- How to Check GCC Version on Ubuntu
- Open the Terminal
- Option 1: “gcc –version”
- Option 2: “gcc -v”
- Option 3: “aptitude show gcc”
- Commands and Functions:
- Conclusion
- How to Install GCC on Ubuntu 22.04 | 20.04
- Update Ubuntu
- Method 1: Install GCC with Ubuntu Repository
- Method 2: Install GCC with Ubuntu Toolchain PPA
- Configure Alternative Versions of the GCC Compiler
- Test GCC Compiler: Create a Test Application
- Conclusion
How to Check GCC Version on Ubuntu
When working with C and C++ programming languages, it is essential to use a compatible compiler that supports the desired language features and optimizes the code accordingly. GCC, the GNU Compiler Collection, is a popular choice for compiling C, C++, Objective-C, Fortran, Ada, and other languages. It is crucial to know the version of GCC installed on your Ubuntu system to ensure that it supports the code you are working with, especially when dealing with recent language features or libraries.
In this guide, we will walk you through the process of checking the GCC version on an Ubuntu system. By following these steps, you will be able to determine if your system has the appropriate version of GCC installed and if an upgrade or downgrade is necessary to meet your development needs.
Open the Terminal
To begin, open the terminal application on your Ubuntu system. You can either search for “Terminal” in the applications menu or press Ctrl + Alt + T to open a new terminal window.
Option 1: “gcc –version”
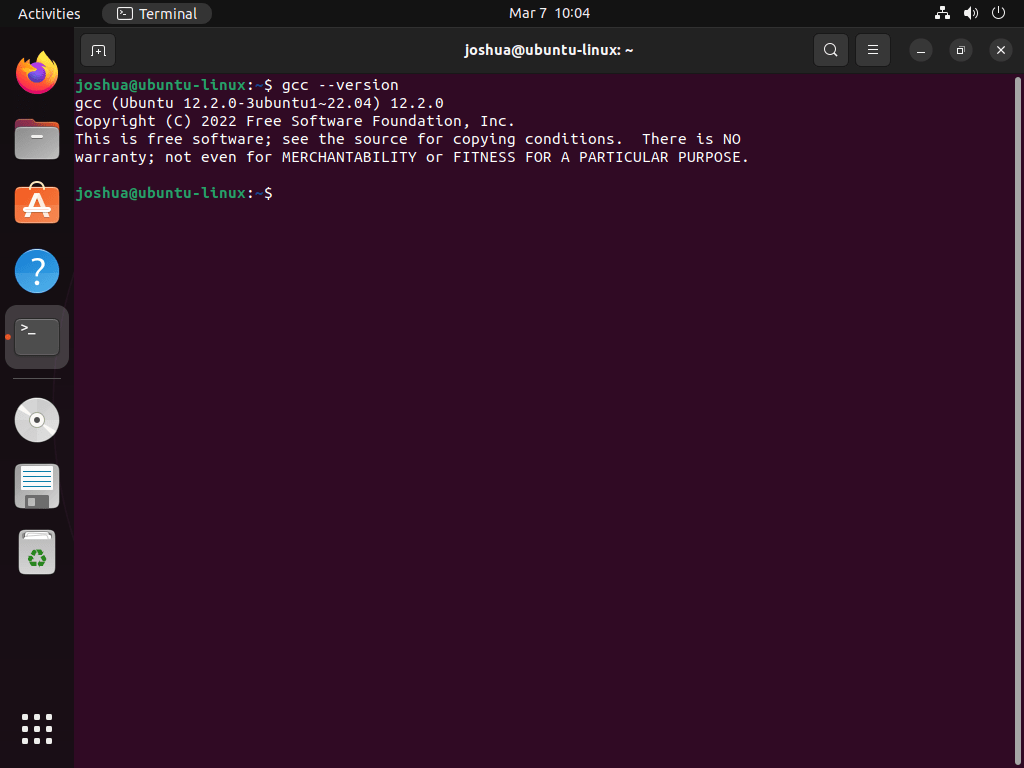
Once the terminal is open, enter the following command to check the installed GCC version:
This command will display the current GCC version installed on your system, along with additional information about the compiler.
