- Installing the GNU C compiler and GNU C++ compiler
- Installing the GNU Java compiler
- Installing the GNU Fortran compilers
- Installing the GNU autotools
- 32-bit Builds on AMD64
- Installing the Intel Compiler Suite Professional Edition 10.x
- Get the License Number and Extract to a path without spaces
- On 64-bit systems you may also need to issue these commands
- Run the Installation Script
- Edit /etc/bash.bashrc to add the installation path to the PATH environment variable
- Installing the X11 development compilers
- Установка GCC в Ubuntu
- Набор компиляторов GCC
- Установка GCC в Ubuntu
- Использование GCC в Ubuntu
- Выводы
Installing the GNU C compiler and GNU C++ compiler
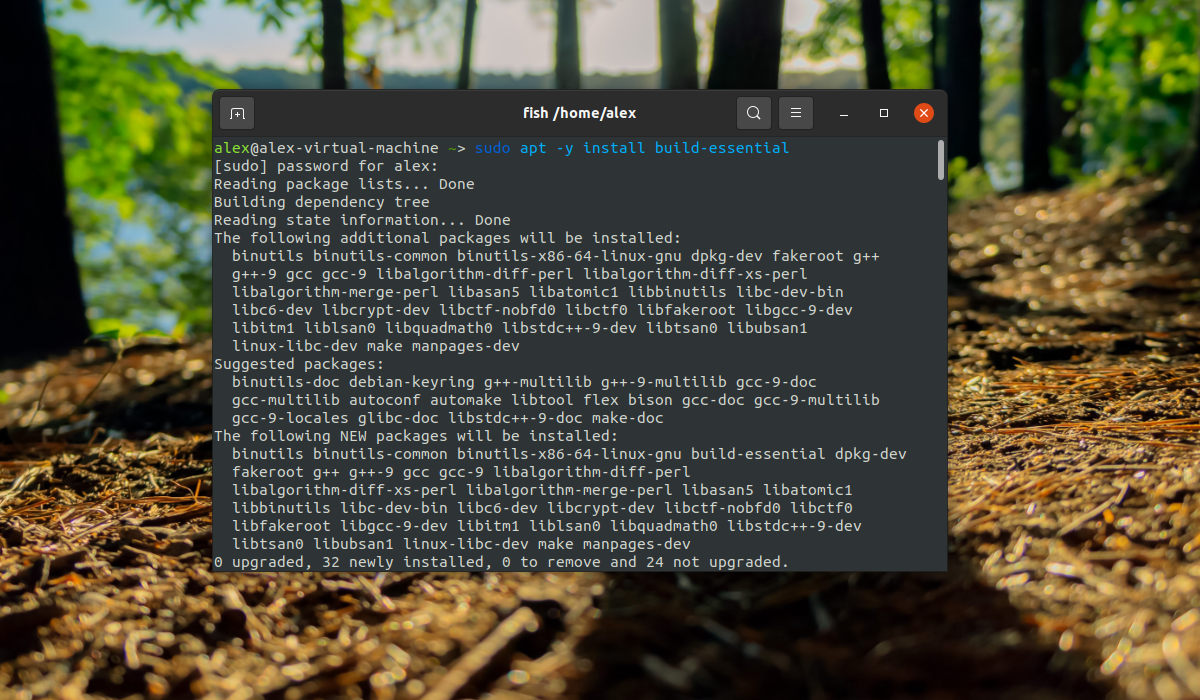
To install the gcc and g++ compilers, you will need the build-essential package. This will also install GNU make.
build-essential contains a list of packages which are essential for building Ubuntu packages including gcc compiler, make and other required tools.
