- How to create symbolic links in Ubuntu
- What are the types of symbolic links in Ubuntu
- How to create a symbolic link for a directory in Ubuntu
- How to create a symbolic link for a file in Ubuntu
- How to overwrite a symbolic link in Ubuntu
- How to remove symbolic link in Ubuntu
- How to find and delete broken symbolic links in Ubuntu
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Sharqa Hameed
- How to Symlink a Directory in Linux
- How to Create Symlink (soft-link) in Linux
- How to Create a Symlink (soft link) to a File
- How to Create a Symlink (Soft Link) of the Folder/Directory
- How to Overwrite the Symlink (Soft Link) in Linux:
- How to Remove Symlink (Soft Link) in Linux:
- Conclusion
- About the author
- Sam U
How to create symbolic links in Ubuntu
A symbolic link is a shortcut file for any directory or file. The symlink or soft link are the other names of the symbolic link. In Ubuntu, symbolic links work like a string that generates paths between various files and directories. These links are frequently utilized for linking libraries. It also ensures that files exist in consistent locations. Symbolic links are used for storing numerous copies of the same file in several locations while still referring to the same file.
What are the types of symbolic links in Ubuntu
- Soft Link: A soft link or symbolic link refers to the original file’s location or path. On the internet, it functions similarly to a hyperlink.
- Hard Link: A hard link works by generating a new filename related to the original file’s inode data (reference file). This is equivalent to making a copy of the specific file.
Want to create symbolic links? In this article, we will explain how you can create symbolic links in Ubuntu. So let’s start!
How to create a symbolic link for a directory in Ubuntu
Ubuntu users utilize the “ln” command for creating symbolic links in their system. This command creates hard links by default. However, you can add the “-s” or the “–symbolic” option if you want to create a soft link.
Now, check out the syntax of the “ln” command:
To follow up the procedure of creating a symbolic link using the “ln” command, firstly, open your Ubuntu terminal by pressing “CTRL+ALT+T”. We will utilize the “ln” command for creating a symbolic link to any specific directory. Adding the “-s” option indicates that a soft link will be created for the specified directory. Here is the syntax of the “ln” command:
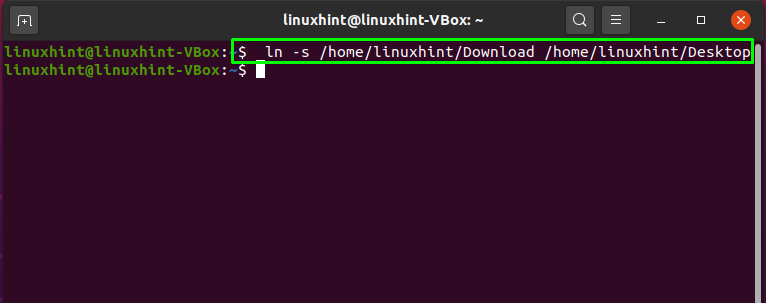
We will execute the below-given command to create a soft symbolic link for the “Download” folder. This command will save the symbolic link to our “Desktop”:
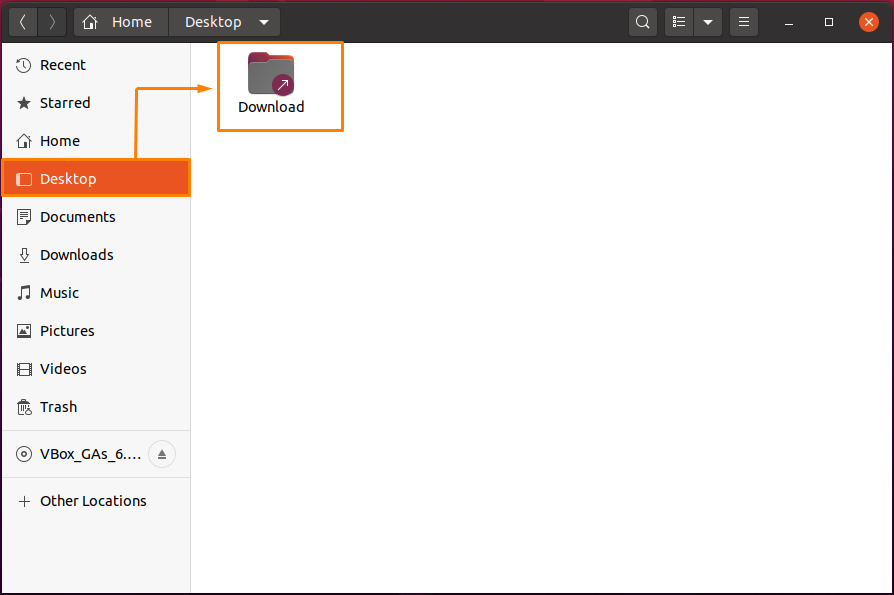
The error-free output declares that the symbolic link for the “Download” folder is successfully created. We will open our “Desktop” directory using Ubuntu UI to check the existence of the “Download” symbolic link:
How to create a symbolic link for a file in Ubuntu
In this section, we will show how you can create a symbolic link for a specific file. The below-given image has a highlighted “testfile” that’s because now we will create a symbolic link for this “testfile”:
If you want to create a symbolic link for a file, then check out the syntax of the “ln” command:
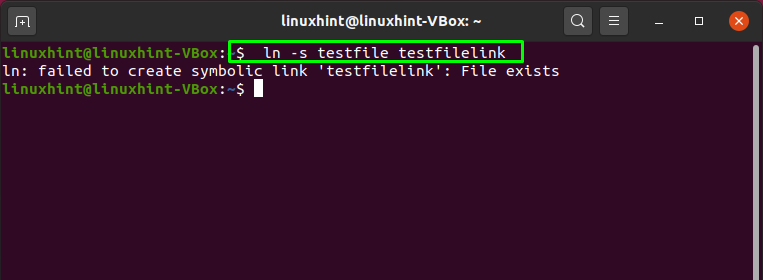
As we have shown you, we have selected our “testfile” for creating a symbolic link. This “testfile” is a text file located in our home directory. To create a symbolic link for this “testfile”, we will write out this command in our Ubuntu terminal:
The execution of the above-given command will create a symbolic link named “testfilelink” of the “testfile”. The symbolic link will be saved at the location of the source file:
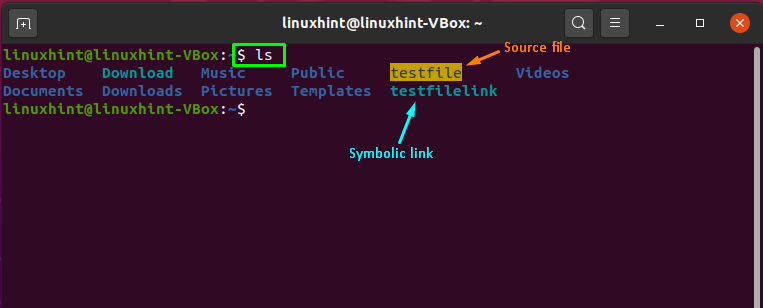
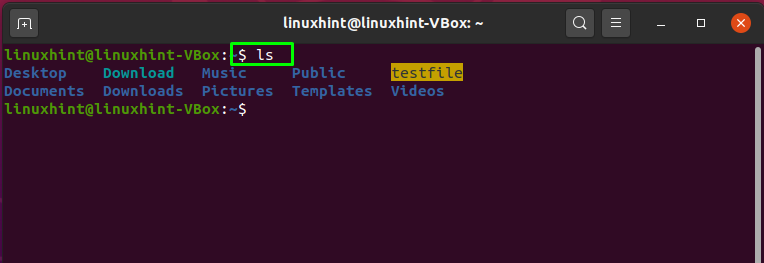
You can execute the “ls” command to verify the presence of the created symbolic link:
From the output, you can see that symbolic link “testfilelink” is created, and both of the files are present in the home directory:
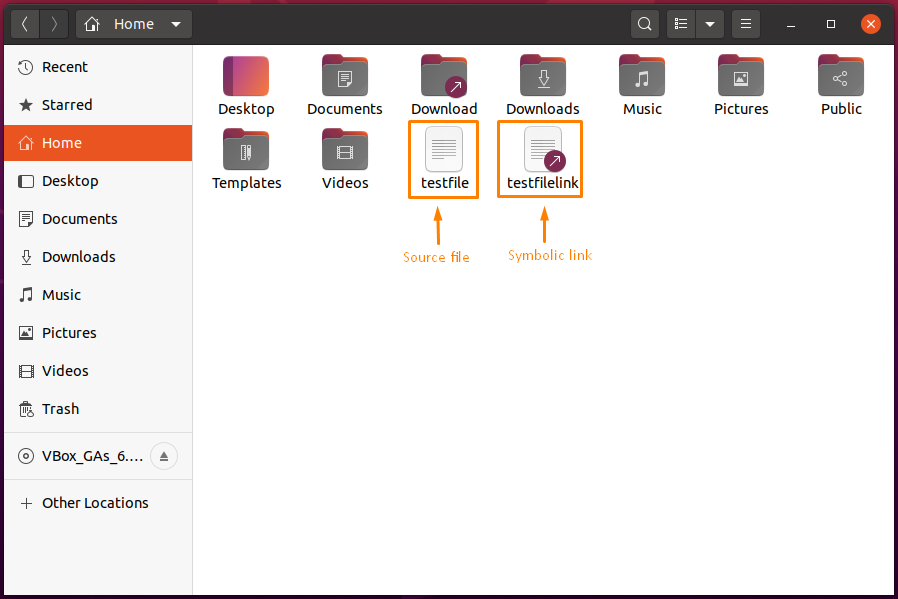
Ubuntu UI can also show you the created symbolic link file located in the system home directory:
How to overwrite a symbolic link in Ubuntu
