How to Dual Boot Linux Mint and Windows 10?
Dual booting allows users to run two operating systems on the same computer, giving them the flexibility to choose between different platforms based on their needs. In this article, we will explore the process of dual-booting Linux Mint and Windows 10, enabling you to enjoy the best of both worlds. Whether you’re interested in Linux or need specific applications available on Windows, this guide will help you set up a dual boot configuration seamlessly.
Introduction
Dual booting is the practice of installing two operating systems on a single computer, each residing on its dedicated partition. Dual booting involves partitioning the computer’s hard drive into multiple sections, with each partition dedicated to a different operating system. By dual booting Linux Mint and Windows 10, you can switch between the two operating systems at startup, granting you access to their respective features, applications, and capabilities.
Use Linux Inside Windows in a Virtual Machine
If you want to explore the features of Linux without a full installation, running Linux inside a virtual machine is an excellent option. Virtual machines enable you to create a virtual environment within your Windows operating system, where you can install and run Linux Mint. Follow the steps,
- Select and download a virtualization software that suits your needs. Popular options include Oracle VirtualBox, VMware Workstation, and Hyper-V.
- Download the ISO file of the Linux Mint from the official website.
- Open the VM software and click on the option to create a new virtual machine. Follow the on-screen options like name and location.
- Allocate the desired amount of RAM and storage for the virtual machine. Select the ISO file for installation to set up the virtual machine. Please ensure that there is at least 20 GB of space allocated for the VM machine.
- Start the virtual machine. It will typically boot from the Linux distribution ISO file. Follow the installation process of the Linux distribution within the virtual machine.
- After the Linux installation is complete, the virtual machine will reboot, and we can use the Linux OS within the virtual machine.
The virtualization feature should be enabled in Windows to use the virtual machines. You can check if this option is enabled from the control panel. If it is not enabled, we can use the BIOS menu to enable virtualization.
Use a Live Version of Linux
Another way to experience Linux without installing it alongside Windows is by using a live version of the Linux distribution. Using a live version allows you to run the operating system directly from a USB drive or DVD without installing it on your computer. This allows you to run Linux Mint from the external media without making any changes to your existing Windows installation. Follow the steps,
- Download the ISO file and Linux Mint and also Obtain a USB drive with sufficient capacity. You will also need to download any of the tools like Rufus, UNetbootin, or Etcher to create the bootable USB.
- Insert the bootable USB drive with sufficient capacity into your computer.
- Restart your computer and access the BIOS or UEFI settings by pressing the appropriate key during startup.
- In the BIOS settings, navigate to the boot options and change the boot order to prioritize the USB drive.
- Save the changes and exit the BIOS/UEFI settings. A clear explanation of the BIOS menu is given in the dual boot section.
- Restart your computer, and it should now boot from the USB. The computer will load the live Linux environment from the USB.
Now you can use the live version of Linux through USB. The system will return to its default OS when the USB is removed.
Remove Windows and Linux
If you decide that dual booting is no longer necessary, you can remove either Windows or Linux from your system.
- Before proceeding with the removal of an OS in the boot setup, it’s important to back up the data that you want to keep.
- In the BIOS/UEFI settings, navigate to the boot options and change the boot order to prioritize the Windows installation media.
- Boot into the operating system that you intend to keep.
- Open the Disk Management utility in Windows by right-clicking on the Start button, and selecting Disk Management from the menu.
- Identify the partition associated with the operating system you wish to remove. Right-click on the partition and select Delete Volume to delete the partition.
- For removing the Linux OS, the partition will typically be in ext4 or another Linux filesystem format.
- Now, we will have unallocated space. Select the unallocated space on your hard drive and click New . Windows will automatically allocate the entire unallocated space for the Windows partition.
We can also perform the above space allocation manually through the following steps,
- In Windows, open the Command Prompt as an administrator. Run the command bcdedit to display the current boot entries.
- Identify the entry corresponding to the deleted operating system. Use the following command to remove the entry,
We have successfully deleted the Linux from the dual-booted system.
Install Linux Alongside Windows
For those who want to keep both Linux Mint and Windows 10 on their computer, installing Linux alongside Windows is the best approach. This method allows you to choose the desired operating system each time you start your computer. For this, we can go with a dual boot which is explained in the next section.
Will dual-booting Linux With Windows Slow Down Your System?
Dual booting Linux with Windows generally does not slow down your system. However, it’s important to consider your hardware specifications and the impact of running multiple operating systems simultaneously. Allocating sufficient resources to each operating system, such as disk space, RAM, and CPU power, will ensure optimal performance. Additionally, having a solid-state drive (SSD) can enhance overall system responsiveness and reduce any potential slowdowns.
Install Linux Mint in Dual Boot With Windows
To dual-boot Linux Mint with Windows 10, you need to perform the following steps,
- Go to the Linux Mint official website and download the Linux Mint ISO file for the desired version of Linux Mint.
[IMAGE 1 An image showing the home page of Linux Mint. START SAMPLE] [IMAGE 1 FINISH SAMPLE]
- Visit the Ventoy website and download the latest version of Ventoy for your operating system or you could also download the Ventoy zip file from the official GitHub link.
