- Как узнать версию Linux
- Скользящие или фиксированные релизы
- Как узнать версию Linux?
- Узнать дистрибутив
- Узнать версию ядра
- Как узнать архитектуру компьютера
- Выводы
- How to Check the OS Version in Linux
- Check OS Version via Command-Line Terminal
- Using the lsb_release Command
- Using /etc/issue File
- Using /etc/os-release File
- Using hostnamectl Command
- Check Kernel Information
- Using uname Command
- Using dmesg Command
- Using /proc/version
- Check OS Version in Linux via Graphical User Interface
- About the author
- Karim Buzdar
- Get linux version in terminal
- How to check your Linux version: easy ways to view the distribution and version number
- How to check Debian version: the quick and easy way
- Lubuntu — The fast and lean Linux distribution
- Xubuntu: the Linux distribution for maximum performance
- Ubuntu backups: A step-by-step guide
Как узнать версию Linux
Когда вы сами устанавливали систему и все настраивали, то точно знаете какой дистрибутив у вас установлен, какая версия и какая версия ядра. Но совсем другая ситуация, когда вы покупаете VPS или пытаетесь настроить компьютер другу или знакомому с Linux. Довольно часто может возникнуть вопрос как узнать версию Linux потому что эта информация часто очень важна. Например, уязвимости в программном обеспечении часто затрагивают только определенные релизы.
