- FTP Server
- vsftpd — FTP Server Installation
- Anonymous FTP Configuration
- User Authenticated FTP Configuration
- Securing FTP
- References
- Как настроить FTP на Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
- Установка FTP-сервера
- Защита передачи данных при помощи SSL/TLS
- Настройка учётной записи FTP-пользователя
- Настройка брандмауэра
- Проверка подключения к FTP-серверу
FTP Server
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a TCP protocol for downloading files between computers. In the past, it has also been used for uploading but, as that method does not use encryption, user credentials as well as data transferred in the clear and are easily intercepted. So if you are here looking for a way to upload and download files securely, see the OpenSSH documentation instead.
FTP works on a client/server model. The server component is called an FTP daemon. It continuously listens for FTP requests from remote clients. When a request is received, it manages the login and sets up the connection. For the duration of the session it executes any of commands sent by the FTP client.
Access to an FTP server can be managed in two ways:
In the Anonymous mode, remote clients can access the FTP server by using the default user account called “anonymous” or “ftp” and sending an email address as the password. In the Authenticated mode a user must have an account and a password. This latter choice is very insecure and should not be used except in special circumstances. If you are looking to transfer files securely see SFTP in the section on OpenSSH-Server. User access to the FTP server directories and files is dependent on the permissions defined for the account used at login. As a general rule, the FTP daemon will hide the root directory of the FTP server and change it to the FTP Home directory. This hides the rest of the file system from remote sessions.
vsftpd — FTP Server Installation
vsftpd is an FTP daemon available in Ubuntu. It is easy to install, set up, and maintain. To install vsftpd you can run the following command:
Anonymous FTP Configuration
By default vsftpd is not configured to allow anonymous download. If you wish to enable anonymous download edit /etc/vsftpd.conf by changing:
During installation a ftp user is created with a home directory of /srv/ftp . This is the default FTP directory.
If you wish to change this location, to /srv/files/ftp for example, simply create a directory in another location and change the ftp user’s home directory:
sudo mkdir -p /srv/files/ftp sudo usermod -d /srv/files/ftp ftp After making the change restart vsftpd:
sudo systemctl restart vsftpd.service Finally, copy any files and directories you would like to make available through anonymous FTP to /srv/files/ftp , or /srv/ftp if you wish to use the default.
User Authenticated FTP Configuration
By default vsftpd is configured to authenticate system users and allow them to download files. If you want users to be able to upload files, edit /etc/vsftpd.conf :
sudo systemctl restart vsftpd.service Now when system users login to FTP they will start in their home directories where they can download, upload, create directories, etc.
Similarly, by default, anonymous users are not allowed to upload files to FTP server. To change this setting, you should uncomment the following line, and restart vsftpd:
Warning
Enabling anonymous FTP upload can be an extreme security risk. It is best to not enable anonymous upload on servers accessed directly from the Internet.
The configuration file consists of many configuration parameters. The information about each parameter is available in the configuration file. Alternatively, you can refer to the man page, man 5 vsftpd.conf for details of each parameter.
Securing FTP
There are options in /etc/vsftpd.conf to help make vsftpd more secure. For example users can be limited to their home directories by uncommenting:
You can also limit a specific list of users to just their home directories:
chroot_list_enable=YES chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd.chroot_list After uncommenting the above options, create a /etc/vsftpd.chroot_list containing a list of users one per line. Then restart vsftpd:
sudo systemctl restart vsftpd.service Also, the /etc/ftpusers file is a list of users that are disallowed FTP access. The default list includes root, daemon, nobody, etc. To disable FTP access for additional users simply add them to the list.
FTP can also be encrypted using FTPS. Different from SFTP, FTPS is FTP over Secure Socket Layer (SSL). SFTP is a FTP like session over an encrypted SSH connection. A major difference is that users of SFTP need to have a shell account on the system, instead of a nologin shell. Providing all users with a shell may not be ideal for some environments, such as a shared web host. However, it is possible to restrict such accounts to only SFTP and disable shell interaction.
To configure FTPS, edit /etc/vsftpd.conf and at the bottom add:
Also, notice the certificate and key related options:
rsa_cert_file=/etc/ssl/certs/ssl-cert-snakeoil.pem rsa_private_key_file=/etc/ssl/private/ssl-cert-snakeoil.key By default these options are set to the certificate and key provided by the ssl-cert package. In a production environment these should be replaced with a certificate and key generated for the specific host. For more information on certificates see Security — Certificates.