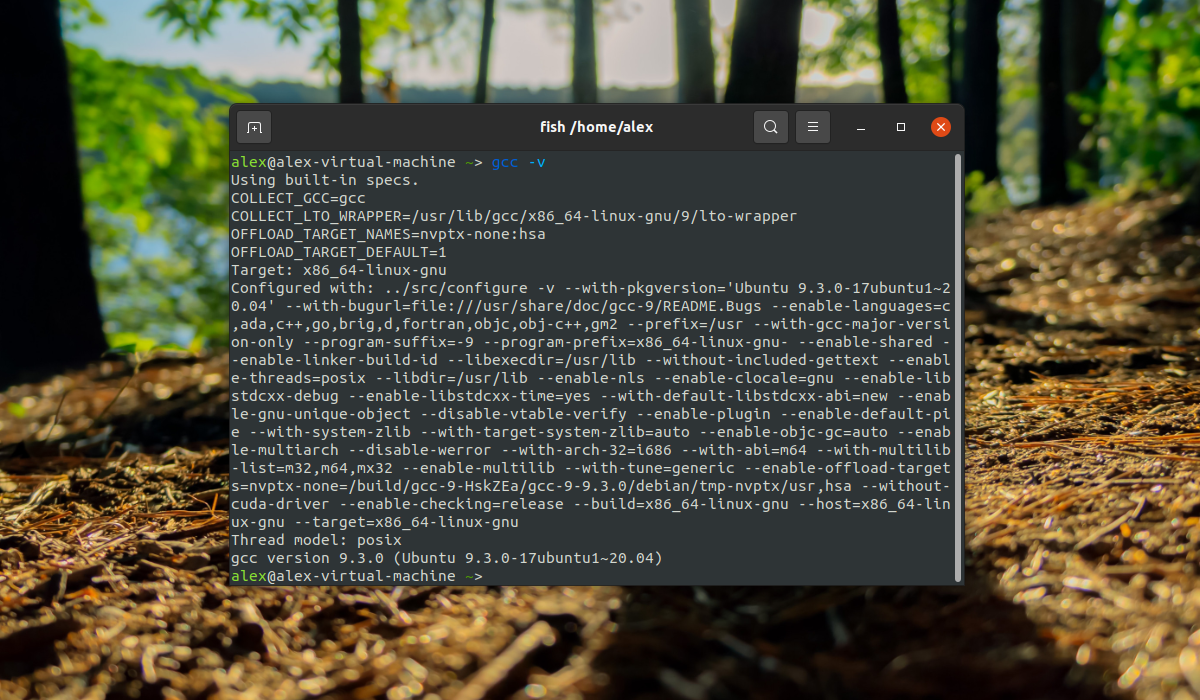
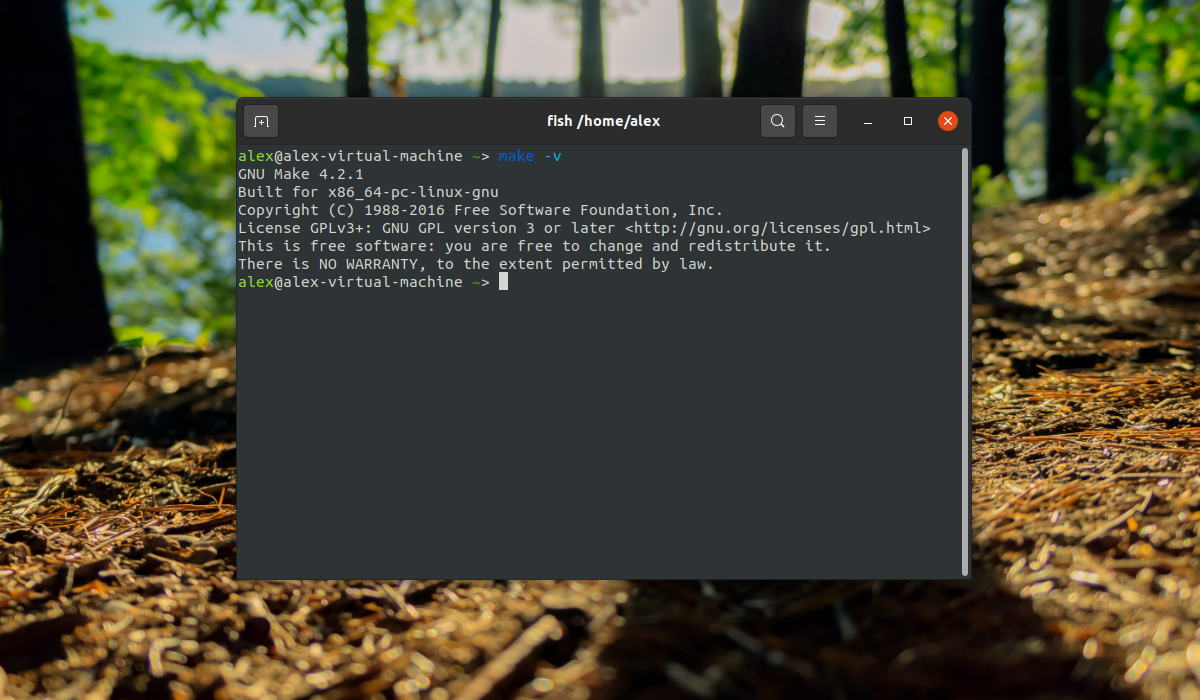
$ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get upgrade $ sudo apt-get install build-essential $ gcc -v $ make -v
Now, you should able to compile software using C / C++ compilers.
