- Free linux for mobile
- What others say
- Architecture
- AnLinux: простой способ установить Linux-окружение на Android-телефон без рута
- Что такое AnLinux?
- С чего начать?
- Что же, приступим
- А что с графической оболочкой?
- Distributions offering Plasma Mobile
- Mobile
- Manjaro ARM
- Download
- Installation
- postmarketOS
- Download
- Nightly Builds
- Arch Linux ARM
- Download
- openSUSE
- Download
- Fedora
- Debian
- Desktop Devices
- Fedora
- postmarketOS
- Arch Linux
- Manjaro
- Download
- KDE Neon
- KDE Patrons
- Donate to KDE Why Donate?
- Visit the KDE MetaStore
Free linux for mobile
PINE64 PinePhone
We are sick of not receiving updates shortly after buying new phones. Sick of the walled gardens deeply integrated into Android and iOS. That’s why we are developing a sustainable, privacy and security focused free software mobile OS that is modeled after traditional Linux distributions. With privilege separation in mind. Let’s keep our devices useful and safe until they physically break! What is the current state of postmarketOS? Where can I download the latest release? Which devices run postmarketOS? How do I port my device?
What others say
Samsung Galaxy S II
— Drew DeVault, FLOSS pioneer and creator of Sourcehut and Sway
«[postmarketOS] is my personal favourite. It has a true stable channel where only select tested packages get updated to make sure it’s always a solid, reliable and stable experience.»
«With the widespread move to mobile devices, users lose control over their computing devices. PostmarketOS gives us the ability to run code that we can read and modify on these devices.»
Architecture
We avoid Android’s build system entirely. Instead of building a monolithic system image for each and every device, the whole OS is divided into small packages. These same package binaries can be installed on all devices that share the same CPU architecture. Device specific parts are kept as minimal as possible, ideally there is only one device package. In practice there is often the downstream Linux kernel too, but we are replacing those with Mainline wherever possible. In the spirit of most other Linux distributions, multiple user interfaces from independent projects are packaged for postmarketOS, such as Plasma Mobile, Phosh and Sxmo.
OnePlus 6
postmarketOS is based on Alpine Linux, which is so tiny (less than 10 MB in size) that development of pmOS can be done quickly on any Linux distribution. We install Alpine in multiple chroots to cross compile packages, build and flash postmarketOS, run it in a VM with QEMU or interactively port new hardware. All with our lightweight Python program pmbootstrap, without installing anything on the host system. Writing packages is easy, by the way: as long as you know how to write shell scripts, you are good to go. We have continuous integration in place that makes sure everything builds that gets submitted to our packages repository, among other sanity checks.
The above design decisions make it feasible to keep the system up-to-date, for all devices at once! Compared to Android, it makes development more efficient and democratic: you don’t need to afford a powerful and expensive PC to rebuild the entire OS. Just build the tiny part that you are interested in modifying.
Speaking of modifying, due to the free software nature of the project, you can change pretty much everything. We don’t even require running proprietary Android userspace drivers. In fact all proprietary components (even the WLAN, cellular modem and bluetooth firmware) can be excluded if building your own image with pmbootstrap.
AnLinux: простой способ установить Linux-окружение на Android-телефон без рута
Любой телефон или планшет, работающий на Android, — это устройство, которое управляется ОС Linux. Да, очень модифицированной ОС, но все же основа Android — ядро Linux. Но, к сожалению, для большинства телефонов опция «снести Android и поставить дистрибутив по своему вкусу» недоступна.
Поэтому, если хочется Linux на телефоне, приходится покупать специализированные гаджеты вроде PinePhone, о котором мы уже писали в одной из статей. Но есть еще один способ получить Linux-окружение практически на любом смартфоне, причем без root-доступа. Поможет в этом инсталлятор, который называется AnLinux.
Что такое AnLinux?
Это специализированное ПО, которое дает возможность использовать Linux на телефоне при помощи монтирования образа, содержащего root-файловую систему любого из дистрибутивов, включая Ubuntu, Kali, Fedora, CentOS, OpenSuse, Arch, Alpine и многих других. Инсталлятор использует PRoot для эмуляции root-доступа.
PRoot перехватывает все выполняемые пользователем вызовы, которые требуют в обычной ситуации root-доступа, и обеспечивает их работоспособность в обычных условиях. В PRoot используется системный вызов ptrace для отладки ПО, который помогает достичь цели. С PRoot все это можно сделать как с chroot, но без root-прав. Кроме того, PRoot предоставляет фейковый доступ пользователю для пседвофайловой системы.
AnLinux — небольшая программа. Но этого достаточно, ведь единственное ее предназначение — установка образов систем и запуск скриптов, поднимающих пользовательское окружение. Когда все сделано, пользователь получает вместо смартфона Linux-ПК, причем Android продолжает работать на фоне. Подключаемся к устройству при помощи VNC-вьювера или терминала, и можно работать.
