- Символические и жесткие ссылки Linux
- Символические ссылки
- Жесткие ссылки
- Использование ссылок в Linux
- Создание символических ссылок
- Создание жестких ссылок
- Выводы
- Linux ln – How to Create a Symbolic Link in Linux [Example Bash Command]
- What is the difference between soft and hard links in Linux?
- How to create a symlink to a file
- How to create a symbolic link to a directory
- How to remove a symbolic link
- How to overwrite symlinks
- How to learn more about the ln command
- Conclusion
Символические и жесткие ссылки Linux
Символические и жесткие ссылки — это особенность файловой системы Linux, которая позволяет размещать один и тот же файл в нескольких директориях. Это очень похоже на ярлыки в Windows, так как файл на самом деле остается там же где и был, но вы можете на него сослаться из любого другого места.
В Linux существует два типа ссылок на файлы. Это символические и жесткие ссылки Linux. Они очень сильно отличаются и каждый тип имеет очень важное значение. В этой небольшой статье мы рассмотрим чем же отличаются эти ссылки, зачем они нужны, а также как создавать ссылки на файлы в Linux.
Символические ссылки
Символические ссылки более всего похожи на обычные ярлыки. Они содержат адрес нужного файла в вашей файловой системе. Когда вы пытаетесь открыть такую ссылку, то открывается целевой файл или папка. Главное ее отличие от жестких ссылок в том, что при удалении целевого файла ссылка останется, но она будет указывать в никуда, поскольку файла на самом деле больше нет.
Вот основные особенности символических ссылок:
- Могут ссылаться на файлы и каталоги;
- После удаления, перемещения или переименования файла становятся недействительными;
- Права доступа и номер inode отличаются от исходного файла;
- При изменении прав доступа для исходного файла, права на ссылку останутся неизменными;
- Можно ссылаться на другие разделы диска;
- Содержат только имя файла, а не его содержимое.
Теперь давайте рассмотрим жесткие ссылки.
Жесткие ссылки
Этот тип ссылок реализован на более низком уровне файловой системы. Файл размещен только в определенном месте жесткого диска. Но на это место могут ссылаться несколько ссылок из файловой системы. Каждая из ссылок — это отдельный файл, но ведут они к одному участку жесткого диска. Файл можно перемещать между каталогами, и все ссылки останутся рабочими, поскольку для них неважно имя. Рассмотрим особенности:
- Работают только в пределах одной файловой системы;
- Нельзя ссылаться на каталоги;
- Имеют ту же информацию inode и набор разрешений что и у исходного файла;
- Разрешения на ссылку изменяться при изменении разрешений файла;
- Можно перемещать и переименовывать и даже удалять файл без вреда ссылке.
Использование ссылок в Linux
Теоретические отличия вы знаете, но осталось закрепить все это на практике, поэтому давайте приведем несколько примеров работы со ссылками в Linux. Для создания символических ссылок существует утилита ln. Ее синтаксис очень прост:
$ ln опции файл_источник файл_ссылки
- -d — разрешить создавать жесткие ссылки для директорий суперпользователю;
- -f — удалять существующие ссылки;
- -i — спрашивать нужно ли удалять существующие ссылки;
- -P — создать жесткую ссылку;
- -r — создать символическую ссылку с относительным путем к файлу;
- -s — создать символическую ссылку.
