- Best way to find the OS name and version on a Unix/Linux platform
- 10 Answers 10
- Example Runs
- No args
- Header with names and custom separator
- Filtered output
- How to Check Your Ubuntu Version
- Check Ubuntu Version via Command Line
- Check Ubuntu Version with lsb_release Command
- Check Ubuntu Version with cat /etc/lsb-release Command
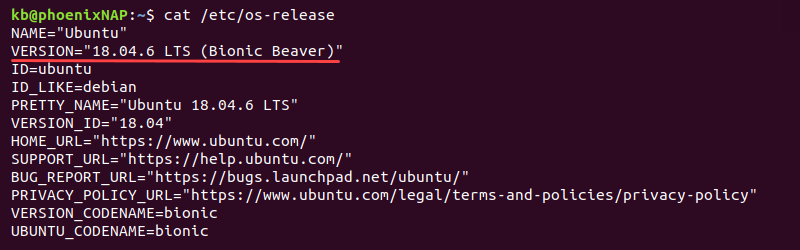
- Check Ubuntu Version with cat /etc/*release Command
- Check Ubuntu Version with hostnamectl Command
- Check Ubuntu Version with cat /etc/issue Command
- Check Ubuntu Version Using screenfetch
- Check Ubuntu Version using neofetch
- Check Ubuntu Version via Graphical Interface
- How do I find out what version of Linux I’m running?
- 9 Answers 9
Best way to find the OS name and version on a Unix/Linux platform
But it does not seem to be the best solution, as LSB_RELEASE support is no longer for RHEL 7.
Is there a way that will work on any Unix or Linux platform?
uname is in most unix environments and guaranteed to be on every LSB compliant linux distro: refspecs.linuxfoundation.org/LSB_2.0.1/LSB-Core/LSB-Core/…
@Niraj — By reading the manpage linux.die.net/man/1/uname and grokking its output (assuming it is supported in RH6.5) . either way there is no (single) portable way to get this because it is mostly irrelevant info. Portable programs should probe for required features, not use some whitelist of prechecked distros.
10 Answers 10
This work fine for all Linux environments.
$ cat /etc/*-release DISTRIB_ID=Ubuntu DISTRIB_RELEASE=10.04 DISTRIB_CODENAME=lucid DISTRIB_DESCRIPTION="Ubuntu 10.04.4 LTS" $ cat /etc/*-release DISTRIB_ID=Ubuntu DISTRIB_RELEASE=12.04 DISTRIB_CODENAME=precise DISTRIB_DESCRIPTION="Ubuntu 12.04.4 LTS" NAME="Ubuntu" VERSION="12.04.4 LTS, Precise Pangolin" ID=ubuntu ID_LIKE=debian PRETTY_NAME="Ubuntu precise (12.04.4 LTS)" VERSION_ID="12.04" $ cat /etc/*-release Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server release 6.5 (Santiago) Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server release 6.5 (Santiago) #!/bin/sh # Detects which OS and if it is Linux then it will detect which Linux # Distribution. OS=`uname -s` REV=`uname -r` MACH=`uname -m` GetVersionFromFile() < VERSION=`cat $1 | tr "\n" ' ' | sed s/.*VERSION.*=\ // ` >if [ "$" = "SunOS" ] ; then OS=Solaris ARCH=`uname -p` OSSTR="$ $($ `uname -v`)" elif [ "$" = "AIX" ] ; then OSSTR="$ `oslevel` (`oslevel -r`)" elif [ "$" = "Linux" ] ; then KERNEL=`uname -r` if [ -f /etc/redhat-release ] ; then DIST='RedHat' PSUEDONAME=`cat /etc/redhat-release | sed s/.*\(// | sed s/\)//` REV=`cat /etc/redhat-release | sed s/.*release\ // | sed s/\ .*//` elif [ -f /etc/SuSE-release ] ; then DIST=`cat /etc/SuSE-release | tr "\n" ' '| sed s/VERSION.*//` REV=`cat /etc/SuSE-release | tr "\n" ' ' | sed s/.*=\ //` elif [ -f /etc/mandrake-release ] ; then DIST='Mandrake' PSUEDONAME=`cat /etc/mandrake-release | sed s/.*\(// | sed s/\)//` REV=`cat /etc/mandrake-release | sed s/.*release\ // | sed s/\ .*//` elif [ -f /etc/debian_version ] ; then DIST="Debian `cat /etc/debian_version`" REV="" fi if [ -f /etc/UnitedLinux-release ] ; then DIST="$[`cat /etc/UnitedLinux-release | tr "\n" ' ' | sed s/VERSION.*//`]" fi OSSTR="$ $ $($ $ $)" fi echo $
The script is useful but for linux it is showing ==Linux RedHat version(Final 2.6.32-431.el6.x86_64 x86_64) .my redhat version is 6.5 but it is not showing in output ?