To install the manpages for c and c++ development, install the manpages-dev package.
Installing the GNU Java compiler
Note that GNU’s Java compiler is not the same as the one developed and distributed by Sun Microsystems, and will not provide Java to the firefox browser. For that, please see Java. To install gcj, the GNU Java compiler, install the following package: gcj.
To install the GNU Java bytecode interpreter, you need the gij package.
To have gcj compile to executables, install libgcj6-dev (otherwise an error during compilation occurs: libgcj.spec: No such file or directory). Use synaptic to install libgcj6-dev.
Installing the GNU Fortran compilers
To install the GNU Fortran 77 compiler — g77, you need the g77 package.
To install the GNU Fortran 95 compiler — gfortran, the package is: gfortran.
Installing the GNU autotools
To install autoconf and automake, you need the autoconf and automake packages.
Apt-get will tell you to explicitly choose a version of automake. If, for example, you decide to use automake1.9, you need to specify the version, such as the automake1.9 package.
32-bit Builds on AMD64
The GNU compilers have options that allow them to create 32-bit object and executable files on 64-bit operating systems, and vica versa. The critical options are -m32 (to build 32-bit) and -m64 (to build 64-bit).
These options will be present when you install the compiler of your choice. However, they won’t actually work unless you install several additional packages.
The first thing you will need is the multilib package for the compiler you are using. For example, to add multilib support to the default version of g++ (4.1 in gutsy), you would install
The multilib packages are compiler runtime packages. Now, you need 32-bit (or 64-bit) versions of whatever libraries you need to link your application program. 64-bit packages have names that start with lib64. Install these on 32-bit systems to support 64-bit builds. 32-bit packages have names that start with lib32. Install these on 64-bit systems to support 32-bit builds. Whatever else you are doing, you will probably need . If you are using g++, you will need
Installing the Intel Compiler Suite Professional Edition 10.x
- gcc, build-essential, libc6-dev (see above)
- ia32-libs, g++-multilib, and libc6-dev-i386 (for 64-bit systems)
- 32-bit packages starting with lib32 (for 64-bit systems)
- alien and rpm for installing the RPM packages that Intel distributes.
- libstdc++5 and libstdc++5-3.3-dev for good measure because Intel’s builds depend on these runtimes.
before you attempt installing the Intel Compiler Suite.
Get the License Number and Extract to a path without spaces
Ensure that you have obtained the license number for your installation and extracted the downloaded installation archive into a path that does not contain any spaces. This last statement is utterly important. The installer script that comes with the package has a bug that does not allow you to install the compiler suite if you have any spaces in the installer script path.
On 64-bit systems you may also need to issue these commands
# cd /usr/lib32 # ln -s libpthread.so libpthread.so.0 # ln -s libm.so libm.so.6 # ln -s libc.so libc.so.6 # ln -s libdl.so libdl.so.2
because the chklic_32_64 license checking utility from Intel dynamically links to these libraries.
Once you’re done preparing to install the compiler suite, it’s time to go to the installer directory and install the compiler (be sure to also read through accompanying documentation; e.g., README, INSTALL.txt):
Run the Installation Script
$ cd /home/user/intel_compiler_suite $ sudo ./install.sh . Follow the wizard as it guides you through the installation process.