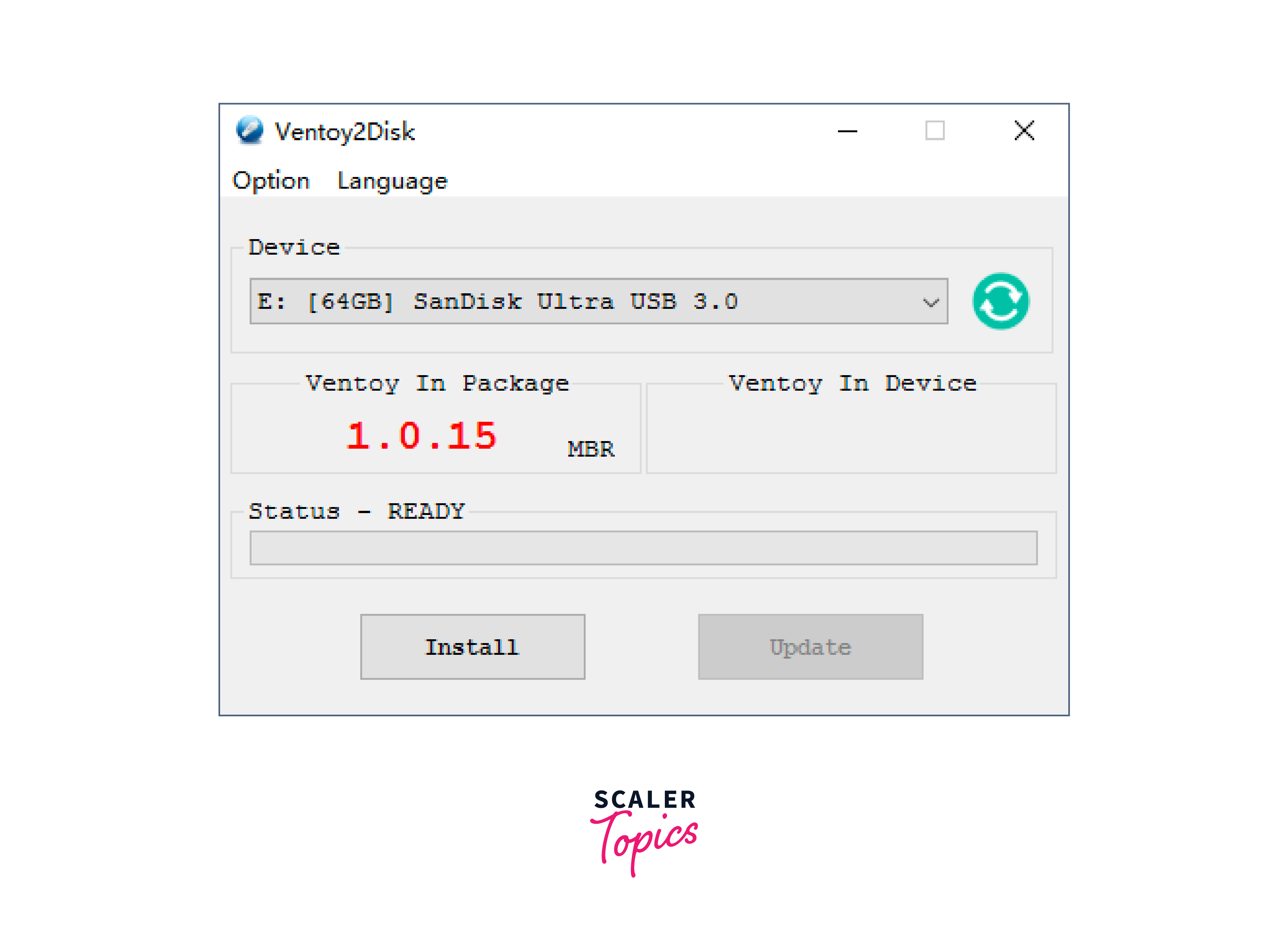
- Insert the USB drive that you want to use for the dual boot installation. Note that all data on the USB drive will be erased, so make sure to back up any important files. Plug in the USB device and launch Ventoy.
- The Vectoy2Disk window will appear, select the USB drive from the drop-down menu. Click on the Install button to install Ventoy on the USB drive.
- After Ventoy is installed, navigate to the USB drive and copy the Linux Mint ISO file from your computer and paste it into the root directory of the USB drive.
You can follow the 6 a) and 7 a) steps for partition of space using the Disk Management utility in Windows or else you can also follow the 6 b) and 7 b) steps to partition the space using the GParted tool in Linux.
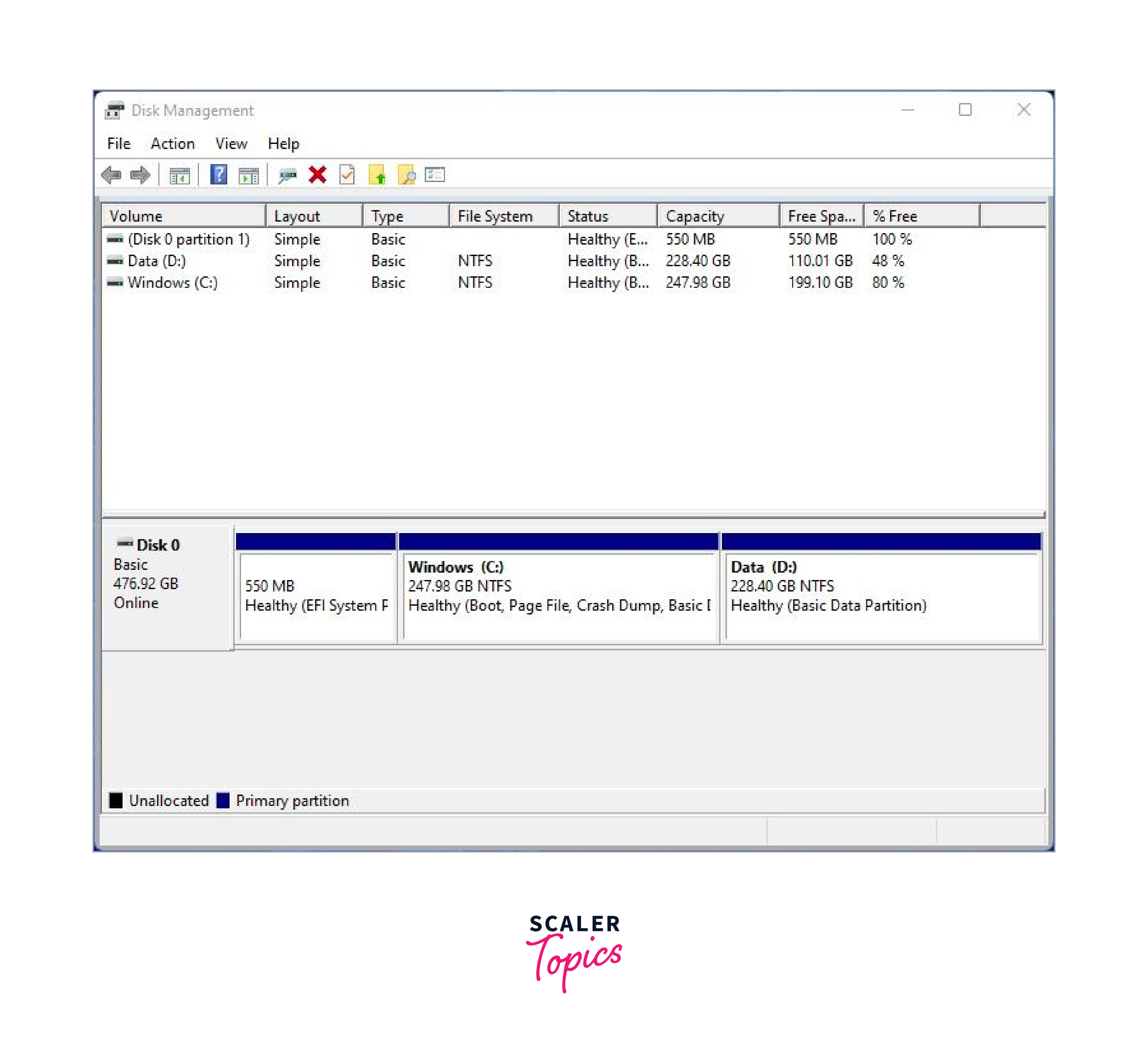
- a) On your Windows 10 system, press the Windows key and type Disk Management . Open the Disk Management utility.
