- Homeros/VoicemanDeb
- Требования к системе
- Загрузка пакетов
- Установка
- Самостоятельная сборка
- Как установить локальный .deb пакет
- Установка скаченных .deb
- Установка без учёта зависимостей
- Установка DEB файла с помощью apt
- Установка пакетов с помощью gdebi
- Связанные статьи:
- How to install and use GDebi on Ubuntu
- How to install GDebi package installer in Ubuntu
- How to install GDebi using terminal in Ubuntu
- How to install GDebi installer using Ubuntu Software Center
- How to use GDebi package installer in Ubuntu
- How to make GDebi a default installer for .deb files
- How to remove GDebi package installer in Ubuntu
- Conclusion
- How To Install Debian Application Packages Using Gdebi On Linux
- HOW TO INSTALL
Homeros/VoicemanDeb
Речевой сервер VoiceMan доступен для загрузки в виде deb-пакетов, пригодных для установки в дистрибутивах Debian и Ubuntu. Подготовку пакетов выполнили Дмитрий Падучих и Tolyangin. На этой странице приводится общая информация об использовании созданных пакетов.
Требования к системе
Подготовленная сборка выполнена с предположением, что система пользователя подключена к репозиторию Игоря Порецкого, в котором доступны необходимые речевые синтезаторы. Репозиторий Игоря Порецкого доступен по этой ссылке.
Загрузка пакетов
Загрузить пакеты для систем Debian и Ubuntu можно по ссылкам ниже:
Установка
Поскольку apt-get в Debian не устанавливает пакеты из файла, нужно либо воспользоваться командой gdebi из пакета gdebi-core , чтобы установить пакет вместе с зависимостями, либо предварительно установить все необходимые пакеты вручную и выполнить установку при помощи dpkg -i . Список зависимостей можно посмотреть следующей командой:
Необходимая информация отображается в полях Depends, Recommends’, Suggests.
Самостоятельная сборка
Файлы, необходимые для сборки пакетов, доступны для загрузки из директории, расположенной по этой ссылке. Для компиляции требуются следующие пакеты: cdbs , debhelper (не ниже 7.0.50), autotools-dev , build-essential , libtool , libao-dev . После этого сборку можно выполнить при помощи следующих команд:
dpkg-source -x voiceman_1.5.0pre2-1.dsc
dpkg-buildpackage -rfakeroot -b -uc
Как установить локальный .deb пакет
Файлы с расширением .deb — это установочные пакеты для Debian и производных дистрибутивов, для таких, как Linux Mint, Kali Linux, Ubuntu.
Типичный способ установки пакета из файла DEB:
sudo apt update sudo apt install ИМЯ_ПАКЕТА
С помощью этих команд устанавливаются пакеты из стандартных репозиториев — это самый надёжный способ в том плане, что для устанавливаемого пакету будут установлены зависимости и в будущем этот пакет будет обновляться вместе с другими программами в системе. То есть установка из стандартных репозиториев является приоритетной.
Установка скаченных .deb
Иногда может потребоваться установка локальных .deb, то есть файлов не из репозиториев. Примеры, когда потребовалась такая установка:
- Как установить Viber на Linux (необходимо отредактировать пакет Viber, иначе его установки приведёт к проблемам к использованию менеджеров пакетов)
- Как установить Java (JDK) в Windows и Linux (Oracle JDK отсутствует в стандартных репозиториях)
Установка без учёта зависимостей
Следующая команда установит пакет без проверки зависимостей:
При выполнении операции менеджером пакетов, например, обновление кэша:
может возникнуть сообщение об отсутствующих зависимостях, исправить это можно командой:
Установка DEB файла с помощью apt
Программа apt также умеет устанавливать пакеты из указанных файлов, при этом одновременно будут установлены необходимые зависимости для этого пакета:
sudo apt install ./ПАКЕТ.deb

Установка пакетов с помощью gdebi
Вы можете установить программу gdebi:
И затем устанавливать пакеты с помощью неё:
sudo gdebi /ПУТЬ/ДО/ФАЙЛА.deb
gdebi также установит необходимые зависимости. На самом деле, gdebi появилась когда apt-get не могла устанавливать локальные файлы (или эта возможность не была документирована), сейчас же вместо gdebi можно использовать apt, которая предустановлена в каждом дистрибутиве, основанном на Debian.
