- How to add entry to /etc/hosts with a built-in command line
- 3 Answers 3
- You must log in to answer this question.
- Related
- Hot Network Questions
- Subscribe to RSS
- How to Edit Hosts File on Linux?
- Why Edit Hosts File?
- How to Edit Hosts File on Linux?
- Block a Website
- Name Service Switch
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Simran Kaur
- How to Edit Hosts File on Linux Mint 21
- What Is the Purpose of Hosts File in Linux Mint 21
- How to Edit the Hosts File in Linux Mint 21
- How to Block a Website through Hosts File
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Aaliyan Javaid
- Файл hosts на Linux
- Как отредактировать файл hosts в Linux
How to add entry to /etc/hosts with a built-in command line
There’s no such tool, but you could script it yourself. Also, what will happen if 10.103.23.18 is already mapped to some hostname?
sudo echo 127.1.2.3 hostname.example.com >> /etc/hosts should be enough for adding entries. Removing them would probably be a simple sed command, also run through sudo. Sanity-checking for duplicate host names with grep is also straightforward enough.
You can add new entry to /etc/hosts with sed -i and $ a option, see stackoverflow.com/a/50003244/658497
3 Answers 3
After seeking for CLI for /etc/hosts , we find : https://github.com/macmade/host-manager
host-manager -add www.example.org 127.0.0.1 host-manager -remove www.example.org I tried to get the host-manager tool listed above to work but it looks like maybe it’s for Windows or macOS? It was trying to cross compile and didn’t look right for Ubuntu. I found this tool ‘Hostess’ though which works great and seems to do exactly what the OP was looking for:
hostess add local.example.com 127.0.0.1 hostess add staging.example.com 10.0.2.16 Just to add to other suggestions — there’s one more option which exists in standard Ubuntu package repositories — hostsed (github page + docs here). As a result install is as easy as apt install hostsed .
You must log in to answer this question.
Related
Hot Network Questions
Subscribe to RSS
To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader.
Site design / logo © 2023 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under CC BY-SA . rev 2023.7.14.43533
Ubuntu and the circle of friends logo are trade marks of Canonical Limited and are used under licence.
By clicking “Accept all cookies”, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
How to Edit Hosts File on Linux?
A Hosts file is supported in Linux, Windows, and Mac; they are plain-text files that work to map hostnames to various IP addresses. It is great to edit the Hosts file when you run the test on the specific network. You can also use the mapping of an IP address to skip the process in which the web browser uses the DNS (Domain Name Server) lookup for translating a domain name to a particular IP address.
When a user types a website’s domain name, the domain name needs to translate into a specific IP address. A Hosts file has a top priority over DNS since an operating system checks its Hosts file for a domain and in case there is no entry for that domain. It starts to query the configured DNS servers for resolving the particular domain name. It was the little information about the Hosts file, and we will consider every single aspect on how to edit Hosts files on Linux easily.
Why Edit Hosts File?
There are various reasons for editing hosts file in the Linux machine:
- You can easily block a website.
- You can handle an attack.
- You can create an alias for different locations on a local server.
- You can override addresses that a DNS server delivers.
- You can easily control access to network traffic.
How to Edit Hosts File on Linux?
Open the terminal from applications > utilities > terminal feature, or you can use CTRL, ALT, and T as shortcut keys.
After opening the terminal, open the Linux Hosts file in the system using the following command:
We have used Vim, but you can use different text editors like nano.
Once you execute the command, the system will prompt you to enter the password to open the Hosts file.
You can easily modify the Hosts file, so the file is formatted like the IP address is written first, and the server’s name is on second.
You can add entries at the end of the Hosts file as per your requirements. In case you want to ignore any line or specify the system to not read the line, then you can put the “#” sign at the starting of that particular line. Finally, you can save the file before and make sure you save it before exiting.
Block a Website
If you want to block a particular website from redirecting it to the localhost’s IP address, change the Hosts file’s domain name. For example, we want to block xxyyzz.com, then we can write:
In the above text, 134.1.0.1 is the IP of the localhost, but if you want to make changes in the default route, then you can write:
In the above text, 0.0.0.0 IP is a default route from this particular Hosts file.
At last, you can press CTRL and X keys simultaneously to save the file.
Name Service Switch
As mentioned, a Hosts file works to bypass a Domain Namer server lookup. Still, it has another file that has the information of the operating system about the order for finding the IP address translation.