В этой небольшой статье мы поговорим о том как посмотреть версию Linux через терминал и какие утилиты для этого используются и в каких конфигурационных файлах можно найти интересующую нас информацию.
Скользящие или фиксированные релизы
Все активные дистрибутивы Linux выпускают новые релизы, только все по-разному. Конечно, дистрибутивы обновляются и между релизами, но пользователям привычен такой порядок, что обновления релиза получают только исправления безопасности и ошибок, а все новые возможности выпускаются новым релизом. Но существуют и другие пути. Сейчас есть два способа выпуска релизов:
Эти способы работают немного по-разному и вам нужно понимать это прежде чем мы перейдем к версии Linux. Скользящие релизы не имеют точек выпуска нового релиза, новые возможности, исправления и улучшения постоянно добавляются в официальный репозиторий и их получают пользователи. Такой подход используется в ArchLinux, Gentoo и OpenSUSE Thumbleweed. Поэтому у таких дистрибутивов нет версий, они всегда имеют самую новую версию после того, как было выполнено обновление пакетов. Но у них есть минус — это более низкая стабильность по сравнению с фиксированными релизами, которые можно хорошо протестировать.
Фиксированные релизы используются в Ubuntu. Каждые 6 месяцев выходит новый релиз, поэтому тут есть четкое разделение на версии, новая версия дистрибутива Linux получает новое программное обеспечение, а затем на протяжении всего термина поддержки получает обновления безопасности.