I tested on RHEL6.3 It is showing output as Linux RedHat 6.3(Santiago 2.6.32-279.22.1.el6.x86_64 x86_64)
Following command worked out for me nicely. It gives you the OS name and version.
The «lsb_release» command provides a certain Linux Standard Base (LSB) and distribution-specific information.
So using the below command we can get the Operating system name and operating system version.
«lsb_release -a«
This command gives you a description of your operating system:
In every distribution, it has different files, so I list the most common ones:
---- CentOS Linux distribution `cat /proc/version` ---- Debian Linux distribution `cat /etc/debian_version` ---- Redhat Linux distribution `cat /etc/redhat-release` ---- Ubuntu Linux distribution `cat /etc/issue` or `cat /etc/lsb-release` In the last one, /etc/issue didn’t exist, so I tried the second one and it returned the right answer.
With quotes:
cat /etc/*-release | grep "PRETTY_NAME" | sed 's/PRETTY_NAME=//g' Without quotes:
cat /etc/*-release | grep "PRETTY_NAME" | sed 's/PRETTY_NAME=//g' | sed 's/"//g' @PeterMortensen in /etc/*-release file original value is stored with double quotes. if you want to save it in database most probably you would want to remove those double quotes as well. 🙂
My own take at @kvivek’s script, with more easily machine parsable output:
#!/bin/sh # Outputs OS Name, Version & misc. info in a machine-readable way. # See also NeoFetch for a more professional and elaborate bash script: # https://github.com/dylanaraps/neofetch SEP="," PRINT_HEADER=false print_help() < echo "`basename $0` - Outputs OS Name, Version & misc. info" echo "in a machine-readable way." echo echo "Usage:" echo " `basename $0` [OPTIONS]" echo "Options:" echo " -h, --help print this help message" echo " -n, --names print a header line, naming the fields" echo " -s, --separator SEP overrides the default field-separator ('$SEP') with the supplied one" ># parse command-line args while [ $# -gt 0 ] do arg="$1" shift # past switch case "$" in -h|--help) print_help exit 0 ;; -n|--names) PRINT_HEADER=true ;; -s|--separator) SEP="$1" shift # past value ;; *) # non-/unknown option echo "Unknown switch '$arg'" >&2 print_help ;; esac done OS=`uname -s` DIST="N/A" REV=`uname -r` MACH=`uname -m` PSUEDONAME="N/A" GetVersionFromFile() < VERSION=`cat $1 | tr "\n" ' ' | sed s/.*VERSION.*=\ // ` >if [ "$" = "SunOS" ] ; then DIST=Solaris DIST_VER=`uname -v` # also: cat /etc/release elif [ "$" = "AIX" ] ; then DIST="$" DIST_VER=`oslevel -r` elif [ "$" = "Linux" ] ; then if [ -f /etc/redhat-release ] ; then DIST='RedHat' PSUEDONAME=`sed -e 's/.*\(//' -e 's/\)//' /etc/redhat-release ` DIST_VER=`sed -e 's/.*release\ //' -e 's/\ .*//' /etc/redhat-release ` elif [ -f /etc/SuSE-release ] ; then DIST=`cat /etc/SuSE-release | tr "\n" ' '| sed s/VERSION.*//` DIST_VER=`cat /etc/SuSE-release | tr "\n" ' ' | sed s/.*=\ //` elif [ -f /etc/mandrake-release ] ; then DIST='Mandrake' PSUEDONAME=`sed -e 's/.*\(//' -e 's/\)//' /etc/mandrake-release` DIST_VER=`sed -e 's/.*release\ //' -e 's/\ .*//' /etc/mandrake-release` elif [ -f /etc/debian_version ] ; then DIST="Debian" DIST_VER=`cat /etc/debian_version` PSUEDONAME=`lsb_release -a 2> /dev/null | grep '^Codename:' | sed -e 's/.*[[:space:]]//'` #elif [ -f /etc/gentoo-release ] ; then #TODO #elif [ -f /etc/slackware-version ] ; then #TODO elif [ -f /etc/issue ] ; then # We use this indirection because /etc/issue may look like # "Debian GNU/Linux 10 \n \l" ISSUE=`cat /etc/issue` ISSUE=`echo -e "$" | head -n 1 | sed -e 's/[[:space:]]\+$//'` DIST=`echo -e "$" | sed -e 's/[[:space:]].*//'` DIST_VER=`echo -e "$" | sed -e 's/.*[[:space:]]//'` fi if [ -f /etc/UnitedLinux-release ] ; then DIST="$[`cat /etc/UnitedLinux-release | tr "\n" ' ' | sed s/VERSION.*//`]" fi # NOTE `sed -e 's/.*(//' -e 's/).*//' /proc/version` # is an option that worked ~ 2010 and earlier fi if $PRINT_HEADER then echo "OS$Distribution$Distribution-Version$Pseudo-Name$Kernel-Revision$Machine-Architecture" fi echo "$$$$$$$$$$$" NOTE: Only tested on Debian 11
Example Runs
No args
Linux,Debian,10.0,buster,4.19.0-5-amd64,x86_64 Header with names and custom separator
OS | Distribution | Distribution-Version | Pseudo-Name | Kernel-Revision | Machine-Architecture Linux | Debian | 10.0 | buster | 4.19.0-5-amd64 | x86_64 Filtered output
How to Check Your Ubuntu Version
Ubuntu is a free, open-source Linux-based operating system, which has a long list of release versions. Finding out which Ubuntu version is running on your system can be important when troubleshooting issues or searching for installation guides.
