- Step-by-Step Guide: Adding Repositories to Kali Linux for Expanded Software Options
- What is Repository in Linux
- How to Add Kali Linux repository for Beginners
- Updating Kali Linux
- Upgrading Kali Linux
- How to add a repository in Kali Linux [Video Tutorial]
- Conclusion:
- Add repositories in Kali Linux 2.0 [closed]
- 1 Answer 1
- Step 1
- Step 2
- Warnings and Other Information
- Final Notes
- 🐧 Как добавить официальные репозитории Kali Linux в sources.list
Step-by-Step Guide: Adding Repositories to Kali Linux for Expanded Software Options
The repository is a big topic and I can’t cover everything in one article. So today I am just going to explain about the Kali Linux repository.
You can add the Kali Linux repository after following simple steps.
What is Repository in Linux
In simple words, a Repository is a storage location, Where all the packages are stored.
Packages refer to tools, utilities, or software that you may install on your Linux system including Kali Linux.
All the packages available on the Kali Linux repository are tested, maintained, and maintained by its developers and managers.
If you will download and install packages on Kali Linux in the future from the repository, it will work fine. because it has been tested by Kali developers.
You will not face any type of problem or crash in your system when you get packages from the repository.
In other words, you can not trust other resources for getting packages/tools.
You are on the client-side, So an apt apt-get package manager helps to install the new and latest packages on your system and update the repositories.
How to Add Kali Linux repository for Beginners
As you know, at the time of updates and upgrades Kali Linux, the apt or apt-get package manager checks only the application stored on its own data repository.
This is good for you and other Kali users, Some updates and upgrades could make Kali Linux nonfunctional, all software is tested by the Kali developers before adding the Kali Linux repository.
There is some third-party application that is not available on the Kali repository, in this case, additional repositories may be needed to be added.
There are simple steps to configure the Kali Linux repository on your system. Follow the given two steps:
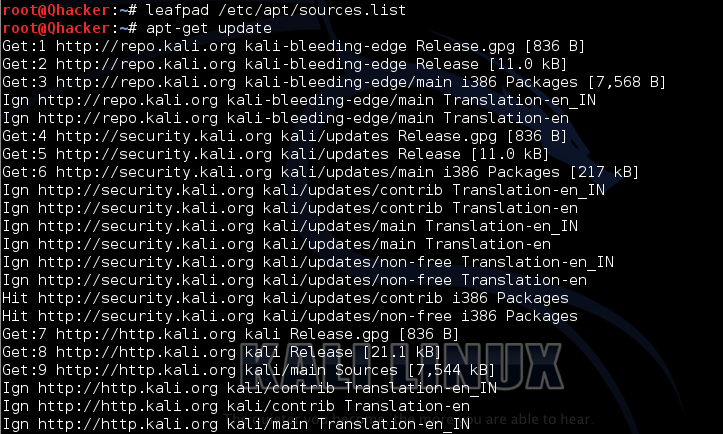
Step 1: Use leafpad or another text editor to open and edit /etc/apt/sources.list.
Step 2: Add the following code to the file and save the file. You can add the following anywhere in the file.
Just copy the following code and paste it into the file.
deb http://http.kali.org/kali kali-rolling main non-free contrib
Step 3: Verify the updated file:
You can use cat command to verify the updated file. You can you have added code properly inside a file or not
Updating Kali Linux
Like other operating systems, Kali has the implicit capability to update both the operating systems and the software, or packages, installed. As upgrades to the package get accessible, they will be presented in the Kali store. This store can then be checked to guarantee the operating systems and provisions are up to date. Upgrades are typically more small fixes that address software bugs, or errors, or are utilized to include new fittings competencies. Use the following commands to update the system :
#apt-get update
Upgrading Kali Linux
Like updating, upgrading Kali can likewise be carried out at the command line with the pt-get utility. Upgrades are regularly significant updates to requisitions or the working framework itself. Updates offer new usefulness and are much bigger than upgrades ordinarily obliging more of a chance and space on the System drive.
How to add a repository in Kali Linux [Video Tutorial]
Conclusion:
I have covered everything required for beginners, Now you have learned how to add the Kali Linux repository. If you want to learn more about it please visit the Official website
If you have any questions please leave them in the comment box.
