- How To Install GUI On Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 & 8 Deployed On Azure
- UNDERSTANDING THE SUBJECT MATTER
- Does Red Hat Have A GUI
- ACTION TIME
- Step By Step On How To Install Gui On Red Hat Linux 7 & 8 On Azure And Access The Server Via The GUI
- 1. Verify the availability of the package group
- 2. Install the “Server with GUI” package group.
- 3. verify that the package group is now installed.
- 4. By default, the runtarget is 3, change it to 5 (i.e graphical.target), multi-user and desktop
- 5. verify the changes
- 6. start the graphical.target process and verify again
- 7. From the Azure portal, under Boot diagnostics, verify that you now have the GUI installed.
- 8. Allow RDP port in the firewall rule
- 9. Install the XRDP package
- 9b. Install the Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux repository (EPEL)
- Now Install the XRDP package
- 10. Install the tigervnc-server and the xterm emulator for x windows.
- 11. Start and enable the xrdp service
- 12. Verify the service is started
- 13. RDP into the server
- How to Install GUI on RHEL 8
- Requirements
- Install Gnome Desktop on RHEL 8 Server
- Enabling Graphical Mode in RHEL 8
How To Install GUI On Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 & 8 Deployed On Azure
In this article, you will learn how to install GUI on Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 & 8 deployed on Azure and access the server via the GUI environment.
UNDERSTANDING THE SUBJECT MATTER
For a long time I have been administering Microsoft Azure and Linux servers hosted on Azure, I did not think one day about GUI on Linux, or rather didn’t occur to me that I may want to access the server via the GUI until one morning, I got an email from a customer that he needed to configure a printer and he requested that he access his server via GUI. Yours may be for another reason or whatsoever, hence why I have decided to give a tutorial on this subject matter.
Does Red Hat Have A GUI
Yes, Red Hat has a GUI if you install the “Server with GUI” package group, but Red Hat Enterprise Linux servers deployed on Azure by default comes with minimal installation and not with GUI. There are two ways to verify this.
One of the ways is to use the command,
The output of the command will show that the “Server with GUI” group package is among the “available environmental group” and not in the “installed environment group”
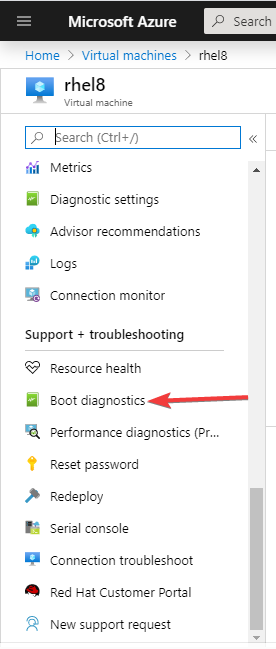
Another way to verify is from Boot Diagnostics on the Azure portal.
From the Azure portal, navigate to virtual machine > Boot diagnostics
When you click on Boot diagnostics, this is what you will see.
You can see that there is no GUI console available compared to when it is available when we install it in the “ACTION TIME” section.
More so, installing the package group is not enough, after installation, there is still a need to access the server via the GUI. Therefore, there will be a need for a tool that can do that. In this tutorial, we will be using the xrdp, tigervnc and the xterm tool.
Now, let’s start the configuration.
ACTION TIME
Step By Step On How To Install Gui On Red Hat Linux 7 & 8 On Azure And Access The Server Via The GUI
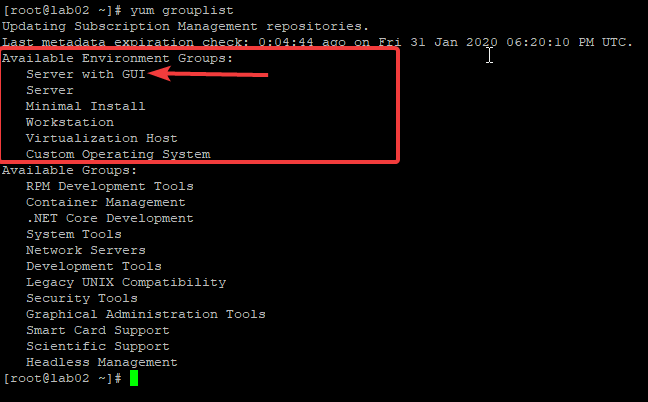
1. Verify the availability of the package group
Updating Subscription Management repositories.
