- How to add existing user to an existing group?
- 8 Answers 8
- Explanation:
- How to Add or Remove Linux User From Group
- Check a User Group in Linux
- Add a User to a Group in Linux
- Remove a User from a Group in Linux
- How to Add a User to the Group in Linux
- How to add users to the group using the terminal in Linux
- How to add users to the group using GUI in Linux
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Taimoor Mohsin
How to add existing user to an existing group?
I want to add the Apache user ( www-data ) to the audio group. I’ve read the man page for useradd , but I’m not having any luck. I’m running xubuntu 11.10. Here’s what I’m doing:
$ sudo useradd -G audio www-data useradd: user 'www-data' already exists $ sudo useradd audio www-data Usage: useradd [options] LOGIN Options: -b, --base-dir BASE_DIR base directory for the home directory. 8 Answers 8
The useradd command will try to add a new user. Since your user already exists this is not what you want.
Instead: To modify an existing user, like adding that user to a new group, use the usermod command.
sudo usermod -a -G groupName userName - The -a (append) switch is essential. Otherwise, the user will be removed from any groups, not in the list.
- The -G switch takes a (comma-separated) list of additional groups to assign the user to.
In general (for the GUI, or for already running processes, etc.), the user will need to log out and log back in to see their new group added. For the current shell session, you can use newgrp :
sudo usermod -a -G [group-name] [user-name] : Just a quickie for those who only glance at the answer after reading the headline
I think the preferred way now is sudo adduser user group . It is simpler and cleaner syntax. See the response from @Bai.
Is there a way to get around the «logout and back in» part? Some type of update-groups command, maybe?
@con-f-use, if you can run sudo login -f YOURUSERNAME , it will start a new shell session. Use the id command to verify that the new session is in the correct set of groups. However, this isn’t «global» — it doesn’t apply to terminals that are already open. So, really, logging out is the best option, where possible
You can use the newgrp [group-name] command to add a new group to the user of the current session without logging out and in again. Only the current session will be affected though.
Removing a user from a group:
@Tejendra’s comment seems to presuppose that using useradd is desirable/mandatory to answer OP’s question; Perhaps this answer is just missing words to indicate that adduser/deluser is a better alternative.
After adding to a existing user:
You may need to logout and login to get the groups permissions from /etc/group .
FYI: I think the id command should indicate you were added to the group without needing to exit. id myuser
sudo gpasswd -a myuser mygroup I’m posting this as an answer because I don’t have enough reputation to comment. As @dpendolino’s mentioned, for the effects of this command to persist:
sudo usermod -a -G groupName userName
. you need to logout/login again.
However, if you need a shortcut to start using your new group membership immediately (and you have the correct sudo privileges) I have found this work-around:
$ sudo su - # su [userName] $ groups - sudo su — will give you a root shell
- su [userName] returns you to a shell with your user
- groups when run now will show the group you added with the usermod -aG command
In my case I was trying to add the ‘docker’ group to my user
$ groups userName adm cdrom sudo dip plugdev lpadmin sambashare wireshark lxd $ groups userName adm cdrom sudo dip plugdev lpadmin sambashare wireshark lxd docker Another option to apply the group membership is sudo login -f
sudo usermod -a -G groupName userName will work just fine, but I had to reboot entirely, just log out and log in again did not do the job.
On Ubuntu, since logging in as root is not enabled, users in the sudo group can elevate privileges for certain restricted commands. Any restricted command must be prepended with sudo to elevate privilege.
sudo usermod -a -G group userwill add the existing user user to a supplemental group named group . The user’s primary group will remain unchanged.
To permanantely add a user to a group, run this command:
Then log out and log in again (or reboot if necessary).
Explanation:
The usermod command will modify the /etc/group file to list the specified username in the line relevant to that group. If you run grep /etc/group , you should see your username in the output.
In Linux, every process is assigned to a user and groups, and any child processes inherit the user and groups of the parent process. So, for this change to take effect and propogate, you need to log out and log in again (at which point /etc/group is read and used). On Wayland, I’ve found that a full reboot is necessary.
If you run the command groups , you can see if the current process has the expected groups or not.
