- Linux Gaming with Ubuntu Desktop Part 1: Steam & Proton
- Installing Steam on Ubuntu Desktop
- Native vs Steam Play
- What is Proton?
- Check your games on ProtonDB (or contribute your experiences)!
- Why Ubuntu Desktop is great for Linux gaming
- Talk to us today
- Как настроить Ubuntu для игр
- Шаг 1. Установка драйверов видеокарты
- Для видеокарт nVidia:
- Для видеокарт AMD/Intel:
- Шаг 2. Установка последней версии Wine
- Шаг 3. Установка последней версии Lutris
- Шаг 4. Установка и настройка Steam
- Шаг 5. Включение игрового режима
- Добавить комментарий
Linux Gaming with Ubuntu Desktop Part 1: Steam & Proton
A few years before joining Canonical as the Ubuntu Desktop Product Manager, I was a video game producer (with at least one of my titles getting a native Linux port you’ll be pleased to hear). So improving the gaming experience on Ubuntu is high on my to-do list. With the Linux user base on Steam breaking the 1% ceiling earlier this year- which may or may not be related to the upcoming Linux-based Steam Deck– 2022 is shaping up to be a great year for Linux gaming!
In the first of a mini-series of blogs, I wanted to break down some of the easiest ways to get started with gaming on Ubuntu. With part 1 we start with the obvious; Steam (and Proton).
Installing Steam on Ubuntu Desktop
You can find Steam in the Ubuntu Software app with a quick search, or alternatively install it from the command line with:
Native vs Steam Play
Since Linux gamers are not exactly the dominant demographic in PC gaming, there aren’t that many titles that are developed explicitly for us. Filtering by Linux in the steam store produces around 9,000 results at the time of writing.
That’s not a small number by any means, and while it only represents 15% of all the games available on Steam, it does include some of the most popular PC games of all time. More than enough to get started gaming on Linux!
However, Steam also features a secret weapon – Steam Play. A feature that auto-installs compatibility tools that enable you to play titles that were built for other operating systems.
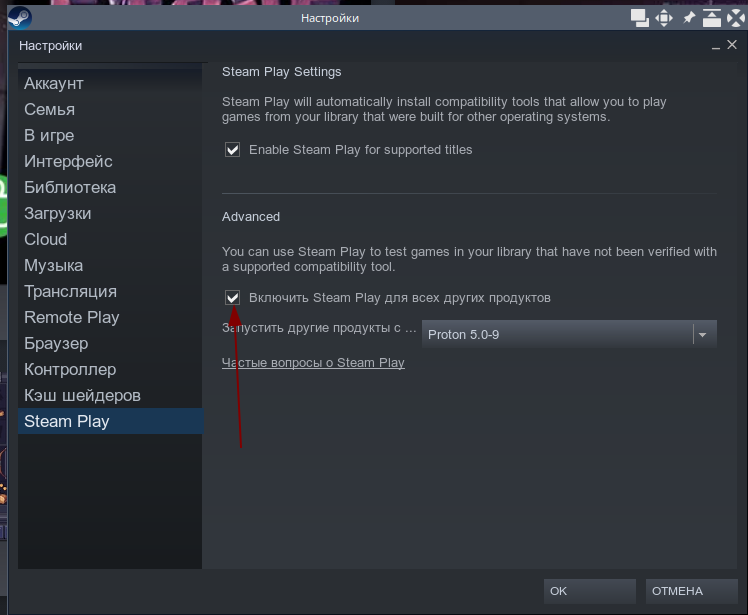
You can activate Steam Play (if it’s not active already) by going to Steam -> Settings -> Steam Play and checking Enable Steam Play for supported titles and Enable Steam Play for all other titles.
By doing this you’ll see that games previously unsupported on Linux become playable.
Here is one of my favourite games before Steam Play.
(Don’t judge my playtime, I was mostly playing the previous HD edition!)
Is this magic? No, it’s Proton.
What is Proton?
Proton is a compatibility layer built into Steam, it translates Windows APIs into a Linux readable format. This works differently to a traditional emulator approach to gaming (where you might run a virtual Windows machine and play games inside it) since it enables you to fully leverage the benefits of your PC’s hardware. This results in comparable performance to a native build of the game.
Proton is open source and based on a fork of Wine (Wine Is Not an Emulator) which has been in development for around 28 years. Whilst it’s currently in beta and not all Windows titles run successfully via Proton, Valve are heavily promoting Proton support to developers as a way of enabling Steam Deck compatibility. Because of this, we should expect the library of Linux playable titles to increase dramatically over the next year, whether you own a Steam Deck or not!
