- How to Use Fdisk Format Partition in Linux [2023 Ultimate Guide]
- What Is Fdisk in Linux?
- How to Use Fdisk Format Partition in Linux?
- Bonus Tip: The Overview of Linux File System Format
- Conclusion
- FAQs About Fdisk Format Partition in Linux
- Как отформатировать разделы диска в Linux
- Проверка разделов
- Форматирование раздела диска в Linux
- Форматирование раздела диска с файловой системой ext4
- Форматирование раздела диска с файловой системой FAT32
- Форматирование раздела диска с файловой системой NTFS
- Монтирование раздела диска в Linux
- Понимание файловой системы Linux
How to Use Fdisk Format Partition in Linux [2023 Ultimate Guide]
Do you know how to use fdisk format partitions in Linux? Fdisk is included in all versions of MS-DOS and earlier versions of Windows and is also present in Linux. But it has been replaced by the Diskpart command in Windows. So, some users may not be aware of fdisk. This article will briefly introduce fdisk and guide users on how to use fdisk to format partitions in Linux. Continue to read.
What Is Fdisk in Linux?
Do you know what is fdisk in Linux? Here is the definition of it by Wikipedia:
In computing, the fdisk command-line utility provides disk-partitioning functions, preparatory to defining file systems. In versions of the Windows NT operating system line from Windows 2000 onwards, fdisk is replaced by a more advanced tool called diskpart. Similar utilities exist for Unix-like systems. – by Wikipedia
Fdisk is a text-based utility that comes pre-installed on Linux distributions. It can be used to view and manage partitions on Linux. It can:
- Create, edit, and delete partitions
- Copy or move data to new disks (partitions)
- Delete, change, resize and organize space for partitions
- Support for all major partition tables, including GPT, MBR, Sun, SGI, and BSD
Using fdisk, you can divide a disk into a primary partition and multiple logical partitions. If you create a new partition, you need to format the partition and assign a file system to it. Next, I will describe the detailed steps to use the fdisk format partition in Linux.
How to Use Fdisk Format Partition in Linux?
For managing disk partitions, fdisk is a command line partition editor. And fdisk provides an interactive mode. It offers more control and security over partition formatting operations. This guide will manage partitions with fdisk and format them with the mkfs utility. Next is a detailed step-by-step procedure.
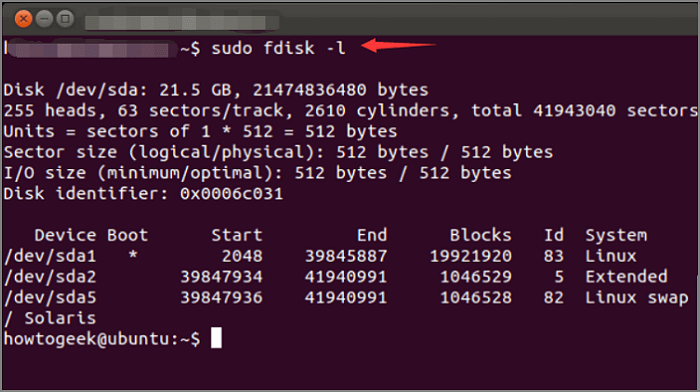
Step 1. Type «sudo fdisk -l» to list all the partitions and see their /dev names. For example, /dev/sda, /dev/sdb or /dev/sdc.
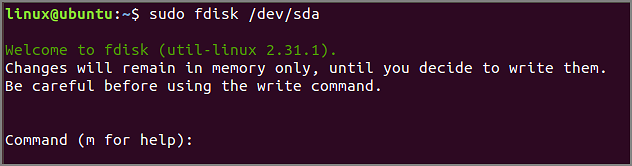
Step 2. Use the «sudo fdisk /dev/sda» to view all fdisk commands.
Step 3. Type «m» to view all actions performed on /dev/sda.
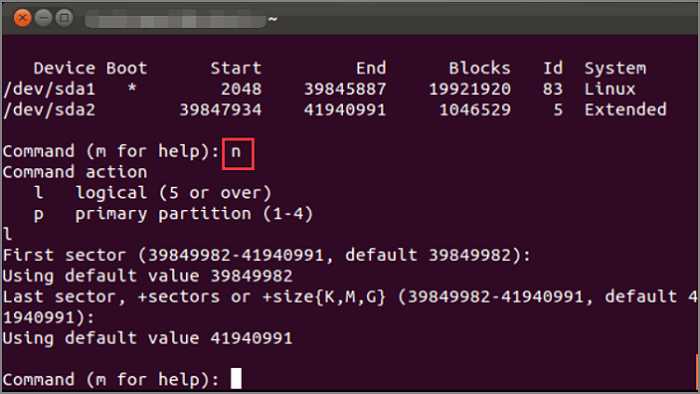
Step 4. Use the command: «sudo fdisk /dev/sda» to access the partition. And then, you can type «n» to create a new partition.
