Проверка контрольной суммы Linux
Контрольная сумма — это цифра или строка, которая вычисляется путем суммирования всех цифр нужных данных. Ее можно использовать в дальнейшем для обнаружения ошибок в проверяемых данных при хранении или передаче. Тогда контрольная сумма пересчитывается еще раз и полученное значение сверяется с предыдущим.
В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрим что такое контрольная сумма Linux, а также как выполнять проверку целостности файлов с помощью контрольных сумм md5.
Что такое MD5?
Контрольные суммы Linux с вычисляемые по алгоритму MD5 (Message Digest 5) могут быть использованы для проверки целостности строк или файлов. MD5 сумма — это 128 битная строка, которая состоит из букв и цифр. Суть алгоритма MD5 в том, что для конкретного файла или строки будет генерироваться 128 битный хэш, и он будет одинаковым на всех машинах, если файлы идентичны. Трудно найти два разных файла, которые бы выдали одинаковые хэши.
В Linux для подсчета контрольных сумм по алгоритму md5 используется утилита md5sum. Вы можете применять ее для проверки целостности загруженных из интернета iso образов или других файлов.
Эта утилита позволяет не только подсчитывать контрольные суммы linux, но и проверять соответствие. Она поставляется в качестве стандартной утилиты из набора GNU, поэтому вам не нужно ничего устанавливать.
Проверка контрольных сумм в Linux
Синтаксис команды md5sum очень прост:
$ md5sum опции файл
Опций всего несколько и, учитывая задачи утилиты, их вполне хватает:
- -c — выполнить проверку по файлу контрольных сумм;
- -b — работать в двоичном формате;
- -t — работать в текстовом формате;
- -w — выводить предупреждения о неверно отформатированном файле сумм;
- —quiet — не выводить сообщения об успешных проверках.
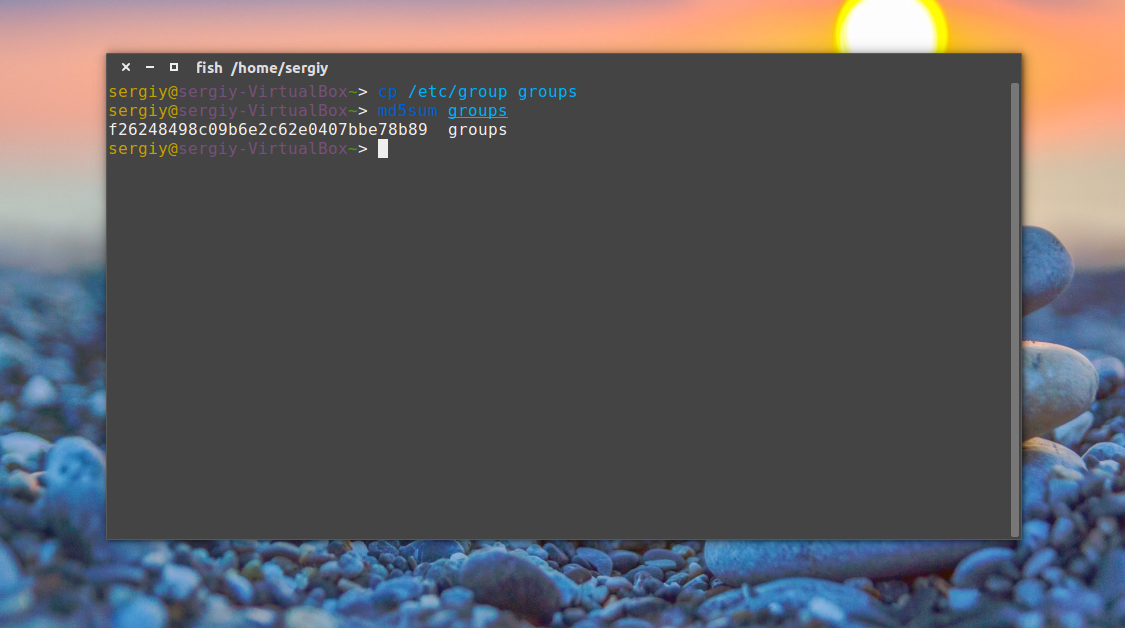
Сначала скопируйте файл /etc/group в домашнюю папку чтобы на нем немного поэкспериментировать:
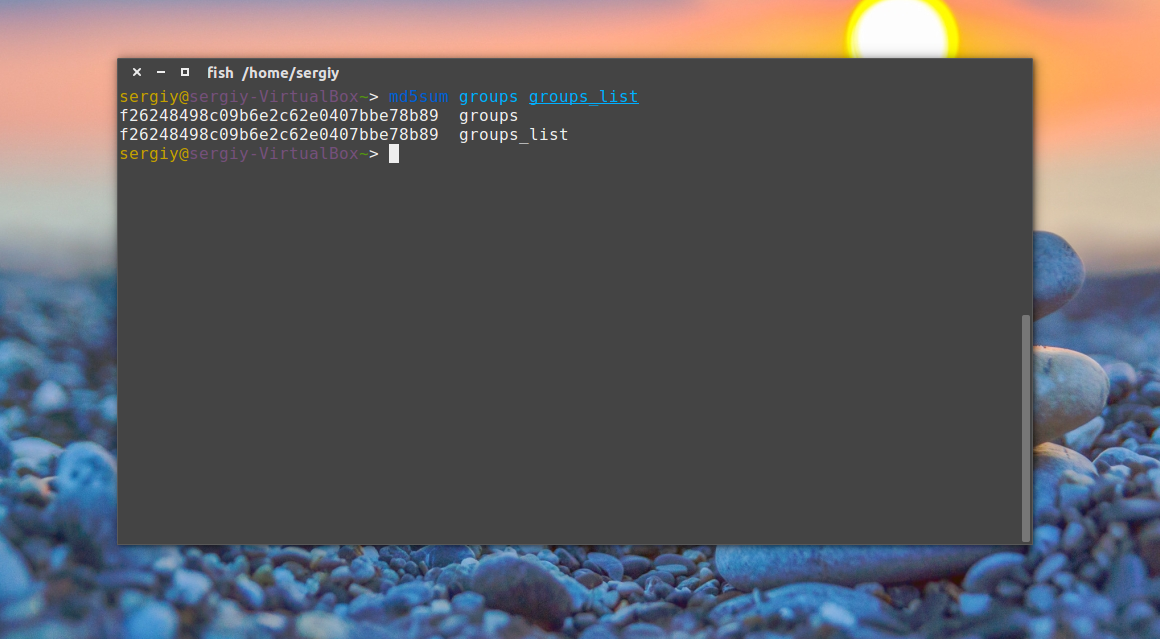
Например, давайте подсчитаем контрольную сумму для файла /etc/group:
Или вы можете сохранить сразу эту сумму в файл для последующей проверки:
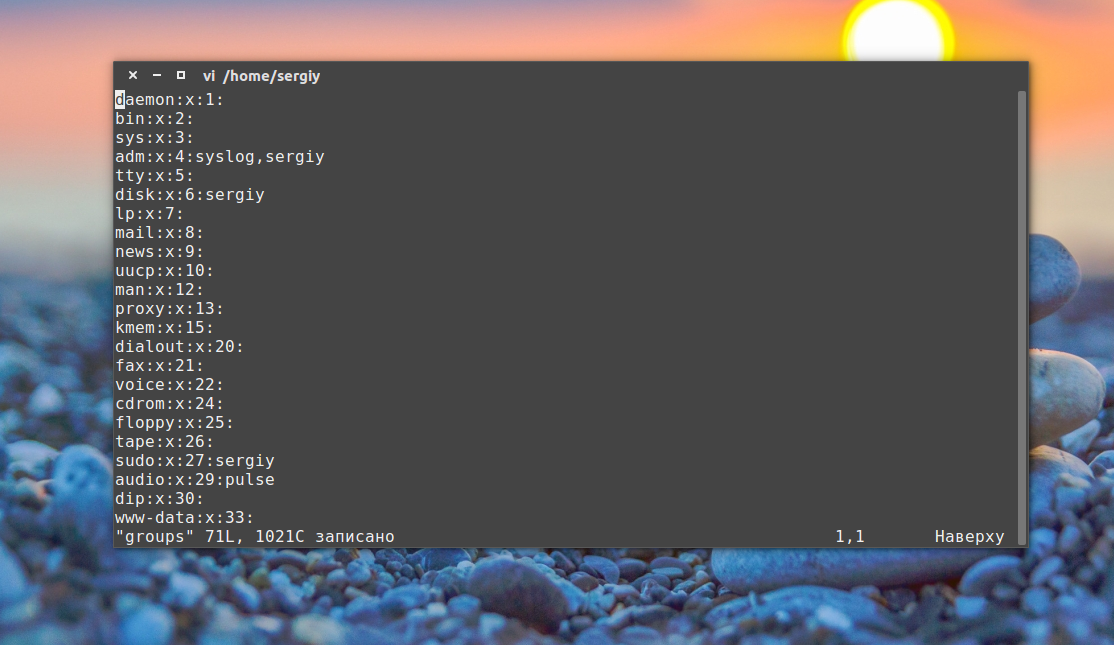
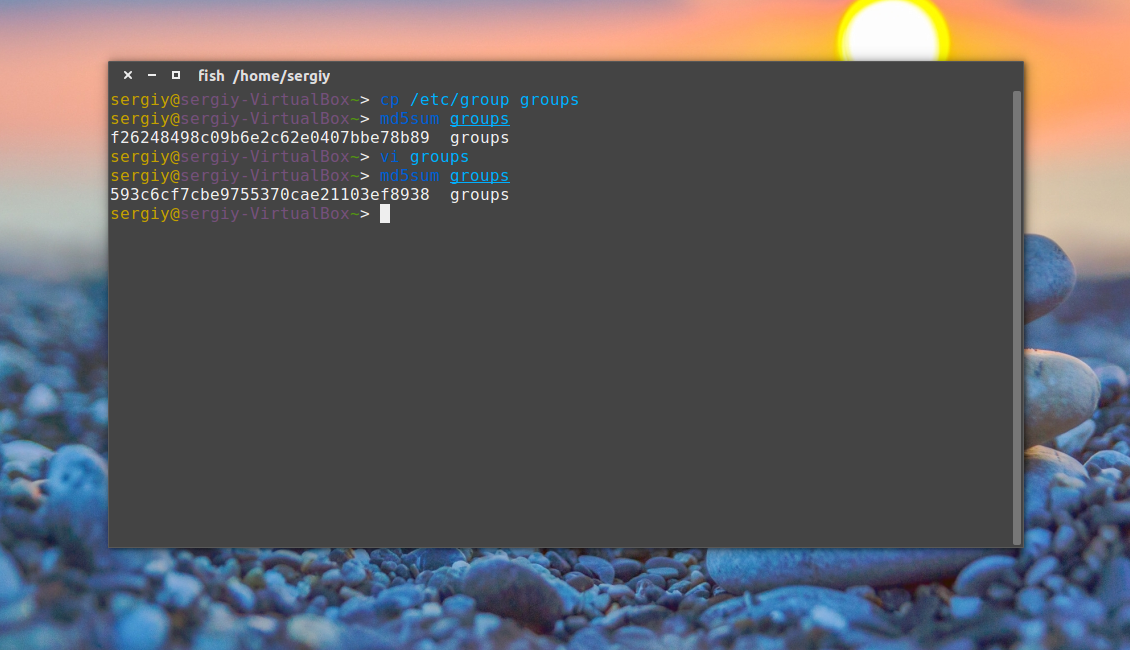
Затем каким-либо образом измените этот файл, например, удалите первую строчку и снова подсчитайте контрольные суммы:
Как видите, теперь значение отличается, а это значит, что содержимое файла тоже изменилось. Дальше верните обратно первую строчку root:x:0: и скопируйте этот файл в groups_list и
