- Where does pip install its packages?
- 10 Answers 10
- Where Are Python Packages Installed in Linux
- Previous Necessary Step: Learning the Installed Python Version
- Where Are Python Packages Stored When Installed Without Packages Manager
- Where Are Python Packages When Installed Through Pip
- Where Are Python Packages Installed in Debian/Ubuntu Distributions
- Where Are Python Packages Installed in Red Hat Based Distributions & SUSE
- How to Find Installed Python Packages Independently of the Installation Method
- Finding Python Modules
- Conclusion
- About the author
- David Adams
- Где установлены пакеты Python в Linux
- Предыдущий необходимый шаг: изучение установленной версии Python
- Где хранятся пакеты Python при установке без диспетчера пакетов
- Где находятся пакеты Python при установке через Pip
- Где установлены пакеты Python в дистрибутивах Debian/Ubuntu
- Где установлены пакеты Python в дистрибутивах на основе Red Hat и SUSE
- Как найти установленные пакеты Python независимо от метода установки
- Поиск модулей Python
- Вывод
Where does pip install its packages?
and Django successfully downloaded. Now, I want to open up the Django folder. Where is the folder located? Normally it would be in «downloads», but I’m not sure where it would be if I installed it using pip in a virtualenv.
Can the directory in which to install packages be overridden via CLI args, environment variables or a config file?
LOL. Well, @AndersRuneJensen in the 4 years it took you to answer my question, my Python Fu has improved significantly. I wish I’d remembered I posted this adorable question and come to answer it myself but you beat me to it! Thank you, though, for not answering a very naive question rudely. +1 to you , sir!
10 Answers 10
pip show will provide the location for Windows and macOS, and I’m guessing any system. 🙂
> pip show cvxopt Name: cvxopt Version: 1.2.0 . Location: /usr/local/lib/python2.7/site-packages i’m using python 3.6 on windows and «pip» refers to pip for python 3. i don’t need to specify «pip3».
pip list -v can be used to list packages’ install locations, introduced in https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/news/#b1-2018-03-31
Show install locations when list command ran with “-v” option. (#979)
>pip list -v Package Version Location Installer ------------------------ --------- -------------------------------------------------------------------- --------- alabaster 0.7.12 c:\users\me\appdata\local\programs\python\python38\lib\site-packages pip apipkg 1.5 c:\users\me\appdata\local\programs\python\python38\lib\site-packages pip argcomplete 1.10.3 c:\users\me\appdata\local\programs\python\python38\lib\site-packages pip astroid 2.3.3 c:\users\me\appdata\local\programs\python\python38\lib\site-packages pip . This feature is introduced in pip 10.0.0b1. On Ubuntu 18.04 (Bionic Beaver), pip or pip3 installed with sudo apt install python-pip or sudo apt install python3-pip is 9.0.1 which doesn’t have this feature.
Where Are Python Packages Installed in Linux
By reading this tutorial, you will learn where the Python packages and modules are installed in your system and other Linux distributions. But the most important teaching in this tutorial is in the last section, where you will learn how to find the Python packages without memorizing the directories independently of the Linux distribution or installation method.
All examples shown in this article include screenshots, making it easy for every Linux user to understand them independently of their knowledge level.
Previous Necessary Step: Learning the Installed Python Version
To follow all instructions described in this article, you must first know the Python version installed in your system.
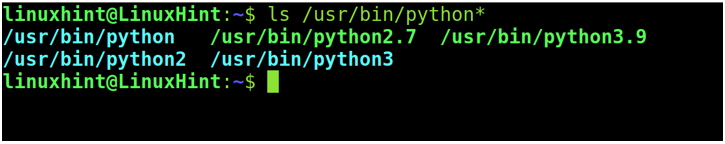
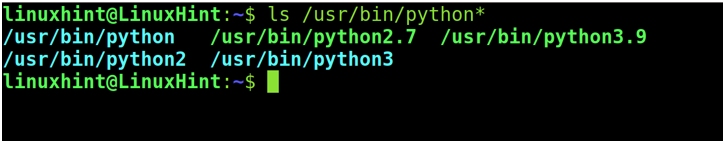
To learn it, you can use the ls command followed by the executable files path and replace the version with a wildcard as shown in the following:
As you can see, there are two Python versions currently installed in my system: Python 3.9 and Python 2.7. The other paths belong to the symbolic links.
Where Are Python Packages Stored When Installed Without Packages Manager
If the Python installation was done from sources or from Python installation mechanisms (like easy_install or Python setup.py) and not from a packages manager like apt-get or aptitude among others, Python packages are stored under the /usr/local/lib/python/ directory.