Как узнать версию Linux?
На самом деле для этого есть очень много методов, начиная от общих признаков и до открыть файл и точно посмотреть версию и имя дистрибутива. Рассмотрим только самые популярные из них.
Узнать дистрибутив
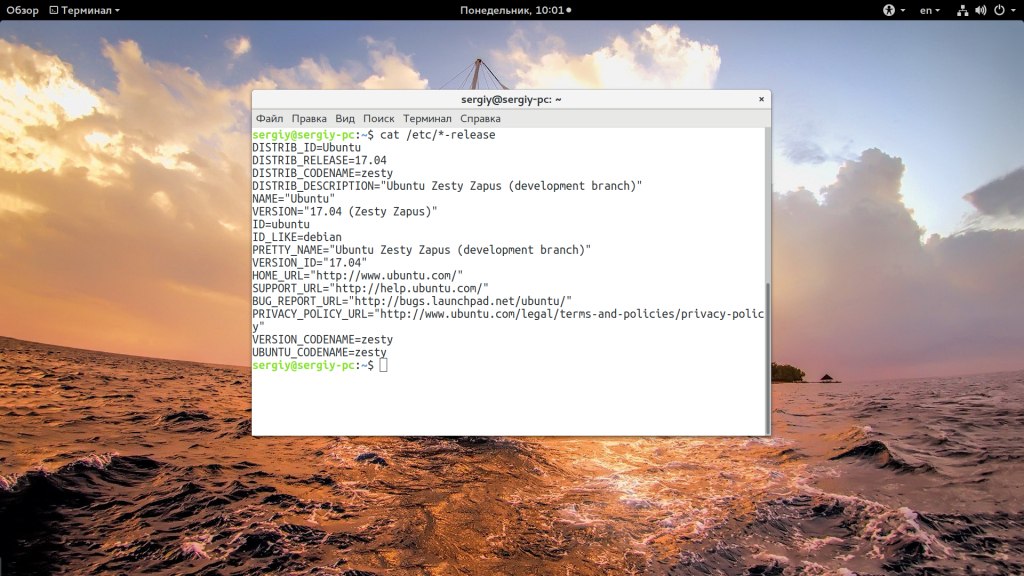
Прежде всего давайте узнаем имя дистрибутива и его версию если это возможно. Для этого будем смотреть содержимое файлов в папке /etc/, которые заканчиваются на release:
В Ubuntu утилита выведет содержимое двух файлов /etc/lsb-release и /etc/os-release. В них будет содержаться исчерпывающая информация о имени дистрибутива и версии его релиза:
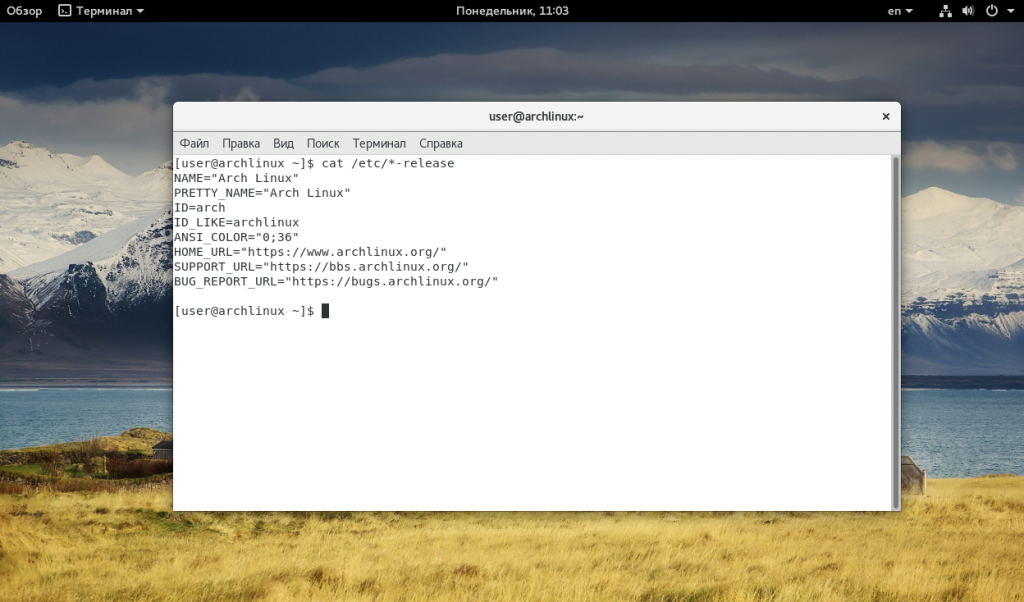
Но если мы выполним ту же команду в ArchLinux то получим совсем другой результат:
Тут уже нет версии, есть только имя дистрибутива, поскольку ArchLinux использует систему скользящих релизов. Немного меньше, но почти всю ту же информацию можно получить используя команду lsb_release:
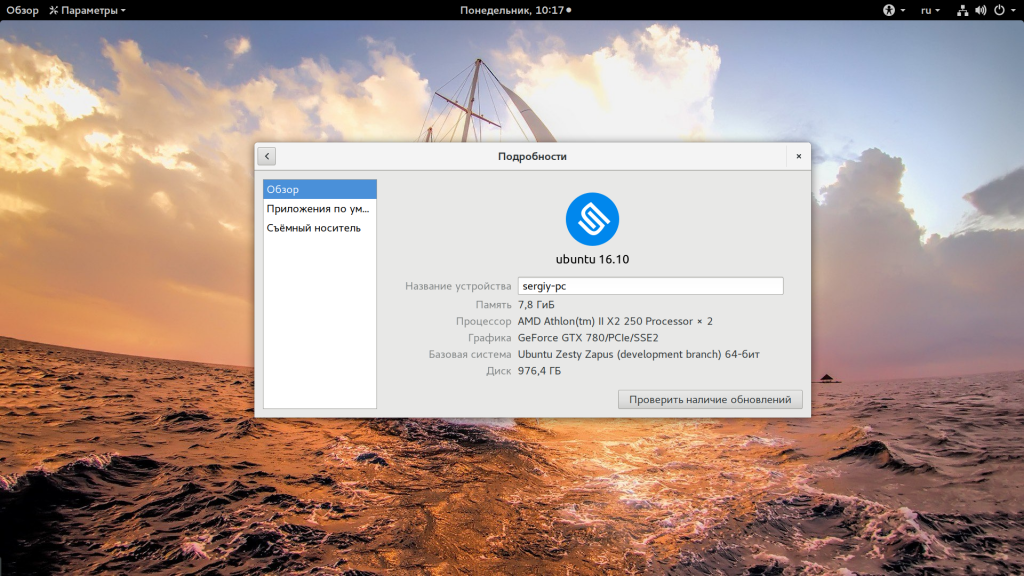
Также очень часто вы можете узнать имя дистрибутива посмотрев пункт «О программе» для любого системного приложения или лучше утилиты «Настройки»:
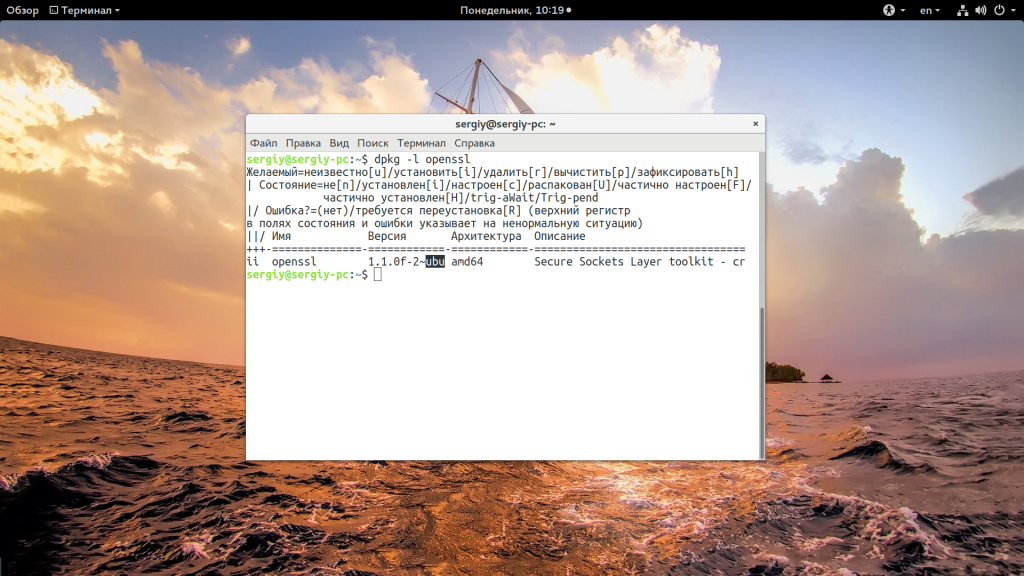
И еще один способ увидеть версию дистрибутива в основанных на Debian системах — посмотреть информацию о сборке пакета:
Узнать версию ядра
Во многих случаях нам нужна не столько версия дистрибутива linux, сколько версия ядра, которое в нем используется. Для просмотра этой информации тоже есть несколько команд:
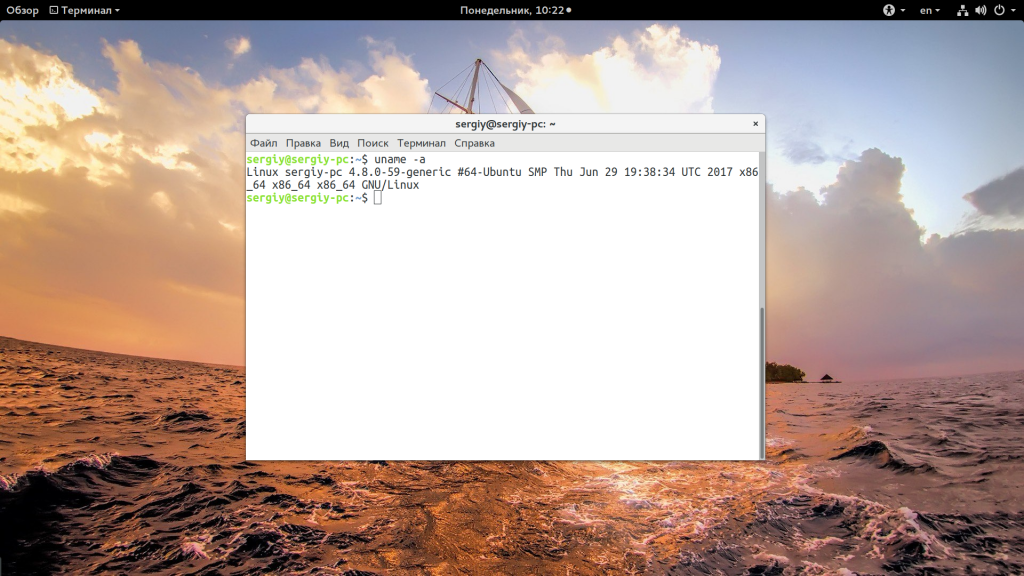
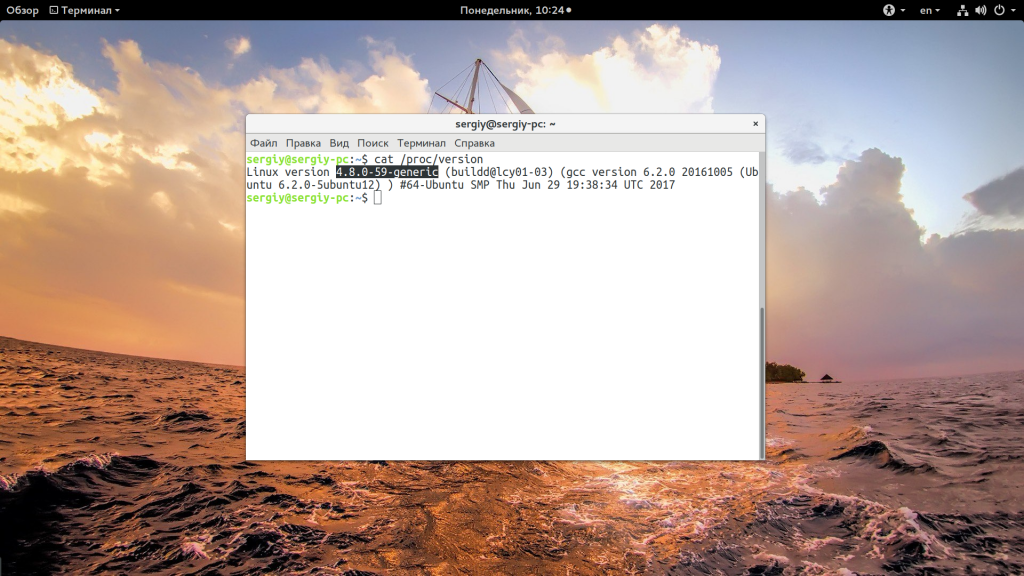
У меня используется версия ядра 4.8.0-59, тут же мы видим архитектуру системы — x86_64. Обозначение SMB означает, что ядро поддерживает многоядерные процессоры или несколько процессоров. Но мы можем узнать ту же информацию, посмотрев содержимое файла /proc/version:
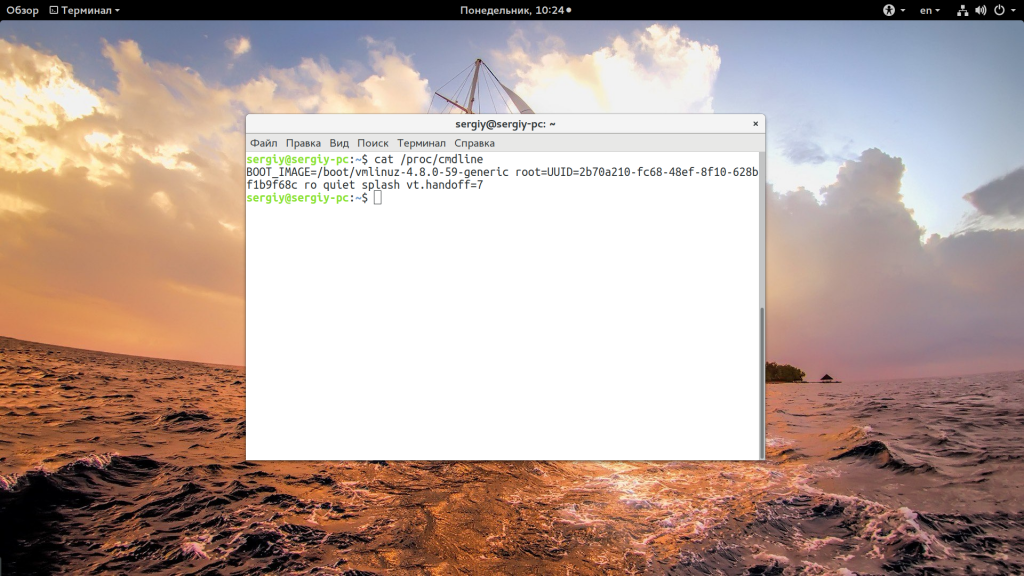
А еще можно посмотреть строку параметров запуска ядра, она тоже содержит версию:
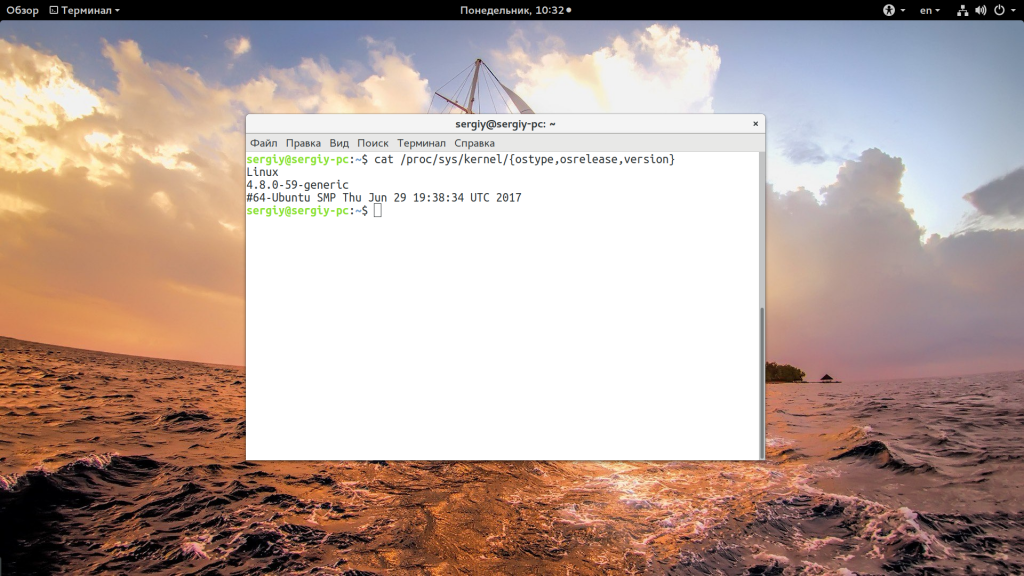
Есть еще несколько файлов с подобной информацией:
Как узнать архитектуру компьютера
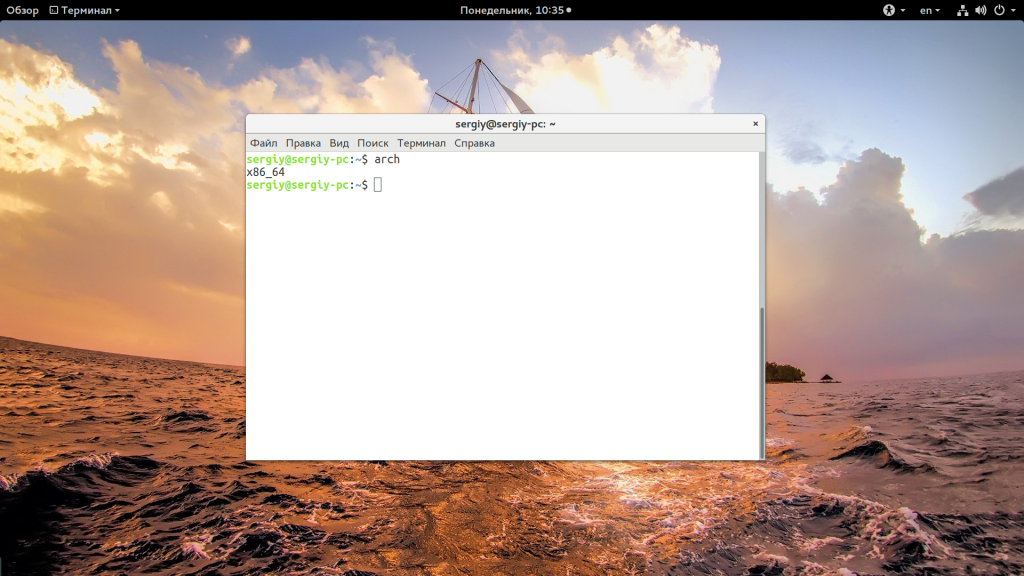
Вы уже знаете как узнать версию Linux, имя дистрибутива и ядро, архитектура уже проскальзывала в командах выше, но существует отдельная команда, которая выводит только архитектуру:
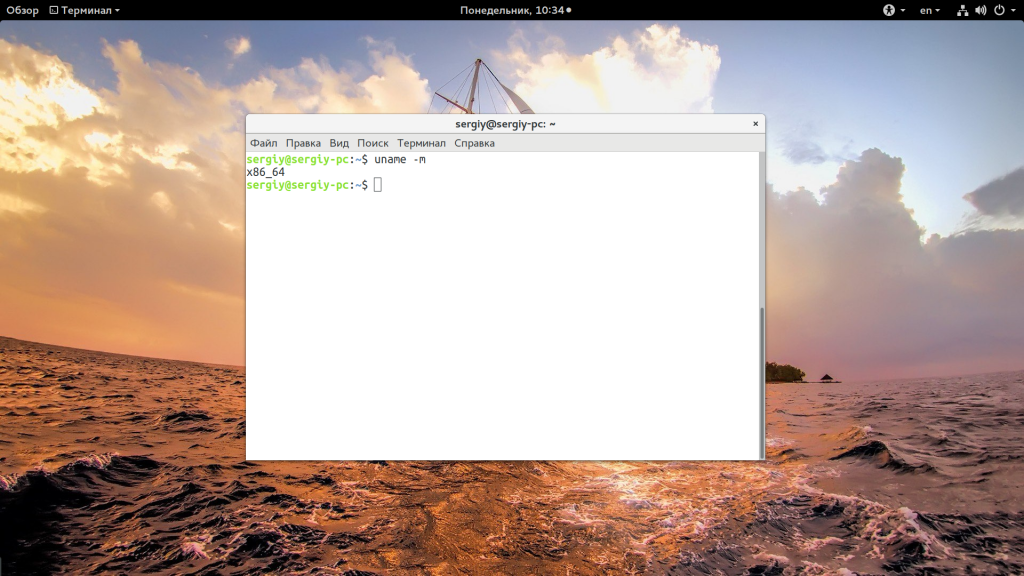
Для этих же целей можно использовать uname:
Выводы
Теперь вы знаете как посмотреть версию Linux. Как видите, в Linux достаточно много способов для решения этой задачи. Надеюсь, эта информация была полезной для вас.

Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
How to Check the OS Version in Linux