Связанные статьи:
How to install and use GDebi on Ubuntu
GDebi is a package installer to install Debian executable packages on Debian-based distribution of Linux. It is foreseen that while installing the Debian packages on Ubuntu, a dependency error comes; that won’t allow you to install the package; the GDebi package installer will resolve the dependency issue. Ubuntu uses the default software installer to install .deb packages; GDebi can also be used because it is more efficient and quicker as compared to the default Ubuntu installer. Ubuntu is well known for its resource consumption; that’s why it would be a good option to use GDebi as a default installer for .deb packages: inspired by this; we have compiled a detailed guide on installation and use of GDebi package installer:
How to install GDebi package installer in Ubuntu
You can install the GDebi on Ubuntu by two ways:
How to install GDebi using terminal in Ubuntu
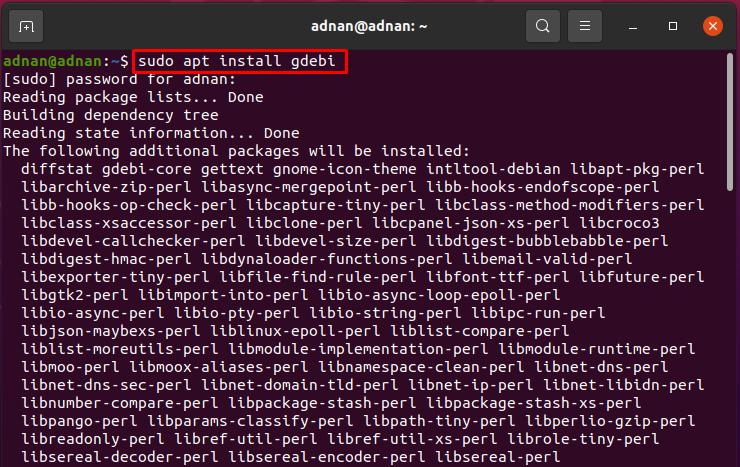
Open your Ubuntu command terminal using shortcut “Ctrl+Alt+T”; use the command given below to install the GDebi package:
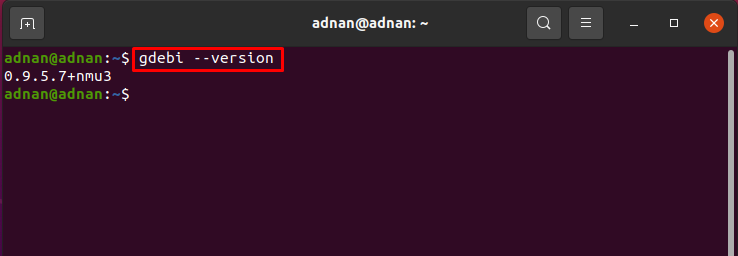
Once it is installed; you can verify the installation by checking the version of the package using command given below:
How to install GDebi installer using Ubuntu Software Center
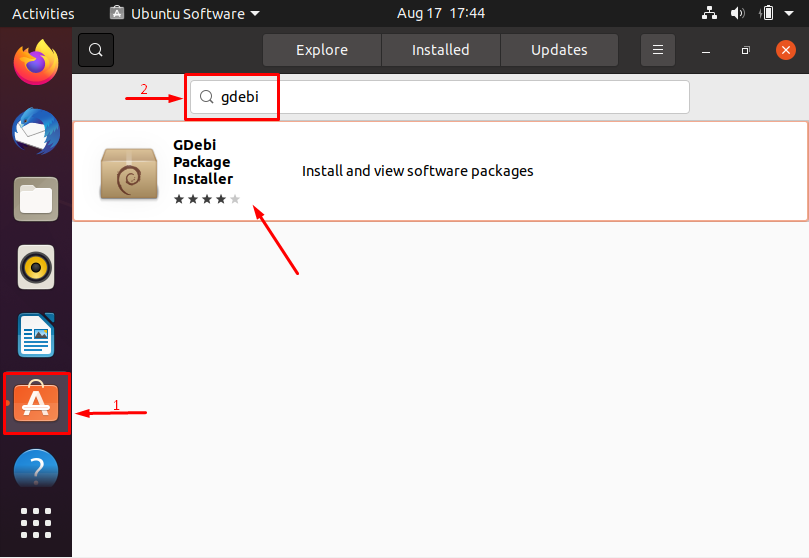
Open the Ubuntu Software Center app; and search for “gdebi”; you will see the required result in few moments:
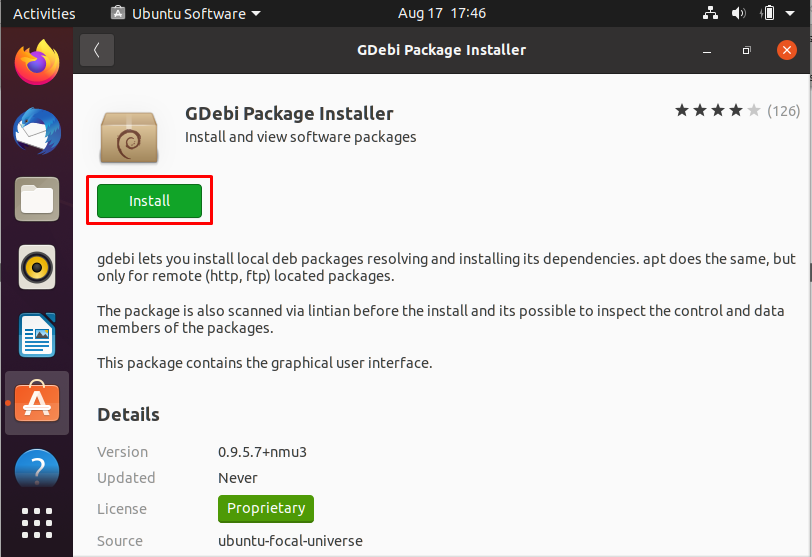
Click on the package installer; the next window contains the green “Install” button; click on that button to start the installation:
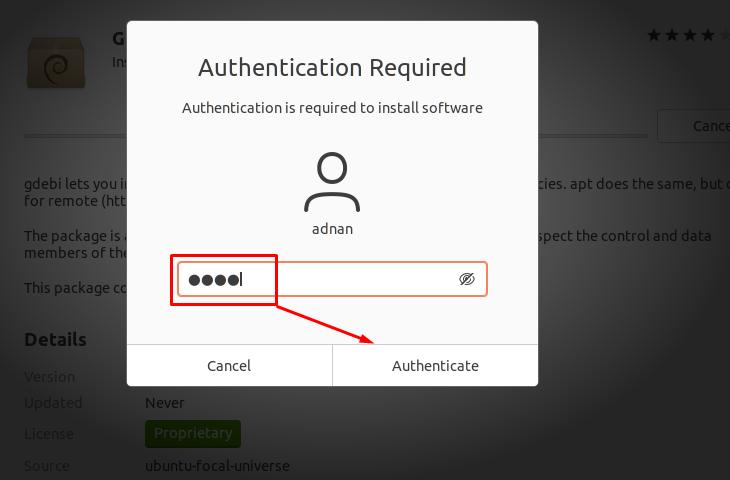
The time you click on “Install”; it confirms your decision by asking for Ubuntu user password as shown below:
Enter the password and click on “Authenticate” to move forward:
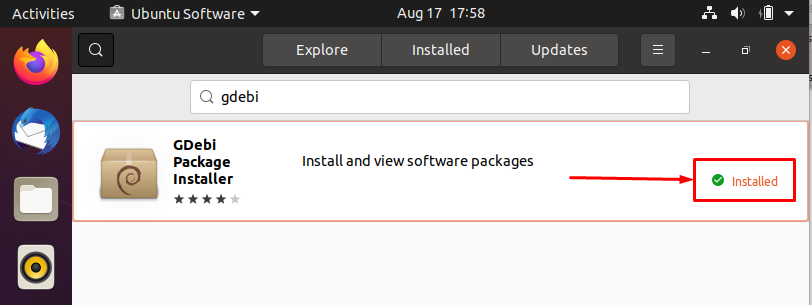