Check your games on ProtonDB (or contribute your experiences)!
To check whether your favourite game is playable via Proton, you can visit protondb.com. ProtonDB is a site that aggregates gamers’ experiences into an easy-to-view database that lets you look up how well a title performs on Linux.
Currently, there have been close to 150,000 reports submitted, resulting in 17,000 titles confirmed to run well. Whilst this includes games that already included native Linux support, it still roughly doubles the catalogue of available games on Linux. And that percentage is heavily weighted towards the more popular titles on the store.
You can search for games in your library from the home page or link your Steam Account to see the status of all of them in one go. Once linked, you can also contribute your experiences to ProtonDB by filling in a short survey. If your favourite game is currently missing from ProtonDB try it out and let them know how it works!
Note: To contribute to ProtonDB you need to set your profile and games library to public in your profile privacy settings on Steam. In addition you will be asked to provide your system information.
Why Ubuntu Desktop is great for Linux gaming
As the world’s most popular Linux desktop, Ubuntu is often the target platform for native Linux game developers. But it’s also the most common distribution for ProtonDB testing. We feel confident that by gaming on Ubuntu you’ll be getting the most out of your Steam library.
But we don’t want to get complacent, we know there is still a lot more we can do to improve the gaming experience on Ubuntu Desktop. We’re keen to hear from you on the issues or areas we should focus on in 2022.
To accompany this blog series I’ve started a thread in the Ubuntu Desktop Discourse to gather feedback and ideas. Let us know what you think!
You can download Ubuntu Desktop here.
Talk to us today
Interested in running Ubuntu in your organisation?
Как настроить Ubuntu для игр
С ростом популярности Ubuntu в частности и Linux в целом всё более доступными становятся игры на Linux, даже те, которые официально поддерживаются только на Windows. Сегодня мы расскажем, как превратить машину с Ubuntu 20.04 в игровую станцию.
Перед началом необходимо выполнить обновление всех компонентов системы, для этого выполните:
$ sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -yПри необходимости (если попросит система), перезагрузите компьютер по завершении выполнения этих команд.
Шаг 1. Установка драйверов видеокарты
Сначала нужно установить проприетарные драйвера видеокарты с поддержкой GPU. Тип драйвера будет зависеть от установленной видеокарты.
Для видеокарт nVidia:
Добавьте репозиторий с драйверами и установите драйвера и библиотеку Vulkan:
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:graphics-drivers/ppa $ sudo apt install nvidia-driver-440 libnvidia-gl-440 libnvidia-gl-440:i386 $ sudo apt install libvulkan1 libvulkan1:i386По завершении работы команд перезагрузите компьютер.
Для видеокарт AMD/Intel:
Добавьте возможность устанавливать 32-разрядные приложения и установите драйвера видеокарты и библиотеку Vulkan для них:
$ sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386 $ sudo apt install libgl1-mesa-dri:i386 $ sudo apt install mesa-vulkan-drivers mesa-vulkan-drivers:i386По завершении работы команд перезагрузите компьютер.
Шаг 2. Установка последней версии Wine
Поскольку большинство игр, к сожалению, продолжают выпускаться только на Windows, необходимо установить эмулятор Wine. Для этого выполняем следующие команды:
$ sudo dpkg --add-architecture i386 $ wget -nc https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/winehq.key $ sudo apt-key add winehq.key $ sudo apt-add-repository 'deb https://dl.winehq.org/wine-builds/ubuntu focal main' $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install --install-recommends wine-staging $ sudo apt-get install libgnutls30:i386 libldap-2.4-2:i386 libgpg-error0:i386 libxml2:i386 libasound2-plugins:i386 libsdl2-2.0-0:i386 libfreetype6:i386 libdbus-1-3:i386 libsqlite3-0:i386После установки Wine перезагрузка не требуется.
Шаг 3. Установка последней версии Lutris
Игровой клиент Lutris позволяет автоматизировать сценарии установки игр под Linux. Для его установки выполните следующие команды:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:lutris-team/lutrissudo apt-get updatesudo apt-get install lutris
Шаг 4. Установка и настройка Steam
Если вы игрок, вам не нужно объяснять, что такое Steam и зачем он нужен. Установить Steam в Ubuntu проще простого, для этого выполните команду:
sudo apt-get install steamПосле установки откройте Steam, зайдите в свой аккаунт, перейдите в меню Steam — Настройки, в разделе Steam Play установите флажок «Включить Steam Play для всех других продуктов», чтобы включить поддержку эмулятора Proton для всех игр:
После этого нужно будет перезапустить Steam.