ehowstuff@ubuntu14:~$ gcc --version gcc (Ubuntu 4.8.2-19ubuntu1) 4.8.2 Copyright (C) 2013 Free Software Foundation, Inc. This is free software; see the source for copying conditions. There is NO warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Option 2: “gcc -v”
Alternatively, you can type “gcc -v” command:
ehowstuff@ubuntu14:~$ gcc -v Using built-in specs. COLLECT_GCC=gcc COLLECT_LTO_WRAPPER=/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-linux-gnu/4.8/lto-wrapper Target: x86_64-linux-gnu Configured with: ../src/configure -v --with-pkgversion='Ubuntu 4.8.2-19ubuntu1' --with-bugurl=file:///usr/share/doc/gcc-4.8/README.Bugs --enable-languages=c,c++,java,go,d,fortran,objc,obj-c++ --prefix=/usr --program-suffix=-4.8 --enable-shared --enable-linker-build-id --libexecdir=/usr/lib --without-included-gettext --enable-threads=posix --with-gxx-include-dir=/usr/include/c++/4.8 --libdir=/usr/lib --enable-nls --with-sysroot=/ --enable-clocale=gnu --enable-libstdcxx-debug --enable-libstdcxx-time=yes --enable-gnu-unique-object --disable-libmudflap --enable-plugin --with-system-zlib --disable-browser-plugin --enable-java-awt=gtk --enable-gtk-cairo --with-java-home=/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.5.0-gcj-4.8-amd64/jre --enable-java-home --with-jvm-root-dir=/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.5.0-gcj-4.8-amd64 --with-jvm-jar-dir=/usr/lib/jvm-exports/java-1.5.0-gcj-4.8-amd64 --with-arch-directory=amd64 --with-ecj-jar=/usr/share/java/eclipse-ecj.jar --enable-objc-gc --enable-multiarch --disable-werror --with-arch-32=i686 --with-abi=m64 --with-multilib-list=m32,m64,mx32 --with-tune=generic --enable-checking=release --build=x86_64-linux-gnu --host=x86_64-linux-gnu --target=x86_64-linux-gnu Thread model: posix gcc version 4.8.2 (Ubuntu 4.8.2-19ubuntu1)
The “gcc -v” command provides more detailed information about your GCC installation compared to “gcc –version”. When you execute this command, it displays information about the compiler’s configuration, including the target system, supported languages, and the options used during the compilation process. This information can be helpful if you need to know the specifics of your GCC installation, such as the target architecture or enabled features.
Option 3: “aptitude show gcc”
Another alternative is to execute “aptitude show gcc” command:
ehowstuff@ubuntu14:~$ aptitude show gcc Package: gcc State: installed Automatically installed: yes Version: 4:4.8.2-1ubuntu6 Priority: optional Section: devel Maintainer: Ubuntu Developers Architecture: amd64 Uncompressed Size: 42.0 k Depends: cpp (>= 4:4.8.2-1ubuntu6), gcc-4.8 (>= 4.8.2-5~) Recommends: libc6-dev | libc-dev Suggests: gcc-multilib, make, manpages-dev, autoconf, automake1.9, libtool, flex, bison, gdb, gcc-doc Conflicts: gcc-doc (< 1:2.95.3), gcc-doc (< 1:2.95.3), gcc Provides: c-compiler Description: GNU C compiler This is the GNU C compiler, a fairly portable optimizing compiler for C. This is a dependency package providing the default GNU C compiler.
The "aptitude show gcc" command gives you information about the GCC package from the package manager's perspective. Aptitude is a package manager used in Debian and Ubuntu systems, and the command provides details such as the package version, dependencies, a description of the package, and its file size. This information can be useful when managing software packages on your system, especially when dealing with dependencies or determining which version of GCC is available through the package manager.
Commands and Functions:
- gcc - The GNU Compiler Collection command
- --version - An option that displays the version information of the installed GCC
- gcc -v - This command displays verbose information about the installed GCC version, including the configuration options used during the compilation process, supported languages, and the target architecture.
- aptitude show gcc - This command provides detailed package information for the installed GCC compiler, including package version, dependencies, description, and file size. Aptitude is a package manager for Debian and Ubuntu systems that simplifies the management of software packages.
Conclusion
By following these steps, you have successfully checked the GCC version on your Ubuntu system. With this information, you can now determine whether your current GCC installation meets the requirements for your development projects. If necessary, you can upgrade or downgrade your GCC installation to a version that supports the desired language features and optimizations.