After Authentication; installation will take few minutes to complete; once the installation is finished you can observe that the status of GDebi package is changed to “Installed”:
How to use GDebi package installer in Ubuntu
Once the package manager is installed successfully, you can use it in multiple ways to install Debian files on your Ubuntu: this section contains the following ways to use the GDebi package manager:
Method 1: Using package manager app to install program
Method 2: Directly open the Debian file using “GDebi” package manager
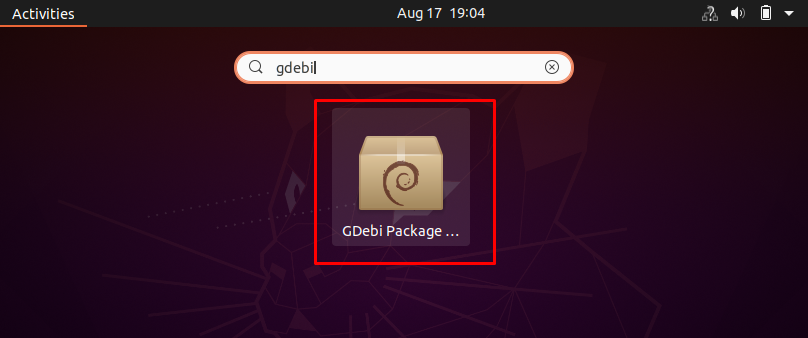
Method 1: Locate the GDebi in your applications; and click on it to open:
Once it is opened, move to the directory where .deb file is saved and click on it to open the file:
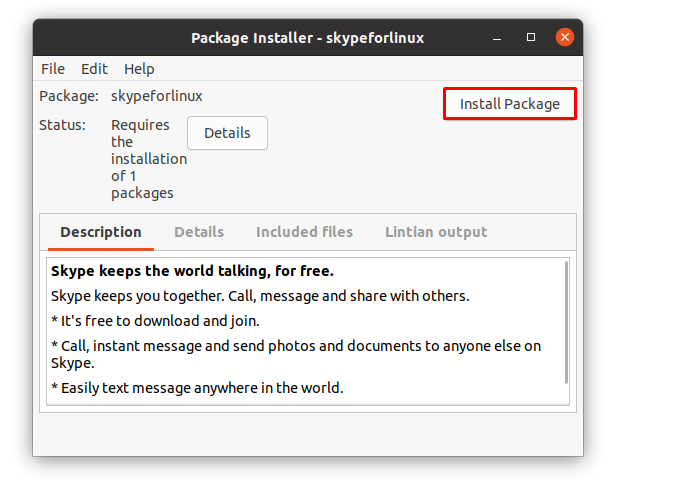
You will notice that the files of the .deb files will be loaded, and you can click on “Install Package” to start the installation using GDebi manager.