After installing the compiler, you need to tell your shell the location of these executables by adding their parent paths to the PATH environment variable.
Edit /etc/bash.bashrc to add the installation path to the PATH environment variable
export PATH=/opt/intel/cc/10.1.012/bin:/opt/intel/idb/10.1.012/bin:$
Where 10.1.012 is the version of the compiler suite installed.
Installing the X11 development compilers
Install script for X11 development libs
$ sudo apt-get -y install libx11-dev
InstallingCompilers (последним исправлял пользователь cable-31-58 2012-08-10 10:18:50)
The material on this wiki is available under a free license, see Copyright / License for details
You can contribute to this wiki, see Wiki Guide for details
Установка GCC в Ubuntu
Большинство программ в Linux написаны на C или С++, и если вы хотите собирать их из исходников, то вам обязательно понадобиться компилятор, также он понадобиться, если захотите начать писать свои программы на одном из этих языков.
Существует два основных компилятора в Linux — это GCC и Clang, они похожи по своим возможностям, но так сложилось, что первый считается стандартом для Ubuntu. GCC расшифровывается как GNU Compiler Collection. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как выполняется установка GCC в Ubuntu, а также рассмотрим базовые приемы работы с этим набором программ в терминале.
Набор компиляторов GCC
Все программы представляют собой набор машинных команд, которые выполняются процессором. Эти команды — последовательность бит. Но писать программы наборами бит очень неудобно, поэтому были придуманы языки программирования высокого уровня. Код на языке программирования хорошо читаем и понятен для человека, а когда из него нужно сделать программу, компилятор ubuntu преобразует все в машинные команды.
В базовую поставку компилятора входят такие программы:
- libc6-dev — заголовочные файлы стандартной библиотеки Си;
- libstdc++6-dev — заголовочные файлы стандартной библиотеки С++;
- gcc — компилятор языка программирования Си;