Создание символических ссылок
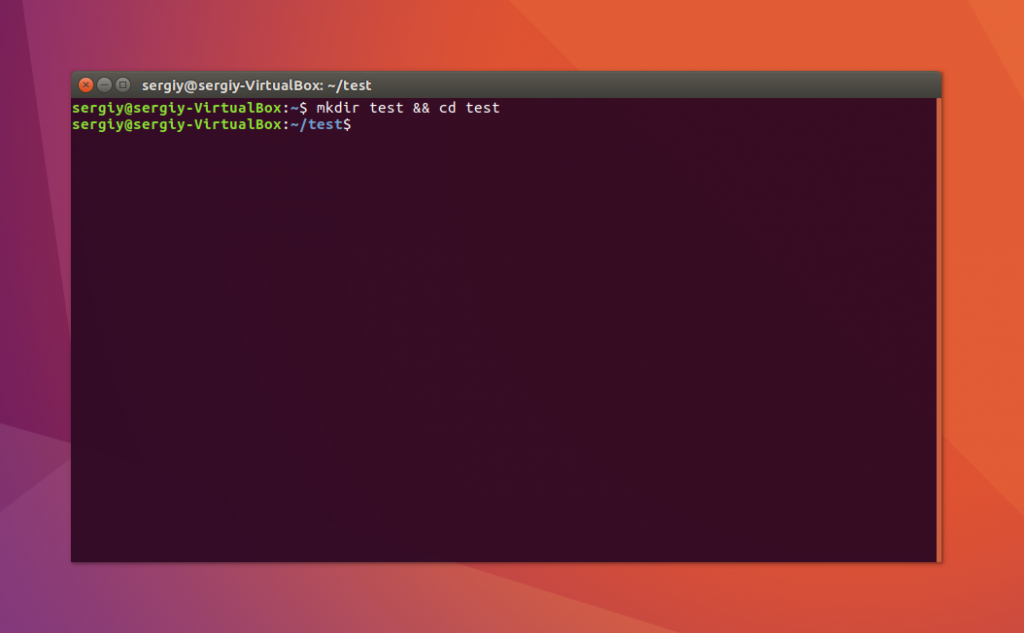
Сначала создайте папку test и перейдите в нее:
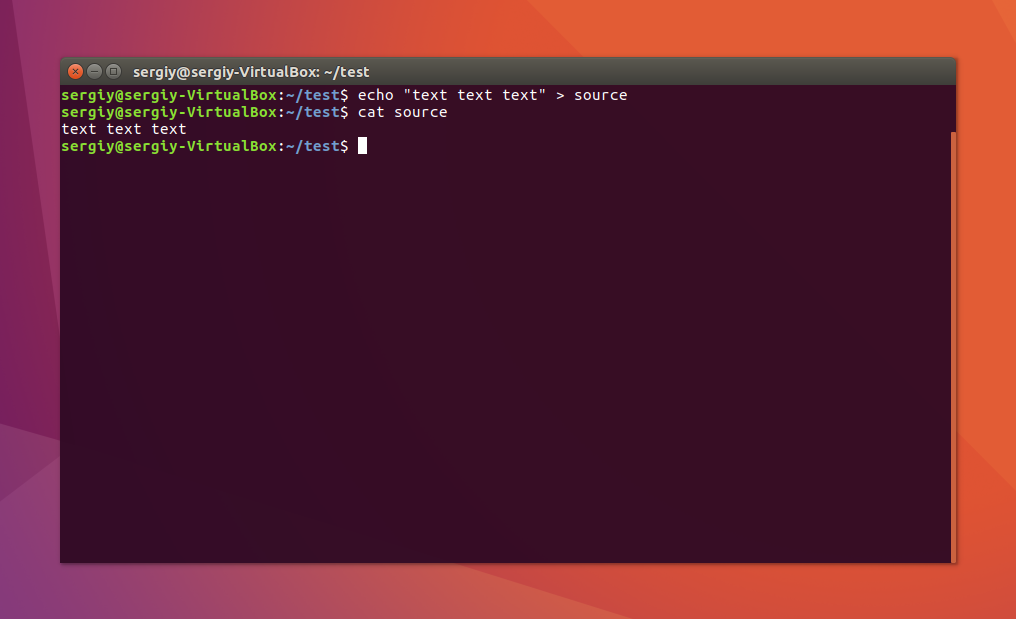
Затем создайте файл с именем source с каким-либо текстом:
echo «текст текст текст текст» > source
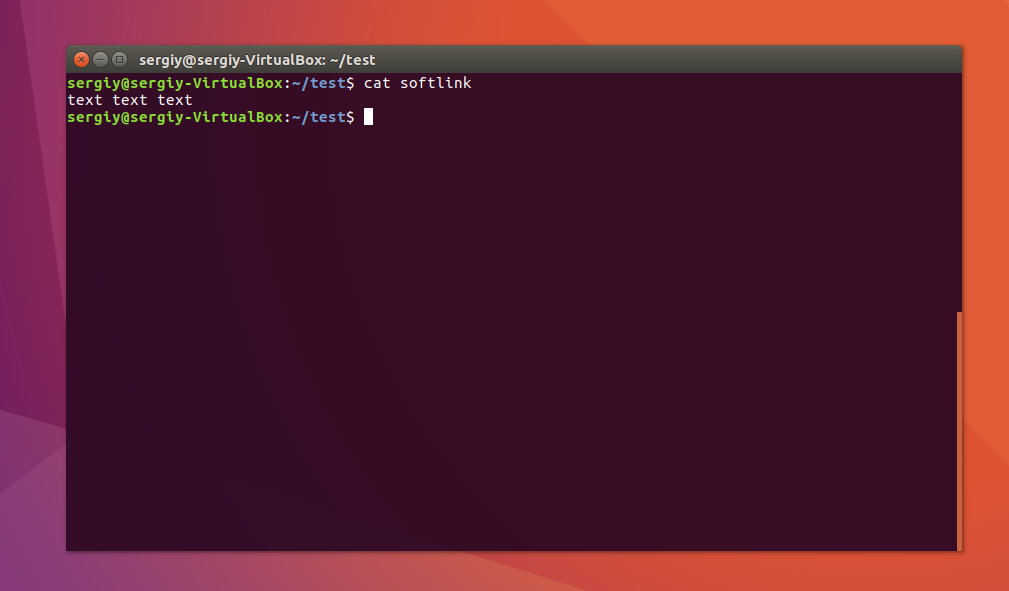
$ cat source
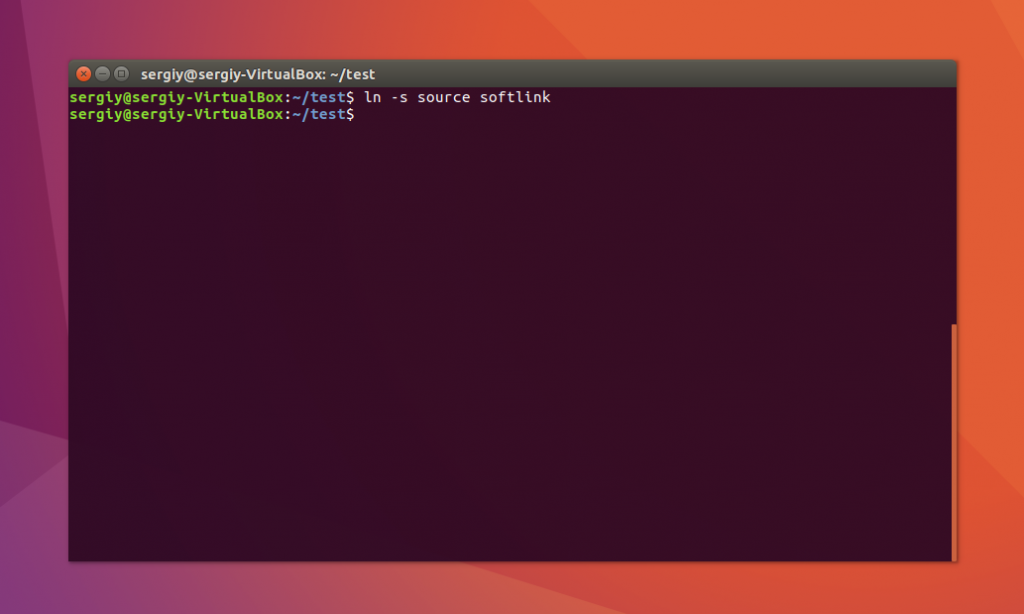
