How to Set Up a Guest Wi-Fi Network
An MIT graduate who brings years of technical experience to articles on SEO, computers, and wireless networking.
Michael Heine is a CompTIA-certified writer, editor, and Network Engineer with 25+ years’ experience working in the television, defense, ISP, telecommunications, and education industries.
- Wi-Fi & Wireless
- The Wireless Connection
- Routers & Firewalls
- Network Hubs
- ISP
- Broadband
- Ethernet
- Installing & Upgrading
What to Know
- Log in to the router as an administrator, enable the Guest Wi-Fi option, and define the SSID that the guest network should use.
- Create a password for guests to use and turn on the SSID broadcast to keep the network name visible to others.
- If the router supports it, restrict access to everything but the internet, or let guests access local devices and resources like file shares.
Some routers support guest networks, which are part of the primary network but use a different password (or none at all). They may also limit certain features. Guest networks are often customary for businesses but are increasingly common for home networks.
This article explains how to set up a guest Wi-Fi network on most routers, and includes a number of tips for using a guest network.
How to Set Up a Guest Wi-Fi Network
Follow these steps to set up a guest network at home:
- Log in to the router as an administrator. This is often done in a web browser through a specific IP address such as 192.168.1.1, but your router may use a different IP address or have a companion mobile app for logins.
Enable the Guest Wi-Fi option. Most routers have guest networking disabled by default but provide an on/off option to control it.
Some routers automatically set the name of a guest network to be the name of the primary network with a guest suffix, like mynetwork_guest, while others allow you to choose a name.
Turn SSID broadcast on or off to either keep the network name visible or to hide it from potential guests. Leave SSID broadcast on so that guests can see which network to use. If you disable the broadcast, provide guests with the network name and security details so that they can set up the network, something you may want to avoid when you have many guests.
Unless you block certain access, guests can do anything that you, the administrator, can do. That means they can download torrents illegally, spread viruses to other devices, or monitor network traffic and website passwords.
Enable other options as needed. If the router supports it, restrict access to everything but the internet, or let guests access local resources like file shares. Some Netgear routers, for example, provide a check box for administrators to allow guests to see each other and access the local network. Leaving that option disabled blocks guests from reaching local resources but allows them to get online through the shared internet connection. You may also want to limit how many guests can connect to your network at the same time. Choose a reasonable number to prevent the network from overloading and slowing to a halt.
If these instructions do not work with your router, visit the manufacturer’s site for more detail. Guest networking is available from these manufacturers and others: Linksys, D-Link, Google, NETGEAR, ASUS, and Cisco.
Benefits of Guest Wi-Fi Networking
A guest Wi-Fi network is beneficial for the owner of the network and those who use it. Guest networking provides a way for users to access a network in seconds with little to no setup on their part. Depending on how the guest network is configured, they can access the internet and local resources on the network like files, printers, and hardware peripherals.
From the administrator’s point of view, the guest network broadens the reach of the network to visitors without needing to give out a network password. Guest networks also improve security because the owner can limit what guests can access, for example, the internet but not local resources. This prevents the spread of viruses that may enter from a guest’s device.
Using a Guest Network
Joining a guest wireless network works in much the same way as connecting to a public Wi-Fi hotspot or the Wi-Fi at a friend’s house. Guests must be provided with the network name and password to access the network.
However, some guest networks are open, meaning there isn’t a password to access them. In such cases, the network name (SSID) may be called Guest, Guest Wifi, CompWifi, Free Wifi, or another variation.
Open and free Wi-Fi for guests is often found in malls, restaurants, parks, and other public places. In places like hotels, you’ll often receive the guest Wi-Fi information from the staff. For guest networks running from home, you’ll most likely need to ask the owner for their Wi-Fi password.
If you upload or download a lot of data, let the administrator know in advance. Drawing a lot of bandwidth causes the network to slow down, so it’s always best to get permission.
Does Your Router Support Guest Networking?
Business-class routers are common platforms for guest networks, but some home routers have guest networking capabilities. Check the manufacturer’s website to be sure, or look in the router settings to see if there’s an option for a guest network.