The nsswitch.conf is a file completely configured for finding the DNS, then skips the Hosts file and goes in the DNS lookup. You can use the below command line for configuration checking easily:
xyz@xyz-virtualBox:~$ cat etc nsswttch.conf
# /etc/nsswitch.conf
#
# Example configuration of GNU Name Service Switch functionality.
# If you have the ‘glibc-doc-reference’ and ‘info’ packages installed, try:
# ‘info libc «Name Service Switch»‘ for information about this file.
passwd: compat systemd
group: compat systemd
shadow: compat
gshadow: files
hosts: files mdns4_minimal [ NOTFOUND = return ] dns myhostname files
networks: db files
protocols: db files
services: db files
ethers: db files
rpc: db files
netgroup: nis
xyz @ xyz-VirtualBox: ~$
There is an entry called “Hosts,” ensuring that the files should be listed in the right-hand column in the above results. In case it is not listed like this, then open your file editor using the below command:
This command will open the Vim text editor to make changes and set the files at the beginning for appropriate use.
Conclusion
The Hosts files are beneficial to perform multiple tasks for domain names and IP addresses. It was the complete information on the Hosts file and how you can easily edit the Hosts file on Linux. This procedure is tried and tested on multiple Linux machines, but you have to carefully follow every step.
About the author
Simran Kaur
Simran works as a technical writer. The graduate in MS Computer Science from the well known CS hub, aka Silicon Valley, is also an editor of the website. She enjoys writing about any tech topic, including programming, algorithms, cloud, data science, and AI. Travelling, sketching, and gardening are the hobbies that interest her.
How to Edit Hosts File on Linux Mint 21
Host file of Linux mint primarily maps the IP address with the domain names of the system thus making it useful for various purposes which include blocking a website and accessing any computer remotely. If you are unaware of how to edit a host file in your Linux Mint 21 and want to use it for multiple purposes, then read this guide.
What Is the Purpose of Hosts File in Linux Mint 21
Host file as mentioned above contains the IP addresses and hostname of the Linux system, but there are multiple uses of host file and those are:
- Blocking any websites
- Remotely accessing any Alias
- Blocking advertisers and trackers
- Testing an application
- Adding or blocking specific networks
How to Edit the Hosts File in Linux Mint 21
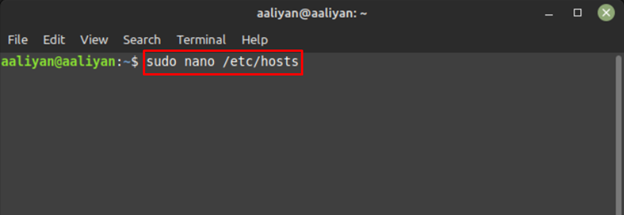
The process of editing the host file of Linux Mint 21 is quite easy; open the host file on your Linux Mint 21 by using any terminal-based text editor, for example, nano:
Now edit the host file by entering the data like IP addresses and host names for the connections you either want to block or access.
How to Block a Website through Hosts File
When it comes to security or parental control hosts file plays a crucial role as it can be used to block unwanted websites. The process of blocking a website is mentioned below:
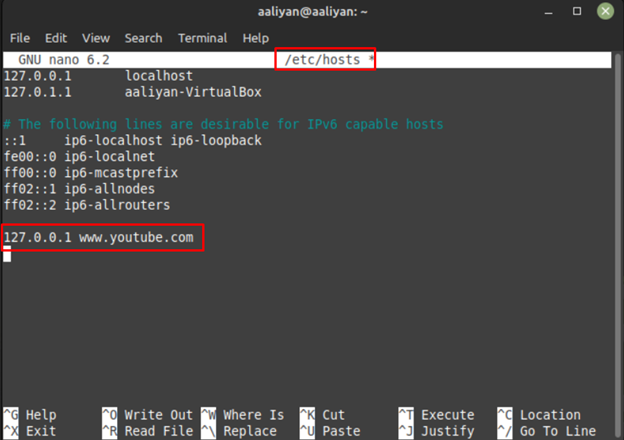
For instance, if you want to block YouTube then use:
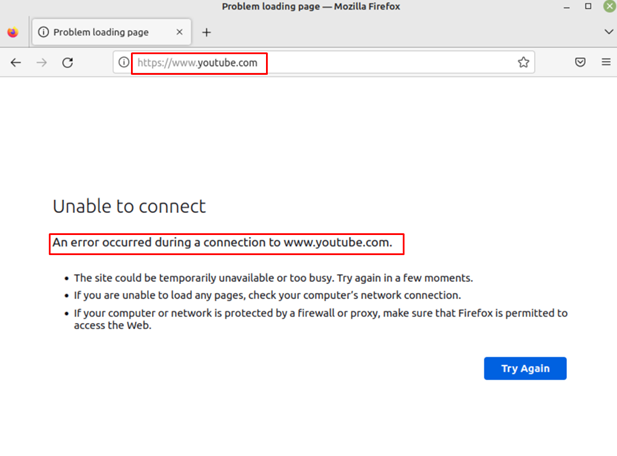
Next save the file and open the website on the browser of Linux Mint to see if the site is blocked or not:
Conclusion
Host files in an operating system generally contain the IP address and the domain name of that system, there are multiple uses of a host file which can be achieved by editing it and it can be done by stating its path with nano command.