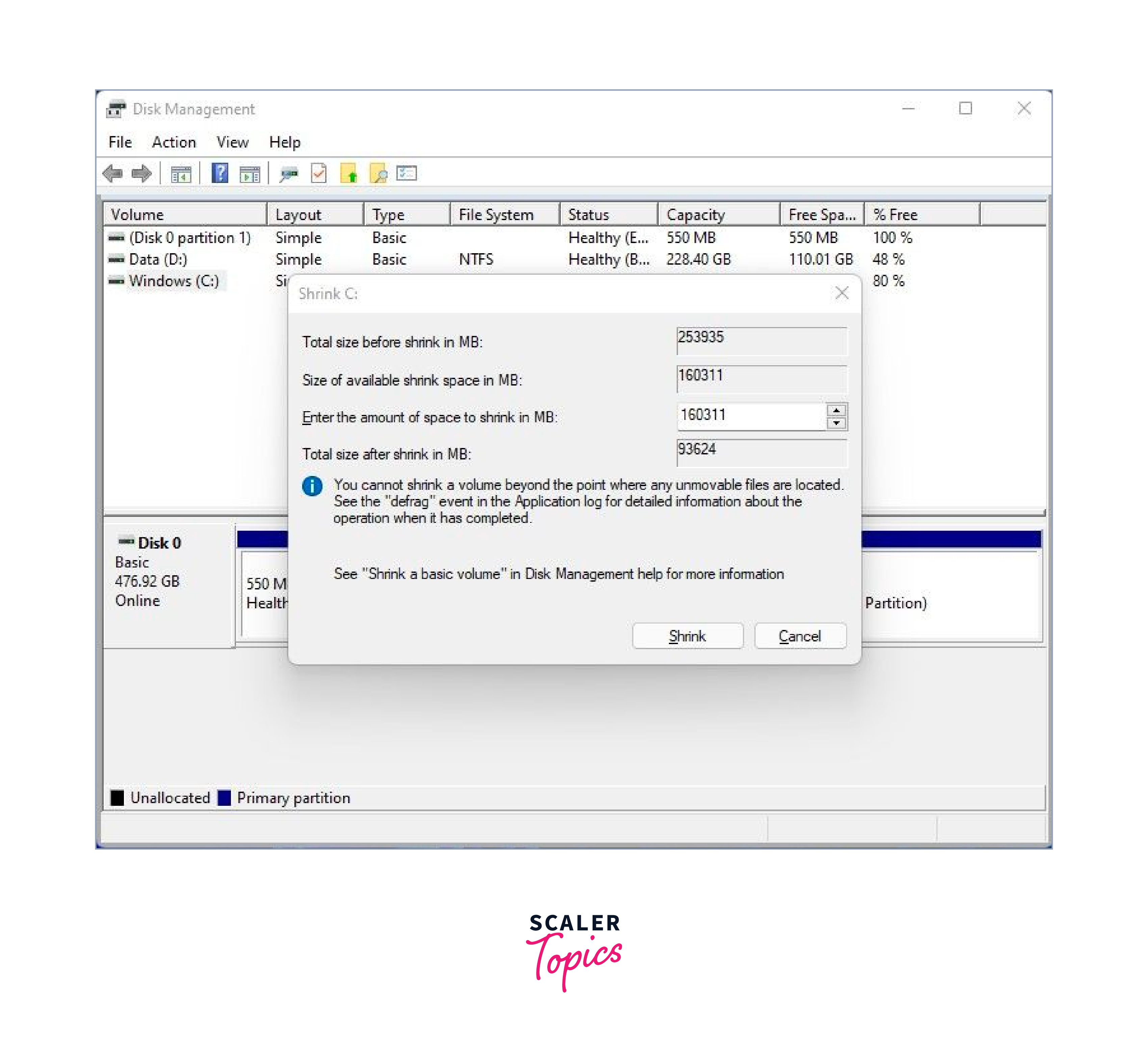
- a) Right-click on the Windows partition, select Shrink Volume , and specify the desired size for the Linux Mint partition. Click Shrink to create unallocated space for the Linux Mint installation.
- Restart your computer to enter the BIOS or UEFI settings.
- To enter the BIOS settings, you have to know the key to access the BIOS or UEFI settings. It may be F2, F10, F12, Esc, or Del keys depending on your computer. To access the BIOS menu, press it repeatedly before the operating system starts loading or the logo is displayed. If you miss the time, you can restart the computer and try again.
- To configure the boot order to prioritize booting from USB devices, navigate to Boot Options and disable the Secure Boot option for this system. Also, use the F5 and F6 keys to change the boot priority order(first) of ventoy USB to use it as the primary boot option.