The guest network option in a router is usually called Guest Network or something similar, but there are some exceptions:
- D-Link routers typically call it the Guest Zone.
- Google Wifi names this feature Guest Wi-Fi.
- Linksys supports a Guest Access tool through its Linksys Smart Wi-Fi remote management interface.
Some routers support only one guest network, while others can run multiple guest networks simultaneously. Dual-band wireless routers often support two—one on the 2.4 GHz band and one on the 5 GHz band. While there’s no practical reason why a person needs more than one per band, some Asus RT wireless routers provide for up to six guest networks.
When a guest network is active, its devices operate on a separate IP address range from that of other devices. Some Linksys routers, for example, reserve the address ranges 192.168.3.1 through 192.168.3.254 and 192.168.33.1 through 192.168.33.254 for guest devices.
[Wireless Router] How to set up Guest Network?
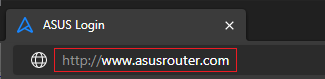
Step 1. Connect your computer to the router via wired or WiFi connection and enter your router LAN IP or router URL http://www.asusrouter.com to the WEB GUI.
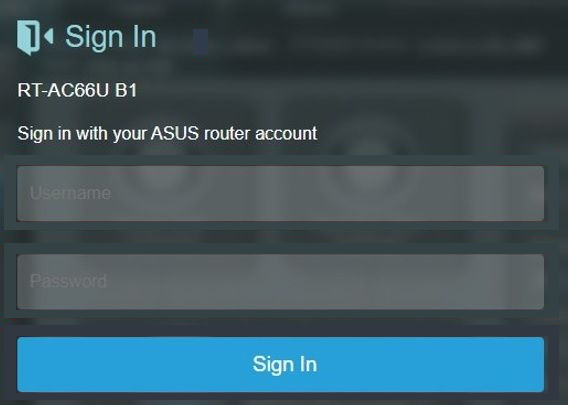
Step 2. Key in your router’s username and password to log in.
Note: If you forget the user name and/or password, please restore the router to the factory default status and setup.
Please refer to [Wireless Router] How to reset the router to factory default setting? for how to restore the router to default status.
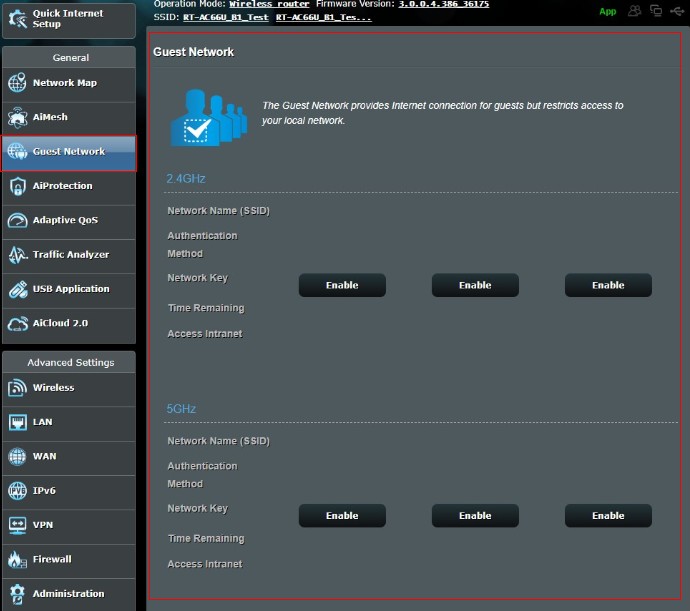
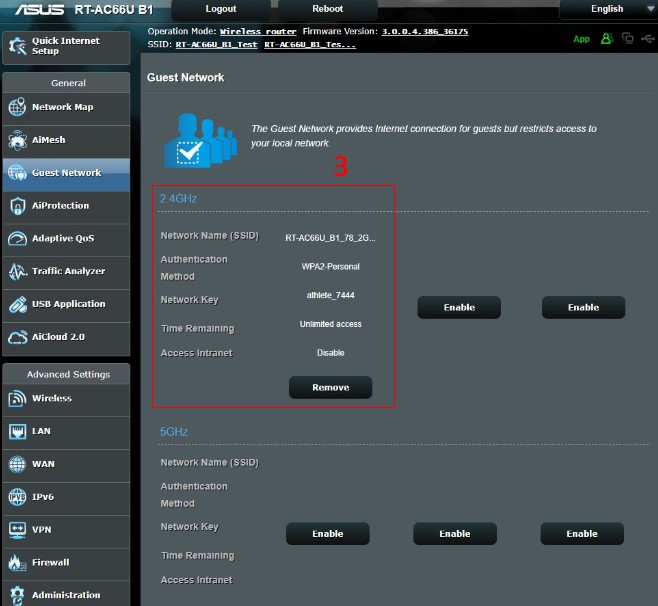
Step 3. Click Guest Network
How to set up Guest Network?