“Do you know what version of the operating system you have? The administrators and even normal Linux users should know the OS version they are using. It can be useful in various scenarios, such as installing a new application that needs a particular OS version, upgrading the system, checking the availability of various features and troubleshooting issues. Luckily, every Linux distribution lets you check the OS version through multiple ways. This article will describe how you can check the OS version in Linux through both the command-line and the graphical ways.”
Note: We have demonstrated the methods discussed here on Debian 11. The command line method is applicable to all Linux distributions. However, the graphical method will only apply to those systems with GUI installed.
Check OS Version via Command-Line Terminal
In this section, we will discuss some command line ways to check the OS version in a Linux OS. These commands work for all Linux distributions.
You can open the Terminal by pressing the super key on your keyboard and then search for it using the search box at the top. When the Terminal icon appears, click on it to open.
Using the lsb_release Command
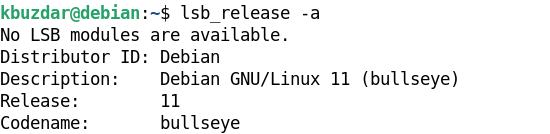
The lsb_release command provides the LSB (Linux Standard Base) and distribution-specific information about a Linux distribution. The information comprises of distributor ID, release number, codename, and a brief description. The lsb_release command may not be installed in some Linux versions due to minimal OS installation or another issue. In this case, if you try to run the lsb_release command, you will get the “No LSB modules are available” error.