Конечно, это не идеальный вариант «завести» Linux на смартфоне, но он вполне рабочий.
С чего начать?
Основное — Android-смартфон с версией ОС не ниже Lollipop. Кроме того, пойдет и 32-битное или 64-битное ARM или x86-устройство. Кроме того, потребуется солидный объем свободного файлового пространства. Для этого можно использовать карту памяти или просто устройство с большим объемом внутренней памяти.
- AnLinux (вот ссылка на Google Play).
- Termux (снова понадобится Google Play).
- VNC Client (VNC Viewer — хороший вариант).
- Bluetooth-клавиатура (опционально).
- Bluetooth-мышь (опционально).
- HDMI кабель для мобильного телефона (опционально).
Что же, приступим
Как только установлен Termux, получаем полноценную консоль. Да, рута нет (если телефон не рутован), но ничего страшного. Следующий шаг — установка образа для дистрибутива Linux.
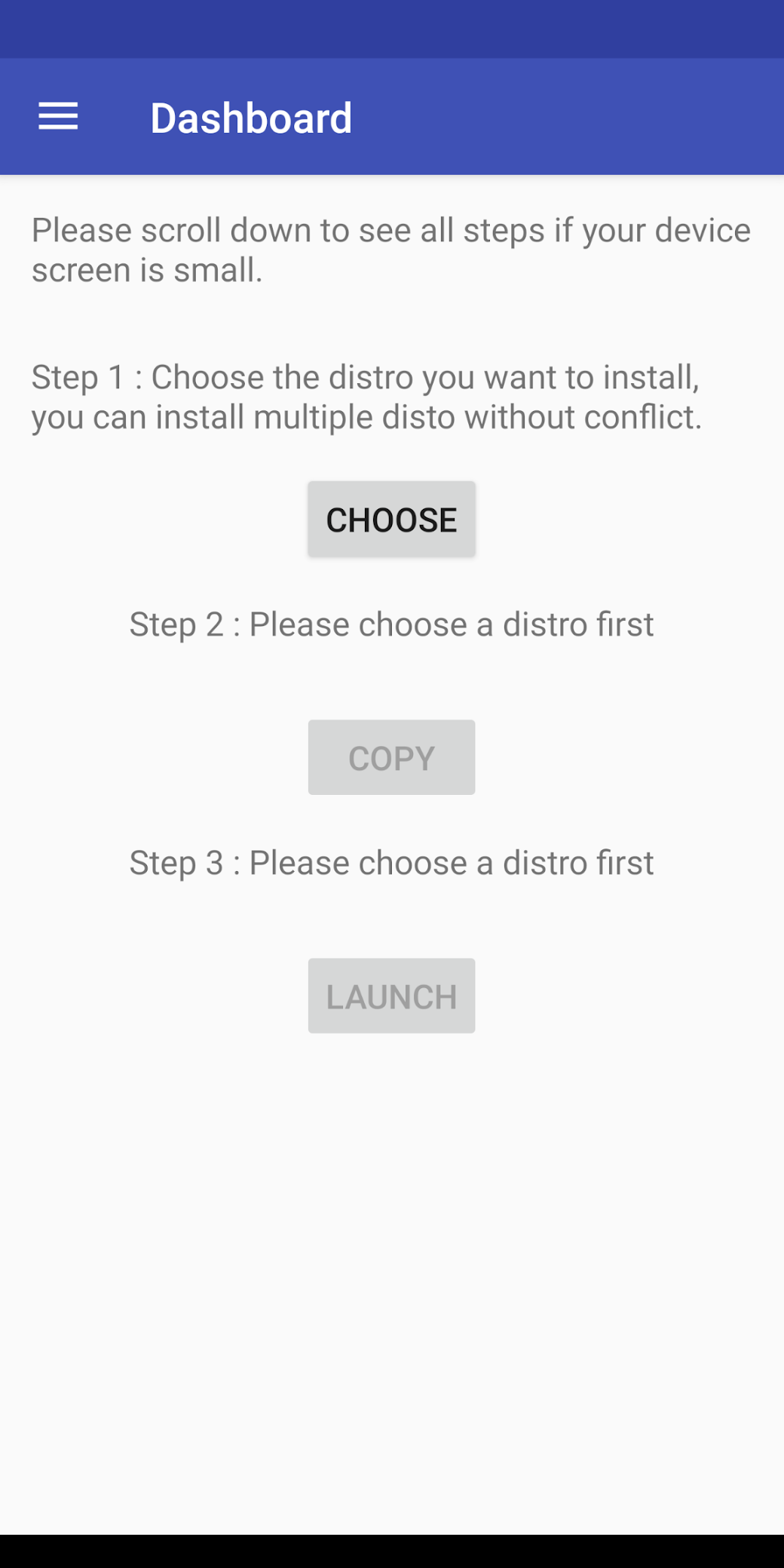
Теперь нужно открыть AnLinux и затем — выбрать Dashboard из меню. Всего есть три кнопки, но выбрать можно лишь одну, первую. После этого появляется меню выбора дистрибутива. Можно выбрать даже не один, а несколько, но в этом случае понадобится большой объем свободного файлового пространства.