- g++ — компилятор языка программирования C++;
- make — утилита для организации сборки нескольких файлов;
- dpkg-dev — инструменты сборки пакетов deb.
Все эти пакеты являются зависимостями пакета build-essential, поэтому для установки всего необходимого достаточно установить этот пакет.
Установка GCC в Ubuntu
Если вас устраивает текущая версия GCC, которая есть в официальных репозиториях дистрибутива, то вам достаточно установить пакет build-essential. Для этого выполните команду:
sudo apt -y install build-essential
После завершения установки все необходимое для компиляции программ будет установлено. И вы сможете использовать компилятор. Рассмотрим версии и расположение файлов компилятора:
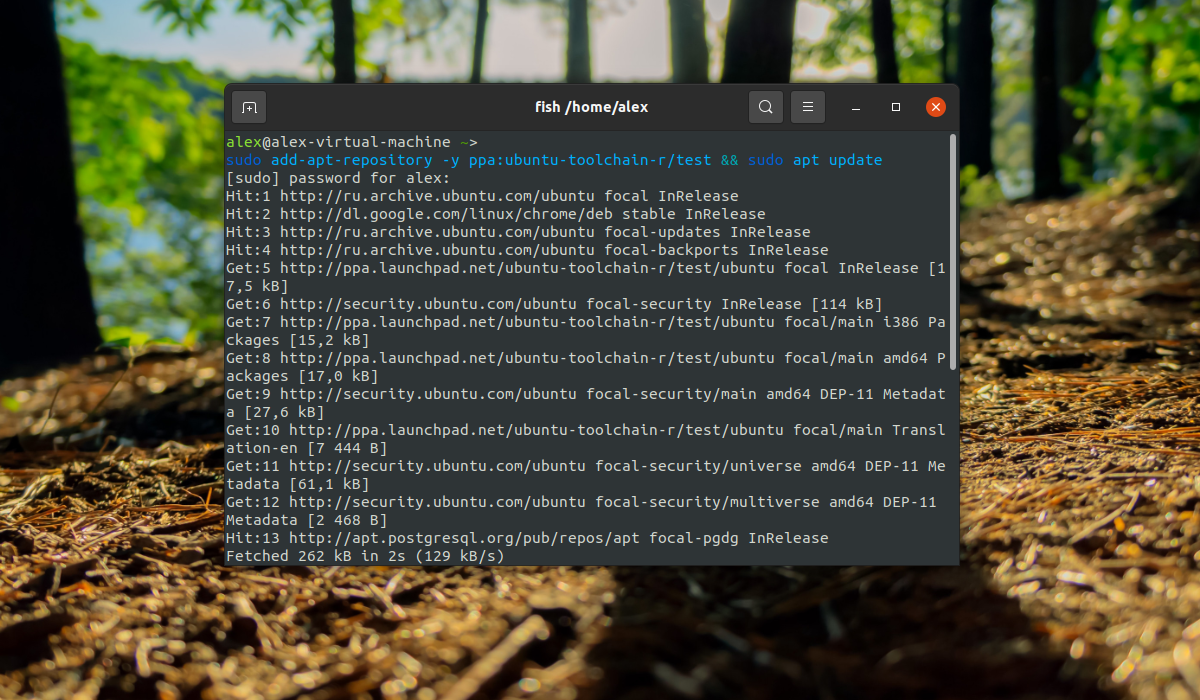
Если необходима более новая версия компилятора, например, на данный момент последняя версия — 11, то можно использовать PPA разработчиков с тестовыми сборками. Для добавления PPA в систему выполните команды:
sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:ubuntu-toolchain-r/test && sudo apt update
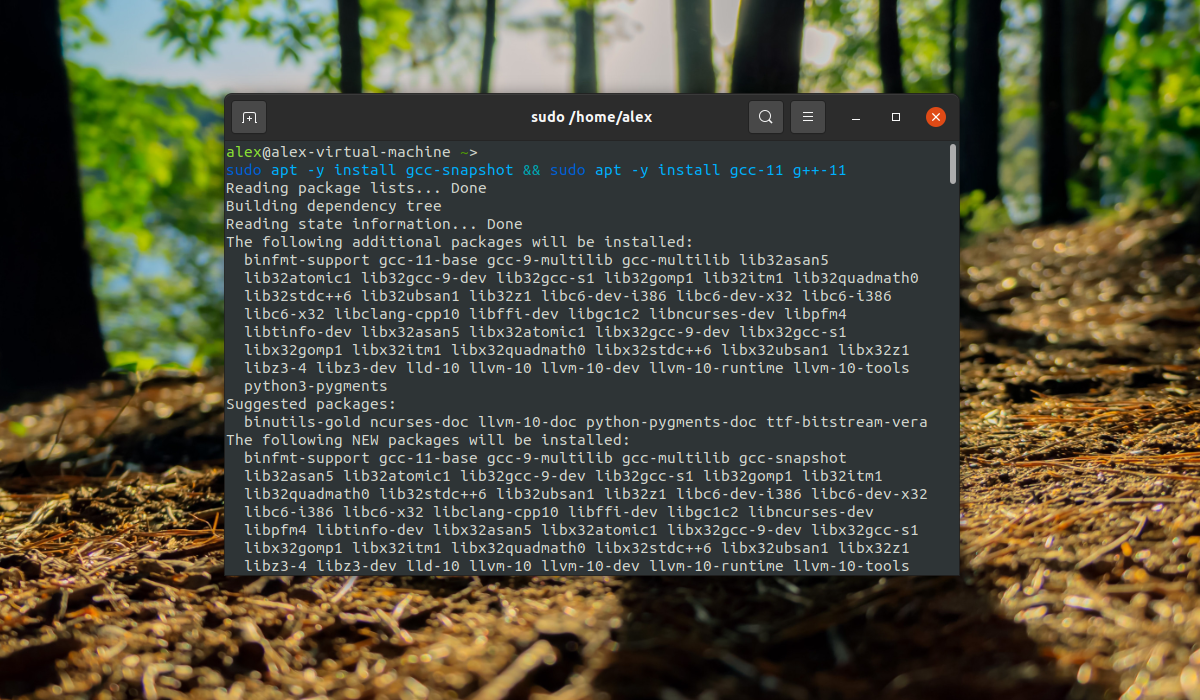
Далее установите сам компилятор:
sudo apt -y install gcc-snapshot && sudo apt -y install gcc-11g++-11
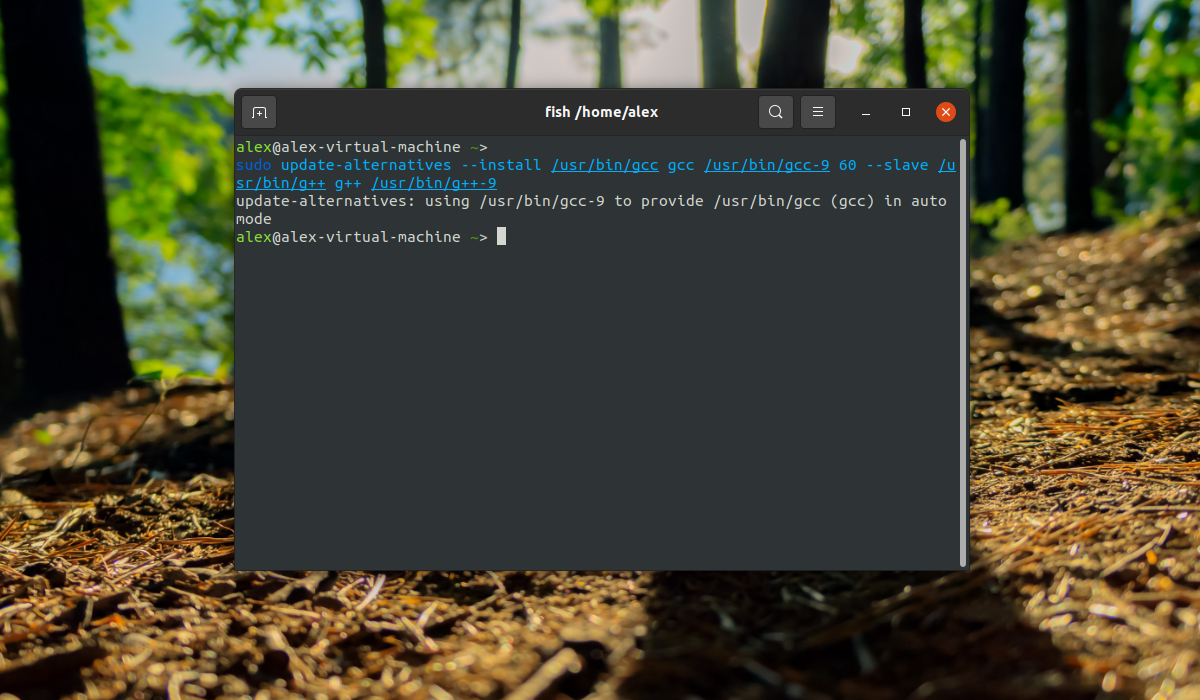
Это не заменит ваш текущий компилятор на новый. В системе просто появятся 2 версии компиляторов gcc-11 и g++11, которые вы можете использовать для своих программ. Это лучший вариант на данный момент, но если вы хотите все же сделать gcc-9 компилятором по умолчанию, выполните:
sudo update-alternatives —install /usr/bin/gcc gcc /usr/bin/gcc-9 60 —slave /usr/bin/g++ g++ /usr/bin/g++-9
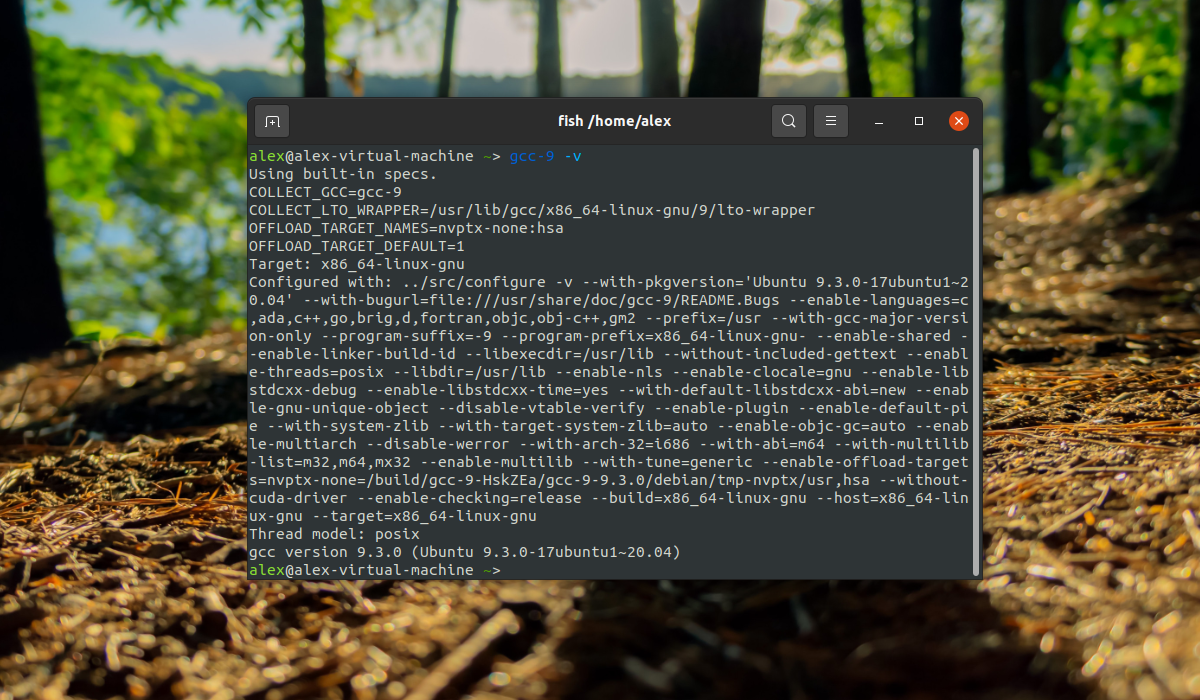
Готово, теперь вы можете проверить версию gcc-6:
Установка GCC в Ubuntu завершена, и можно переходить к сборке программ. Для удаления компилятора достаточно удалить пакет build-essential при помощи команды:
sudo apt purge -y build-essential && sudo apt-y autoremove
Использование GCC в Ubuntu
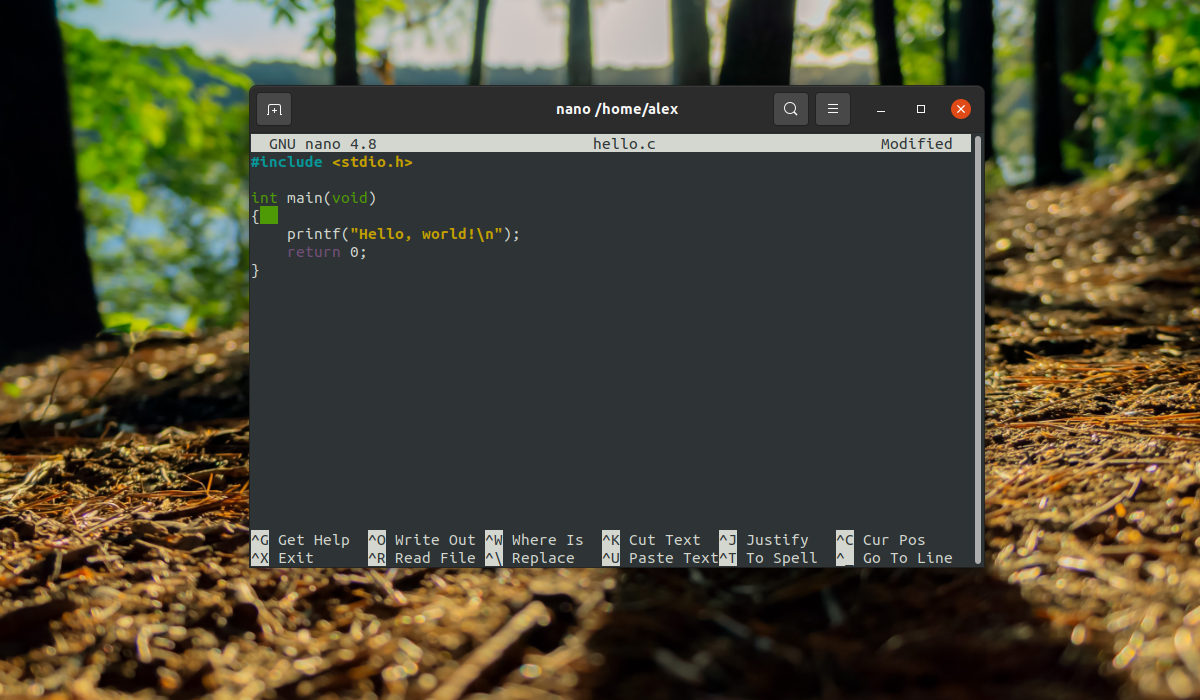