To install lsb_release, open the Terminal and run the command below based on the Linux distribution you have:
For Ubuntu and Debian
For Fedora, CentOS, and RHEL
For Arch Linux and Manjaro
For openSUSE
Once installed, use the command below to check your Linux OS version:
Your system will display an output similar to the one in the image below. It will display the LSB info particular to your Linux distribution, including your Linux system version, which in our case is Debian 11.
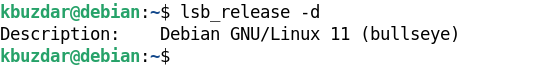
To just display the description that shows the OS version, use the lsb_release command with the -d option:
It will just display the description line of the lsb_release output showing the version number.
Using /etc/issue File
The /etc/issue file contains the system identification text that is displayed before the login prompts. To check your Linux OS version, run the command below:
This command shows the version of your Linux OS. To check the OS version with the point releases, run the command below:
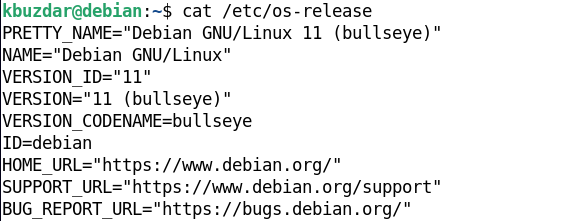
Using /etc/os-release File
The /etc/ost-release file is part of the systemd package and contains OS identification data. You can find this command in every latest Linux distribution, particularly in the systemd distributions. You can also find out the version information of your OS using this file.