This directory can be defined as universal and valid for almost every Linux distribution because it’s based on installation methods available for different distributions independently of their package managers. Of course, this is not valid when Python is installed using a specific distro packages manager.
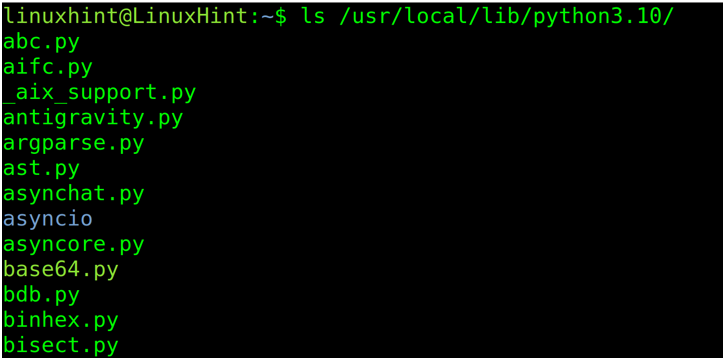
If you compiled Python from sources or installed it using the setup.py or easy_install, you can check this location using the ls command as shown in the following screenshot where 3.10 must be replaced with your actual Python version.
Where Are Python Packages When Installed Through Pip
Python packages installed using the pip command are stored under the /usr/local/lib//dist-packages/pip/ directory.
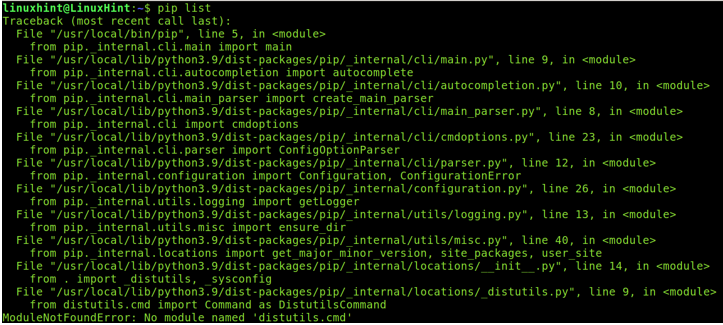
You can find the correct location by using the pip command followed by the list option as shown in the following:
Where Are Python Packages Installed in Debian/Ubuntu Distributions
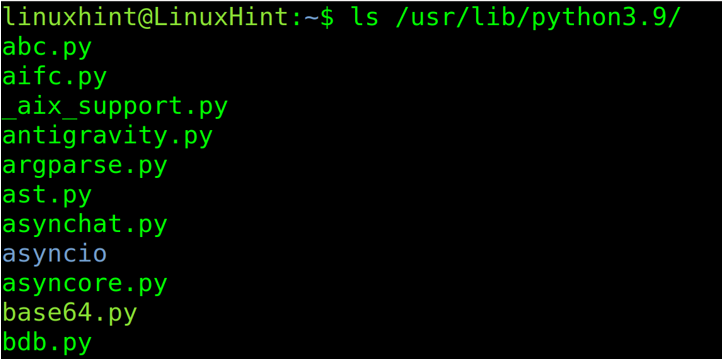
If you are a Debian, Ubuntu, or other based distribution and you installed Python through the dpkg packages manager or one of its frontends like apt-get, apt or aptitude, the packages are stored in the /usr/lib/python directory, as shown in the following image where 3.9 must be replaced with your actual Python version.
Note: As mentioned previously, if you don’t install Python using the dpkg, apt, apt-get or aptitude, the packages will have a different location described in the first section of this document.
Where Are Python Packages Installed in Red Hat Based Distributions & SUSE
Like in Debian/Ubuntu, Python packages without defined specific architecture are installed under the /usr/lib/python directory.
But specific architecture Python packages in Red Hat are stored under a descriptive directory like /usr/lib64/python .
Local Python packages are installed under /home//.local/lib/python/.