Step 5. Run the «w» command to write the changes and reboot the system.
Step 6. Type «t» to change the partition type.
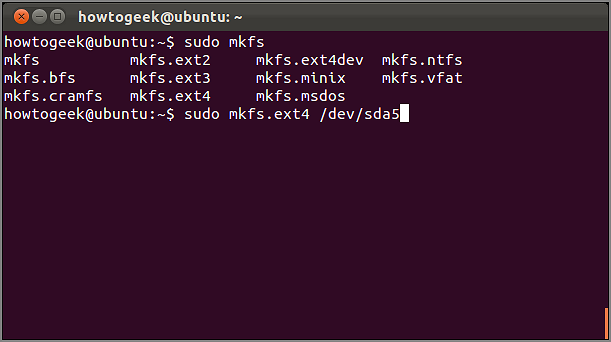
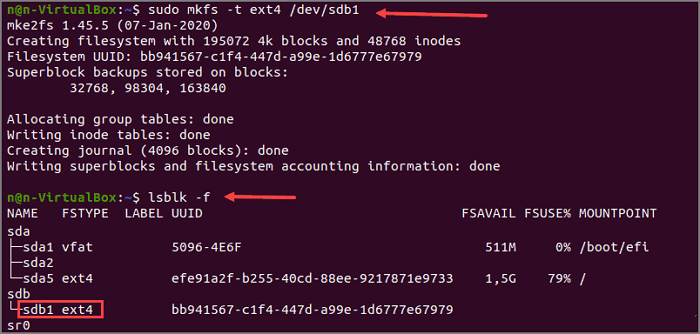
Step 7. Format the partition with the mkfs command. For example: «sudo mkfs.ext4 /dev/sda5». This command will format the fifth partition using the ext4 file system.
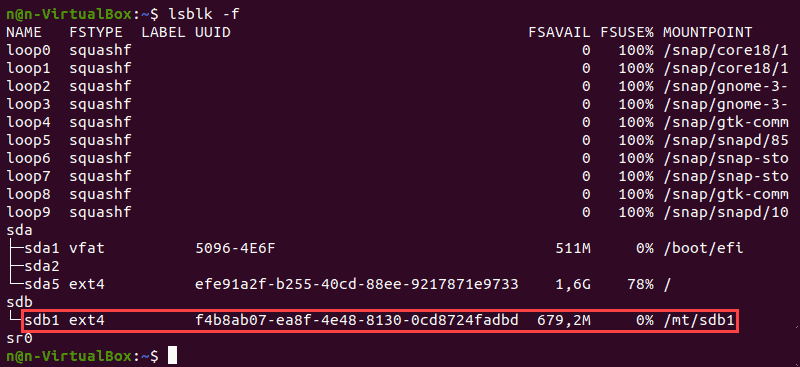
Step 8. Type » lsblk -f» to verify the file system change.
Step 9. Find the partition and make sure it uses the ext4 file system.
Tip You can also format partitions with FAT32 and NTFS file systems. You need to change the command to FAT32 or NTFS. For example: sudo mkfs -t vfat /dev/sdb1.
These are the specific steps for using the fdisk format a disk in Linux. You can click the link below if you still want to know how to run fdisk in Windows.
Do you want to learn how to run fdisk on Windows 10/11? If yes, then you are landed on the right page. Today, we will give you detailed information regarding fdisk, its uses, and other relevant information.
Bonus Tip: The Overview of Linux File System Format
Linux can support multiple file systems. And different type of file system format has the different file size and system compatibility. Here are the most commonly used file systems.
| File System Format | File Size | Compatibility | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| EXT4 | 16 GiB – 16 TiB | Windows, Mac, Linux | For large files |
| NTFS | 16 EiB – 1 KB | Windows, Linux | For Windows files |
| FAT32 | Up to 4 GB | Windows, Mac, Linux | For maximum compatibility |
Linux systems have some other system formats, such as JFS File System, XFS File System, and Btrfs File System, but the FAT32 format is the most compatible, and you can operate it on a wide range of systems. You can convert NTFS to FAT32 to better fit Linux systems. Besides, if you want to know more file system format on Linux, you can click the button to search for the differences of Ext2/Ext3/Ext4 File System Format.