To view the content of the /etc/os-release file, use the command below:
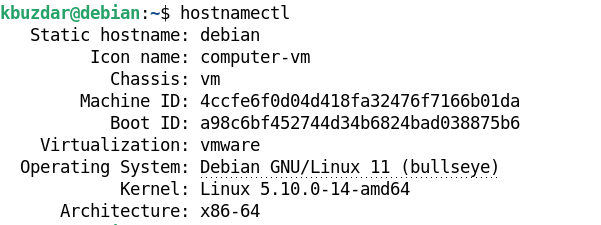
Using hostnamectl Command
The hostnamectl command is also a part of the systemd package. Generally, this command is used to check and configure the hostname. However, you can also use it to check the version of your Linux OS. Similar to the above command, you can also find this command in every latest Linux distribution.
To view your Linux OS version, run the following command in Terminal:
Check Kernel Information
If you want to find out the information related to the kernel of your system, the following are some command-line ways to do so:
Using uname Command
The uname command in Linux displays basic operating system and kernel-related information. You can find the kernel release using the uname with -r option as follows:
You will receive the output similar to this:
To find the kernel version, use the uname with -v option:
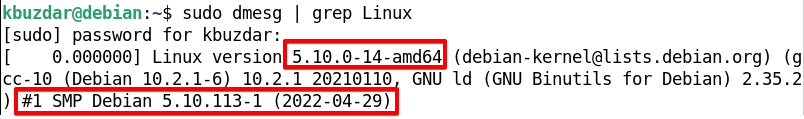
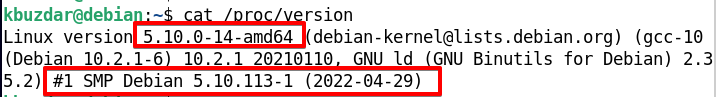
From the above outputs, you can see the kernel release is 5.10.0-14-amd64, whereas the kernel version is #1 SMP Debian 5.10.113-1 (2022-04-29).
Using dmesg Command
The dmesg command is generally used to display the messages from the kernel’s ring buffer, including system startup messages and initialization messages from the hardware devices and drivers. However, it can also be used to check the version of the kernel. To display the kernel information, pipe the dmesg with the grep command as follows:
You will find the Linux kernel release and the version used in your distribution in the output.
Using /proc/version
The /proc/version file contains information about the Linux kernel version and the GCC compiler used to build it. Run the command below to read the kernel information from the /proc/version file:
You will find the Linux kernel release and the version used in your distribution in the output.
Check OS Version in Linux via Graphical User Interface
This method works for most of Linux distributions with GUI. To check your Linux OS version through the graphical user interface, follow the below-given steps:
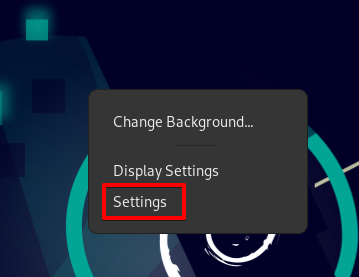
Step 1: Open your system’s Settings utility. Right-click on your desktop, and from the context menu, select Settings as demonstrated in the following screenshot:
On the other hand, you can also look for the Settings utility from the Applications menu. Press the super key and type settings in the search box that will appear at the top. When the icon of the Settings utility appears, click it.