Файл готов, дальше создадим символическую ссылку Linux, для этого используется команда ln с опцией -s:
Попробуем посмотреть содержимое файла по ссылке:
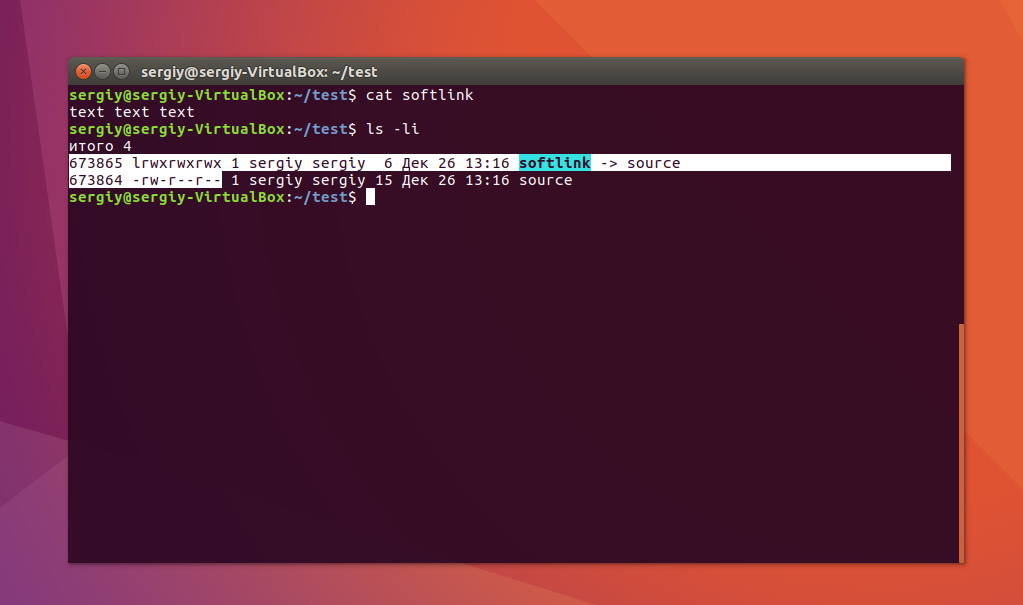
Как видите, нет никакой разницы между ней и исходным файлом. Но утилита ls покажет что это действительно ссылка:
Несмотря на то, что содержимое одинаковое, здесь мы видим, что адрес