Затем опять должна быть выполнена проверка контрольной суммы linux:
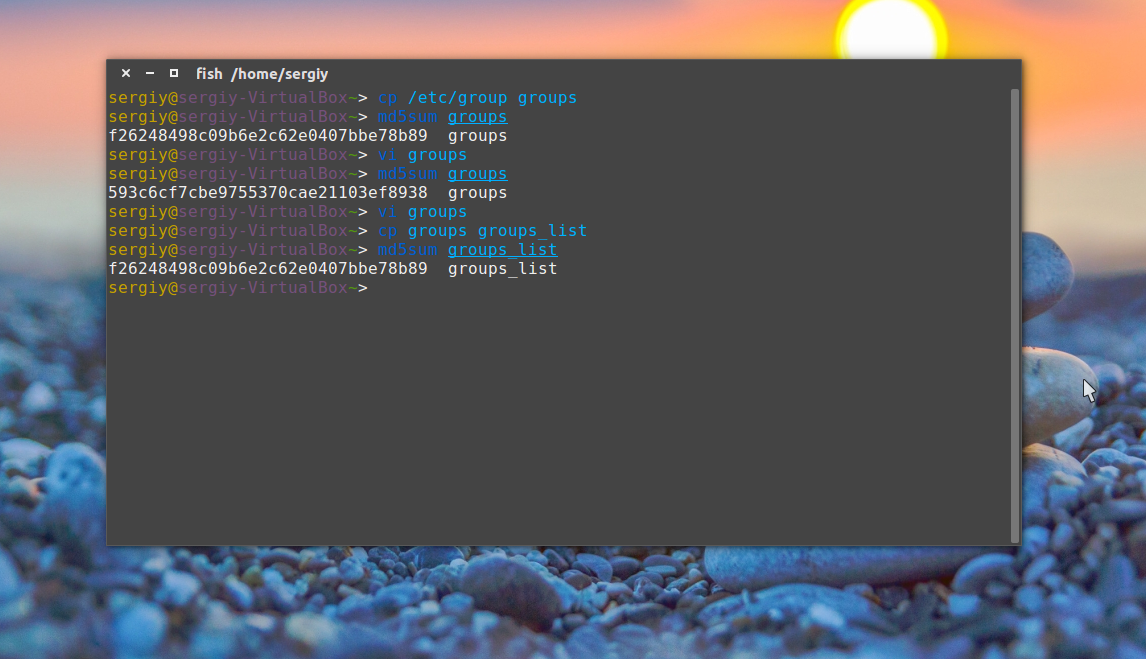
Сумма соответствует первому варианту, даже несмотря на то, что файл был переименован. Обратите внимание, что md5sum работает только с содержимым файлов, ее не интересует ни его имя, ни его атрибуты. Вы можете убедиться, что оба файла имеют одинаковые суммы:
md5sum groups groups_list
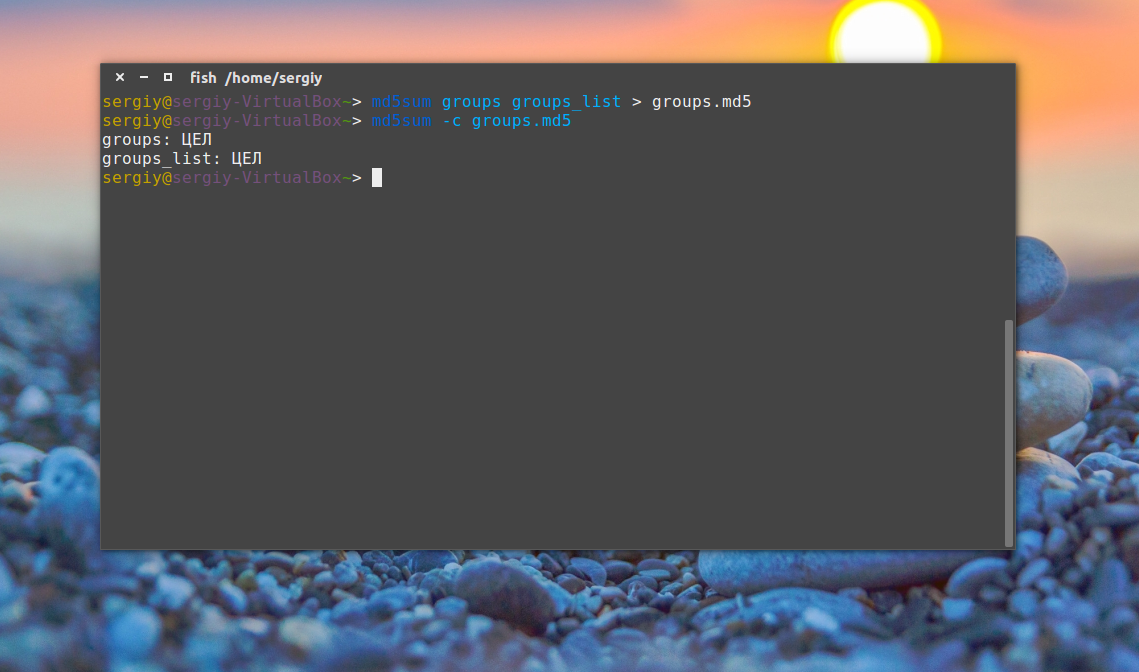
Вы можете перенаправить вывод этой команды в файл, чтобы потом иметь возможность проверить контрольные суммы:
md5sum groups groups_list > groups.md5
Чтобы проверить, не были ли файлы изменены с момента создания контрольной суммы используйте опцию -c или —check. Если все хорошо, то около каждого имени файла появится слово OK или ЦЕЛ:
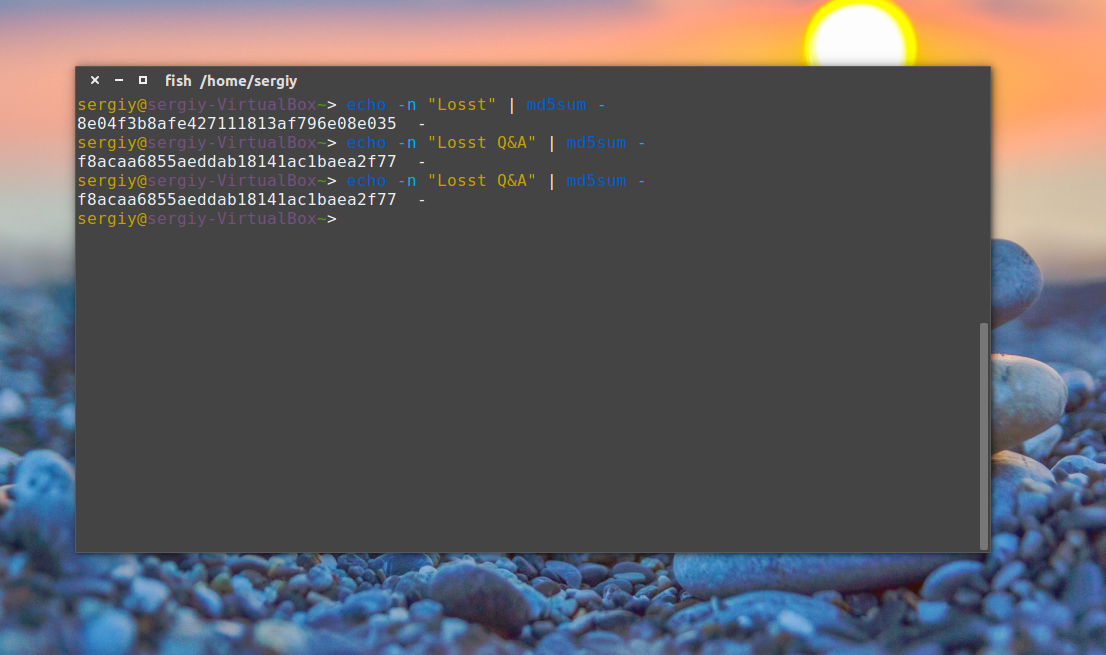
Но теперь вы не можете переименовывать файлы, потому что при проверке утилита будет пытаться открыть их по имени и, естественно, вы получите ошибку. Точно так же все работает для строк:
echo -n «Losst» | md5sum —
$ echo -n «Losst Q&A» | md5sum —
Выводы
Из этой статьи вы узнали как выполняется получение и проверка контрольной суммы linux для файлов и строк. Хотя в алгоритме MD5 были обнаружены уязвимости, он все еще остается полезным, особенно если вы доверяете инструменту, который будет создавать хэши.
