- How to Completely Uninstall Java for Linux?
- How to Completely Uninstall Java for Linux?
- Conclusion
- How to uninstall Java from Ubuntu
- How to check the type of Java on Linux (Ubuntu):
- How to identify the Java version on Linux (Ubuntu):
- How to switch versions of Java on Linux (Ubuntu):
- How to check the installation method of Java on Linux (Ubuntu):
- How to uninstall Java from Linux (Ubuntu):
- Как удалить Java в Ubuntu
- Как удалить Java в Ubuntu 20.04
- 1. Как узнать тип Java
- 2. Как узнать версию Java
- 3. Как узнать способ установки Java
- 4. Удаление Java
- Выводы
- How to completely uninstall Java?
- 9 Answers 9
How to Completely Uninstall Java for Linux?
In Linux, Java is a widely used and well-reputed programming language. Like other programming languages, it offers “JDK (Java Development Kit)” a complete environment for the execution of code. It contains development tools and the “JRE(Java Runtime Environment)” that stores libraries.
While working with Java in Linux, its installation and uninstallation have a key role.
This post shows the procedure to completely remove Java for Linux:
How to Completely Uninstall Java for Linux?
The uninstallation procedure of Java follows some essential steps that are described below:
Step 1: Check the JDK Version
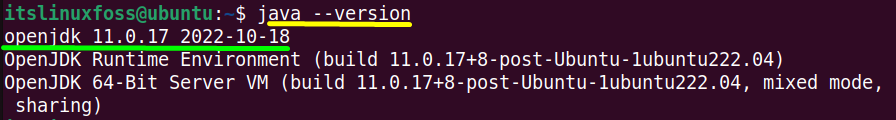
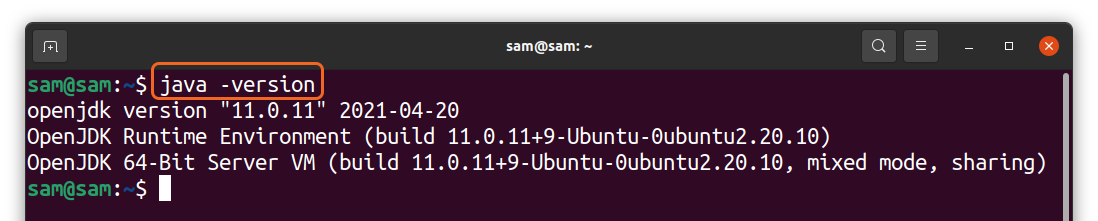