How to Add or Remove Linux User From Group
Linux is by default a multi-user system (meaning many users can connect to it simultaneously and work), thus Linux user management is one of the fundamental tasks of a system administrator, which includes everything from creating, updating, and deleting user accounts or user groups on a Linux system.
In this short quick article, you will learn how to add or remove a user from a group in a Linux system.
Check a User Group in Linux
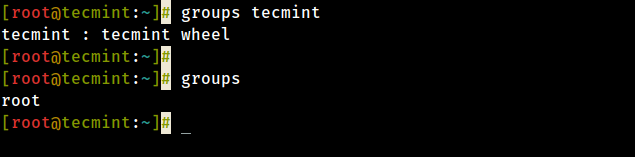
To find out what group a user is in, just run the following groups command and provide the username (tecmint in this example) as an argument.
# groups tecmint tecmint : tecmint wheel
To find out the group of root user in Linux, just run the groups command without any argument.
# group root
Add a User to a Group in Linux
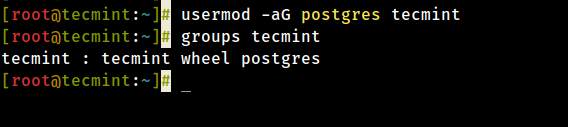
Before trying to add a user to a group, ensure that the user exists on the system. To add a user to a certain group, use the usermod command with the -a flag which tells the usermod to add a user to the supplementary group(s), and the -G option specifies the actual groups in the following format.
In this example, tecmint is the username and postgres is the group name:
# usermod -aG postgres tecmint # groups tecmint
Remove a User from a Group in Linux
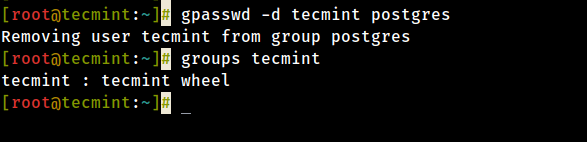
To remove a user from a group, use the gpasswd command with the -d option as follows.
# gpasswd -d tecmint postgres # groups tecmint
Additionally, on Ubuntu and its derivatives, you can remove a user from a specific group using the deluser command as follows (where tecmint is the username and postgres is the group name).
$ sudo deluser tecmint postgres
For more information, see the man pages for each of the different commands we have used in this article.
$ man groups $ man usermod $ man gpasswd $ man deluser
You will also find the following user management guides very useful:
How to Add a User to the Group in Linux
Linux is a multi-user operating system where individual permissions can be specified for each user. However, this can be problematic if there are several users and all are having the same rights and privileges. Because multiple users can connect and work at the same time and they should have the privileges as per their knowledge and experience. So, user management is one of the most important responsibilities of a system administrator which encompasses everything from creating, updating, and deleting user accounts and user groups.
How to add users to the group using the terminal in Linux
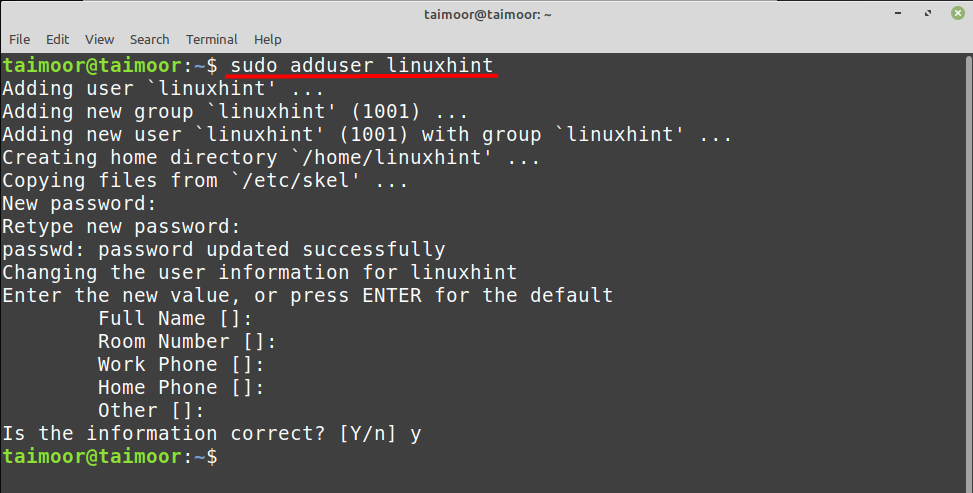
Let’s start with creating a new user first so that we can add them into the group by following the general syntax shown below.