Conclusion
Formatting a partition is helpful for computer performance. Fdisk is a good solution for the command line interface. After studying the step-by-step guide in the passage, you should be able to understand what fdisk is and be able to use fdisk format partitions in Linux. This article provides detailed steps to create and format partitions with a fdisk.
FAQs About Fdisk Format Partition in Linux
In addition to the detailed steps about using fdisk format partitions in Linux, here are some frequently asked questions about partitions.
1. What is the use of the fdisk command in Linux?
Fdisk is a command in Linux for creating and manipulating disk partitions. It can directly view, complete, and delete partitions. And it can change the size of partitions and copy and move partitions.
2. How do I format a partition in Linux?
You can format the partition with the NTFS file system in Linux.
Step 1. Run the mkfs command and specify the NTFS file system to format the disk: sudo mkfs -t ntfs /dev/sdb1
Step 2. Use the lsblk-f command to verify the file system changes
Step 3. Locate the partition to confirm the use of the NFTS system.
3. How can I see all partitions in Linux?
You can use the fdisk command to see all partitions in Linux. It is used for viewing and manipulating disk partitions. For example, you can type «fdisk -l» at the command prompt and see the partitions.
Как отформатировать разделы диска в Linux
Перед использованием раздел диска необходимо отформатировать и смонтировать. Процесс форматирования также может быть выполнен по ряду других причин, таких как изменение файловой системы, исправление ошибок или удаление всех данных.
В этом руководстве вы узнаете, как форматировать и монтировать разделы диска в Linux с использованием файловой системы ext4, FAT32 или NTFS.
Проверка разделов
Перед форматированием найдите раздел, который хотите отформатировать. Для этого запустите команду lsblk , которая отображает блочные устройства. Блочные устройства — это файлы, которые представляют такие устройства, как жесткие диски, RAM-диски, USB-накопители и CD/ROM.
Терминал покажет список всех блочных устройств, а также информацию о них:
- NAME — имена устройств
- MAJ:MIN — старший или младший номер устройства
- RM — является ли устройство съемным (1, если да, 0, если нет)
- SIZE — размер устройства
- RO — доступно ли устройство только для чтения
- TYPE — тип устройства
- MOUNTPOINT — точка монтирования устройства
В качестве примера мы будем использовать раздел /dev/sdb1 .
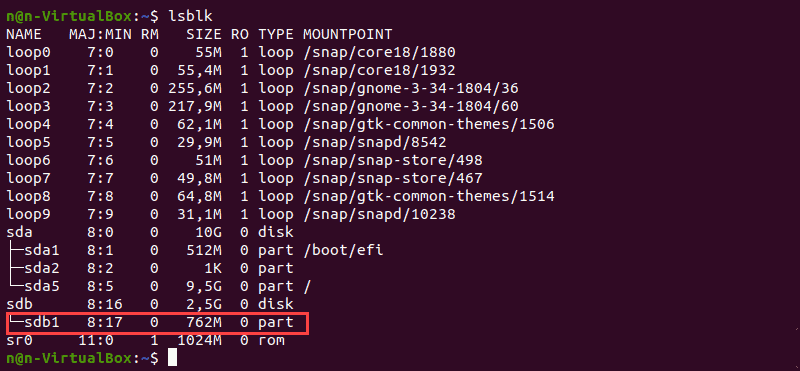
Команда lsblk без дополнительных параметров не отображает информацию о файловых системах устройств.
Чтобы отобразить список, содержащий информацию о файловой системе, добавьте параметр -f :
Терминал покажет список всех блочных устройств. Разделы, не содержащие информации об используемой файловой системе, являются неформатированными разделами.
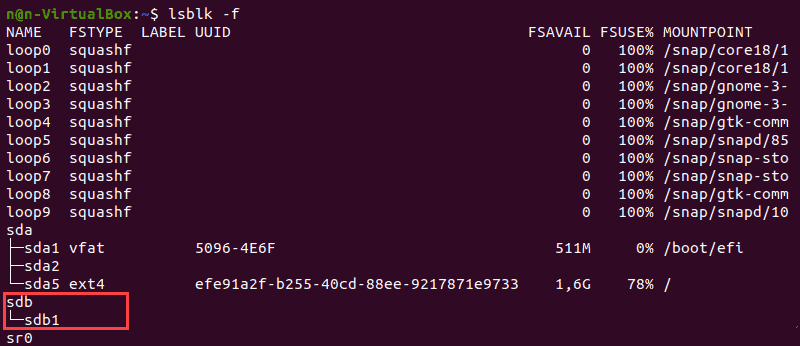
Форматирование раздела диска в Linux
В зависимости от типа файловой системы существует три способа форматирования разделов диска с помощью команды mkfs :
Общий синтаксис форматирования разделов диска в Linux:
mkfs [options] [-t type fs-options] device [size]
Форматирование раздела диска с файловой системой ext4
1. Отформатируйте раздел диска с файловой системой ext4, используя следующую команду:
2. Затем проверьте изменение файловой системы с помощью команды:
Терминал покажет список блочных устройств.
