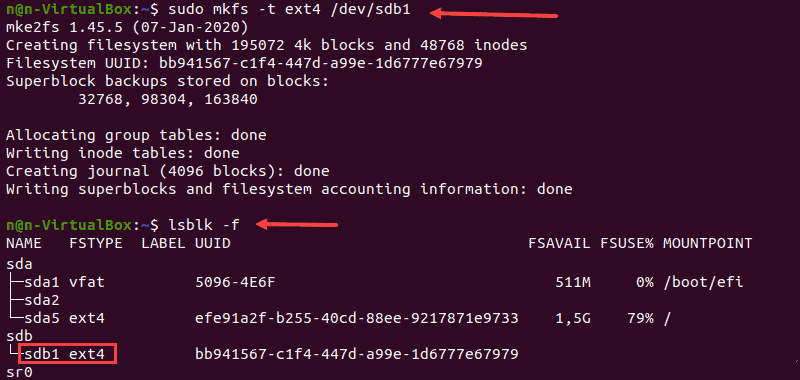
1. Format a disk partition with the ext4 file system using the following command:
2. Next, verify the file system change using the command:
The terminal prints out a list of block devices.
3. Locate the preferred partition and confirm that it uses the ext4 file system.
Formatting Disk Partition with FAT32 File System
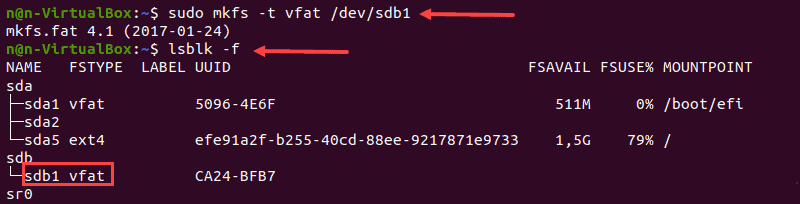
1. To format a disk with a FAT32 file system, use:
2. Again, run the lsblk command to verify the file system change and locate the preferred partition from the list.
Formatting Disk Partition with NTFS File System
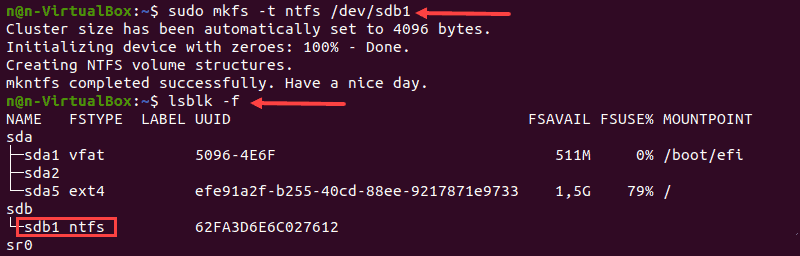
1. Run the mkfs command and specify the NTFS file system to format a disk:
The terminal prints a confirmation message when the formatting process completes.
2. Next, verify the file system change using:
3. Locate the preferred partition and confirm that it uses the NFTS file system.
Mounting the Disk Partition in Linux
Before using the disk, create a mount point and mount the partition to it. A mount point is a directory used to access data stored in disks.
1. Create a mount point by entering:
2. After that, mount the partition by using the following command:
sudo mount -t auto /dev/sdb1 [mountpoint]Note: Replace [mountpoint] with the preferred mount point (example: /usr/media ).
There is no output if the process completes successfully.
3. Verify if the partition is mounted using the following command:
Understanding the Linux File System
Choosing the right file system before formatting a storage disk is crucial. Each type of file system has different file size limitations or different operating system compatibility.
The most commonly used file systems are:
Their main features and differences are:
| File System | Supported File Size | Compatibility | Ideal Usage |
| FAT32 | up to 4 GB | Windows, Mac, Linux | For maximum compatibility |
| NTFS | 16 EiB – 1 KB | Windows, Mac (read-only), most Linux distributions | For internal drives and Windows system file |
| Ext4 | 16 GiB – 16 TiB | Windows, Mac, Linux (requires extra drivers to access) | For files larger than 4 GB |
Note: Refer to our Introduction to Linux File System article to learn more about the evolution and features of different Linux file systems.
After following this tutorial, you should be able to format and mount a partition in Linux in various file systems. Partition manipulation is essential for efficient data management, and next, we recommend learning how to delete a partition in Linux.