Проверка целостности файлов Linux — это очень важный аспект использования системы. Контрольная сумма файла Linux используется не только вручную при проверке загруженных файлов, но и во множестве системных программ, например, в менеджере пакетов. Если у вас остались вопросы, спрашивайте в комментариях!
На завершение небольшое видео по теме:
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Hash file md5 linux
NAME
md5sum - compute and check MD5 message digest
SYNOPSIS
DESCRIPTION
Print or check MD5 (128-bit) checksums. With no FILE, or when FILE is -, read standard input. -b, --binary read in binary mode -c, --check read MD5 sums from the FILEs and check them --tag create a BSD-style checksum -t, --text read in text mode (default) The following five options are useful only when verifying checksums: --ignore-missing don't fail or report status for missing files --quiet don't print OK for each successfully verified file --status don't output anything, status code shows success --strict exit non-zero for improperly formatted checksum lines -w, --warn warn about improperly formatted checksum lines --help display this help and exit --version output version information and exit The sums are computed as described in RFC 1321. When checking, the input should be a former output of this program. The default mode is to print a line with checksum, a space, a character indicating input mode ('*' for binary, ' ' for text or where binary is insignificant), and name for each FILE. BUGS
The MD5 algorithm should not be used any more for security related purposes. Instead, better use an SHA-2 algorithm, implemented in the programs sha224sum(1), sha256sum(1), sha384sum(1), sha512sum(1)
AUTHOR
Written by Ulrich Drepper, Scott Miller, and David Madore.
REPORTING BUGS
GNU coreutils online help: http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/> Report md5sum translation bugs to http://translationproject.org/team/>
COPYRIGHT
Copyright © 2016 Free Software Foundation, Inc. License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html>. This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it. There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
SEE ALSO
Full documentation at: http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/md5sum> or available locally via: info '(coreutils) md5sum invocation'
© 2019 Canonical Ltd. Ubuntu and Canonical are registered trademarks of Canonical Ltd.