Рассмотрим пример компиляции минимальной программы hello.c для освоения работы с gcc. Вот код программы, откройте любой текстовый редактор и сохраните его в файле с названием hello.c:
#include
int main(void) printf(«Hello, world!\n»);
return 0;
>
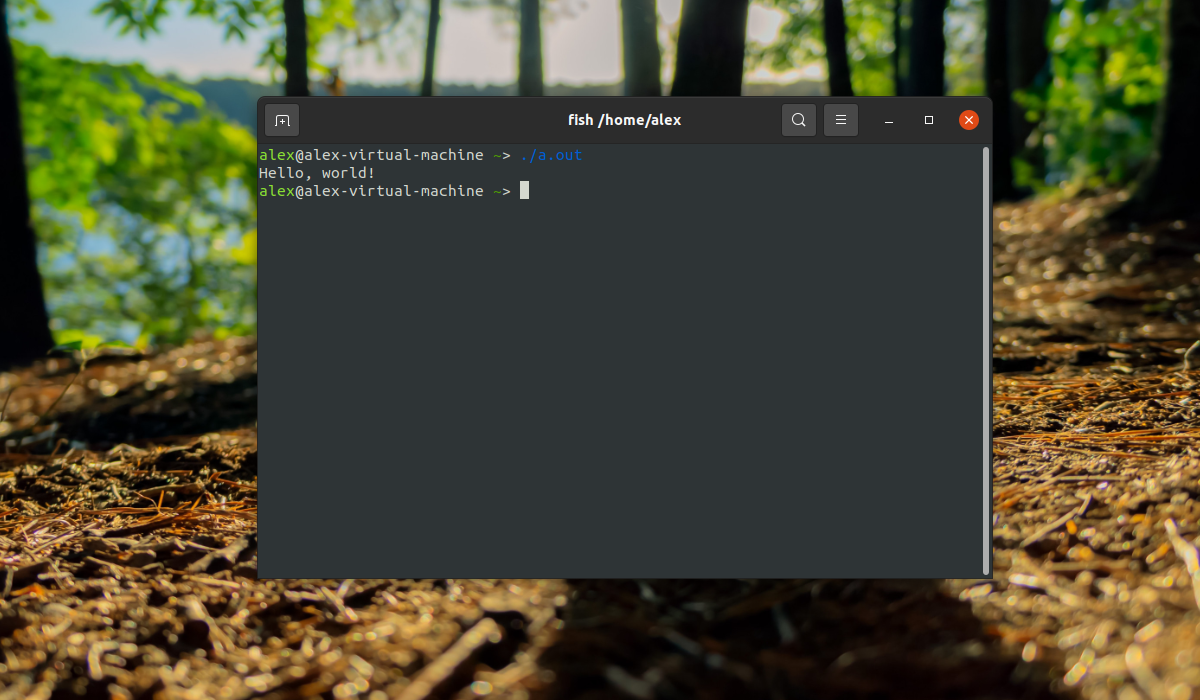
Теперь запустим сборку программы:
Когда сборка программы будет завершена, на выходе появится файл с названием a.out. a.out –это имя исполняемого файла, которое по умолчанию, сгенерировано при помощи gcc. Далее можно запустить данный файл:
Готово, компилятор прекрасно работает в системе, и теперь можно писать свои программы или собирать чужие.
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели, как установить gcc в Ubuntu 20.04, это один из самых популярных компиляторов для этой операционной системы. И устанавливается он очень просто, если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
На завершение видео с демонстрацией самого процесса:

Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.