- Then save the BIOS options and exit using the F10 or F12 keys.
- Then the Ventoy boot menu appears; you will see both the Windows 10 and Linux Mint options. Use the arrow keys to select Linux Mint and press Enter
Perform the following steps only if you haven’t performed the steps 6a and 7a . These steps show how to partition the disk using the Gparted tool in Linux,
- b) Then we need to free up space for installation; we can use the GParted tool in Linux for this purpose. Search for the Gparted tool and launch it. You may need to enter your password to authenticate.
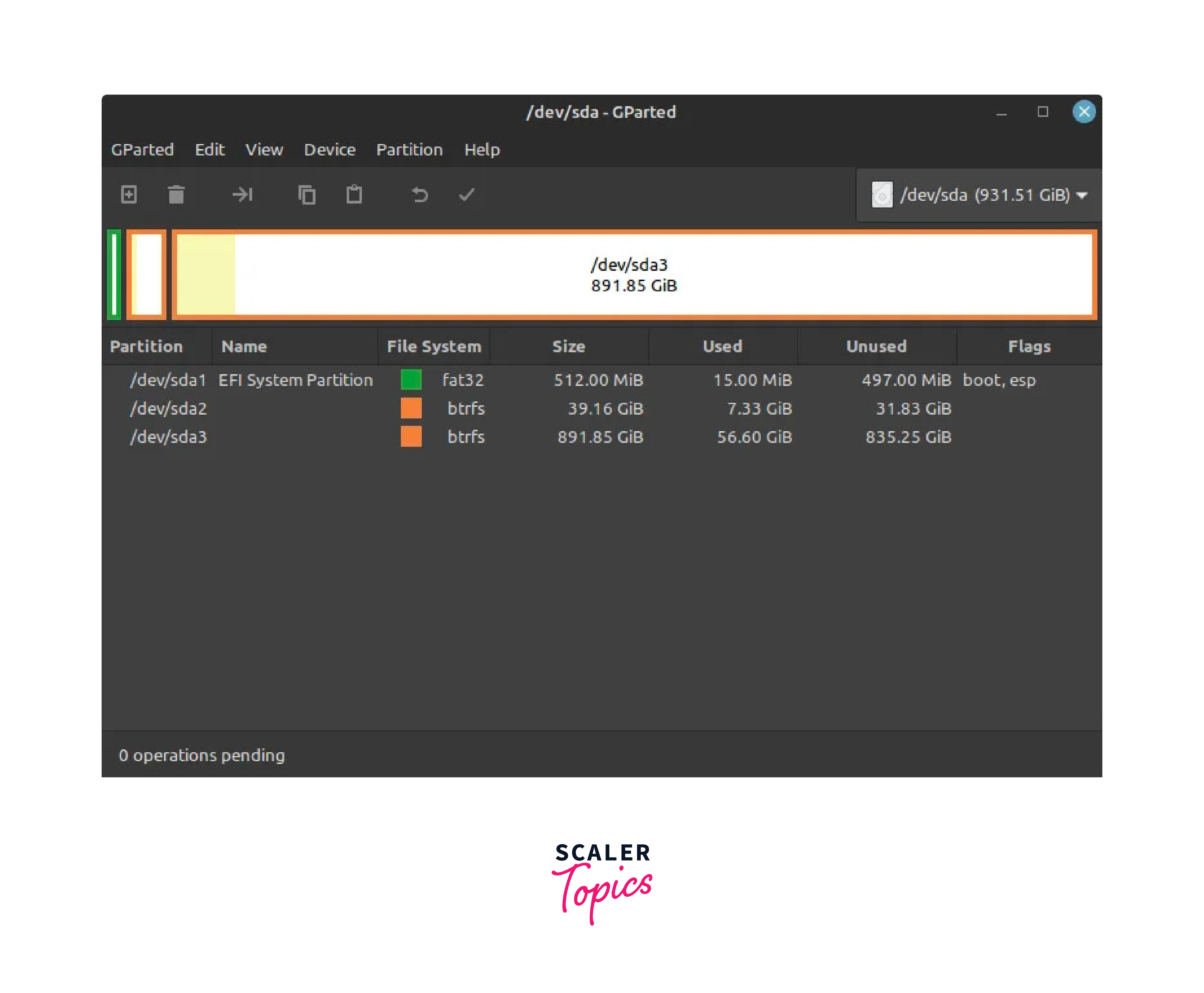
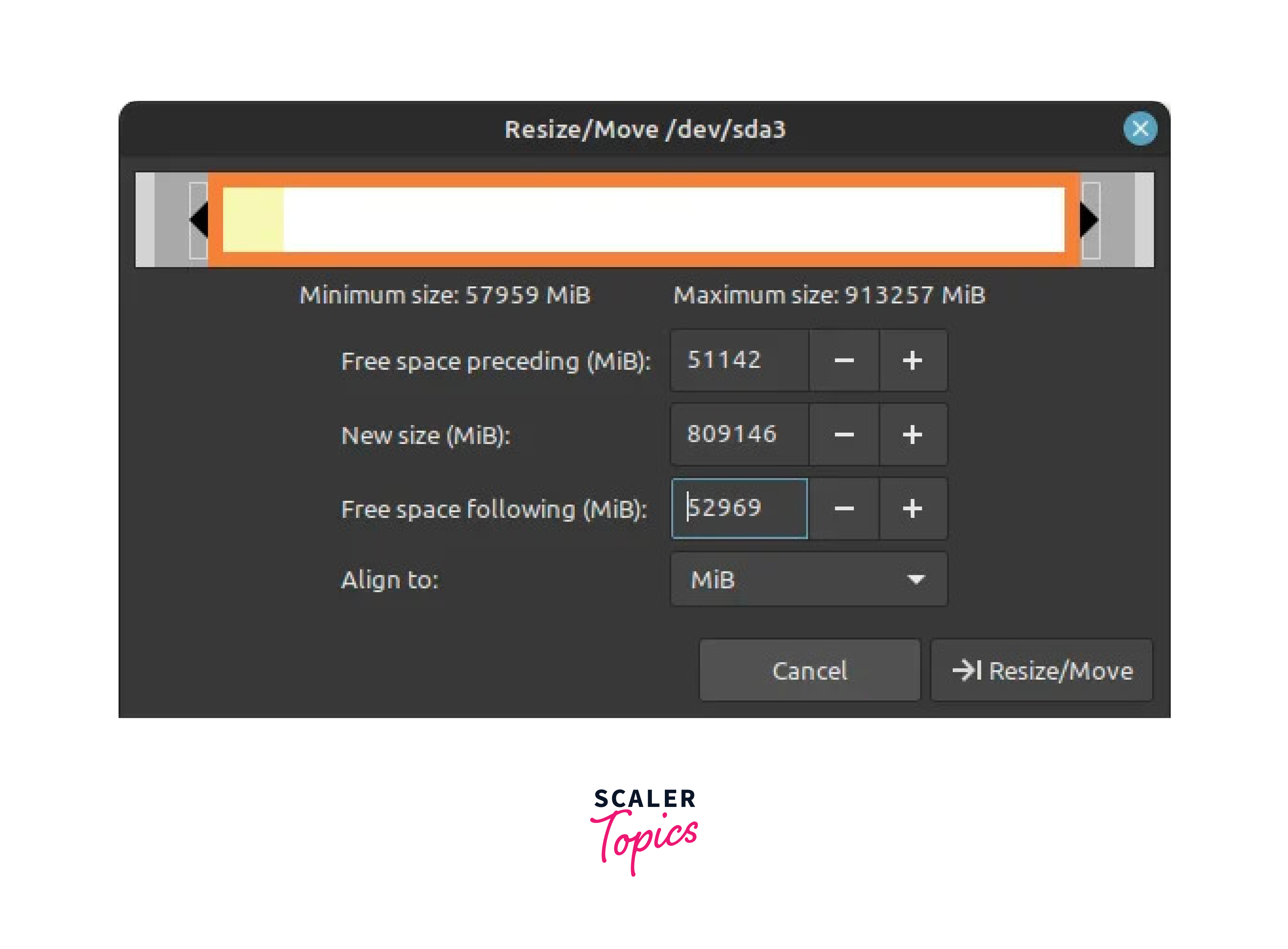
- b) In GParted, you will see a list of available disks in the top right corner of the window. Locate the partition that contains the Windows operating system files. This partition is typically the largest one (e.g.,/dev/sda3). Right-click on the Windows partition(s) and select Resize/Move.