иноды и права доступа к файлам отличаются, кроме того, явно показано что это символическая ссылка Linux.
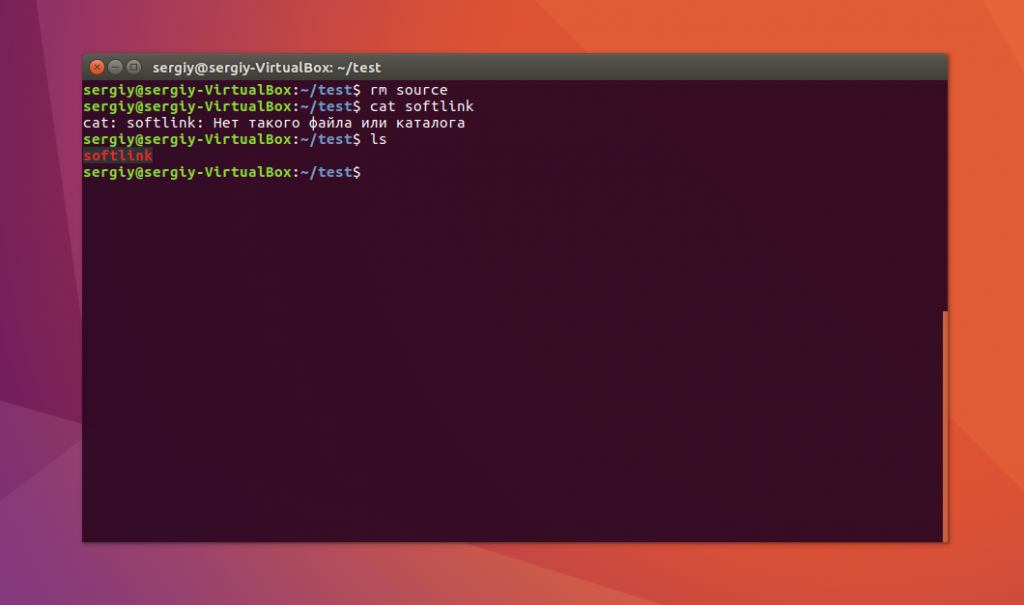
Теперь удалите исходный файл и посмотрите что будет:
Вы получите ошибку, что такого файла не существует, потому что мы действительно удалили исходный файл. Если вы удалите ссылку, то исходный файл останется на месте.