Шаг 5. Включение игрового режима
В Ubuntu 20.04 появился игровой режим. Запущенное в этом режиме приложение позволяет переводить процессоры CPU и GPU в режим повышенной производительности (т.е. фактически отключает режим экономии энергии).
По умолчанию gamemode установлен в Ubuntu 20.04, но если этого пакета нет, его можно установить командой:
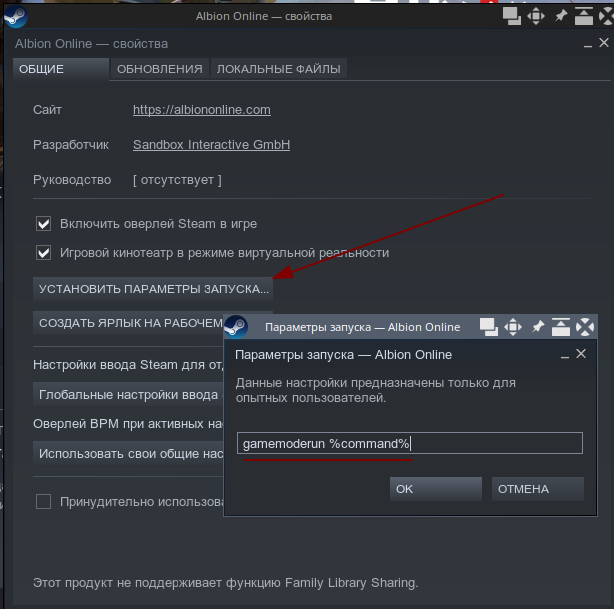
sudo apt-get install gamemodeДля того, чтобы запускать приложения в игровом режиме, зайдите в библиотеку Steam, нажмите правой кнопкой мыши на названии игры и выберите «Свойства».
В открывшемся окне нажмите кнопку «Установить параметры запуска», а собственно в параметрах запуска укажите команду
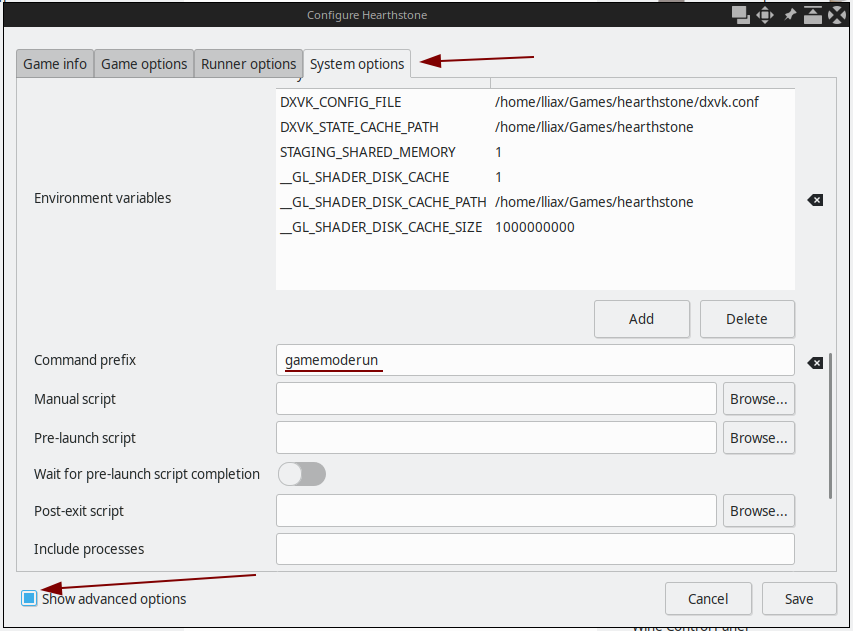
Для задания запуска в игровом режиме в Lutris нажмите на игре правой кнопкой мыши, в меню выберите Configure:
В открывшемся окне перейдите на вкладку System options, установите флажок Show advanced options в нижней части, а затем введите gamemoderun в поле Command prefix.
Добавить комментарий
Этот сайт использует Akismet для борьбы со спамом. Узнайте, как обрабатываются ваши данные комментариев.