The EFI (Extensible Firmware Interface) boot process is a modern method of booting computers that replaces the traditional BIOS. In our sample, the /dev/sda1 has the programs required for utilizing the EFI boot in Linux.
In the resize dialog, adjust the partition size to free up space for Linux Mint. Ensure you leave enough space for Windows as well. You must have at least 50 GB of unallocated disk space to proceed. Click Resize/Move to apply the changes. You should now see unallocated space created from resizing the Windows partition.
- Now on the desktop, click on the Install Linux Mint icon. The installer will open, and you will be prompted to select your preferred language. Choose the language from the drop-down menu.
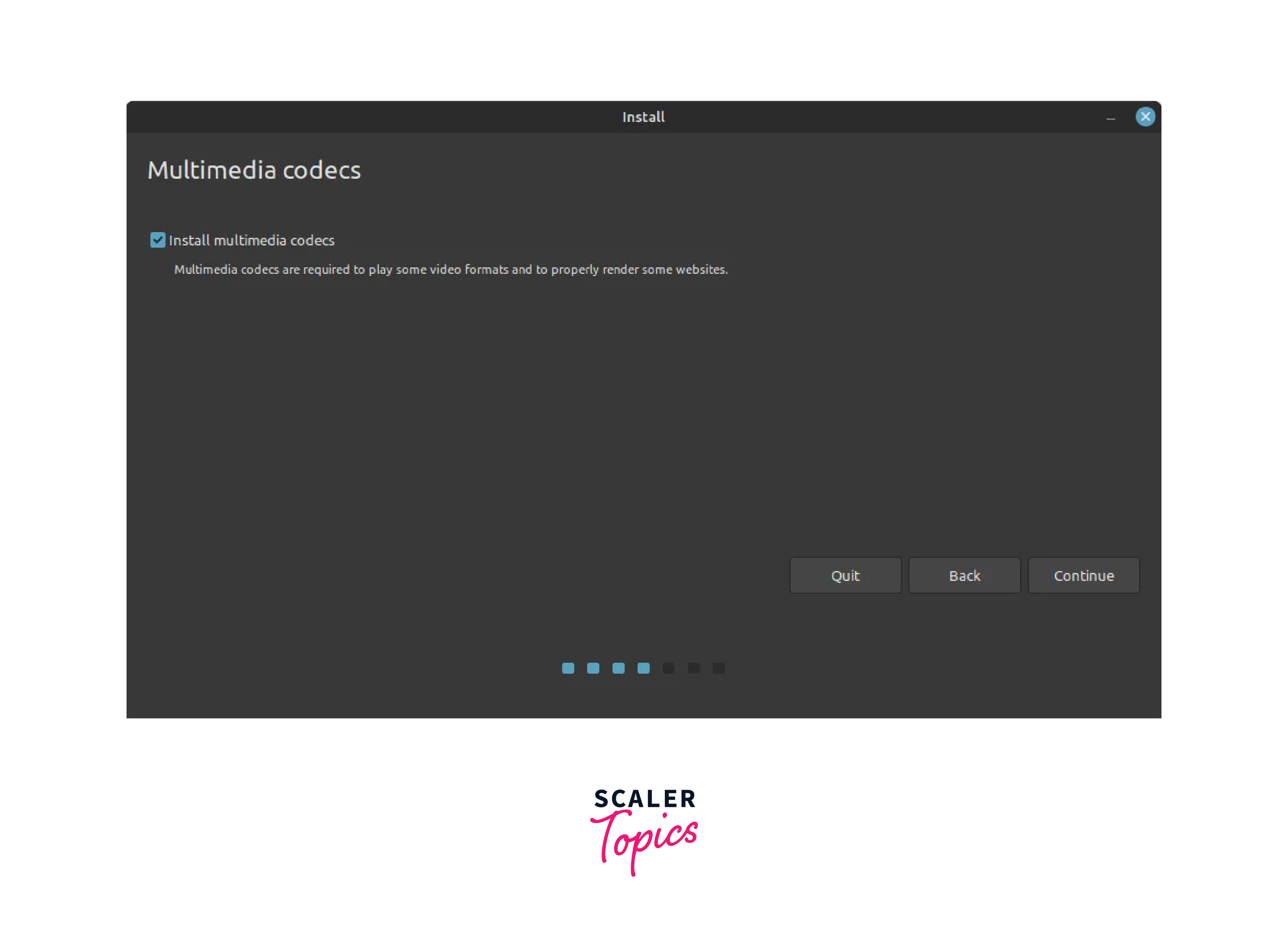
- The next step asks you for permission to install multimedia codecs, which are software components that enable the playback and encoding of multimedia files, including audio and video formats, in Linux operating systems. This is optional, and remember that you will need a network connection to install this.