Создание жестких ссылок
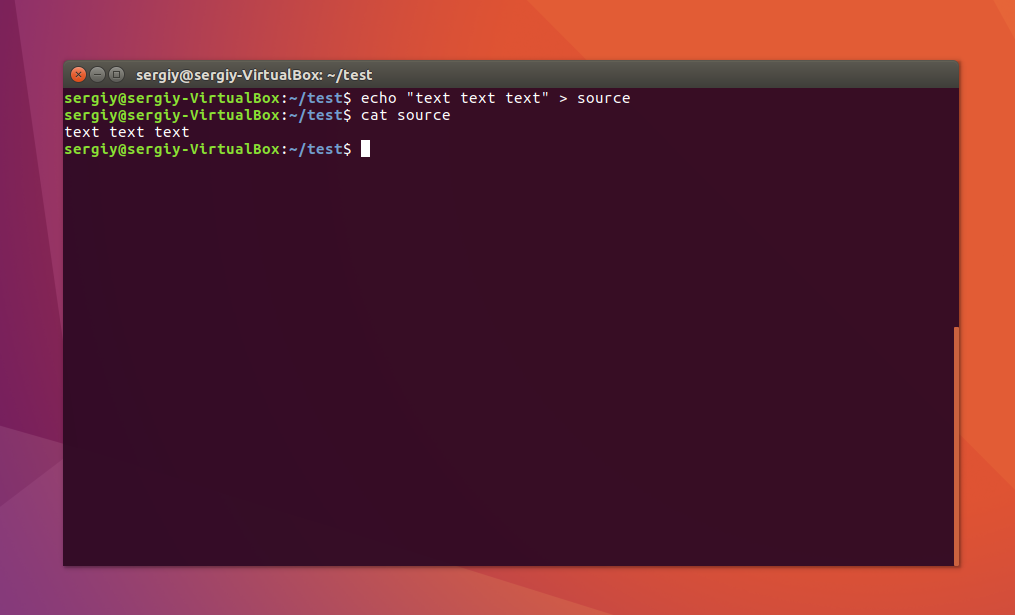
Снова создайте файл source с произвольным текстом:
echo «текст текст текст текст» > source
$ cat source
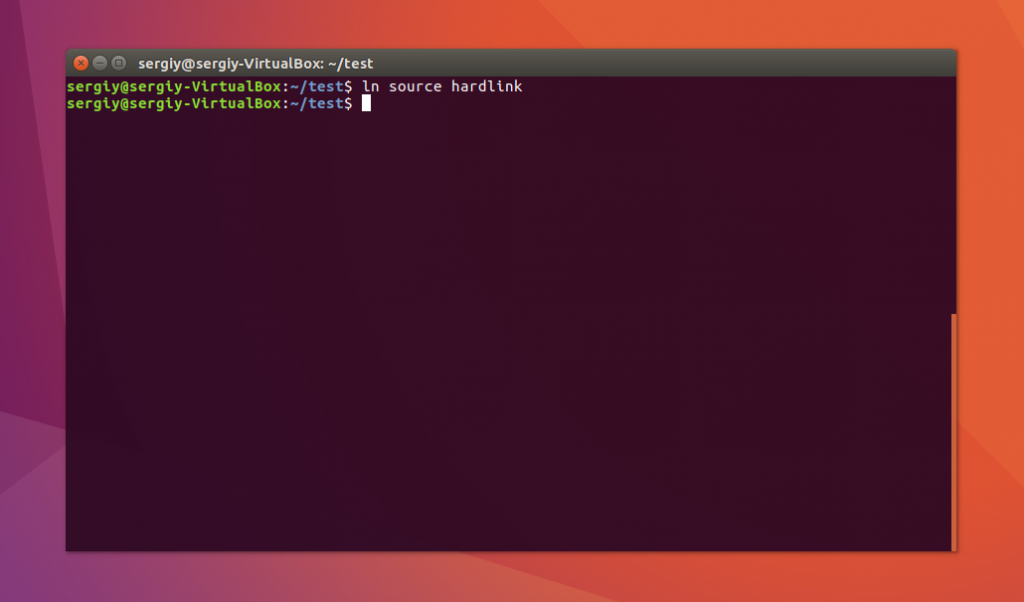
Теперь создадим жесткую ссылку Linux. Для этого достаточно вызвать утилиту без параметров:
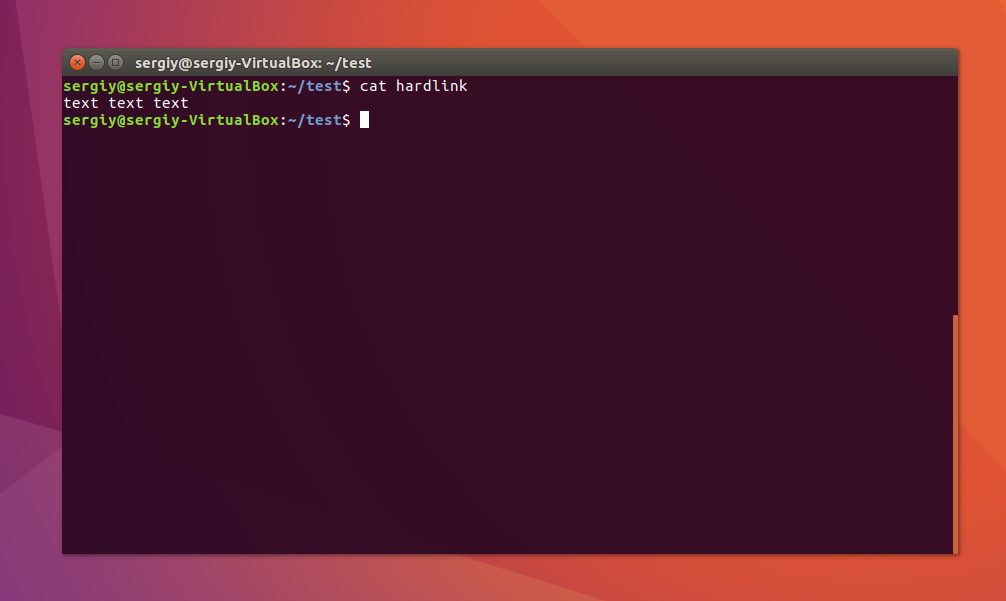
Посмотрите содержимое файла:
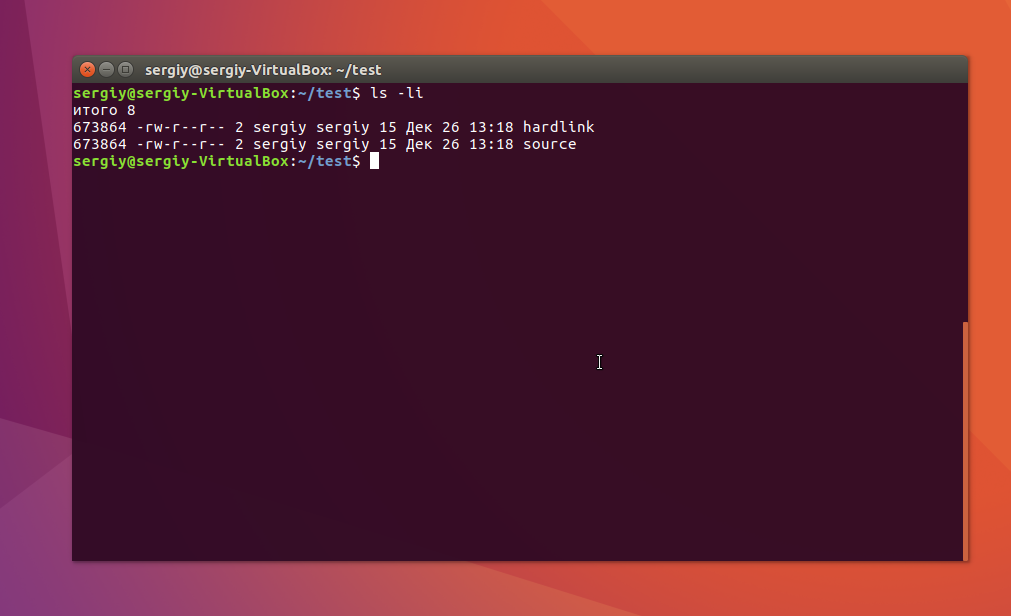
Данные те же самые, а если мы посмотрим вывод утилиты ls, то увидим что inode и права доступа тоже совпадают:
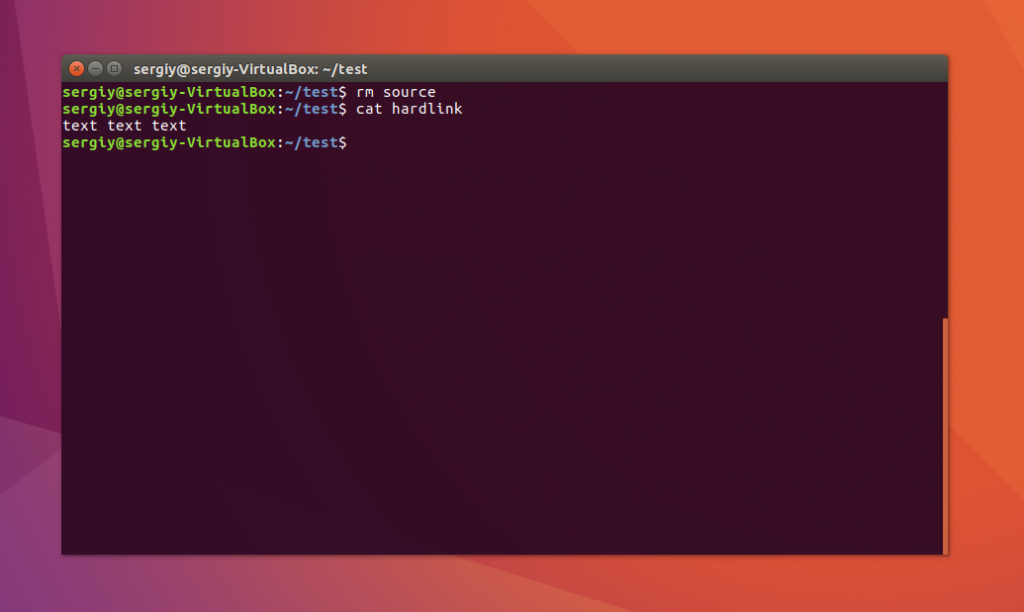
Если для одного из файлов поменять разрешения, то они изменяться и у другого. Теперь удалите исходный файл:
Затем посмотрите содержимое:
Как видите, ничего не произошло и ссылка по-прежнему указывает на нужный участок диска, это главное отличие жесткой ссылки от символической. Мы можем сделать вывод, что жесткая ссылка linux это обычный файл. Каждый файл имеет как минимум одну ссылку, но для некоторых мы можем создать несколько ссылок.
Выводы