3. Найдите нужный раздел и убедитесь, что он использует файловую систему ext4.
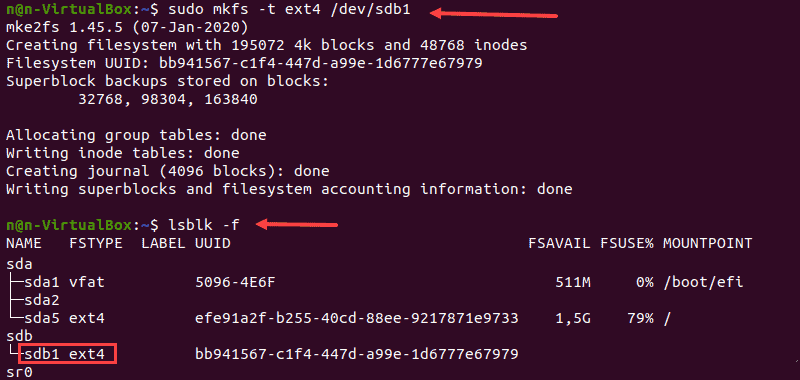
Форматирование раздела диска с файловой системой FAT32
1. Чтобы отформатировать диск в файловой системе FAT32, используйте:
2. Снова запустите команду lsblk , чтобы проверить изменение файловой системы и найти нужный раздел в списке.
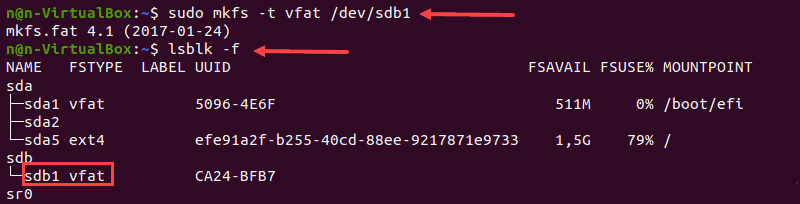
Форматирование раздела диска с файловой системой NTFS
1. Запустите команду mkfs и укажите файловую систему NTFS для форматирования диска:
Терминал покажет подтверждающее сообщение, когда процесс форматирования завершится.
2. Затем проверьте изменение файловой системы, используя:
3. Найдите нужный раздел и убедитесь, что он использует файловую систему NFTS.
Монтирование раздела диска в Linux
Перед использованием диска создайте точку монтирования и смонтируйте к ней раздел. Точка монтирования — это каталог, используемый для доступа к данным, хранящимся на дисках.
1. Создайте точку монтирования, введя:
2. После этого смонтируйте раздел с помощью следующей команды:
sudo mount -t auto /dev/sdb1 [mountpoint]
Если процесс завершился успешно, вывода нет.
![sudo mount -t auto /dev/sdb1 [mountpoint]](https://wiki.merionet.ru/images/kak-otformatirovat-razdely-diska-v-linux/7.png)
3. Убедитесь, что раздел смонтирован, используя следующую команду:
Понимание файловой системы Linux
Выбор правильной файловой системы перед форматированием диска для хранения имеет решающее значение. Каждый тип файловой системы имеет разные ограничения размера файла или разную совместимость с операционной системой.
Наиболее часто используемые файловые системы: FAT32, NTFS и ext4
Их основные особенности и отличия:
| Файловая система | Поддерживаемый размер файла | Совместимость | Идеальное использование |
| FAT32 | до 4 ГБ | Windows, Mac, Linux | Для максимальной совместимости |
| NTFS | 16 EiB — 1 КB | Windows, Mac (только для чтения), большинство дистрибутивов Linux | Для внутренних дисков и системного файла Windows |
| Ext4 | 16 GiB — 16 TiB | Windows, Mac, Linux (для доступа требуются дополнительные драйверы) | Для файлов размером более 4 ГБ |