We hope this guide has been helpful in learning how to check the GCC version on your Ubuntu system. If you have any suggestions or improvements, please feel free to leave a comment below.
How to Install GCC on Ubuntu 22.04 | 20.04
The GNU Compiler Collection, commonly known as GCC, is a comprehensive and versatile compiler system that supports various programming languages. It has played a vital role in the development and growth of the open-source software ecosystem since its inception in 1987. Below is a detailed introduction to GCC, highlighting its key features, languages supported, and its significance in the software development world.
Key Features of GCC:
- Cross-Platform: GCC is available for a wide range of operating systems, including Linux, Windows, and macOS. This cross-platform compatibility makes it an excellent choice for developers who work on multiple platforms.
- Multi-Language Support: GCC supports a multitude of programming languages, including C, C++, Objective-C, Fortran, Ada, D, Go, and many others. This enables developers to use a single compiler for various projects with different language requirements.
- Optimization: GCC offers various levels of code optimization, allowing developers to fine-tune the performance of their applications. This feature helps in generating efficient code that can run faster and use less memory.
- Extensions and Language Features: GCC supports many language extensions and features that go beyond the standard specifications. This helps developers take advantage of cutting-edge language features and use them to create more efficient and powerful applications.
- Active Development and Support: GCC enjoys a strong community of developers and contributors who continually work to improve and expand its features. This ensures that the compiler remains up-to-date and compatible with the latest language standards and operating systems.
Significance of GCC in Software Development:
GCC has been a crucial tool for open-source software development and is the default compiler for many Linux distributions. It is widely used by developers worldwide to build, optimize, and debug applications. The flexibility offered by GCC, its support for multiple languages, and continuous development efforts have made it an indispensable tool in the software development world.
In the following guide, we will demonstrate how to install GCC on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy Jellyfish or Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa with CLI commands using two methods: Ubuntu’s default repository or installing the Ubuntu Toolchain Launchpad PPA that contains the latest versions of all support versions of GCC, including GCC 12, GCC 11, GCC 10, and GCC 9.
Update Ubuntu
Before you begin, update your system to ensure all existing packages are up to date to avoid any conflicts during the installation.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeMethod 1: Install GCC with Ubuntu Repository
The first recommended option to install GCC is to install either the GCC package directly or the build-essential package containing GCC and many other essential development tools such as make, g++, and dpkg-dev.
To begin the installation, use the following command.
sudo apt install build-essentialOnce installed, verify the installation and check the version using the following command.
Method 2: Install GCC with Ubuntu Toolchain PPA
The next method will install the latest GCC Compiler or alternative versions you may seek from the Ubuntu Toolchain PPA. To import this PPA, run the following command:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ubuntu-toolchain-r/ppa -yAfter importing the PPA, update your Ubuntu sources list to reflect the changes made by running the following command in your terminal:
To install a specific version of the GCC compiler on your Ubuntu system using the Ubuntu ToolChain PPA, use the following commands in your terminal:
sudo apt install g++-12 gcc-12sudo apt install g++-11 gcc-11sudo apt install g++-10 gcc-10After running the appropriate command for the version you want to install, the GCC compiler will be successfully installed on your Ubuntu system.
Configure Alternative Versions of the GCC Compiler
As a developer or specific user, you may need to install multiple GCC compiler versions. Follow these steps to configure alternative versions of GCC on your Ubuntu system.
First, install the versions of GCC you need. You can install multiple versions of GCC along with G++ using the following command:
sudo apt install gcc-9 g++-9 gcc-10 g++-10 gcc-11 g++-11 g++-12 gcc-12Once you have installed the necessary versions, use the update-alternatives command to configure the priority of each version. The following example command sets the priority split between GCC 9, GCC 10, GCC 11, and the latest GCC 12.
sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/gcc gcc /usr/bin/gcc-12 100 --slave /usr/bin/g++ g++ /usr/bin/g++-12 --slave /usr/bin/gcov gcov /usr/bin/gcov-12 sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/gcc gcc /usr/bin/gcc-11 80 --slave /usr/bin/g++ g++ /usr/bin/g++-11 --slave /usr/bin/gcov gcov /usr/bin/gcov-11 sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/gcc gcc /usr/bin/gcc-10 60 --slave /usr/bin/g++ g++ /usr/bin/g++-10 --slave /usr/bin/gcov gcov /usr/bin/gcov-10 sudo update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/gcc gcc /usr/bin/gcc-9 40 --slave /usr/bin/g++ g++ /usr/bin/g++-9 --slave /usr/bin/gcov gcov /usr/bin/gcov-9The above commands set GCC 12 as the highest priority with a value of 100. However, you can configure the priorities based on your preferences.