- Following the previous step, if the system automatically detects the Windows, you can click on continue and then click on the Install button to complete the process and continue from step 20 or else follow the next steps.
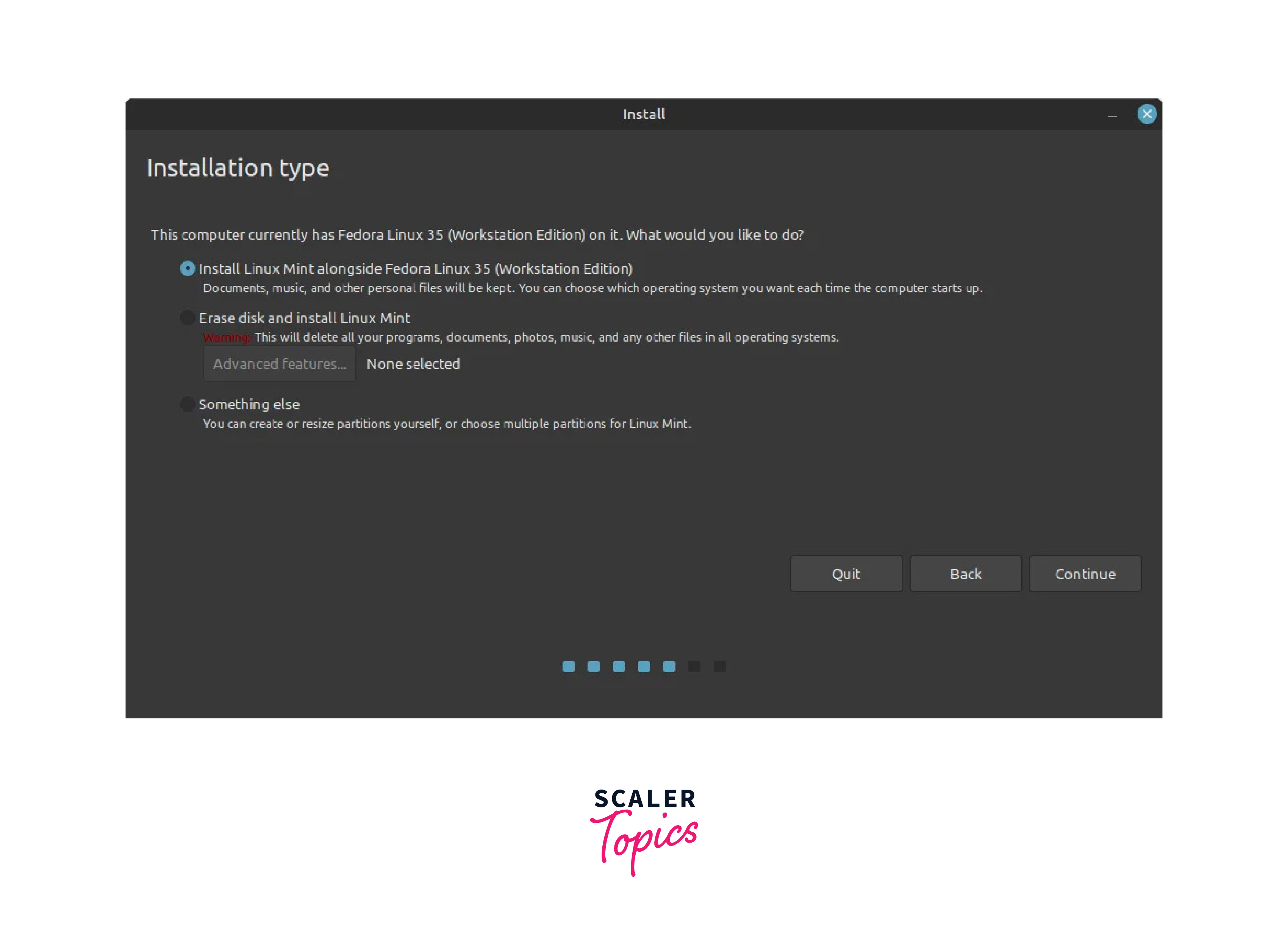
- In the next step, the Installation Type window opens, select Something else to manually partition the disk and customize the installation.