How to Find Installed Python Packages Independently of the Installation Method
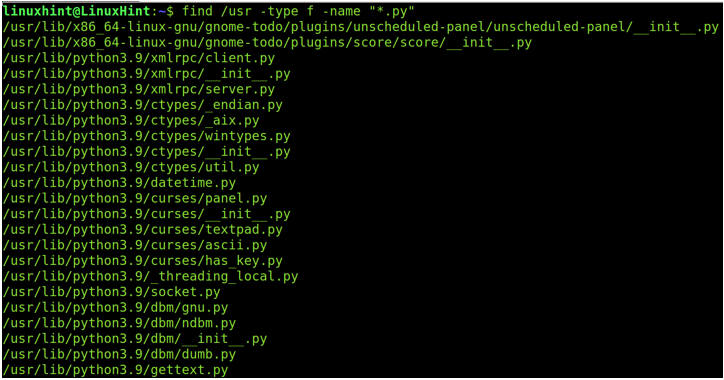
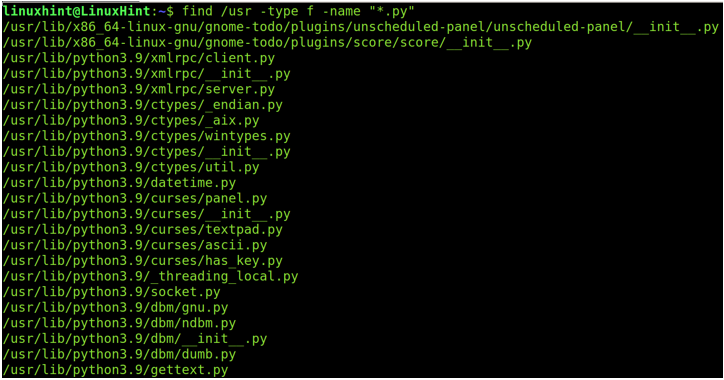
Whatever is your Linux distribution, you can always use the find command to search the files by type, in this case to find the Python packages using its .py extension as shown in the following figure where /usr is the parent directory in the recursive search, -type f defines that you are searching files and not directories, and “*.py” is the extension of files that you are looking for.
Finding Python Modules
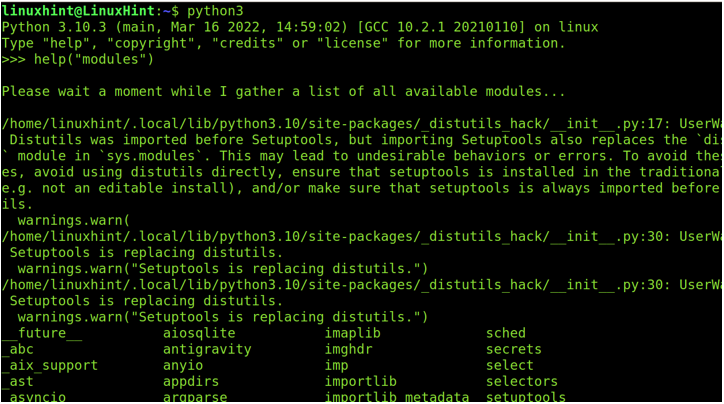
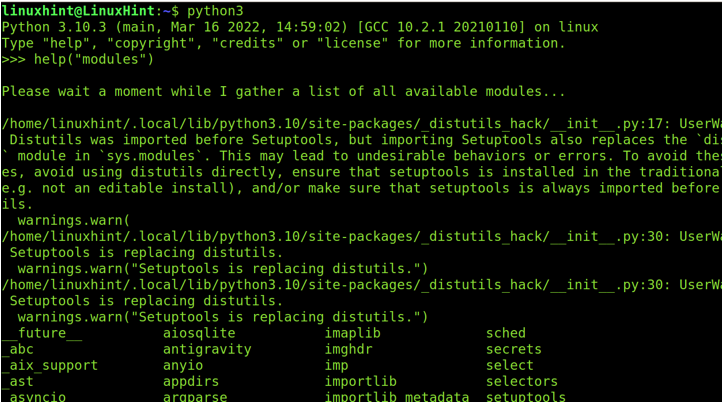
To find the Python modules, open the Python console by executing the python, where must be replaced with your actual Python version. Then, run the command help(“modules”) as shown in the following example:
In our case, using the Python 3, we execute the following code:
Then, we also execute this following code:
Conclusion
As you can see, Python packages are installed in different locations depending on the Linux distribution, installation methods, and in some cases, depending on the architecture. But the find command is useful to search all Python packages independently of the installation method, distribution, or architecture, and is a valid technique for every Linux distribution. Learning the program versions or how to find the files by type or extension is extremely easy and mandatory for all the Linux users independently of their knowledge level. It is important to clarify that while this article provides examples including Python 2, this version was discontinued and Python 3 is the current version, with many improvements. Always try to install Python using your Linux distribution packages manager, automatically resolving the dependencies and easing the removal process before problems.
Thank you for reading this article. We hope it was useful. Keep following Linux Hint for more professional Linux tips and tutorials.
About the author
David Adams
David Adams is a System Admin and writer that is focused on open source technologies, security software, and computer systems.
Где установлены пакеты Python в Linux
Прочитав это руководство, вы узнаете, где в вашей системе и других дистрибутивах Linux установлены пакеты и модули Python. Но самое важное учение в этом уроке находится в последнем разделе, где вы узнаете как найти пакеты Python, не запоминая каталоги, независимо от дистрибутива Linux или метода установки .