Это все, что вам было необходимо знать про символические и жесткие ссылки linux. Надеюсь, вы получили общее представление об этих возможностях файловой системы и сможете использовать их для решения своих задач.
На завершение видео про ссылки в Linux:

Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
Linux ln – How to Create a Symbolic Link in Linux [Example Bash Command]
A symlink (symbolic) is a type of file that points to other files or directories (folders) in Linux.
You can create a symlink (symbolic) by using the ln command in the command line.
Symbolic links are useful because they act as shortcuts to a file or directory.
In this article, I will go over how to use the ln command to create a symlink to a file or directory.
What is the difference between soft and hard links in Linux?
A soft link or symbolic link will point to the original file on your system. A hard link will create a copy of the file.
Soft links can point to other files or directories on a different file system, whereas hard links cannot.
How to create a symlink to a file
You can find the command line using the Terminal application on Mac or using the Command Prompt on Windows.
Here is the basic syntax for creating a symlink to a file in your terminal.
ln -s existing_source_file optional_symbolic_link You use the ln command to create the links for the files and the -s option to specify that this will be a symbolic link. If you omit the -s option, then a hard link will be created instead.
The existing_source_file represents the file on your computer that you want to create the symbolic link for.
The optional_symbolic_link parameter is the name of the symbolic link you want to create. If omitted, then the system will create a new link for you in the current directory you are in.
Let’s take a look at an example to better understand how this works.
On my Desktop I have a file called example_fcc_file.txt .
I will need to first open up my terminal, and then make sure I am in the Desktop directory. I can run the command cd Desktop to navigate to my Desktop.