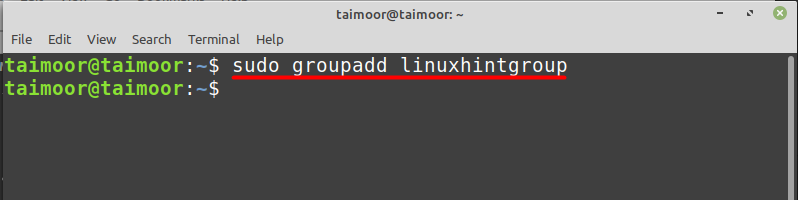
Now let’s create a new group using the general syntax shown below.
Now the general syntax to add any user to the group is:
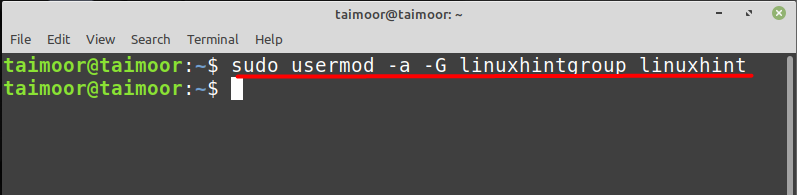
To add the user ‘linuxhint’ in the group ‘linuxhintgroup’, use the below mentioned command:
Here ‘-a’ option represents the addition process whereas ‘-G’ option represents the group option and ‘usermod’ shows that we are dealing with a user to add in the specific group, and at the end we have written the group name first and then the username.
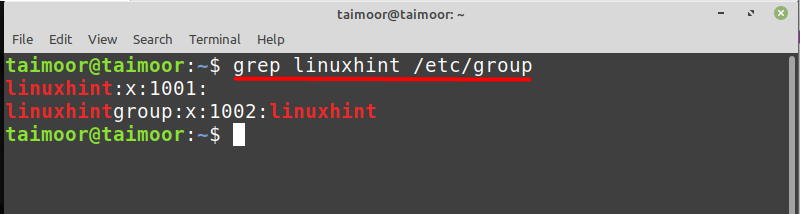
Now if you like to verify that if a user is added to the group or not then you can do that by following the general syntax mentioned below.
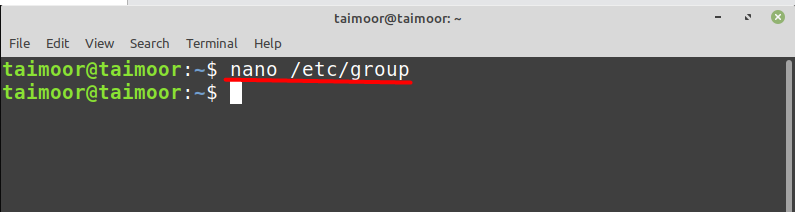
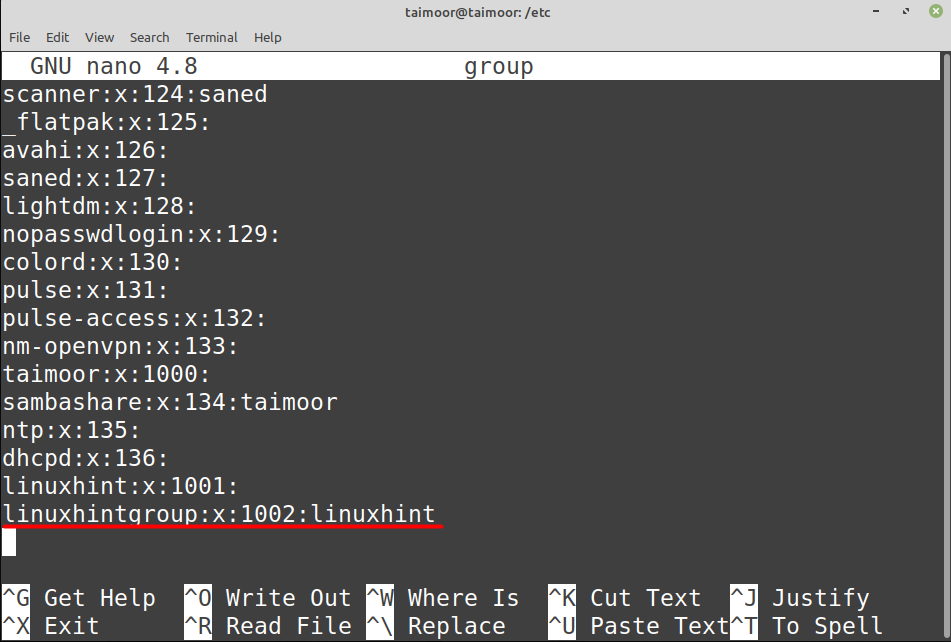