About the author
Aaliyan Javaid
I am an electrical engineer and a technical blogger. My keen interest in embedded systems has led me to write and share my knowledge about them.
Файл hosts на Linux
В этой статье мы расскажем, что такое файл hosts Linux, как его использовать и как изменить файл hosts в Linux.
Данные любого сайта находятся на физическом сервере. Чтобы браузер нашёл нужный сервер, он должен знать его IP-адрес. Узнать, какому IP соответствует домен, можно с помощью DNS-системы. DNS ― это своеобразная телефонная книга, где записаны абсолютно все домены и соответствующие им IP-адреса. До появления DNS использовался hosts. Hosts ― это текстовый файл, в котором находятся данные домена и его IP.
С появлением DNS hosts поменял сферу применения. Настройки в файле для браузера более приоритетны. Поэтому, перед тем как обратиться к DNS, браузер проверяет настройки hosts. Если в файле нет никаких данных по нужному хосту (домену), браузер обращается к DNS-системе. Эту особенность можно использовать. С помощью файла hosts можно:
- Указать псевдоним для локальной сети.
- Запретить посещение какого-либо сайта. Такой метод часто применяется на рабочих компьютерах, чтобы сотрудники не отвлекались на развлекательные сайты. Также ограничения можно установить для детских устройств. Например, вы не хотите, чтобы ребёнок посещал сайт youtube.com, впишите в hosts 127.0.0.1 youtube.com. 127.0.0.1 ― эта запись заставляет систему обращаться к собственному компьютеру.
- Просмотреть сайт до внесения его в DNS-систему. Если вы прописали DNS-серверы для домена, изменения вступят в силу в течение 24 часов. В некоторых случаях увидеть свой сайт нужно быстрее. Для этого вручную впишите свой домен и соответствующий ему IP. Тогда браузеру будет неважно, есть ли данные о этом сайте в единой системе.
Как добавить нужные данные, мы расскажем в инструкции ниже.
Как отредактировать файл hosts в Linux
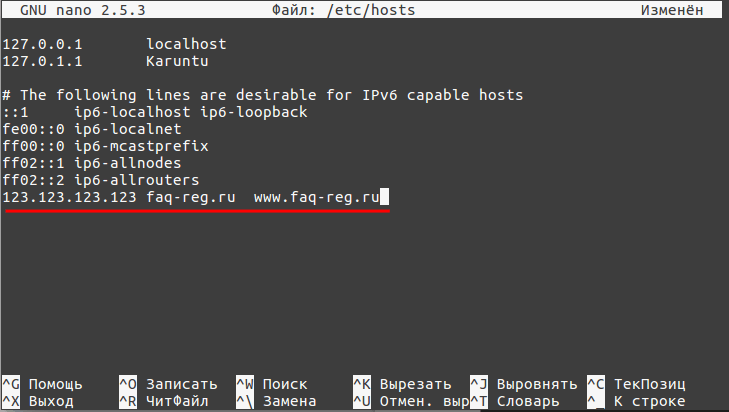
В Linux файл hosts находится в папке /etc/hosts. Обратите внимание! Обычно для редактирования hosts нужен доступ суперпользователя.
Чтобы отредактировать его:
Hosts Linux настройка
123.123.123.123 faq-reg.ru www.faq-reg.ru
- 123.123.123.123 — IP-адрес сервера или хостинга,
- faq-reg.ru — имя домена.
Ubuntu файл hosts
Файл hosts редактируется одинаково во всех Unix-системах.
Google Chrome может игнорировать файл hosts. Если вы хотите заблокировать какой-либо сайт в этом браузере, вводите http:// в начале каждого адреса. Например, вводите не youtube.com, а http:/youtube.com. При таких настройках Google Chrome не будет игнорировать hosts.
Если вы не хотите разбираться, как работать с файлом hosts, но заблокировать нежелательные сайты нужно, воспользуйтесь приложением Linux Mint Domain Blocker. Оно самостоятельно добавит домены, которые нужно заблокировать, в файл hosts. Эта программа пользуется тем же способом, что и пользователь при ручной блокировке. Linux Mint Domain Blocker вместо правильного IP добавляет 127.0.0.1.