Now restart vsftpd, and non-anonymous users will be forced to use FTPS:
sudo systemctl restart vsftpd.service To allow users with a shell of /usr/sbin/nologin access to FTP, but have no shell access, edit /etc/shells adding the nologin shell:
# /etc/shells: valid login shells /bin/csh /bin/sh /usr/bin/es /usr/bin/ksh /bin/ksh /usr/bin/rc /usr/bin/tcsh /bin/tcsh /usr/bin/esh /bin/dash /bin/bash /bin/rbash /usr/bin/screen /usr/sbin/nologin This is necessary because, by default vsftpd uses PAM for authentication, and the /etc/pam.d/vsftpd configuration file contains:
auth required pam_shells.so The shells PAM module restricts access to shells listed in the /etc/shells file.
Most popular FTP clients can be configured to connect using FTPS. The lftp command line FTP client has the ability to use FTPS as well.
References
Как настроить FTP на Ubuntu 20.04 LTS
FTP – это протокол, который позволяет передавать файлы по сети от одного узла другому. Данный протокол является самым старым протоколом прикладного уровня, который появился намного раньше, чем HTTP или TCP/IP. С помощью протокола FTP могут быть организованы соединения с удаленными серверами для просмотра и передачи необходимых данных. При подключении к серверам и рабочим станциям при помощи протокола FTP необходимо использовать специальные приложения, которые именуются FTP-клиентами. Далее о том, как настроить работу с протоколом FTP на сервере, работающем под управлением Ubuntu 20.04 LTS.
Для того чтобы развернуть свой FTP-сервер на Ubuntu 20.04 LTS, необходимо:
- установить FTP-сервер с поддержкой SSL для безопасного подключения;
- настроить учетную запись FTP-пользователя;
- проверить подключение к FTP-серверу.
Установка FTP-сервера
Как всегда при работе с Ubuntu необходимо произвести первоначальную настройку сервера в соответствии с посвящённой данной процедуре статье. Далее следует обновить списки пакетов:
После чего необходимо установить программу vsftpd :
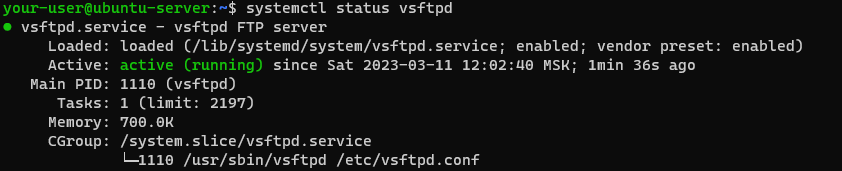
По окончании установки можно убедиться, что сервис vsftpd уже успешно работает:
Далее необходимо произвести некоторые настройки в конфигурационном файле. Для этого откройте при помощи текстового редактора файл vsftpd.conf :
Вот те основные изменения, которые необходимо внести для корректной работы FTP-сервера:
listen=YES listen_ipv6=NO anonymous_enable=NO local_enable=YES write_enable=YES dirmessage_enable=YES use_localtime=YES xferlog_enable=YES connect_from_port_20=YES xferlog_std_format=YES chroot_local_user=YES secure_chroot_dir=/var/run/vsftpd/empty pam_service_name=vsftpd allow_writeable_chroot=YESПосле внесения изменений в файл настроек необходимо сохранить их и перезапустить службу vsftpd :
