- How to Clear Terminal Screen in Ubuntu and Other Linux Distributions [Beginner’s Tip]
- Clear Linux terminal with clear command
- Other ways to clear terminal screen in Linux
- 4 Useful Commands to Clear Linux Terminal Screen
- 1. Clear Linux Terminal Using clear Command
- 2. Clear Linux Terminal Screen Using CTRL+L Shortcut
- 3. Reset (Clear) Linux Terminal Using reset Command
- 4. Clear the Terminal Using the Escape Code
- How to Clear a Terminal Screen in Linux
- Importance of the Linux Terminal
- 1. Run System Update and Upgrade Commands
- 2. File System Navigation and Management
- 3. A Perfect Test Environment
- Why Clear the Linux Terminal Screen?
- Clearing a Terminal Screen in Linux
- Clear Terminal via reset Command
- Clear Terminal via Ctrl+L / Ctrl+Shift+K Shortcut
- Clear Terminal via alias Command
How to Clear Terminal Screen in Ubuntu and Other Linux Distributions [Beginner’s Tip]
When you are working in the terminal, often you’ll find that your terminal screen is filled up with too many commands and their outputs.
You may want to clear the terminal to declutter the screen and focus on the next task you are going to perform. Clearing the Linux terminal screen helps a lot, trust me.
Clear Linux terminal with clear command
So, how do you clear terminal in Linux? The simplest and the most common way is to use the clear command:
You need no option with the clear command. It’s that simple but there are some additional things you need to know about it.
The clear command and other methods of clearing screen may depend on the terminal emulator you are using. Terminal emulator is the terminal application that you use for accessing the Linux shell (command line).
If you use clear command on Ubuntu with GNOME Terminal, it will clear the screen and you won’t be able to see what else you had on the screen previously.
In many other terminal emulators or Putty, it may just clear the screen for one page. If you scroll with mouse or PageUp and PageDown keys, you can still access the old screen outputs.
Frankly, it depends on your need. If you suddenly realize that you need to refer to the output of a previously run command, perhaps having that option available will be helpful.
Other ways to clear terminal screen in Linux
Clear command is not the only way to clear the terminal screen.
You can use Ctrl+L keyboard shortcut in Linux to clear the screen. It works in most terminal emulators.
If you use Ctrl+L and clear command in GNOME terminal (default in Ubuntu), you’ll notice the difference between their impact. Ctrl+L moves the screen one page down giving the illusion of a clean screen but you can still access the command output history by scrolling up.
Some other terminal emulators have this keyboard shortcut set at Ctrl+Shift+K.
You can also use reset command for clearing the terminal screen. Actually, this command performs a complete terminal re-initialization. It could take a bit longer than clear command, though.
There are a couple of other complicated ways to clear the screen when you want to clear the screen completely. But since the command is a bit complicated, it’s better to use it as alias in Linux:
You can add this alias to your bash profile so that it is available as command.
I know this was a pretty basic topic and most Linux users probably already knew it but it doesn’t harm in covering the elementary topics for the new Linux users. Isn’t it?
Got some secretive tip on clearing terminal screen? Why not share it with us?
4 Useful Commands to Clear Linux Terminal Screen
Just like any other operating system, Linux also supports a rich Graphical User interface (GUI). In fact, it supports multiple graphical desktop environments such as – GNOME, KDE, Cinnamon, and the list goes on.
However, most Linux administrators and power users prefer to use the command line interface, because it allows us to automate repetitive tasks using the scripts.
One of the trivial downsides of this approach is that often times the terminal gets filled up with the command’s or script’s output. So, in some cases, cleaning up the terminal becomes necessary.
In this guide, we will discuss various methods that allow us to clean up the Linux terminal. After following this guide, Linux users can use one of the methods while working with Linux’s command line interface.
1. Clear Linux Terminal Using clear Command
The clear command is one of the most commonly used commands for clearing the Linux terminal. This command simply clears the terminal screen including its scroll-back buffers.
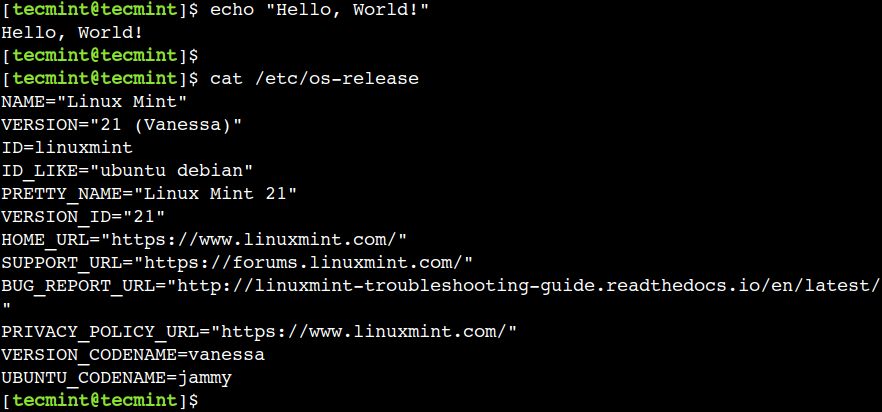
To understand the usage of the command, let’s execute a few commands in the terminal:
$ echo "Hello, World!" $ cat /etc/os-release
Now, to clean up the screen, just execute the clear command without any argument:
2. Clear Linux Terminal Screen Using CTRL+L Shortcut
In a similar way, we can use the ctrl+L shortcut to clear the terminal screen. However, this method doesn’t clean up the scroll-back buffers.
To illustrate this, first clear the terminal screen using the ctrl+L shortcut and then scroll up the screen using the mouse:
In this example, we can see the previous output by scrolling up the terminal.
3. Reset (Clear) Linux Terminal Using reset Command
Additionally, we can also use the reset command to clear the terminal screen. Just like the clear command the reset command also clears the scroll-back buffers.
The reset command reinitializes the terminal hence it takes more time compared to the clear command.
4. Clear the Terminal Using the Escape Code
We can use the c escape code to clear the terminal. Let’s understand with a simple example.