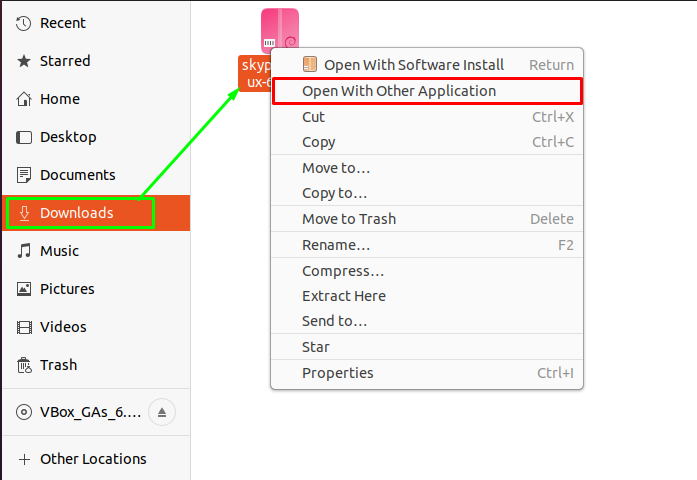
Method 2: This method refers to opening the installation file in GDebi manager. For that purpose, and select “Open With Other Application” to navigate to the list of available package managers:
After clicking that, you will see the possible installing managers, choose “GDebi Package Installer” and click on “Select” to continue:
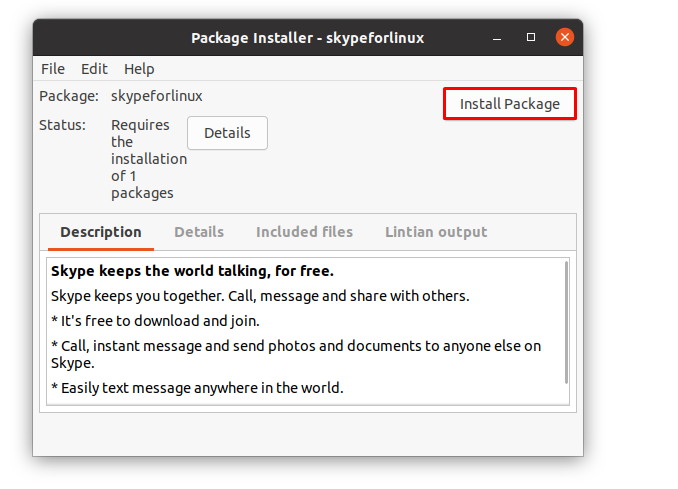
The time you click on “Select”, the installer will load the files and you can click on “Install Package” to start the installation:
How to make GDebi a default installer for .deb files
There is another interesting way to avoid long steps for installation as above; you can set the “GDebi Installer” as a default install manager for .deb files. To do this, right click on any of the .deb files and click on the properties:
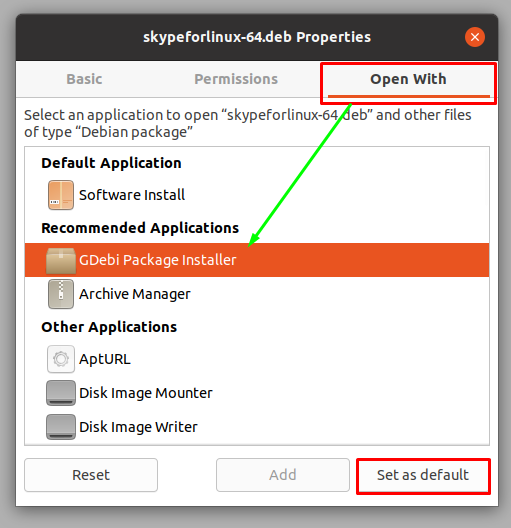
The properties options contain three tabs, you have to click on the “Open With” tab. This tab contains the available applications that can be used to install .deb files.
Choose “GDebi Package Installer” and click on “Set as default” to set it as default installer for .deb files. Now whenever you double click on .deb files, it will open with “GDebi manager”.