We have already created a symbolic link “testfilelink” for the “testfile“. So, when you execute the below-given command again in your Ubuntu terminal, it will show you a “failed to create symbolic link” error:
Add the “-f” option in the “ln” command to overwrite the already created symbolic link forcefully:
How to remove symbolic link in Ubuntu
The symbolic link becomes unusable if you remove the source file or transfer it to another location. In that case, you can delete the symbolic link by using two commands: The “rm” and “unlink” commands.
First, check out the syntax of the rm command that we are going to utilize for deleting the symbolic link:
Now, we will execute the below-given “rm” to remove or delete the “Download” symbolic link:
However, if the symbolic link is present inside your current working directory, you only specify its name in the “unlink” or “rm” command. Write out the below-given “unlink” command to delete the “testfilelink” symbolic link:
Now, you can execute the “ls” command to verify that the symbolic link is deleted or not:
How to find and delete broken symbolic links in Ubuntu
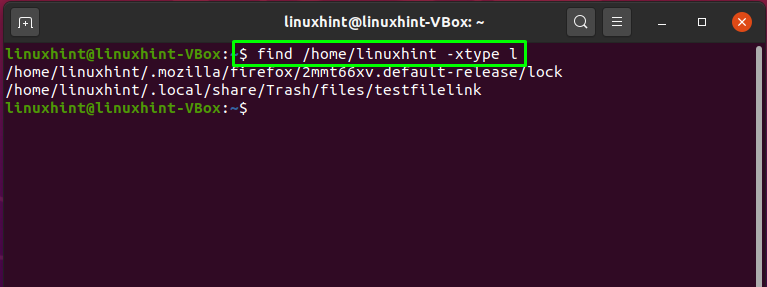
Ubuntu also provides you the facility to find and delete the broken symbolic link on the system. To do so, we will utilize the “find” command, having the following syntax:
Here, “-xtype” is used to define the type of file we are searching for, and “l” denotes that we are looking for the broken symbolic links:
The output of the above-given command will show you the broken symbolic link present in the specified directory:
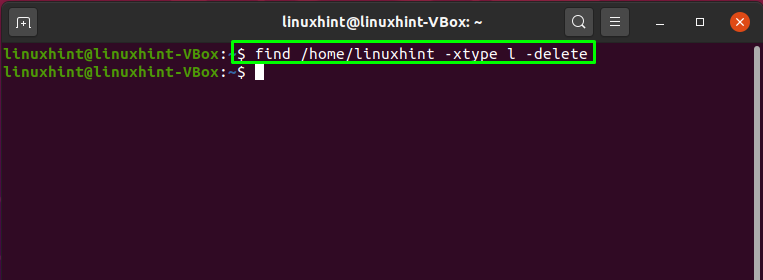
You can also add the “-delete” parameter to delete those broken symbolic links from your home directory:
Conclusion
Symbolic links are a unique feature of Linux-based operating systems like Ubuntu. Symbolic links are used to create shortcuts to the Linux files system. Ubuntu users utilize the “ln” command for creating symbolic links. We have explained how you can create symbolic links in Ubuntu using the “ln” command. Moreover, we have also provided you the method to overwrite, find, and delete symbolic links in your system.