In the above command ‘grep’ is used to find the specific keyword from any file like in our case we have mentioned the keyword ‘linuxhintgroup’ along with a filename ‘/etc/group’ from where it will find that keyword. By any chance, if you want to access this file then you can do that by typing:
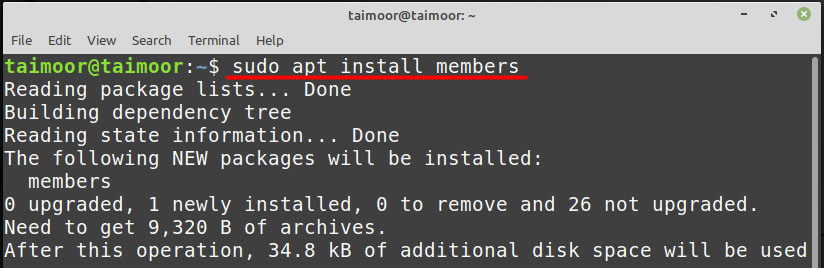
You can also verify if the user has been added to a group or not by installing a third-party application with the name of “members” by typing:
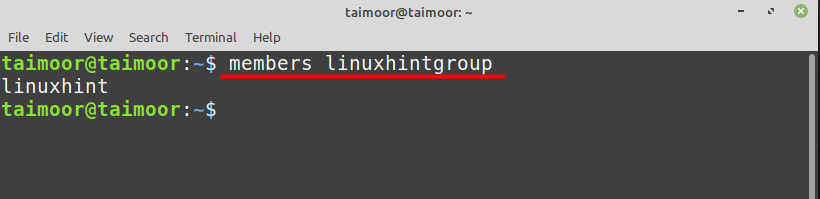
After the installation, the general syntax that can be used to find the members in any group is:
As you can see, the above commands show only one user which is ‘linuxhint’.
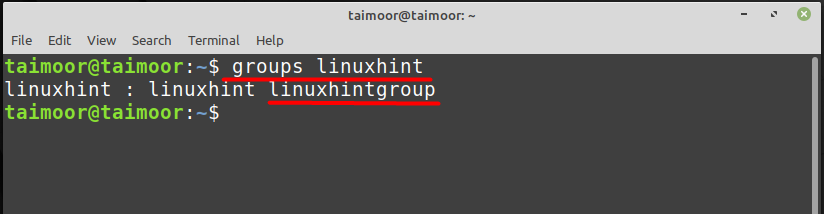
There is one other way to find the users in any group and you can do that by following the general syntax shown below.
The above command will search all the available groups and then it will show you that specific group where “linuxhint” is available.