First, check the “JDK” services installed in the system. It may be “Openjdk” or the “Oracle JDK”. To perform this task use the “java” followed by the “–version” flag in the terminal:
The currently installed “openjdk” version is “11.0.17”.
Step 2: Uninstall OpenJDK
Now, execute the uninstallation command with the help of the default package manager of majorly used Linux distributions. The commands need the administrator privileges i.e “sudo”:
$ sudo yum remove jdk[version] #For CentOS/RHEL $ sudo dnf remove openjdk* #For Fedora $ sudo apt remove --purge openjdk* #For Ubuntu/Debain-Based
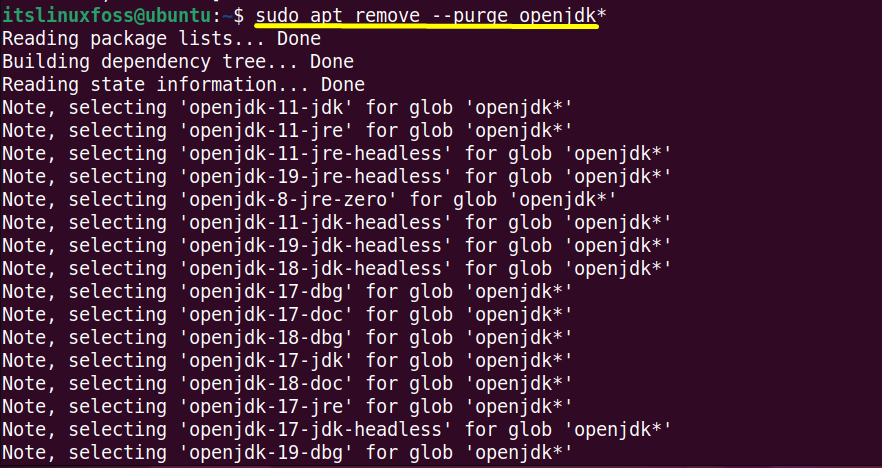
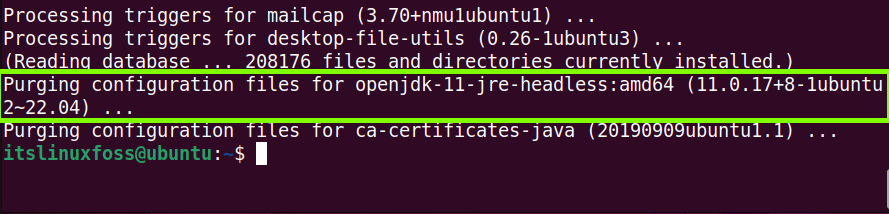
All the configuration and installation files of “OpenJDK” have been removed from the system completely.
Step 3: Completely Remove Java Files
The additional dependencies are installed while installing any application in a Linux system. These dependencies are useless after uninstalling the application.
It is recommended to “auto-remove” all these unneeded dependencies using the default package managers of your Linux system:
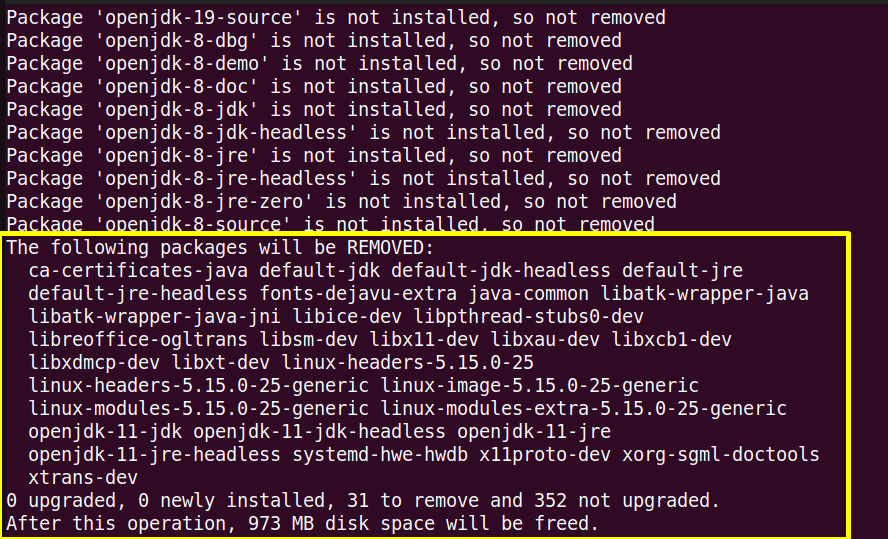
$ sudo yum autoremove jdk[version] #For CentOS/RHEL $ sudo dnf autoremove java[version]openjdk #For Fedora $ sudo apt autoremove openjdk* #For Ubuntu/Debain-Based
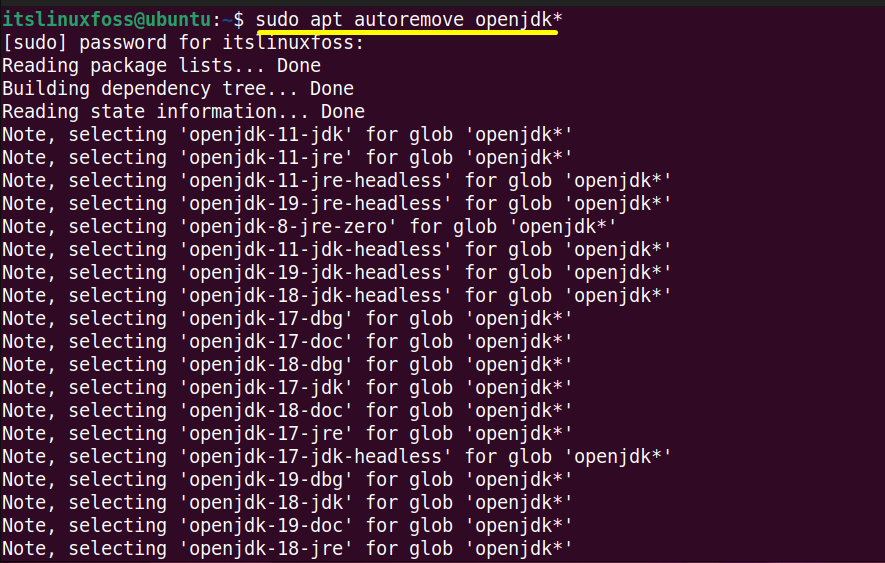
Here “31” Java packages have been removed from the current Linux system Ubuntu.