Learn How to Generate and Verify Files with MD5 Checksum in Linux
A checksum is a digit which serves as a sum of correct digits in data, which can be used later to detect errors in the data during storage or transmission. MD5 (Message Digest 5) sums can be used as a checksum to verify files or strings in a Linux file system.
MD5 Sums are 128-bit character strings (numerals and letters) resulting from running the MD5 algorithm against a specific file. The MD5 algorithm is a popular hash function that generates 128-bit message digest referred to as a hash value, and when you generate one for a particular file, it is precisely unchanged on any machine no matter the number of times it is generated.
It is normally very difficult to find two distinct files that results in same strings. Therefore, you can use md5sum to check digital data integrity by determining that a file or ISO you downloaded is a bit-for-bit copy of the remote file or ISO.
In Linux, the md5sum program computes and checks MD5 hash values of a file. It is a constituent of GNU Core Utilities package, therefore comes pre-installed on most, if not all Linux distributions.
Take a look at the contents of /etc/group saved as groups.cvs below.
root:x:0: daemon:x:1: bin:x:2: sys:x:3: adm:x:4:syslog,aaronkilik tty:x:5: disk:x:6: lp:x:7: mail:x:8: news:x:9: uucp:x:10: man:x:12: proxy:x:13: kmem:x:15: dialout:x:20: fax:x:21: voice:x:22: cdrom:x:24:aaronkilik floppy:x:25: tape:x:26: sudo:x:27:aaronkilik audio:x:29:pulse dip:x:30:aaronkilik
The md5sums command below will generate a hash value for the file as follows:
$ md5sum groups.csv bc527343c7ffc103111f3a694b004e2f groups.csv
When you attempt to alter the contents of the file by removing the first line, root:x:0: and then run the command for a second time, try to observe the hash value:
$ md5sum groups.csv 46798b5cfca45c46a84b7419f8b74735 groups.csv
You will notice that the hash value has now changed, indicating that the contents of the file where altered.
Now, put back the first line of the file, root:x:0: and rename it to group_file.txt and run the command below to generate its hash value again:
$ md5sum groups_list.txt bc527343c7ffc103111f3a694b004e2f groups_list.txt
From the output above, the hash value is still the same even when the file has been renamed, with its original content.
Important: md5 sums only verifies/works with the file content rather than the file name.
The file groups_list.txt is a duplicate of groups.csv, so, try to generate the hash value of the files at the same time as follows.
You will see that they both have equal hash values, this is because they have the exact same content.
$ md5sum groups_list.txt groups.csv bc527343c7ffc103111f3a694b004e2f groups_list.txt bc527343c7ffc103111f3a694b004e2f groups.csv
You can redirect the hash value(s) of a file(s) into a text file and store, share them with others. For the two files above, you can issues the command below to redirect generated hash values into a text file for later use:
$ md5sum groups_list.txt groups.csv > myfiles.md5
To check that the files have not been modified since you created the checksum, run the next command. You should be able to view the name of each file along with “OK”.
The -c or —check option tells md5sums command to read MD5 sums from the files and check them.
$ md5sum -c myfiles.md5 groups_list.txt: OK groups.csv: OK
Remember that after creating the checksum, you can not rename the files or else you get a “No such file or directory” error, when you try to verify the files with new names.
$ mv groups_list.txt new.txt $ mv groups.csv file.txt $ md5sum -c myfiles.md5
md5sum: groups_list.txt: No such file or directory groups_list.txt: FAILED open or read md5sum: groups.csv: No such file or directory groups.csv: FAILED open or read md5sum: WARNING: 2 listed files could not be read
The concept also works for strings alike, in the commands below, -n means do not output the trailing newline:
$ echo -n "Tecmint How-Tos" | md5sum - afc7cb02baab440a6e64de1a5b0d0f1b -
$ echo -n "Tecmint How-To" | md5sum - 65136cb527bff5ed8615bd1959b0a248 -
In this guide, I showed you how to generate hash values for files, create a checksum for later verification of file integrity in Linux. Although security vulnerabilities in the MD5 algorithm have been detected, MD5 hashes still remains useful especially if you trust the party that creates them.
Verifying files is therefore an important aspect of file handling on your systems to avoid downloading, storing or sharing corrupted files. Last but not least, as usual reach us by means of the comment form below to seek any assistance, you can as well make some important suggestions to improve this post.