About the author
Sharqa Hameed
I am a Linux enthusiast, I love to read Every Linux blog on the internet. I hold masters degree in computer science and am passionate about learning and teaching.
How to Symlink a Directory in Linux
Symlink, also known as a symbolic link in Linux, creates a link to a file or a directory for easier access. To put it in another way, symlinks are links that points to another file or folder in your system, quite similar to the shortcuts in Windows. Some users refer to symlinks as soft-links. Before moving forward, let’s elaborate soft-links and hard-links.
Hard-links: Hard-links are the links that mirror or copy the original file. Hard-links have the same inode numbers.
Soft-links: Soft-links are simple links that points to the original file. You can access the original file through soft links. Soft-links can point to a file or folder in any partition and have different inode numbers.
Learning about creating symlink in Linux is a great way to improve your grip on the Linux terminal. So, let’s learn the steps involved in making the soft-links in Linux.
How to Create Symlink (soft-link) in Linux
To make symlink or soft link, we use the “ln” command. The syntax to follow to create symlink is mentioned below:
In the first argument after the “-s” option, you will be giving the path of the file of a folder you want to create the symlink of. While in the second argument, pass the name you want to give that symlink. To check the created links, use the following command:
To check inode numbers, use the command mentioned below:
How to Create a Symlink (soft link) to a File
Creating a soft link to a file is simple; use the syntax mentioned below:
Important to note that if you do not specify the “[symbolic name]”, then the command will create a symlink by the original file’s name. Let’s understand it through an example.
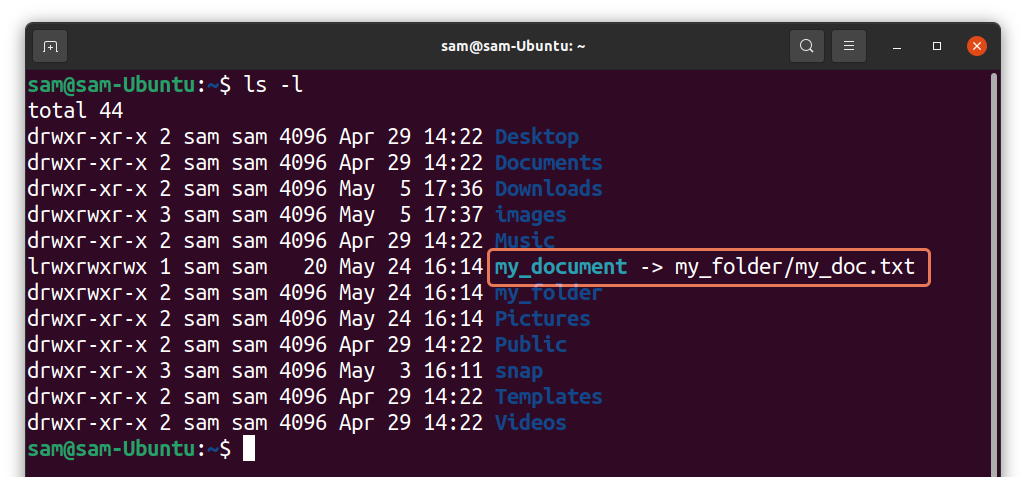
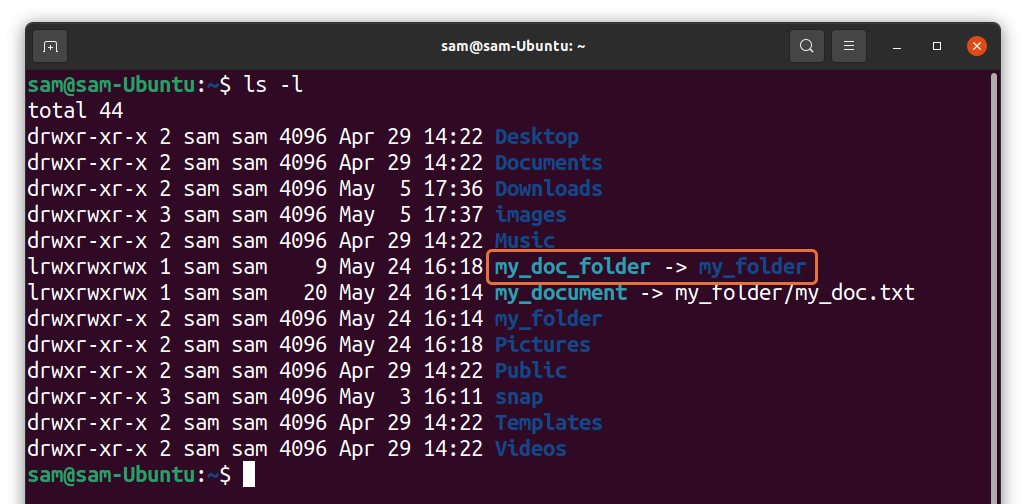
I have created a directory “my_folder” that contains a text file “my_doc.txt”. Now, to create symlink to “my_doc.txt” file, I will use:
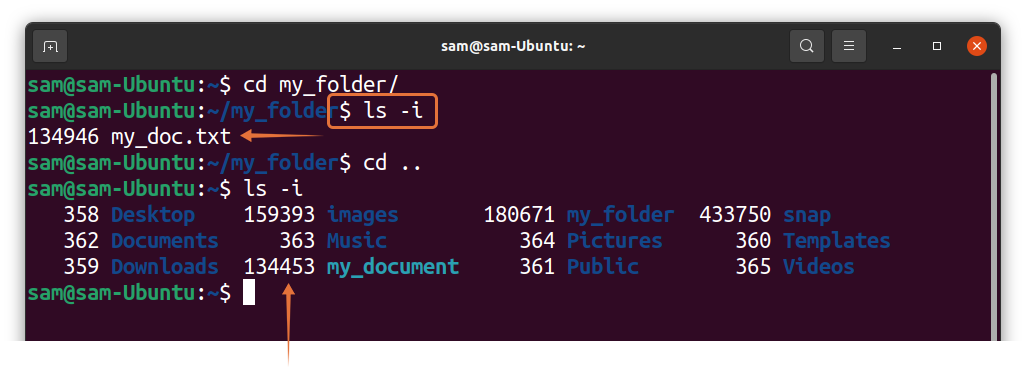
As it can be seen in the above output, “my_document” is pointing to “my_folder/my_doc.txt” file. Both the symlink and the original file would have different inode number. To check inode numbers used:
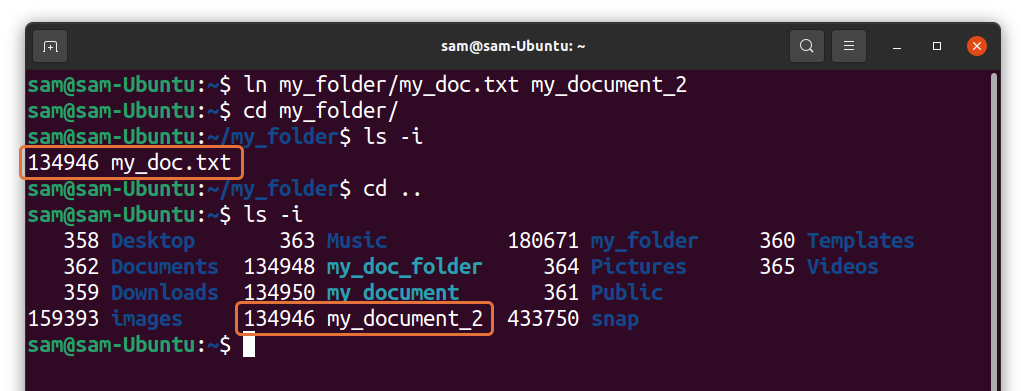
Hard links will always have same inode numbers. To verify, I created a hard link of “my_doc.txt” file and name it “my_document_2”:
It can be seen in the output that the original file and the hard link have same inode numbers.