Last metadata expiration check: 0:04:44 ago on Fri 31 Jan 2020 06:20:10 PM UTC.
Available Environment Groups:
Server with GUI
Server
Minimal Install
Workstation
Virtualization Host
Custom Operating System
Available Groups:
RPM Development Tools
Container Management
.NET Core Development
System Tools
Network Servers
Development Tools
Legacy UNIX Compatibility
Security Tools
Graphical Administration Tools
Smart Card Support
Scientific Support
Headless Management
[root@lab02 ~]#
2. Install the “Server with GUI” package group.
[root@Linuxserver ~]# yum groupinstall “Server with GUI”
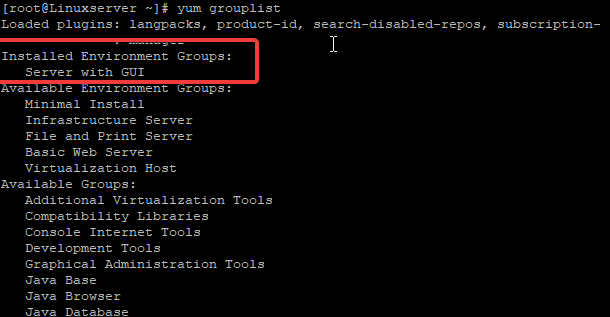
3. verify that the package group is now installed.
[root@Linuxserver ~]# yum grouplist
Loaded plugins: langpacks, product-id, search-disabled-repos, subscription-
: manager
Installed Environment Groups:
Server with GUI
Available Environment Groups:
Minimal Install
Infrastructure Server
File and Print Server
Basic Web Server
Virtualization Host
4. By default, the runtarget is 3, change it to 5 (i.e graphical.target), multi-user and desktop
[root@Linuxserver ~]# systemctl set-default graphical.target
Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/default.target.
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/default.target to /usr/lib/systemd/system/graphical.target.
[root@Linuxserver ~]#
5. verify the changes
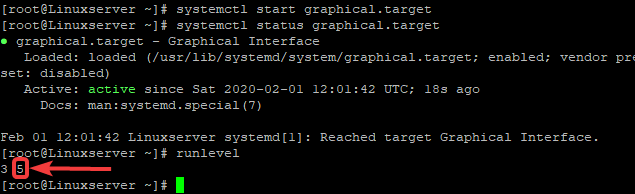
[root@Linuxserver ~]# runlevel
N 3
[root@Linuxserver ~]# systemctl status graphical.target
● graphical.target – Graphical Interface
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/graphical.target; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: inactive (dead)
Docs: man:systemd.special(7)
6. start the graphical.target process and verify again
[root@Linuxserver ~]# systemctl start graphical.target
[root@Linuxserver ~]# systemctl status graphical.target
● graphical.target – Graphical Interface
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/graphical.target; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active since Sat 2020-02-01 12:01:42 UTC; 18s ago
Docs: man:systemd.special(7)
Feb 01 12:01:42 Linuxserver systemd[1]: Reached target Graphical Interface.
7. From the Azure portal, under Boot diagnostics, verify that you now have the GUI installed.
Now that you have the GUI installed, we need a GUI console. I usually use Xming for my KVM vm’s and RDP for Azure VM’s anytime I need to use the GUI.
8. Allow RDP port in the firewall rule
[root@Linuxserver ~]# firewall-cmd – -add-port=3389/tcp – -permanent
success
[root@Linuxserver ~]# firewall-cmd – -reload
9. Install the XRDP package
NOTE: The XRDP package is not in the default Red Hat Repositories, the reason you will need to add an extra repository.