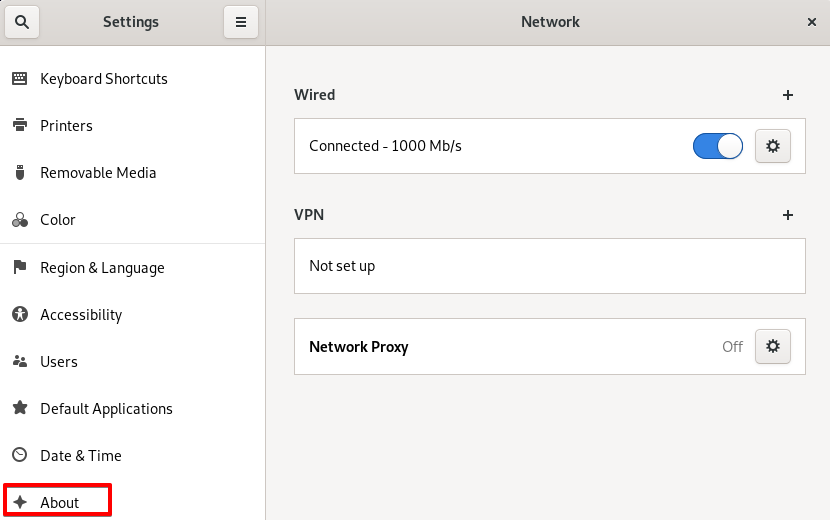
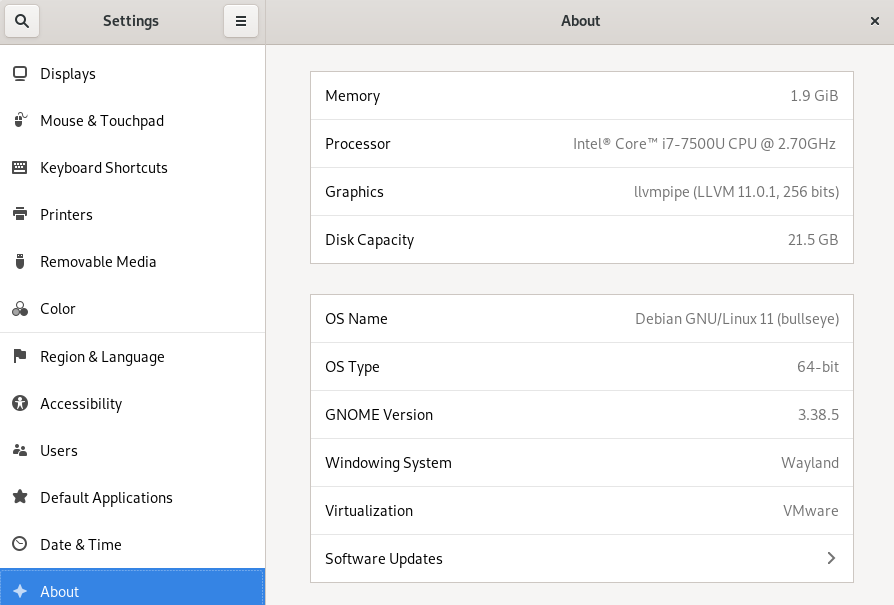
Step 2: In the Settings utility, go to the About section, as shown in the following screenshot, to get details regarding your OS.
In the About section, you will find the version of your OS, which is Debian 11. Apart from the OS version, you will find some other information as well, such as OS type, memory, processor, graphics, disk capacity etc.
Note: To find out Debian Latest versions, including the old releases, visit the following page:
Knowing your operating system’s version is important so you can install the right version of the software and follow the proper guide if you run into any issues. In this article, we have covered some methods, including both the graphical and the command line, through which you can view the version of OS as well as the version of the kernel you are running on your system. If you know of some other method that we have missed, we would love to know in the comments below!
About the author
Karim Buzdar
Karim Buzdar holds a degree in telecommunication engineering and holds several sysadmin certifications. As an IT engineer and technical author, he writes for various web sites. He blogs at LinuxWays.
Get linux version in terminal
How to check your Linux version: easy ways to view the distribution and version number
You can find your current Linux version and distribution in a few easy steps. This information is crucial when it comes to updates, tools, and troubleshooting. Keep reading to find out how to check your Linux version and distribution.
How to check Debian version: the quick and easy way
Knowing which Debian version you have not only helps you to choose the right install package for a program – you also need it to get appropriate support in forums. There are several different methods to check your Debian version. In this step-by-step guide, we’ll explain how to check your version using Terminal and Hardinfo.
Lubuntu — The fast and lean Linux distribution
Lubuntu is an ideal solution for upgrading older computers due to its low hardware and memory requirements. But the Linux distribution is also suitable for other purposes. In our article, we take a closer look at the Ubuntu derivative, who it’s suitable for, and what Lubuntu’s system requirements are. Read on for more.
Xubuntu: the Linux distribution for maximum performance
Xubuntu is a community-developed derivative of the Ubuntu operating system. The distribution is suitable for users who appreciate speed, ease of use, and an elegant look, and want to get the most out of their laptops, desktops, or netbooks. In this article we take a look at Xubuntu’s advantages and system requirements.
Ubuntu backups: A step-by-step guide
It’s important to regularly make backups in Ubuntu. That’s the best way to protect yourself from accidents like the loss of data or a system crash. We’ll explain how to carry out a backup in Ubuntu, what you’ll need, and how you can schedule backups for later. We also touch on solutions for server backups in Ubuntu. Read on for more.