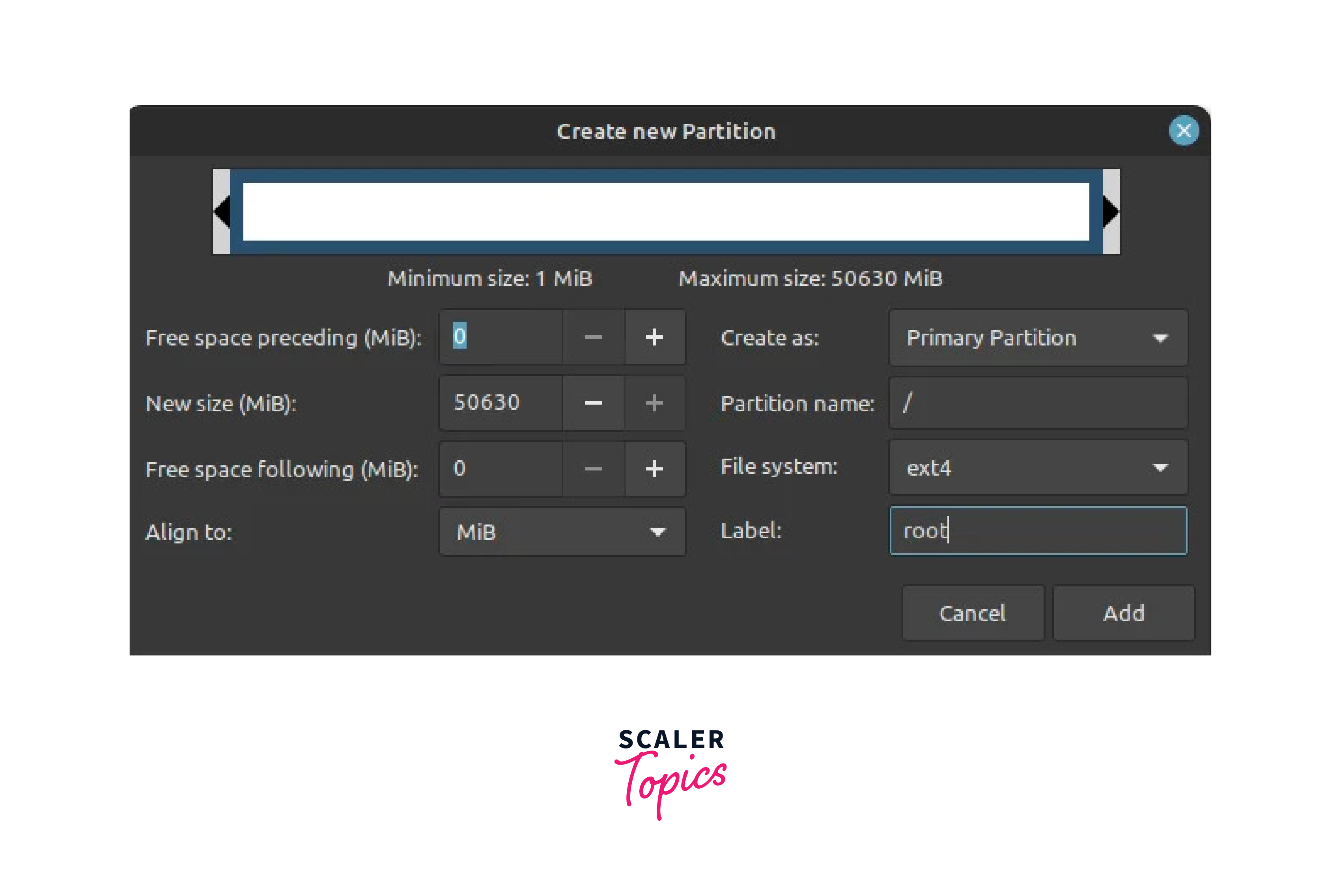
- Identify the unallocated space you created earlier using GParted or Windows Disk Management tools. Right-click on the unallocated space and select New . Create a new partition with the desired size for Linux Mint. Set the partition type to ext4 and the mount point to / (root).
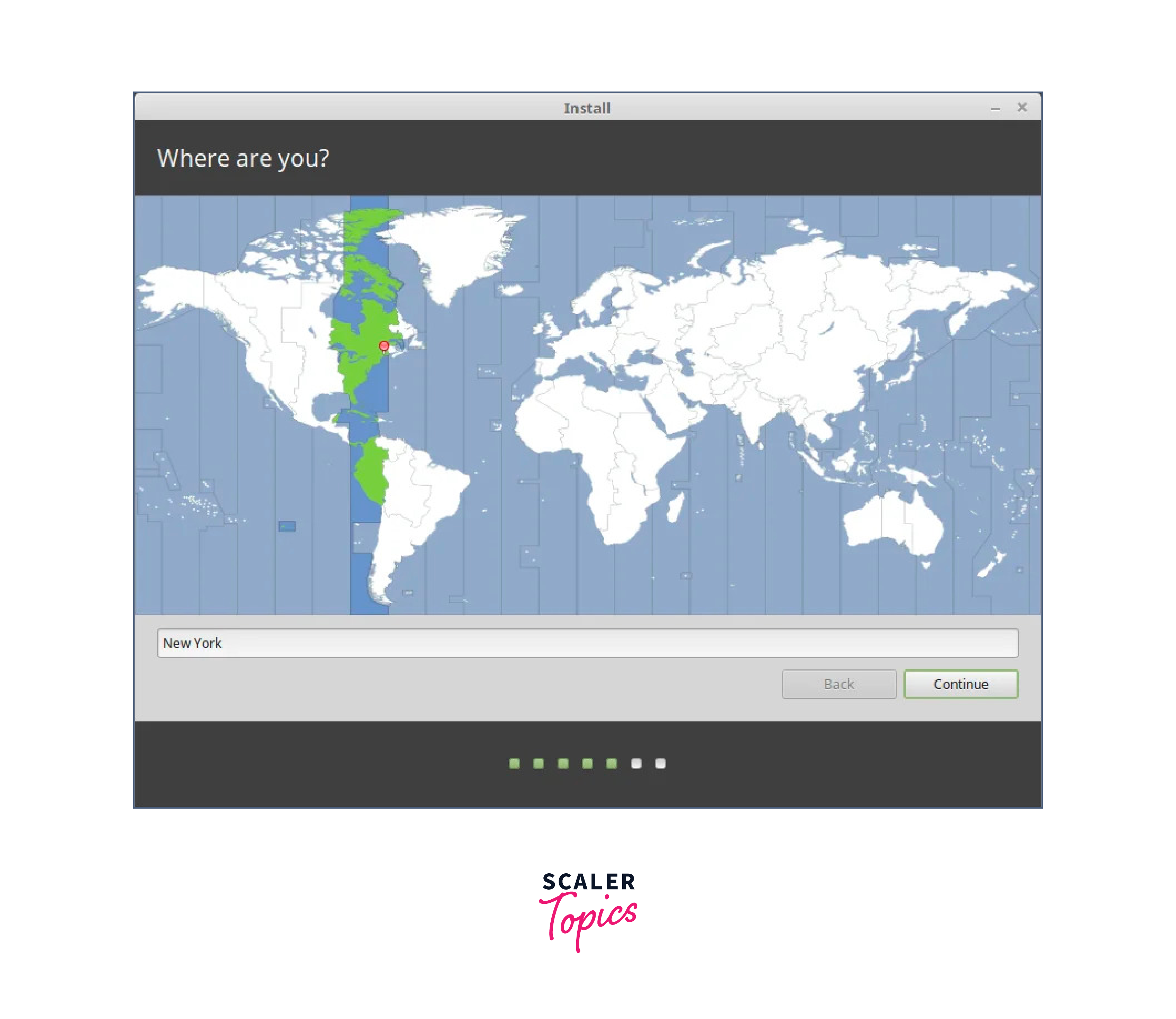
- After creating the partition, you will see it listed in the partition manager. Select the new partition and click Install Now to proceed with the Linux Mint installation. Follow the remaining on-screen instructions to set the location.