Add repositories in Kali Linux 2.0 [closed]
Requests for learning materials (tutorials, how-tos etc.) are off topic. The only exception is questions about where to find official documentation (e.g. POSIX specifications). See the Help Center and our Community Meta for more information.
1 Answer 1
Step 1
To add repositories on most (if not all) Debian Derivative systems, the main way to go about doing this is to edit your sources.list file, found in /etc/apt/sources.list . To do this, use any editor of your choice to open the file. Once editing the file, it should look like this if you have never modified the sources.list file, and Kali was installed correctly:
deb http://http.kali.org/kali sana main non-free contrib
deb http://security.kali.org/kali-security sana/updates main contrib non-free
Now you can add any repositories you like.
Step 2
The next step is to clean out all cached and non-wiped files from /var/cache/apt/archives/ and /var/cache/apt/archives/partial/ . To do this, run the command apt-get clean . Next, update your package index files (so you can install packages from the repository you added) by running apt-get update . Upgrade all installed packages so you can download dependencies and resolve out-conflicts by running apt-get upgrade . The new repository you added may have some core packages, or system applications that need to be installed, so do so by using a smart dependency conflict resolution update with apt-get dist-upgrade . You should now be ready to go.
Warnings and Other Information
Generally for Kali (and usually for Kali only) it is a very bad idea to add repositories to your system, because they might break your Kali install. Because one of the main core functionalities of Kali is all the packages that come preinstalled, in a system manner of speaking, it is very unstable. If you install one package that needs certain dependencies or updates certain dependencies to so it is not backwards compatible, then you will essentially break some (or all) of the packages preinstalled in Kali, defeating the purpose of having Kali at all. Because of this mentality, Kali has grown to become very fragile. While Kali works perfectly well out of the box or with packages that you install from the official repositories, adding repositories may potentially break your system. According to the official Kali docs,
Any additional repositories added to the Kali sources.list file will most likely BREAK YOUR KALI LINUX INSTALL.
meaning that you should generally stay away from unofficial repositories while using Kali. In fact, according to the Kali docs,
The single most common causes of a broken Kali Linux installation are following unofficial advice, and particularly arbitrarily populating the system’s sources.list file with unofficial repositories.
So, if you are following an internet tutorial or the like, be warned that adding unofficial repositories to you sources.list is the most common cause of a broken Kali system.
Final Notes
While this methods works on Debian Derivative GNU/Linux systems, it is advisable to stick with the official Kali Repositories for the most part. If you want to, certainly go ahead and add the repositories, but it is important to know what the repositories provide, and what, if any, packages will be updated when initiating apt-get upgrade , because they may break your other packages. For more information on Kali Repositories see here:
🐧 Как добавить официальные репозитории Kali Linux в sources.list
Мануал
После установки Kali Linux из файла ISO вам может потребоваться вручную обновить файл APT sources.list официальным списком репозиториев.
Apt требует наличия репозиториев программного обеспечения для загрузки пакетов и их установки на ваш компьютер.
$ cat /etc/os-release PRETTY_NAME="Kali GNU/Linux Rolling" NAME="Kali GNU/Linux" ID=kali VERSION="2019.4" VERSION_ID="2019.4" VERSION_CODENAME="kali-rolling" ID_LIKE=debian ANSI_COLOR="1;31" HOME_URL="https://www.kali.org/" SUPPORT_URL="https://forums.kali.org/" BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugs.kali.org/"В терминале проверьте текущий список репозиториев apt, присутствующих в системе.
Если репозитории APT отсутствуют, вставьте приведенный ниже код, чтобы добавить их.
sudo tee -a /etc/apt/sources.listКоманда, показанная выше добавит стандартные и исходные репозитории в /etc/apt/sources.list.