In bash, we can use the \e escape sequence to represent the ESC character. So, to clear the terminal screen we can use the \ec string with the printf command as shown below:
In a similar way, we can use the \033 octal number to represent the ESC character. So to clear the terminal, we can use the \033c string with the printf command:
In addition to this, the hexadecimal number \x1B represents the ESC character. Hence we can use it to clear the screen:
In this guide, we discussed various methods for clearing the Linux terminal screen. Linux users can use one of the methods as per their choice.
Do you know of any other method for clearing the terminal in Linux? Let us know your views in the comments below.
How to Clear a Terminal Screen in Linux
Despite the installation of various Linux operating system distributions being accompanied by an appealing Desktop environment, most Linux users; throughout their transition to using the operating system, tend to define themselves as willing captives of the Linux terminal or command-line environment.
Importance of the Linux Terminal
Despite this environment not being associated with the luxury of graphical icons and an intuitive display, it somehow offers a better user experience for users on the quest of mastering Linux and becoming renowned Linux administrators.
Therefore, before we jump into the main objective of this article, why not take a moment to appreciate some of the functionalities we can achieve through the use of the Linux operating system command-line environment?
1. Run System Update and Upgrade Commands
Depending on your package manager and the Linux operating system distribution you are using, the Linux terminal environment is very effective when it comes to updating your system and upgrading your operating system distribution to the latest release.
$ sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum update && sudo yum upgrade [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux] $ sudo emaint --auto sync [On Gentoo Linux] $ sudo pacman -Syu [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper update [On OpenSUSE]
You will find it easy to install most of your Linux-associated software packages via the Linux command-line environment based on the package manager you are using. Also, when it comes to upgrading these software packages to the latest stable releases, all you need to do is execute the needed package upgrade command.
2. File System Navigation and Management
You will find it flexibly fast to navigate and access your user and system files via the Linux terminal environment than by using the GUI approach. Also, through the use of commands like cat and nano, you can easily preview your files’ configuration and content before editing them to your preference if needed.
$ cat filename $ nano filename
3. A Perfect Test Environment
For users questing to master the software development world, the Linux terminal environment is all that you need in regards to its support of various development servers for testing the behaviors of your applications prior to their introduction onto a production server.
With the above few mentions, perfecting the usage of the Linux terminal environment should introduce us to other exciting milestones. However, we can all agree that our bond with the Linux terminal screen becomes better if we know how to clear our workspace once we are done with the above-mentioned terminal-associated functionalities.
Why Clear the Linux Terminal Screen?
For first-time users or beginners on the Linux operating system command-line environment, you will always find yourselves needing a new and cleaner command-line workspace after executing a series of Linux-associated commands.
Since most of us are newbies at this point in experiencing the Linux terminal environment, we tend to close the currently overpopulated screen and launch a new command-line session before resuming our work.
Alternatively, for users with keen eyesight, we tend to quickly identify the top-left icon on the Linux terminal screen whose functionality is associated with opening a new terminal tab.
Such tweaks are short-lived solutions to dealing with overpopulated terminal screens as we tend to be bored with continuously opening new terminal tabs or closing and opening new terminal sessions.
Clearing a Terminal Screen in Linux
The fastest way to clean up the terminal screen once we feel it is overpopulated is via the Linux clear command. This command does not require any arguments and can be plainly used.
Depending on the terminal emulator you are using, the keyboard key shortcut [Ctrl]+[L] should also work. However, this approach gives you the illusion of a cleared terminal screen since you can still scroll up to the previous terminal screen display.
The reset command is another way of clearing the Linux terminal screen.
However, this command not only clears the terminal screen but also re-initializes it.
[ You might also like: How to Remove a Command from History in Linux ]
Hope you enjoyed the article read. As always, your comments and feedback are appreciated.
How to Clear Terminal in Linux
The clear command is the go-to tool for clearing the terminal screen in Linux. Despite its effectiveness, clear does not reinitialize the terminal, which is sometimes necessary. Some alternative methods provide users with that option as well.
Read this tutorial to learn how to clear the terminal in Linux using different methods.
The command deletes everything, including the scrollback buffer. To keep the scrollback buffer, use clear with the -x argument:

The clear -x command clears the terminal, but previous output is still available. Scroll up or use the PgUp button:

However, in some terminal emulators, clear without arguments doesn’t delete previous output but shifts it upwards (same as clear -x in GNU). In that case, accessing earlier output is possible with the PgUp key.
Additionally, the clear command does not reset the terminal. The shell state remains the same as before.
Clear Terminal via reset Command
Unlike clear , the reset command reinitializes the terminal and restores settings to default. The reinitialization process covers tab extensions, turns off echo and raw modes, and turns on newline translation.
The command resets a terminal that is in an abnormal state and reinitializes the command line:

Executing reset takes a few moments to complete while clear shows effect instantly.
Clear Terminal via Ctrl+L / Ctrl+Shift+K Shortcut
Keyboard shortcuts also work for clearing the terminal, depending on the terminal emulator.
In GNOME, the Ctrl + l shortcut has the same effect as clear -x. The shortcut clears the terminal while leaving the scrollback buffer:

Typing in a new command, like whoami, is done on a clear screen. Still, users can access command output history with PgUp or by scrolling up:

An alternative in some terminal emulators is Ctrl + Shift + K . The command provides the same output as Ctrl + L .
Clear Terminal via alias Command
Alternative methods for clearing the terminal are also more complicated. For instance, the \033 is the ASCII escape character used to start terminal control sequences. When followed by c , the command clears the terminal.

The command clears the terminal screen, including the scrollback buffer. To avoid typing numbers, create an alias for the command. For instance, set x as an alias for printf «\033c» with:
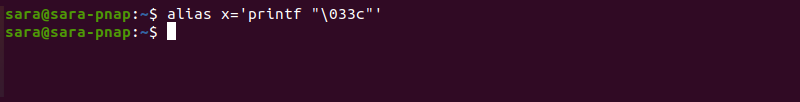
Once the alias is created, running x results in a clear terminal screen.
Now you know how to clear the terminal screen using a few different methods. Next, check out the ultimate guide of all Linux commands everyone should know.