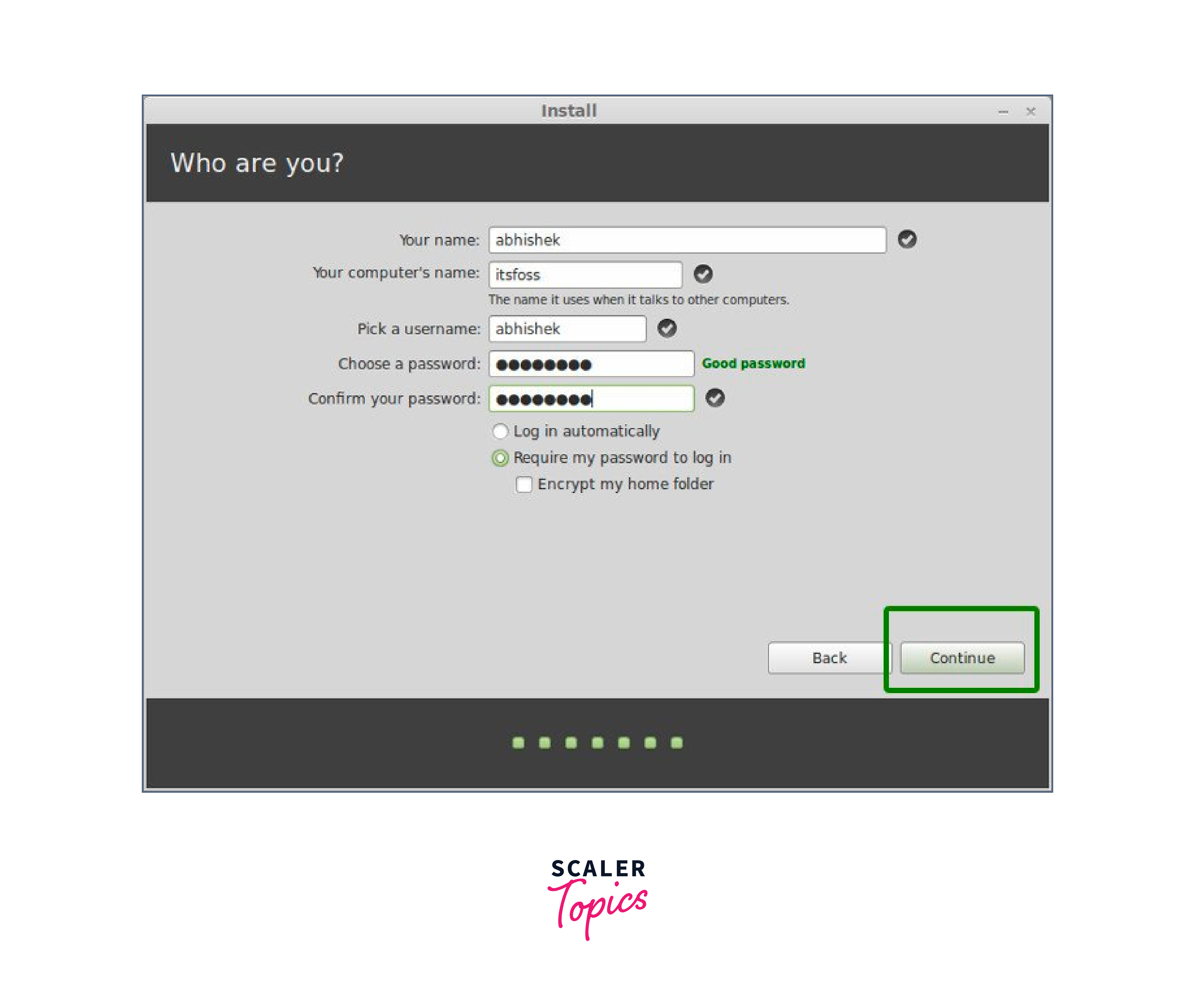
- On the next screen, you will be asked to provide your user information, such as your full name, username, and password. Fill in the required fields and choose a strong password for your user account.
- The installer will now show a summary of the installation settings and partition layout. Review the information to ensure it is accurate and matches your preferences. If you are ready to proceed, click Install to begin the Linux Mint installation process.
You have successfully dual-booted Linux mint and Windows 10 . Now, you can restart your system and select the type of OS to use.
Conclusion
- Dual-booting Linux Mint and Windows 10 provides you with the flexibility to use both operating systems on the same computer.
- Virtual machine is an excellent and easier option for exploring the features of Linux.
- We can use a live version of Linux to run the operating system directly from a USB drive without installation or utilization of space from our main OS.
- To remove an OS in the dual-booted system, we can delete the partition associated with the operating system.
- Dual booting Linux with Windows does not slow down your system unless you don’t have a good hard drive space.
- The important step in dual booting is specifying the desired size for partitioning.
- Remember to follow the necessary precautions, such as backing up your data, before making any changes to your system, as partitioning may result in data loss in some cases.