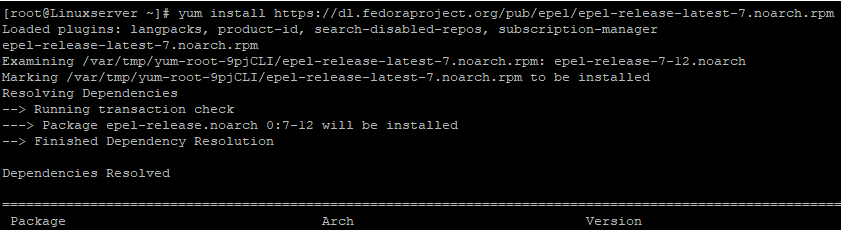
9b. Install the Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux repository (EPEL)
[root@Linuxserver ~]# yum install
https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
Loaded plugins: langpacks, product-id, search-disabled-repos, subscription-manager
epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm | 15 kB 00:00:00
Examining /var/tmp/yum-root-9pjCLI/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm: epel-release-7-12.noarch
Marking /var/tmp/yum-root-9pjCLI/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm to be installed
Resolving Dependencies
–> Running transaction check
—> Package epel-release.noarch 0:7-12 will be installed
–> Finished Dependency Resolution
========================
Package Arch Version Repository Size
========================
Installing:
epel-release noarch 7-12 /epel-release-latest-7.noarch 24 k
Transaction Summary
=========================
Install 1 Package
Total size: 24 k
Installed size: 24 k
Is this ok [y/d/N]:
Now Install the XRDP package
[root@Linuxserver media]# yum install xrdp
Loaded plugins: langpacks, product-id, search-disabled-repos, subscription-
: manager
epel/x86_64/metalink | 27 kB 00:00
epel | 5.3 kB 00:00
rhui-microsoft-azure-rhel7 | 2.1 kB 00:00
rhui-rhel-7-server-dotnet-rhui-debug-rpms | 2.1 kB 00:00
rhui-rhel-7-server-dotnet-rhui-rpms | 2.3 kB 00:00
Total download size: 426 k
Installed size: 2.1 M
Is this ok [y/d/N]:
Retrieving key from file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-7
Importing GPG key 0x352C64E5:
Userid : “Fedora EPEL (7) “
Fingerprint: 91e9 7d7c 4a5e 96f1 7f3e 888f 6a2f aea2 352c 64e5
Package : epel-release-7-12.noarch (@/epel-release-latest-7.noarch)
From : /etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-EPEL-7
Is this ok [y/N]: y
Running transaction check
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded
Running transaction
Installing : 1:xrdp-0.9.12-1.el7.x86_64 1/1
Verifying : 1:xrdp-0.9.12-1.el7.x86_64 1/1
Installed:
xrdp.x86_64 1:0.9.12-1.el7
Complete!
[root@Linuxserver media]#
10. Install the tigervnc-server and the xterm emulator for x windows.
[root@Linuxserver ~]# yum install tigervnc xterm
Loaded plugins: langpacks, product-id, search-disabled-repos, subscription-
: manager
Resolving Dependencies
–> Running transaction check
—> Package tigervnc.x86_64 0:1.8.0-17.el7 will be installed
–> Processing Dependency: tigervnc-icons for package: tigervnc-1.8.0-17.el7.x86_64
–> Processing Dependency: libfltk.so.1.3()(64bit) for package: tigervnc-1.8.0-17.el7.x86_64
–> Processing Dependency: libfltk_images.so.1.3()(64bit) for package: tigervnc-1.8.0-17.el7.x86_64
–> Running transaction check
—> Package fltk.x86_64 0:1.3.4-1.el7 will be installed
–> Processing Dependency: libGLU.so.1()(64bit) for package: fltk-1.3.4-1.el7.x86_64
11. Start and enable the xrdp service
[root@Linuxserver ~]# systemctl start xrdp
[root@Linuxserver ~]# systemctl enable xrdp
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/xrdp.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/xrdp.service.
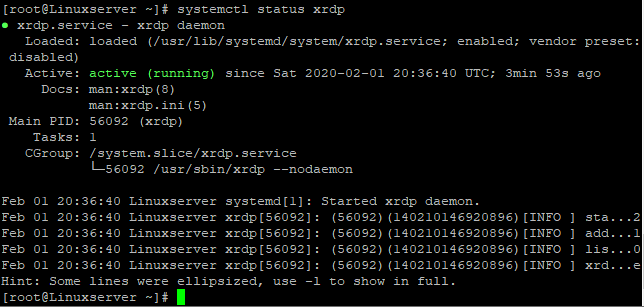
12. Verify the service is started
[root@Linuxserver ~]# systemctl status xrdp
● xrdp.service – xrdp daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/xrdp.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2020-02-01 20:36:40 UTC; 3min 53s ago
Docs: man:xrdp(8)
man:xrdp.ini(5)
Main PID: 56092 (xrdp)
Tasks: 1
CGroup: /system.slice/xrdp.service
└─56092 /usr/sbin/xrdp –nodaemon
Feb 01 20:36:40 Linuxserver systemd[1]: Started xrdp daemon.