$ sudo systemctl restart vsftpdЗащита передачи данных при помощи SSL/TLS
Для защиты передачи ваших данных между FTP-клиентом и FTP-сервером в данной инструкции мы будем использовать генерацию самозаверяющего SSL-сертификата. Закрытый ключ и сертификат будут сохранены в одном файле, для чего следует применить команду:
$ sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 3650 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/ssl/private/vsftpd.pem -out /etc/ssl/private/vsftpd.pemПосле установки SSL-сертификата необходимо внести изменения в конфигурационный файл:
А именно, внесите изменения в следующие строки данного файла:
rsa_cert_file=/etc/ssl/private/vsftpd.pem rsa_private_key_file=/etc/ssl/private/vsftpd.pem ssl_enable=YESНастройка учётной записи FTP-пользователя
Для авторизации на FTP-сервере необходимо создать учетную запись пользователя. Изначально, подключаться к серверу можно и под локальным пользователем. Но более целесообразно для этих целей использовать специальную учётную запись. Для её создания используйте следующую команду:
Таким образом, у нас теперь есть пользователь ftpuser . Следующей командой нужно создать для него домашний каталог:
$ sudo mkhomedir_helper ftpuserПосле этого для него необходимо создать пароль на вход:
Настройка брандмауэра
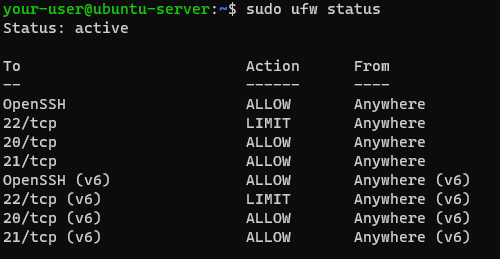
Если вы производили работы по первоначальной настройке виртуального сервера, то на нём должен быть запущен межсетевой экран UFW. Соответственно, для того, чтобы брандмауэр вашего VPS позволял осуществлять подключения, необходимо внести небольшие изменения в настройки UFW. Проще говоря, нужно будет добавить в брандмауэр исключения для TCP-портов 20 и 21. Делается это следующими командами:
$ sudo ufw allow 20/tcp $ sudo ufw allow 21/tcpПосле чего брандмауэр следует перезапустить:
$ sudo ufw disable $ sudo ufw enableИ убедиться, что служба работает без ошибок:
Проверка подключения к FTP-серверу
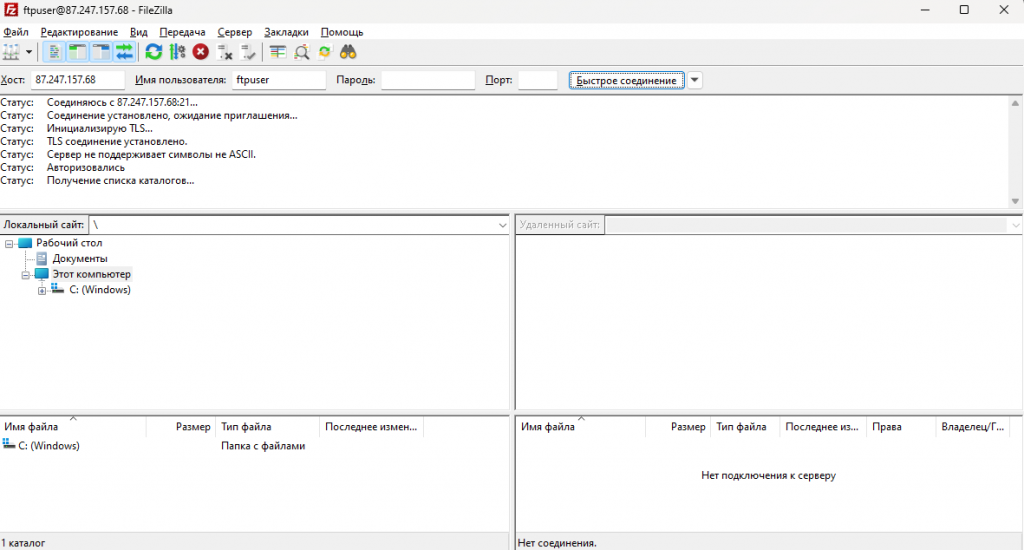
Корректность произведённых настроек можно проверить через осуществление подключения к FTP-серверу. Для этой цели можно воспользоваться бесплатным FTP-клиентом FileZilla. После запуска приложения в FileZilla следует заполнить поля Хост и Имя пользователя . После нажатия кнопки Быстрое соединение система попросит ввести пароль учётной записи, под именем которой происходит подключение к FTP-серверу.
Подключение к серверу осуществлено успешно, значит произведенные настройки в конфигурационном файле корректны. В статусе подключения видно, что в данной сессии TLS соединение установлено , значит передача данных между клиентом и сервером шифруются.