To confirm that GCC 12 is the default version on your system, run the following command:
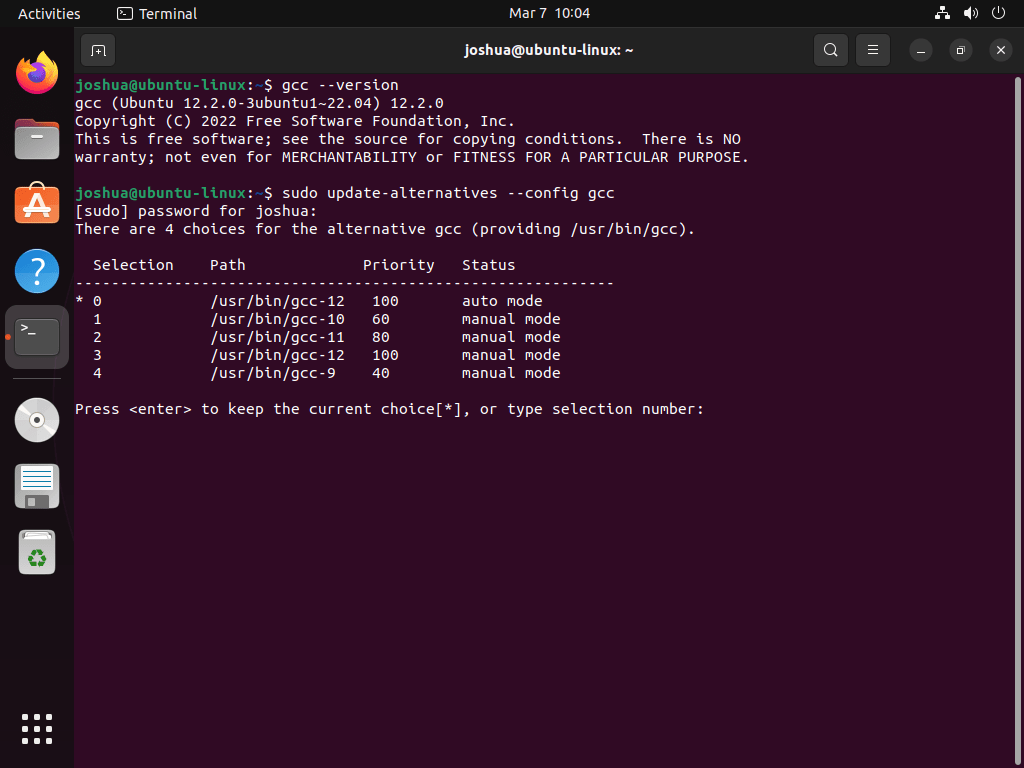
You can reconfigure the default GCC version on your system by using the update-alternatives command. First, use the following command to list the priorities you previously set:
sudo update-alternatives --config gccThis command will display a list of installed GCC versions and their priorities. You can then select the default version by entering the corresponding number.
That’s it! You have successfully configured alternative versions of GCC on your Ubuntu system.
Test GCC Compiler: Create a Test Application
To test compiling with GCC, create the famous “Hello World” program in C using any text editor. This tutorial will use nano.
Open the nano text editor and create a new file named hello.c:
Add the following code to the file:
Save the file by pressing CTRL+O, then exit nano by pressing CTRL+X.
To compile the Hello World program, use the following command:
This command compiles the program and generates an executable file named hello .
Next, run the compiled program by entering the following command:
You should see the following output in your terminal:
Hello, World from Linuxcapable.com!Conclusion
Once installed, GCC can compile and run C and C++ programs on your Ubuntu system. With the addition of the manual pages package, you can also access comprehensive documentation on how to use GCC and its various features. Whether a novice or an experienced developer, having GCC installed on your Ubuntu system is essential for developing and running C and C++ programs.