Take RT-AC66U B1 as an example. (Note: RT-AC66U B1 supports 2.4GHz and 5GHz)
A.Quick set up (default)
Select 2.4GHz or 5GHz frequency band for the guest network that you want to create.
The 2.4GHz band setting is below as an example:
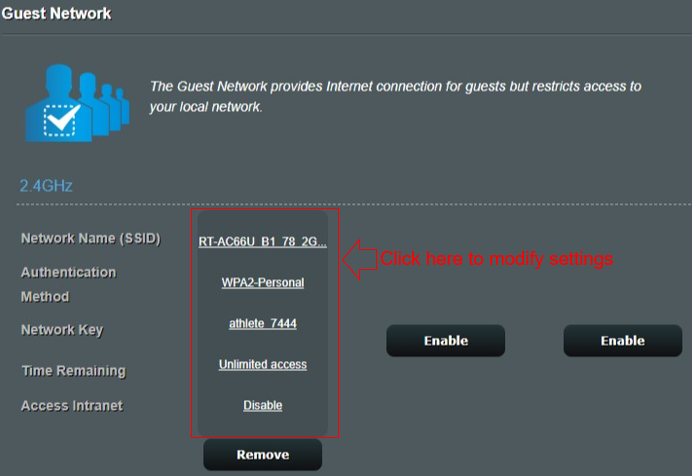
B.Function description (modify, remove)
The 2.4GHz band setting is below as an example:
Note: When the modification is complete, click «Apply» to save your settings.
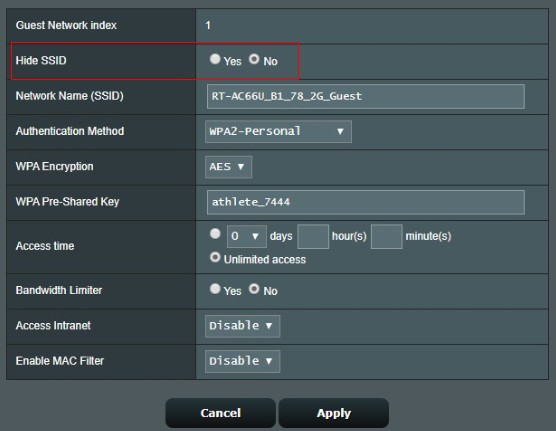
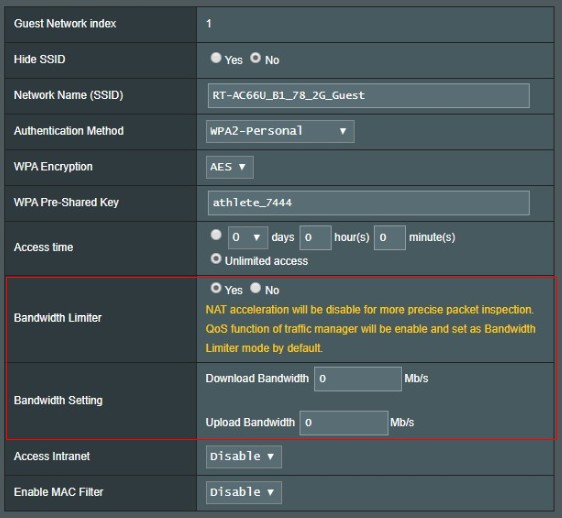
In the Hide SSID field, select YES to prevent wireless devices from detecting your SSID. When this function is enabled, you would need to enter the SSID manually on the wireless device to access the wireless network.