How to add users to the group using GUI in Linux
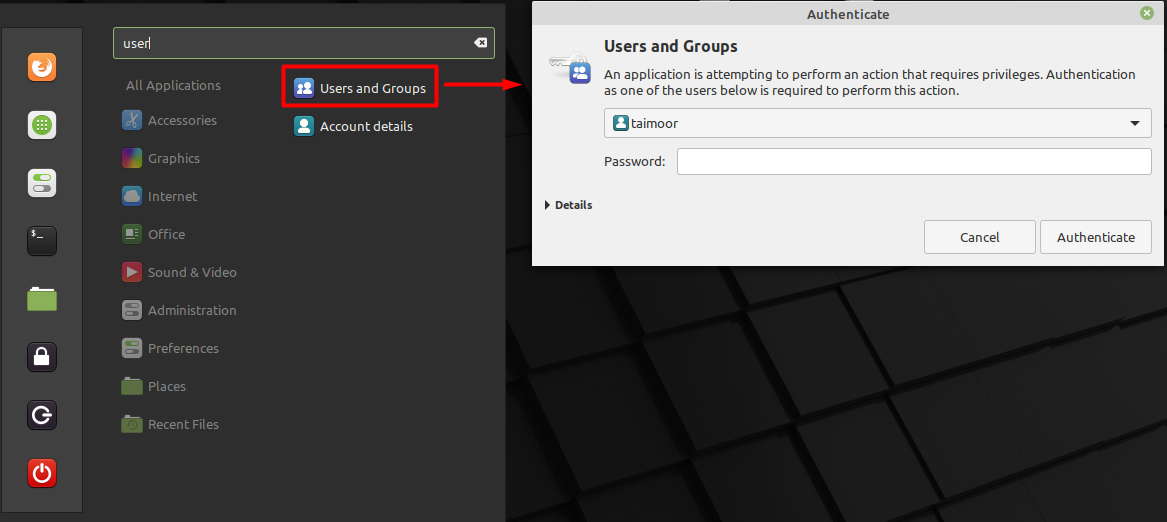
We are currently using Linux mint where you can also add the user to the group by selecting the ‘Users and Groups’ option that you can find in the settings of your Linux distribution as shown below.
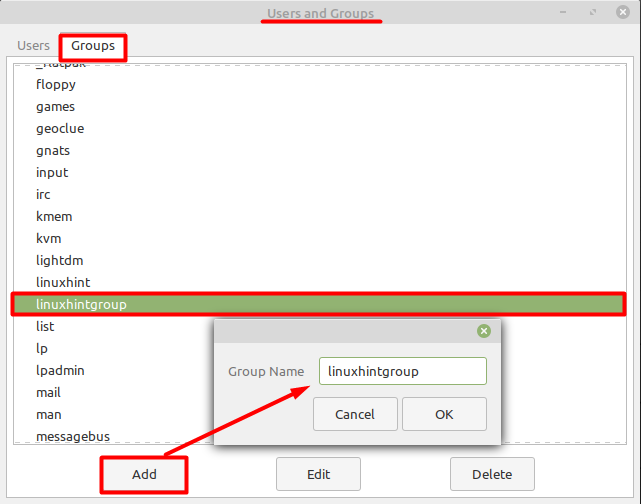
After that, you need to provide the password for authentication and later a new dialogue box will open where you need to select the ‘Groups’ tab and then add any group that you like by clicking on the ‘Add’ button as shown below.
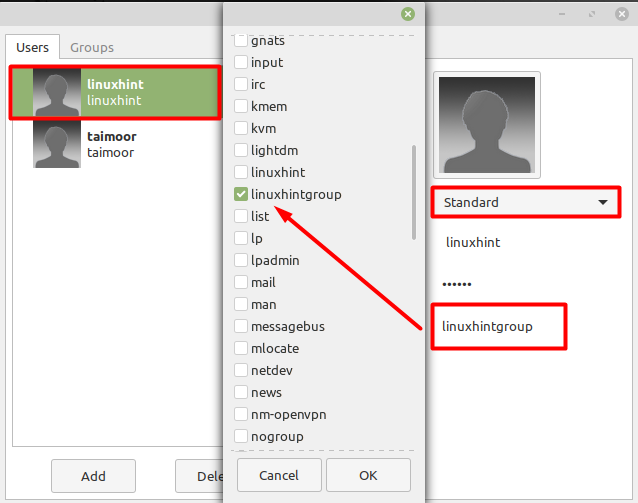
After creating a new group, the next step is to assign a user to this group, and you can do that by selecting the ‘Users’ tab and the new user with the name of ‘linuxhint’.
Now, all you need is to click on the group tab and select the specific group where you want to associate a user as shown below.
Conclusion
Linux is a multi-user operating system in which each user can have their own set of permissions. This is a necessary step because user privileges should be based on their knowledge and expertise otherwise it can be problematic. In this article, we have explained two different ways to add users in the group that can either be using a terminal or it can also be done using a GUI.
About the author
Taimoor Mohsin
Hi there! I’m an avid writer who loves to help others in finding solutions by writing high-quality content about technology and gaming. In my spare time, I enjoy reading books and watching movies.