Feb 01 20:36:40 Linuxserver xrdp[56092]: (56092)(140210146920896)[INFO ] sta…2
Feb 01 20:36:40 Linuxserver xrdp[56092]: (56092)(140210146920896)[INFO ] add…1
Feb 01 20:36:40 Linuxserver xrdp[56092]: (56092)(140210146920896)[INFO ] lis…0
Feb 01 20:36:40 Linuxserver xrdp[56092]: (56092)(140210146920896)[INFO ] xrd…e
Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full.
[root@Linuxserver ~]#
13. RDP into the server
NOTE: You may need to restart the server before you can RDP. If it doesn’t allow you RDP, do a restart.
How to Install GUI on RHEL 8
As a Linux administrator for more than 4 years, I spend most of my time working on Linux console, but there are some situations where I need a Desktop environment instead of command-line. By default, RHEL 8 comes in two main flavors, namely, Server without GUI and Workstation with graphical user interface pre-installed as default.
In this article, we will show how to install a GNOME Desktop Environment in RHEL 8 Server.
Requirements
If you have not enabled RedHat subscription during the RHEL 8 installation, you can enable it now by following our article at: How to Enable RHEL Subscription in RHEL 8.
Install Gnome Desktop on RHEL 8 Server
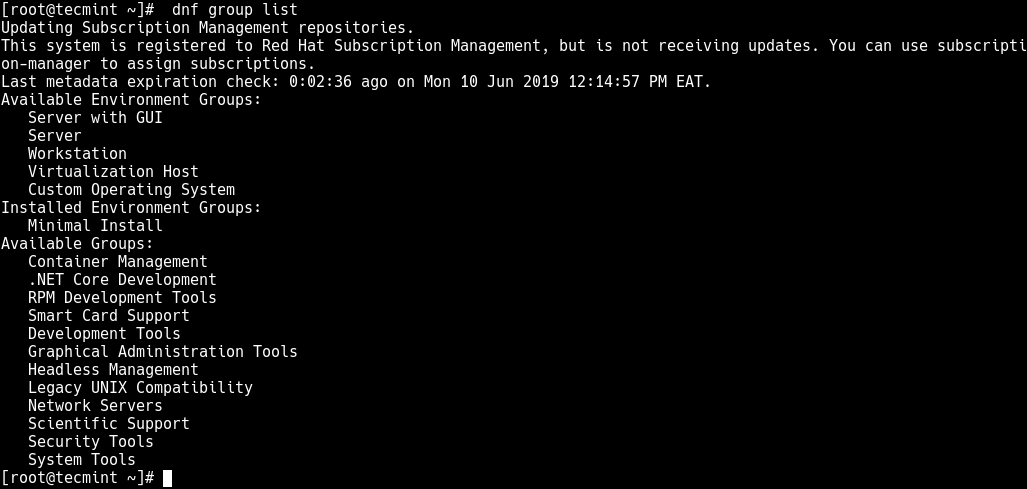
The GNOME package is provided by the “Server with GUI” or “Workstation” package group. To install it, log into the RHEL 8 system via the console or via SSH, then run the following dnf command to view the available package groups.
Looking at the output of the above command, under Available Environment Groups, we have many package groups including Server with GUI and Workstation. Depending on your system type, you can choose one to install the GNOME desktop environment as follows.
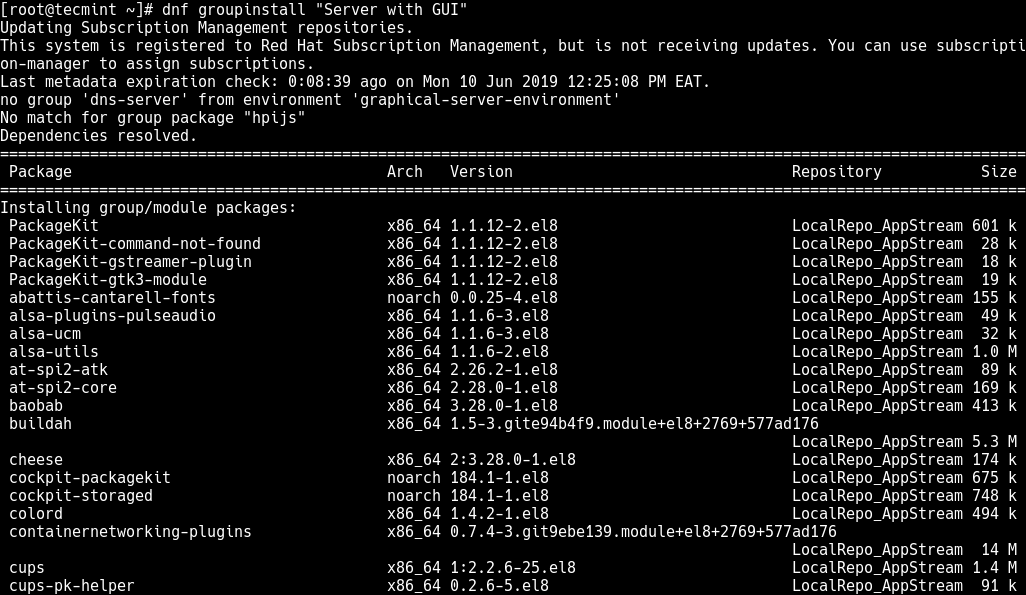
# dnf groupinstall "Server with GUI" #run this on a server environment OR # dnf groupinstall "Workstation" #to setup a workstation
Enabling Graphical Mode in RHEL 8
Once the installation is complete, run the following command to set the graphical mode as the default target for the RHEL 8 system to boot into.