In this tutorial, learn how to check the Ubuntu version running on your machine.
- A system running Ubuntu
- Access to a user account with sudo or root privileges
- A terminal window/command line (Ctrl–Alt–T)
There are two (2) simple ways to determine the Ubuntu version installed on your server. Check the version in the terminal window or use Ubuntu’s default graphical interface.
Check Ubuntu Version via Command Line
If you prefer using the terminal, you can determine the Ubuntu version installed on your machine in seven (7) different ways.
Note: The first method is not convenient if you’re running Ubuntu on a Docker image. Try one of the other methods instead.
Check Ubuntu Version with lsb_release Command
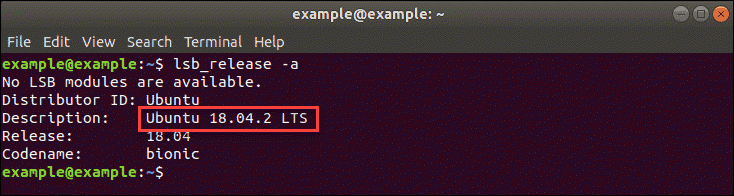
1. Open the terminal (use the Ctrl+Alt+T keyboard shortcut).
2. Type in the following command and hit Enter:
The output displays the current version of Ubuntu. In the example seen in the image above, it is Ubuntu 18.04 (codenamed Bionic Beaver).
3. To display only the description line, use the -d tag:
Show only the description information by adding the -s tag to shorten the output:
4. Add the -c tag to display the codename line as well:
5. Show only the release number by combining the -r and -s tags:
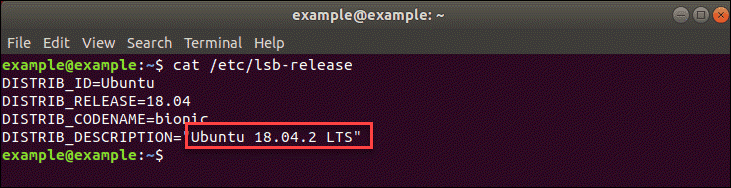
Check Ubuntu Version with cat /etc/lsb-release Command
Alternatively, you can use the command:
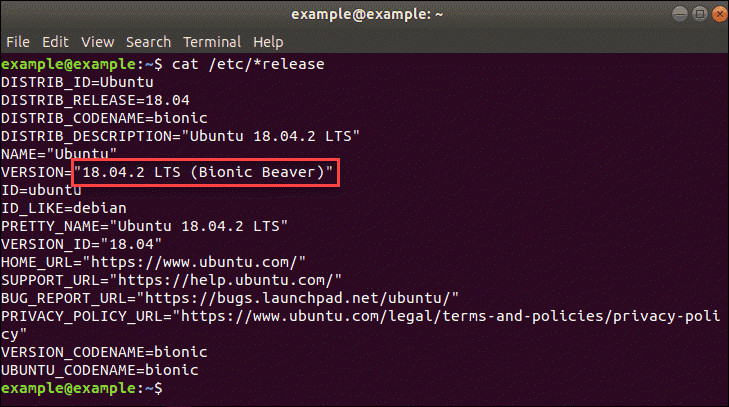
Check Ubuntu Version with cat /etc/*release Command