The network name (SSID) is a unique name that identifies the wireless network. Assign a unique name containing up to 32 characters for your SSID (Service Set Identifier) to identify your wireless network via your assigned SSID.
This field selects the authentication methods for wireless clients.
Select any of these authentication methods:
3-1.Open System: This option provides no security. No network password required.
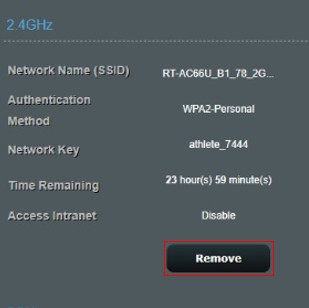
3-2.WPA2-Personal: This option provides strong security. If you select this option, you must use WPA Encryption: AES and enter the WPA Pre-Shared Key (network key).
3-3. WPA-Auto-Personal: This option provides strong security. If you select this option, you must use WPA Encryption: AES (or TKIP+AES) and enter the WPA Pre-Shared Key (network key).
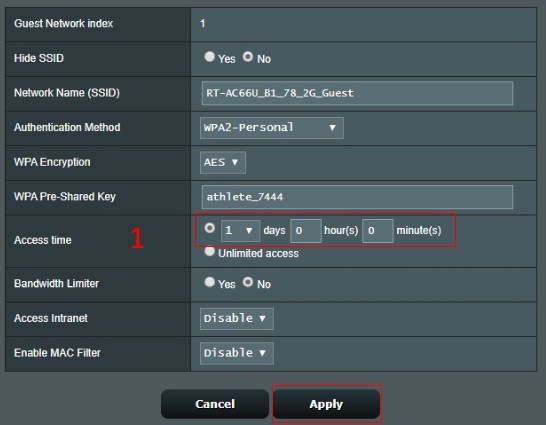
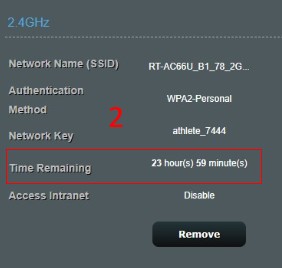
The time allow quest to access internet. Specify the access time or choose “Unlimited access”.
4-1.For example, if you set a day and then click Apply.
4-2.The time remaining is shown here.
If select [Yes], set the speed (megabits per second) limits for your Upload Bandwidth and Download Bandwidth.
Before setting up the upload/download bandwidth, you can use Speedtest.net to measure the bandwidth provided by your ISP.
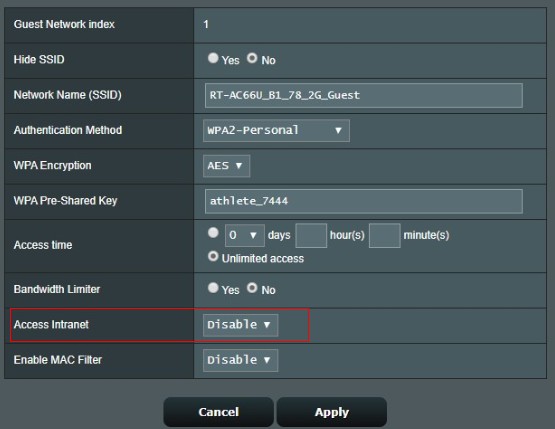
Allow guest to access intranet.
If select [disable], guest would not be able to use devices behind router, which connect by cable.