# systemctl set-default graphical
Next, reboot the system to boot into the graphical mode by running the following command.
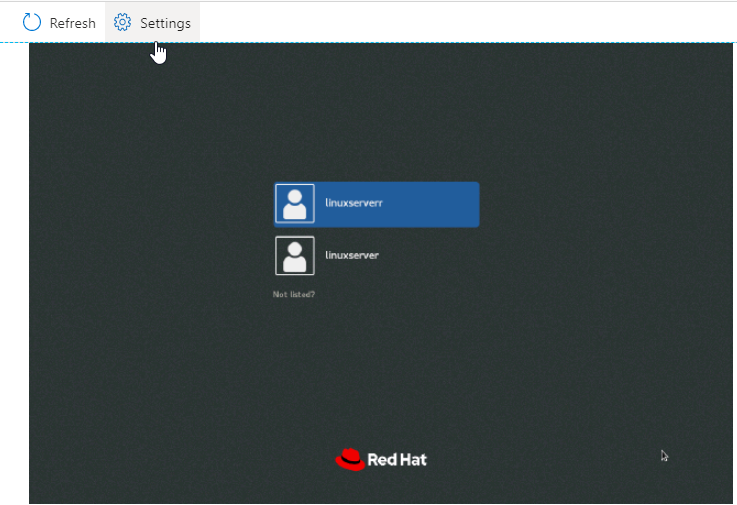
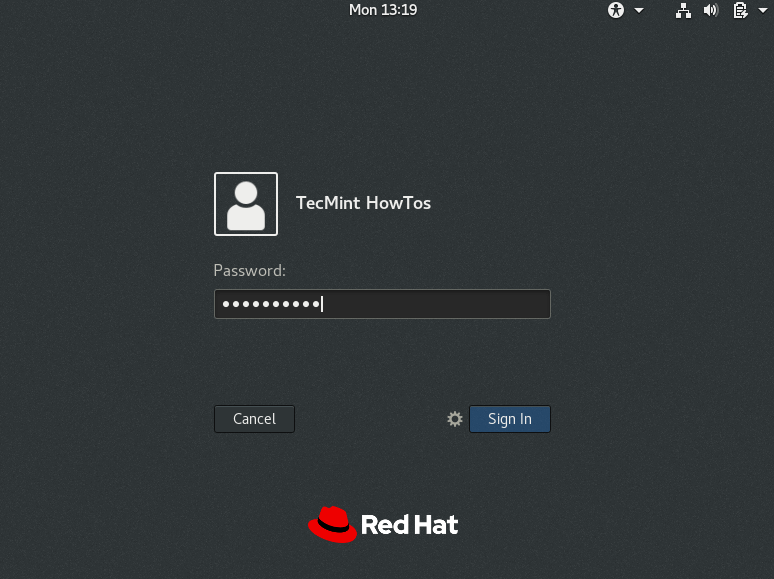
After the system boots, you will access the GNOME login interface, click on the username and enter your password to login as shown in the following screenshots.

After a successful login, the system will take you through a GNOME initial setup. You will be asked to choose a language, keyboard layout, and location settings, once that’s done you will be ready to start using your system via a desktop environment.
Congratulations! You have successfully set up an RHEL 8 server with a GUI. If you have any queries or thoughts to share, use the feedback form below to reach us.