To get more in-depth information about the Ubuntu release, you can also use the command:
The command is platform agnostic. On Ubuntu, the file’s name is os-release and the following command uses the full file name:
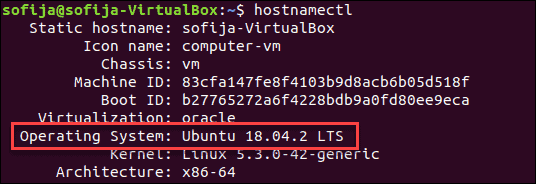
Check Ubuntu Version with hostnamectl Command
Another command that also gives you information about the Ubuntu version is the hostnamectl command:
Check Ubuntu Version with cat /etc/issue Command
The /etc/issue file contains the text which displays when a user connects via SSH. Use the cat command to fetch the contents:
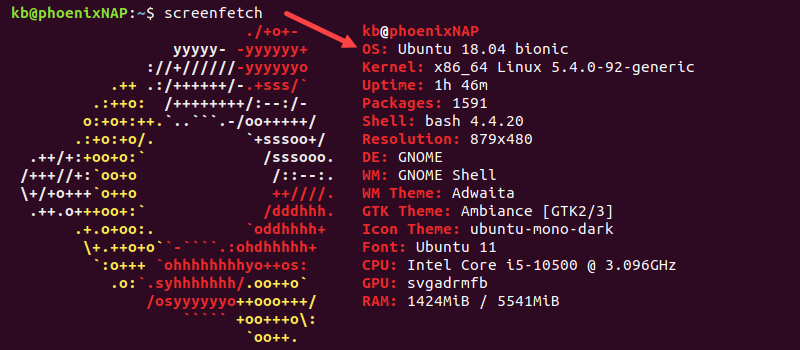
Check Ubuntu Version Using screenfetch
The screenfetch utility is a Bash script for generating useful and visually pleasing OS information.
1. Install screenfetch using the apt package manager:
sudo apt install screenfetch2. The installation asks for confirmation. Press Y to continue.
3. When the installation completes, run the command:
The output displays system information, including the Ubuntu version.
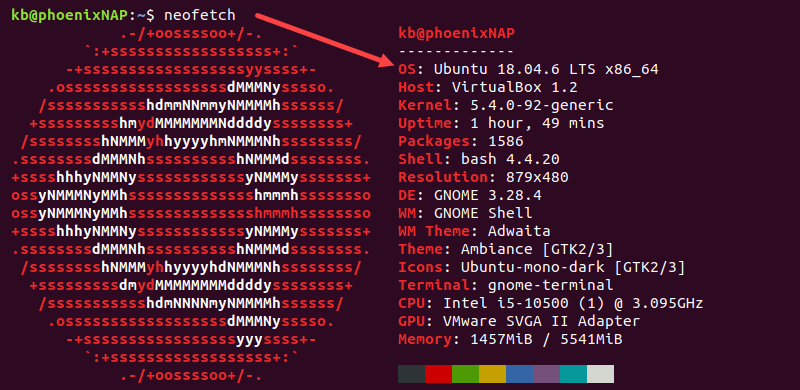
Check Ubuntu Version using neofetch
The neofetch utility is a Bash script and a more modern version of screenfetch . To install and use neofetch, follow the steps below:
1. Install neofetch with the apt package manager:
sudo apt install neofetchThe OS section displays the Ubuntu version.
Check Ubuntu Version via Graphical Interface
You can quickly identify the Ubuntu version running on your system through the graphical interface.