Все примеры, показанные в этой статье, содержат скриншоты, что позволяет каждому пользователю Linux легко понять их, независимо от уровня их знаний.
Предыдущий необходимый шаг: изучение установленной версии Python
Чтобы следовать всем инструкциям, описанным в этой статье, вы должны сначала узнать версию Python, установленную в вашей системе.
Чтобы узнать это, вы можете использовать команду ls, за которой следует путь к исполняемому файлу, и заменить версию подстановочным знаком, как показано ниже:
лс / usr / мусорное ведро / питон *
Как видите, в настоящее время в моей системе установлены две версии Python: Python 3.9 и Python 2.7. Остальные пути относятся к символическим ссылкам.
Где хранятся пакеты Python при установке без диспетчера пакетов
Если установка Python была выполнена из исходников или из механизмов установки Python (таких как easy_install или Python setup.py), а не из менеджера пакетов, такого как apt-получить или способность среди прочего, пакеты Python хранятся в папке /usr/local/lib/python / каталог.
Этот каталог можно определить как универсальный и подходящий почти для каждого дистрибутива Linux, поскольку он на основе методов установки, доступных для разных дистрибутивов независимо от их пакета менеджеры. Конечно, это неверно, если Python устанавливается с помощью менеджера пакетов определенного дистрибутива.
Если вы скомпилировали Python из исходников или установили его с помощью setup.py или же easy_install, вы можете проверить это местоположение с помощью команды ls, как показано на следующем снимке экрана, где 3.10 должен быть заменен вашей реальной версией Python.
лс / usr / местный / библиотека / питон3.10 /
Где находятся пакеты Python при установке через Pip
Пакеты Python, установленные с помощью команды pip, хранятся в папке /usr/local/lib/ /dist-packages/pip/ каталог.
Вы можете найти правильное местоположение с помощью точка команда, за которой следует список вариант, как показано ниже:
Где установлены пакеты Python в дистрибутивах Debian/Ubuntu
Если у вас Debian, Ubuntu или другой дистрибутив, и вы установили Python через дпкг менеджер пакетов или один из его интерфейсов, например способный получить, подходящий или же способность, пакеты хранятся в /usr/lib/python каталог, как показано на следующем изображении, где 3.9 должен быть заменен вашей реальной версией Python.
лс / usr / библиотека / питон3.9 /
Примечание: Как упоминалось ранее, если вы не устанавливаете Python с помощью дпкг, метко, метко-получить или же способность, пакеты будут иметь другое место, описанное в первом разделе этого документа .
Где установлены пакеты Python в дистрибутивах на основе Red Hat и SUSE
Как и в Debian/Ubuntu, пакеты Python без определенной конкретной архитектуры устанавливаются под /usr/lib/python каталог.
Но пакеты Python для конкретной архитектуры в Red Hat хранятся в описательном каталоге, например /usr/lib64/python.
Локальные пакеты Python устанавливаются в /home/ /.local/lib/python / .
Как найти установленные пакеты Python независимо от метода установки
Каким бы ни был ваш дистрибутив Linux, вы всегда можете использовать найти команда для поиска файлов по типу, в данном случае для поиска пакетов Python с использованием его .py расширение, как показано на следующем рисунке, где /usr является родительским каталогом в рекурсивном поиске, -тип ф определяет, что вы ищете файлы, а не каталоги, и «*.py” — это расширение файлов, которые вы ищете.
Поиск модулей Python
Чтобы найти модули Python, откройте консоль Python, выполнив команду python , куда должен быть заменен вашей реальной версией Python. Затем запустите команду помощь(«модули») как показано в следующем примере:
В нашем случае, используя Python 3, мы выполняем следующий код:
Затем мы также выполняем следующий код:
Вывод
Как видите, пакеты Python устанавливаются в разных местах в зависимости от дистрибутива Linux, методов установки и, в некоторых случаях, в зависимости от архитектуры. Но найти Команда полезна для поиска во всех пакетах Python независимо от метода установки, дистрибутива или архитектуры и является допустимым методом для любого дистрибутива Linux. Изучение версий программы или способов поиска файлов по типу или расширению чрезвычайно просто и обязательно для всех пользователей Linux, независимо от их уровня знаний. Важно уточнить, что, хотя в этой статье приведены примеры, включая Python 2, эта версия была снята с производства, а текущей версией является Python 3 со многими улучшениями. Всегда пытайтесь установить Python с помощью диспетчера пакетов дистрибутива Linux, автоматически разрешая зависимости и облегчая процесс удаления перед возникновением проблем.
Спасибо, что прочитали эту статью. Мы надеемся, что это было полезно. Продолжайте следовать Linux Hint, чтобы получить больше профессиональных советов и руководств по Linux.