После выбора дистрибутива активируются две другие кнопки. Вторая позволяет загрузить в буфер обмена команды, необходимые для загрузки и установки Linux. Обычно это pkg, wget команды и скрипт для их выполнения.
Третья кнопка запускает Termux, так что команды можно вставлять в консоль. Как только все сделано, запускается скрипт, позволяющий загрузить окружение дистрибутива. Для вызова дистрибутива нужно каждый раз запускать скрипт, но установку проводим только один раз.
А что с графической оболочкой?
Если она нужна, то следует лишь выбрать меню для десктопного окружения и использовать больше кнопок — появится не три, а больше. Кроме самого дистрибутива, нужно выбрать еще и оболочку, например, Xfce4, Mate, LXQt или LXDE. В целом, ничего сложного.
Потом кроме скрипта, который запускает дистрибутив, потребуется еще один — он активирует сервер VNC. В целом, весь процесс простой и понятный, он вряд ли способен вызвать затруднения.
После запуска сервера VNC подключаемся со стороны клиента, воспользовавшись вьювером. Требуется знать порт и localhost. Все это сообщает скрипт. Если все сделано правильно, то пользователь получает доступ к своей виртуальной Linux-системе. Производительность современных телефонов на высоте, так что особых проблем не будет. Конечно, вряд ли смартфон сможет полностью заменить десктоп, но, в целом, все это работает.
Этот способ может пригодиться, если вдруг нужно срочно подключиться к серверу, а вы в машине, без ноутбука (конечно, в этом случае все описанные выше операции с AnLinux уже должны быть выполнены). Виртуальная Linux-машина позволяет подключиться к рабочему или домашнему серверу. А если в автомобиле по какой-то причине оказался дисплей и беспроводная клавиатура, то за считанные секунды в салоне можно организовать рабочий кабинет.
Distributions offering Plasma Mobile
Listed below are distributions that ship Plasma Mobile.
Please check the information for each distribution to see if your device is supported.
Mobile
Manjaro ARM
Manjaro ARM is the Manjaro distribution, but for ARM devices. It’s based on Arch Linux ARM, combined with Manjaro tools, themes and infrastructure to make install images for your ARM device.
Download
Installation
For the PinePhone, you can find generic information on Pine64 wiki.
postmarketOS
PostmarketOS (pmOS), is a touch-optimized, pre-configured Alpine Linux that can be installed on smartphones and other mobile devices. View the device list to see the progress for supporting your device.
For devices that do not have prebuilt images, you will need to flash it manually using the pmbootstrap utility. Follow instructions here. Be sure to also check the device’s wiki page for more information on what is working.
Download
Nightly Builds
Sineware Plasma Mobile Nightly provides an unofficial Alpine repository and PinePhone/PinePhone Pro images, built nightly from git main/master.
Arch Linux ARM
Arch Linux ARM has been ported to the PinePhone and PineTab by the DanctNIX community.
Download
openSUSE
openSUSE, formerly SUSE Linux and SuSE Linux Professional, is a Linux distribution sponsored by SUSE Linux GmbH and other companies. Currently openSUSE provides Tumbleweed based Plasma Mobile builds.
Download
Fedora
This is a work in progress, stay tuned!
Join the Fedora Mobility matrix channel to get details on the progress.
Links to testing images can be found in the channel.
Debian
Debian does not package Plasma Mobile packages.
However, you can install Mobian and follow the instructions to add a 3rd party repo providing Plasma Mobile packages here.
Desktop Devices
Fedora
Fedora has Plasma Mobile and related applications packaged in their repositories.
postmarketOS
postmarketOS is able to be run in QEMU, and thus is a suitable option for trying Plasma Mobile on your computer.
Read more about it here. During the setup process, simply select Plasma Mobile as the desktop environment.
Arch Linux
Plasma Mobile is available on the AUR.
Manjaro
Manjaro builds x64 images for use on desktop.
Download
KDE Neon
WARNING: This is not actively maintained!
This image, based on KDE neon, can be tested on non-android intel tablets, PCs and virtual machines.
KDE Patrons



Donate to KDE Why Donate?
Visit the KDE MetaStore
Show your love for KDE! Purchase books, mugs, apparel, and more to support KDE.
Maintained by KDE Webmasters (public mailing list). Generated from 3426021. KDE ® and the K Desktop Environment ® logo are registered trademarks of KDE e.V. | Legal