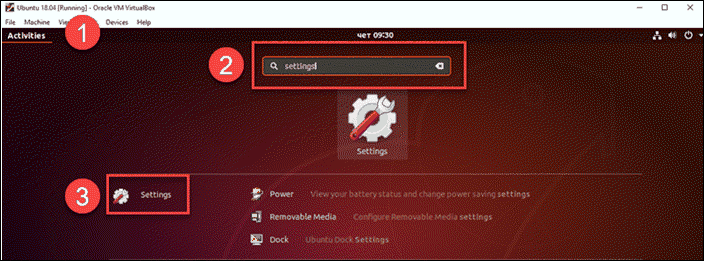
1. First, select Activities in the top left corner.
2. In the search bar, enter Settings and click on the icon once it appears in the results.
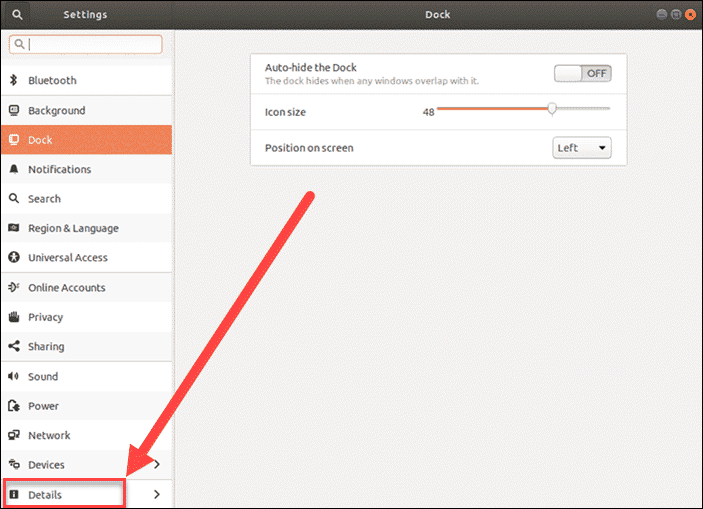
3. In the System Settings window, click on the Details tab.
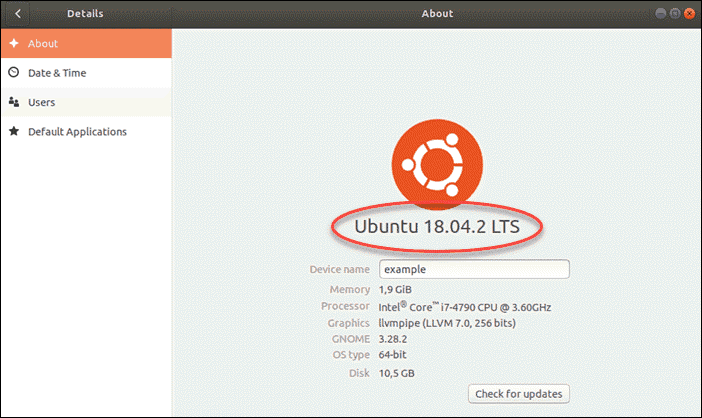
The Details section displays which Ubuntu version number you have, along with other information about your operating system.
The image above indicates that the system running on the machine is Ubuntu 18.04.2 LTS (codenamed Bionic Beaver). LTS is an acronym that stands for Long-Term Support, meaning it’s a major version supported for up to 10 years.
Other Ubuntu LTS releases include:
- Ubuntu 20.04 (Focal Fossa)
- Ubuntu 16.04 (Xenial Xerus) which has an end of life in April 2021
- Ubuntu 14.04 (Trusty Tahr)
After reading this article, you should know how to check which Ubuntu version you are running. Next, explore or even update the central core of the operating system, the Linux kernel.
How do I find out what version of Linux I’m running?
Is there a way to determine what version (distribution & kernel version, I suppose) of Linux is running (from the command-line), that works on any Linux system?
I’d just like to point out for the record how stupid it is that this is a question which needs asking. This is really quite an indictment on the state of every linux distro.
9 Answers 9
The kernel is universally detected with uname :
$ uname -or 2.6.18-128.el5 GNU/Linux There really isn’t a cross-distribution way to determine what distribution and version you’re on. There have been attempts to make this consistent, but ultimately it varies, unfortunately. LSB tools provide this information, but ironically aren’t installed by default everywhere. Example on an Ubuntu 9.04 system with the lsb-release package installed:
$ lsb_release -irc Distributor ID: Ubuntu Release: 9.04 Codename: jaunty Otherwise, the closest widely-available method is checking /etc/something-release files. These exist on most of the common platforms, and on their derivatives (i.e., Red Hat and CentOS).
$ cat /etc/lsb-release DISTRIB_ID=Ubuntu DISTRIB_RELEASE=9.04 DISTRIB_CODENAME=jaunty DISTRIB_DESCRIPTION="Ubuntu 9.04" But Debian has /etc/debian_version :
$ cat /etc/debian_version 5.0.2 Fedora, Red Hat and CentOS have:
Fedora: $ cat /etc/fedora-release Fedora release 10 (Cambridge) Red Hat/older CentOS: $ cat /etc/redhat-release CentOS release 5.3 (Final) newer CentOS: $ cat /etc/centos-release CentOS Linux release 7.1.1503 (Core) $ cat /etc/gentoo-release Gentoo Base System release 1.12.11.1 I don’t have a SUSE system available at the moment, but I believe it is /etc/SuSE-release .
Slackware has /etc/slackware-release and/or /etc/slackware-version .
Mandriva has /etc/mandriva-release .
For most of the popular distributions then,
will most often work. Stripped down and barebones «server» installations might not have the ‘release’ package for the distribution installed.
Additionally, two 3rd party programs you can use to automatically get this information are Ohai and Facter.
Note that many distributions have this kind of information in /etc/issue or /etc/motd , but some security policies and best practices indicate that these files should contain access notification banners.