How to Create a Symlink (Soft Link) of the Folder/Directory
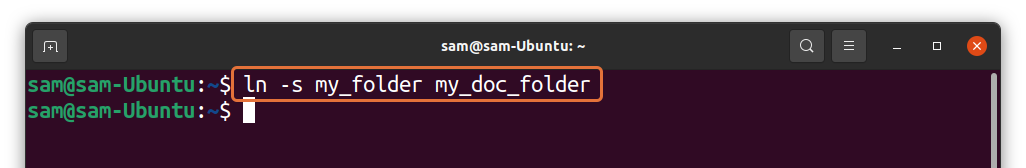
To create a soft-link or symlink to a directory is quite similar to creating a symlink to a file. For instance, I am creating the symlink of the “my_folder” directory using:
The above command will create a symlinked folder in the current directory. To verify it, use:
How to Overwrite the Symlink (Soft Link) in Linux:
If you try to update a symlink with the same name that already exist, then you will get an error:
We will have to use the force flag “-f” to overwrite the new path to the existing symlink.
How to Remove Symlink (Soft Link) in Linux:
In many situation, you need to remove the unnecessary symlinks from your system. To delete symlink, we use the “unlink” command, and the syntax is given below:
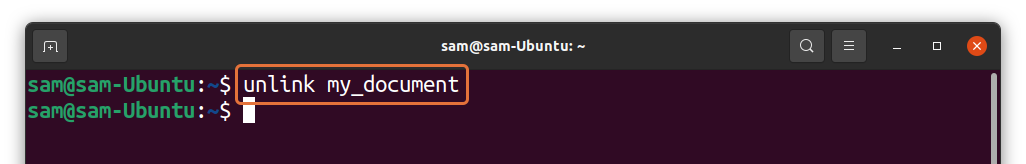
Let’s remove the symlinks we created in the above examples. To unlink a symlink of a file, use:
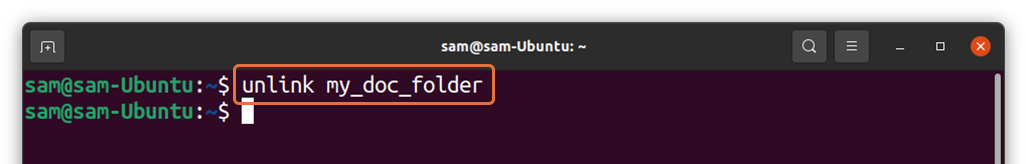
And to unlink the symlink of a directory:
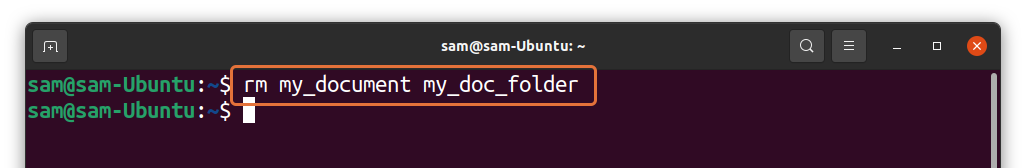
We can also use the “rm” command to remove symlinks.
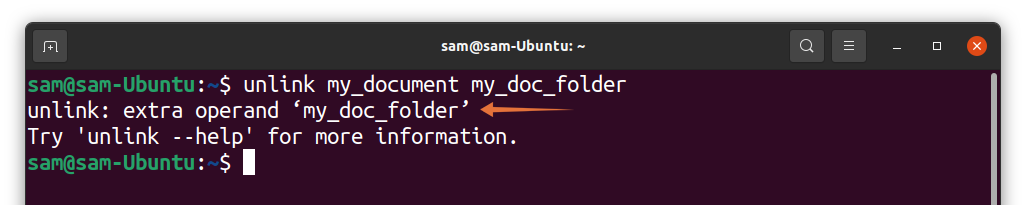
The advantage of “rm” over “unlink” is that you can remove multiple symlinks with the “rm” command, which is not possible with the “unlink” command as shown in the following image:
Note that whether you use the “unlink” or “rm” command, do not use trailing slash “/” even if it is a directory.
Conclusion
Symlinks are an easier way to access the files of your system from multiple locations. This write-up is a thorough guide about creating symlinks to a file or directory and removing them. Remove the symlinks if the original file no longer exists.
Understanding and mastering the Linux terminal is very crucial for any beginner. I hope this post benefitted you to learn a new utility and improve your skills.
About the author
Sam U
I am a professional graphics designer with over 6 years of experience. Currently doing research in virtual reality, augmented reality and mixed reality.
I hardly watch movies but love to read tech related books and articles.