After running that command, you should see you are now in the Desktop.
jessicawilkins@Dedrias-MacBook-Pro-2 ~ % cd Desktop jessicawilkins@Dedrias-MacBook-Pro-2 Desktop % I can then use the ln command to create a new symbolic link called fcc_link.txt .
ln -s example_fcc_file.txt fcc_link.txtWhen you run that command in the terminal, you will notice that nothing was returned. That is because when the ln command is successful, there will be no output and it will return zero.
jessicawilkins@Dedrias-MacBook-Pro-2 Desktop % ln -s example_fcc_file.txt fcc_link.txt jessicawilkins@Dedrias-MacBook-Pro-2 Desktop % To check that your symbolic link was successful, you can use the ls command. The ls command will list information about files and the -l flag represents the symbolic link.
When you run that command, you should see this type of result in the terminal.
lrwxr-xr-x 1 jessicawilkins staff 20 Feb 19 19:56 fcc_link.txt -> example_fcc_file.txt The fcc_link.txt -> example_fcc_file.txt portion of the output shows you that the symbolic link is pointing to the file called example_fcc_file.txt .
You should also see that new symbolic link show up in your directory.
How to create a symbolic link to a directory
In this example, we want to create a symbolic link called my_music that will point to my Music folder in the home directory of my computer.
First, make sure you are in the home directory. You can run cd to get back to your home directory in the command line.
jessicawilkins@Dedrias-MacBook-Pro-2 Desktop % cd jessicawilkins@Dedrias-MacBook-Pro-2 ~ % You can then use the ln command to create a symlink to the Music directory.
ln -s /Users/jessicawilkins/Music ~/my_music If successful, you should see it in the home directory.
How to remove a symbolic link
To remove symlink you can either use the unlink or rm command.
If we wanted to remove the fcc_link.txt symlink we created earlier, then we can use either of these commands:
Now we should see that the symlink was removed from our directory.
How to overwrite symlinks
If we try to create a new symlink called fcc_link.txt , then it will result in an error because it is already being used and pointing to another file.
ln: fcc_link.txt: File exists You can overwrite this error by using the force ( -f ) option.
ln -sf example_fcc_file.txt fcc_link.txtHow to learn more about the ln command
If you want to learn more about the ln command, then you can read about it in the man pages (manual for using Linux commands).
Run man ln in your terminal and you should see the man pages for the ln command.
LN(1) BSD General Commands Manual LN(1) NAME link, ln -- make links SYNOPSIS ln [-Ffhinsv] source_file [target_file] ln [-Ffhinsv] source_file . target_dir link source_file target_file DESCRIPTION The ln utility creates a new directory entry (linked file) which has the same modes as the original file. It is useful for maintaining multiple copies of a file in many places at once without using up storage for the ``copies''; instead, a link ``points'' to the original copy. There are two types of links; hard links and sym- bolic links. How a link ``points'' to a file is one of the differences between a hard and symbolic link. The options are as follows: -F If the target file already exists and is a directory, then remove it so that the link may occur. The -F option should be used with either -f or -i options. If none is specified, -f is implied. The -F option is a no-op unless -s option is specified. -h If the target_file or target_dir is a symbolic link, do not follow it. This is most useful with the -f option, to replace a symlink which may point to a directory. -f If the target file already exists, then unlink it so that the link may occur. (The -f option overridesConclusion
A symlink (symbolic) is a type of file that points to other files or directories (folders) in Linux. You can create a symlink (symbolic) by using the ln command in the command line.
Symbolic links are useful because they act as shortcuts to a file or directory.
Here is the basic syntax for creating a symlink to a file using the terminal:
ln -s existing_source_file optional_symbolic_linkHere is the basic syntax for creating a symlink to a directory using the terminal:
ln -s path_to_existing_directory name_of_symbolic_link To remove symlink you can either use the unlink or rm command:
unlink name_of_symbolic_linkIf you need to remove a symlink then you can use this command:
ln -sf path_to_existing_directory name_of_symbolic_linkI hoped you enjoyed this article on symbolic links and best of luck on your programming journey.
![Linux ln – How to Create a Symbolic Link in Linux [Example Bash Command]](https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/content/images/size/w2000/2022/02/gabriel-heinzer-4Mw7nkQDByk-unsplash.jpg)