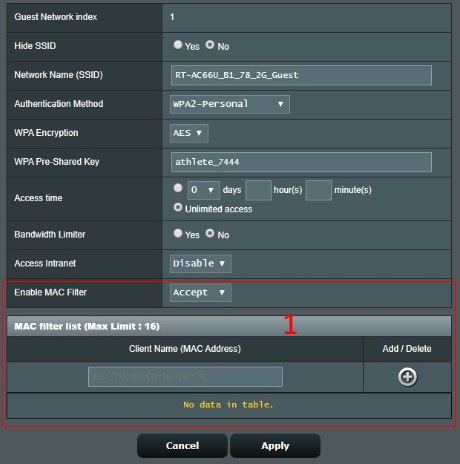
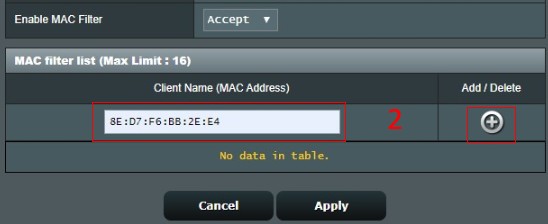
Wireless MAC filter provides control over packets transmitted to a specified MAC (Media Access Control) address on your wireless network.
In Enable MAC Filter dropdown list, select either Disable or Accept or Reject
- Disable: Disable MAC Filter.
- Accept: Select Accept to allow devices in the MAC filter list to access to the wireless network.
- Reject: Select Reject to prevent devices in the MAC filter list to access to the wireless network.
The Accept setting is below as an example:
7-1.Select Accept and show the MAC filter list below
7-2.key in the MAC address of the wireless device and then click to add the setting to MAC filter list.
The format for the MAC address is six groups of two hexadecimal digits, separated by colons (:), in transmission order. (e.g. 8E:D7:F6:BB:2E:E4)
If you delete the MAC address in the MAC filter list, click .
If you want to close the guest network, click Remove then done.
1. Why guest network does not have Access Intranet/Bandwidth Limiter option when in Access point (AP) mode?
- The guest network- Access Intranet/Bandwidth Limiter option is not exist when router is in AP mode.
- When in AP mode, all the IP address are dispatched from the front router/modem above the router, the router does not have any DHCP function when in AP mode, so it cannot manage the device connect to it, the manage control is in the front router/modem.
2. Can I query which devices are connected to the guest network?
- This feature is not supported, there is no ability to manage connected devices in the guest network.
- The guest network is a separate wireless network environment, so the client status on the network map does not show the devices connected to the guest network.
3. Why can’t I setup Guest network under AiMesh node?
- Guest network broadcast from AiMesh router only currently, it is not available in AiMesh node.
- There won’t be any guest network option from the AiMesh node(s).
4. Why Guest network cannot sync and work in AiMesh node?
All router settings can only be done under the AiMesh router, not from AiMesh nodes.
Guest WiFi on all Mesh nodes (all node need to upgrade to 3.0.0.4.386 firmware)
Support list:
ZenWiFi: XT8(RT-AX95Q), XD4(RT-AX56U_XD4), CD6(RT-AC59_CD6)
GT series: GT-AX11000, GT-AC5300, GT-AC2900
RT series: RT-AX88U, RT-AX92U, RT-AX86U, RT-AX82U, RT-AX58U, TUF-AX3000, RT-AX56U, RT-AX55
RT series: RT-AC5300, RT-AC88U, RT-AC3100, RT-AC86U, RT-AC68U
How to get the (Utility / Firmware)?
You can download the latest drivers, software, firmware and user manuals in the ASUS Download Center.
If you need more information about the ASUS Download Center, please refer this link.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/192-168-1-1-login-3b3212ea841648f3b40ec206dad3887c.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/001-guest-network-for-home-tutorial-818204-37a2774c65c945c69093d0c18262042c.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/002-guest-network-for-home-tutorial-818204-11487a97836e43938ff4514e36f4629d.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/003-guest-network-for-home-tutorial-818204-534cf0d97df64cf48722a9deee888e88.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/004-guest-network-for-home-tutorial-818204-5900b0db6bd4427ca9535e18e016a139.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/comtrend-guest-wifi-advanced-settings-4d4331f919bf4a6e8778733c597efd29.png)