How to remove GDebi package installer in Ubuntu
You can remove the installed version of GDebi by two means:
Remove GDebi using terminal in Ubuntu : Open the terminal and execute the following command to remove the package:
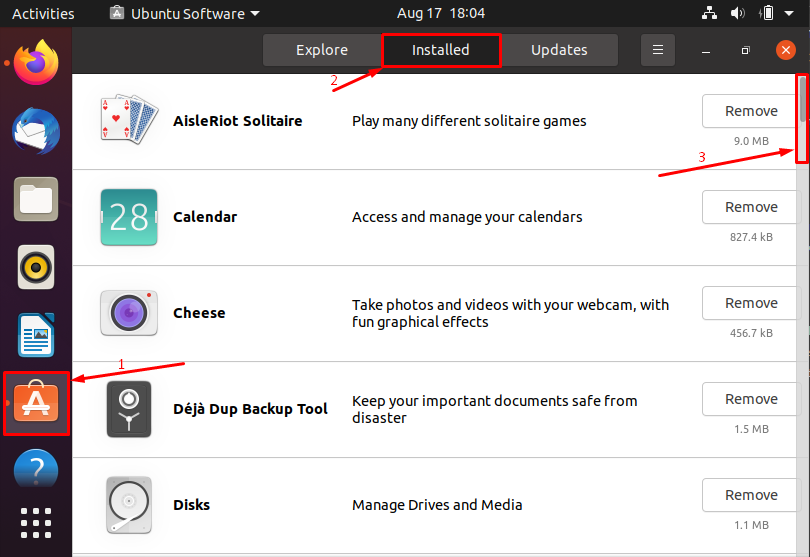
Remove GDebi using “Ubuntu Software” center in Ubuntu : Open the “Ubuntu Software”; click on the “Installed” tab available at the top of the application; you will see a list of all installed packages:
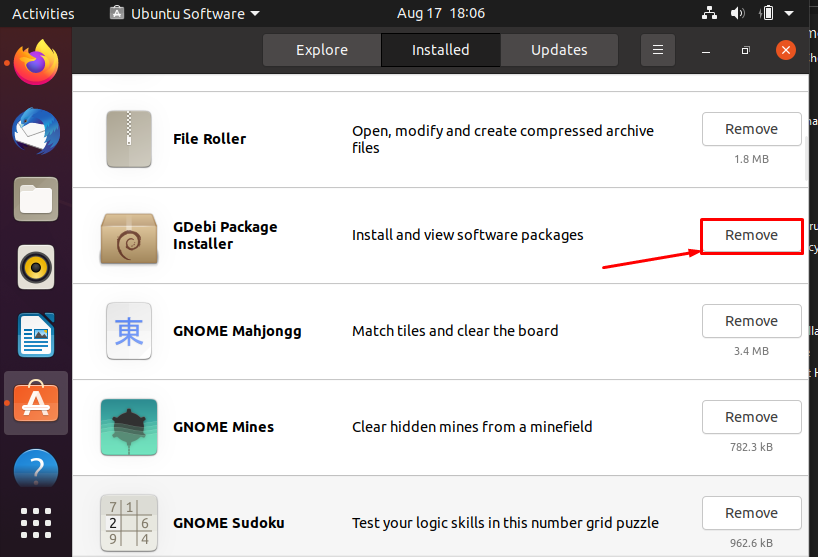
Scroll down on the window to locate “GDebi”; Once it is found; click on “Remove”:
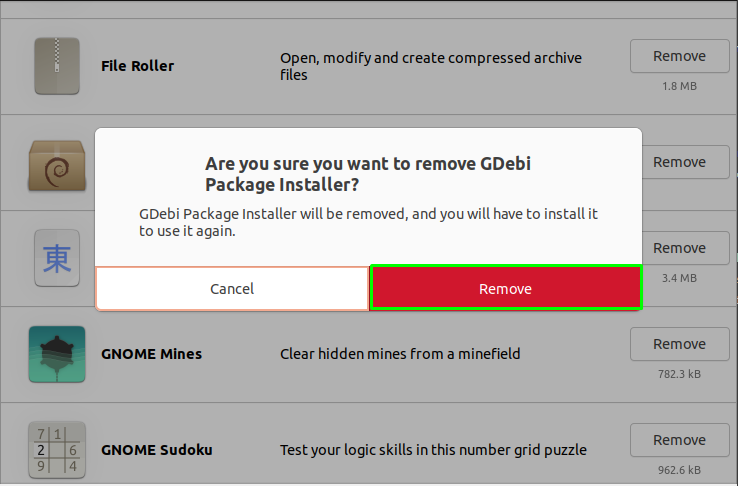
By clicking “Remove”; a prompt window will ask you for confirmation; click on “Remove”:
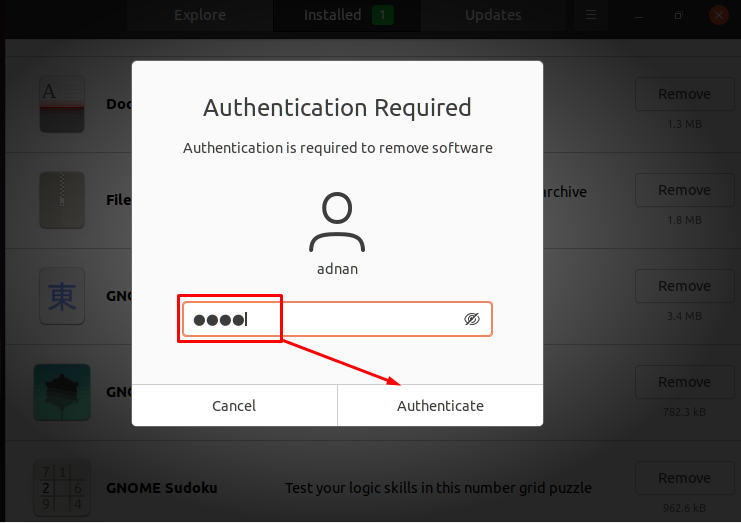
Lastly, you must put your user password and click on “Authenticate” to continue:
Conclusion
While using Debian-based distributions of Linux; you may encounter dependency issues when installing .deb executable files. One of the major reasons for acting up Ubuntu OS is the default installer as it is resource consuming, and because of this performance issue old computers may lag down. Alternate to this, we have provided the installation and usage guide of GDebi package installer. This installer helps you to install .deb files and its efficacy is better than Ubuntu’s default installer. Moreover, you can make GDebi as your default installer for .deb files.
How To Install Debian Application Packages Using Gdebi On Linux
Gdebi is a simple tool to install Debian packages (file with the .deb file extension). This is very important because almost all Debian derivatives and sub-derivatives rely on the Debian package management system. Gdebi let you install a .deb package file locally while also resolving and installing its dependencies.
It has a graphical user interface, but can also be used in your command-line (i.e. terminal). It is a very recommended utility for installing .deb files because of the fact that it is lightweight and fast.
HOW TO INSTALL
Gdebi can be installed on Linux using different ways.
- Using the default Ubuntu software centre: simply search for “gdebi” from the search bar and then click on install. DONE.
- Synaptic Package Manager: Similar to using the Ubuntu software center, gedbi can be installed using the synaptic package manager. To do this, simply open the package manager, then search for “gdebi” and select mark for installation. and then install.
- Using the command line: to install gdebi enter the following commands in the terminal.
First of all update the package directory;
Then install the application;
Then to install any deb package simply right click on the file (.deb) and from the drop-down menu click on select “Open With another Application”, since the default method of installation would be the software centre.
Then you can then select “Gdebi Package Installer” from the options and click on “Select”.
This should open the Gdebi GUI dashboard, with the application.
After loading the application to be installed, Gdebi would give a status update to tell if the dependencies are met or not. If they are not the required decadency packages would be automatically downloaded before installation. If not the status would be: “All deficiencies are satisfied”.
Then click on the Install Package button to install it.
Happy Linux’NG!