$ cat /etc/apt/sources.list # # deb cdrom:[Debian GNU/Linux 2019.4 _Kali-rolling_ - Official Snapshot amd64 LIVE/INSTALL Binary 20191125-10:47]/ kali-last-snapshot contrib main non-free #deb cdrom:[Debian GNU/Linux 2019.4 _Kali-rolling_ - Official Snapshot amd64 LIVE/INSTALL Binary 20191125-10:47]/ kali-last-snapshot contrib main non-free # This system was installed using small removable media # (e.g. netinst, live or single CD). The matching "deb cdrom" # entries were disabled at the end of the installation process. # For information about how to configure apt package sources, # see the sources.list(5) manual. deb http://http.kali.org/kali kali-rolling main non-free contrib deb-src http://http.kali.org/kali kali-rolling main non-free contrib
Обновите список ваших пакетов:
$ sudo apt update Get:1 http://kali.download/kali kali-rolling InRelease [30.5 kB] Get:2 http://kali.download/kali kali-rolling/main Sources [12.8 MB] Get:3 http://kali.download/kali kali-rolling/non-free Sources [130 kB] Get:4 http://kali.download/kali kali-rolling/contrib Sources [60.1 kB] Get:5 http://kali.download/kali kali-rolling/main amd64 Packages [16.4 MB] Get:6 http://kali.download/kali kali-rolling/non-free amd64 Packages [196 kB] Get:7 http://kali.download/kali kali-rolling/contrib amd64 Packages [96.6 kB] Fetched 29.7 MB in 24s (1,237 kB/s) Reading package lists. Done Building dependency tree Reading state information. DoneПри желании вы можете сделать обновление системы
sudo apt -y upgrade sudo systemctl rebootПожалуйста, не спамьте и никого не оскорбляйте. Это поле для комментариев, а не спамбокс. Рекламные ссылки не индексируются!
Друзья, помогите. Установил своюстаренькую Кали 2018.1, а там сертификаты устарели и не обновить не пакеты не саму Кали. Подскажите по шагам как обновить или заменить сертификаты чтобы обновить всё что есть?
- Аудит ИБ (49)
- Вакансии (12)
- Закрытие уязвимостей (105)
- Книги (27)
- Мануал (2 306)
- Медиа (66)
- Мероприятия (39)
- Мошенники (23)
- Обзоры (820)
- Обход запретов (34)
- Опросы (3)
- Скрипты (114)
- Статьи (352)
- Философия (114)
- Юмор (18)
Anything in here will be replaced on browsers that support the canvas element
OpenVPN Community Edition (CE) – это проект виртуальной частной сети (VPN) с открытым исходным кодом. Он создает защищенные соединения через Интернет с помощью собственного протокола безопасности, использующего протокол SSL/TLS. Этот поддерживаемый сообществом проект OSS (Open Source Software), использующий лицензию GPL, поддерживается многими разработчиками и соавторами OpenVPN Inc. и расширенным сообществом OpenVPN. CE является бесплатным для […]
Что такое 404 Frame? Большинство инструментов для взлома веб-сайта находятся в 404 Frame. Итак, что же представляют собой команды? Вы можете отдавать команды, используя повседневный разговорный язык, поскольку разработчики не хотели выбирать очень сложную систему команд. Команды Команды “help” / “commands” показывают все команды и их назначение. Команда “set target” – это команда, которая должна […]
В этой заметке вы узнаете о блокировке IP-адресов в Nginx. Это позволяет контролировать доступ к серверу. Nginx является одним из лучших веб-сервисов на сегодняшний день. Скорость обработки запросов делает его очень популярным среди системных администраторов. Кроме того, он обладает завидной гибкостью, что позволяет использовать его во многих ситуациях. Наступает момент, когда необходимо ограничить доступ к […]
Знаете ли вы, что выполняется в ваших контейнерах? Проведите аудит своих образов, чтобы исключить пакеты, которые делают вас уязвимыми для эксплуатации Насколько хорошо вы знаете базовые образы контейнеров, в которых работают ваши службы и инструменты? Этот вопрос часто игнорируется, поскольку мы очень доверяем им. Однако для обеспечения безопасности рабочих нагрузок и базовой инфраструктуры необходимо ответить […]
Одной из важнейших задач администратора является обеспечение обновления системы и всех доступных пакетов до последних версий. Даже после добавления нод в кластер Kubernetes нам все равно необходимо управлять обновлениями. В большинстве случаев после получения обновлений (например, обновлений ядра, системного обслуживания или аппаратных изменений) необходимо перезагрузить хост, чтобы изменения были применены. Для Kubernetes это может быть […]