Step 4: Verify the Java
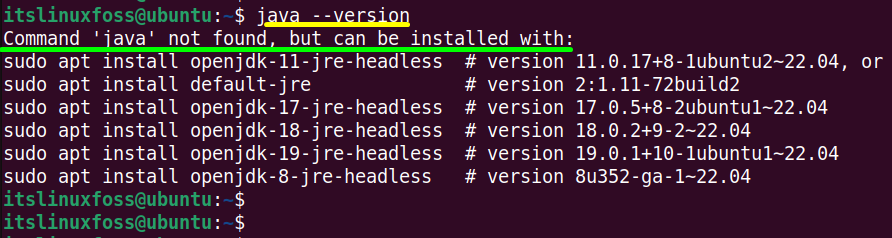
Again execute the “java” version command to verify whether it is completely removed or not:
Now, the output shows that “java not found” which means that it is no more in the system.
Conclusion
In Linux and its frequently used distros, “java” can be completely uninstalled using their default package managers. For this purpose, the “remove” flag uninstalls the executable files of Java while “purge” removes its configuration files. This post has provided a brief detail to completely remove java for Linux.
How to uninstall Java from Ubuntu
Why do we need Java on our computers? There are tons of applications developed using the java environment, so we need to install java on our computers to make the java-based application run with no difficulty.
In many cases, you may need to remove java from your computer, such as installing the latest version of java or freeing up space from your machine. Installing Java on Ubuntu is pretty straightforward, but uninstalling it is a hard nut to crack for many folks. In this guide, we will learn how many versions of java are there, what distinguishes them, and how to erase them from your computer completely.
How to check the type of Java on Linux (Ubuntu):
Before erasing java from your device, the first check is to identify what type of java you have on your PC. If you have installed java just to run the java applications, it would most probably “Java Runtime Environment (JRE).” Or, if you have installed java for development purpose, then you may have one of the following:
The difference between “Open JDK” and “Oracle Java” is that the former is open-source, whereas the latter is license-based. Oracle Java is much better when it comes to performance and stability.
How to identify the Java version on Linux (Ubuntu):
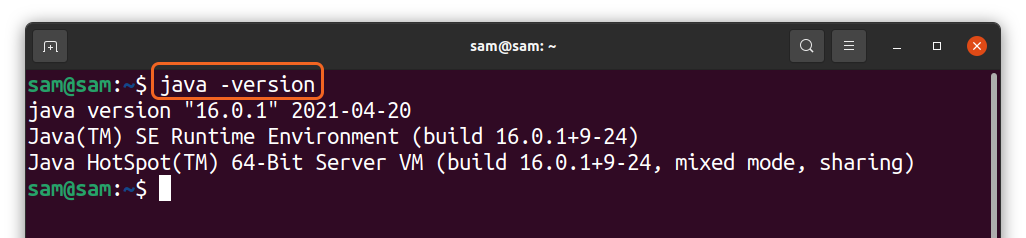
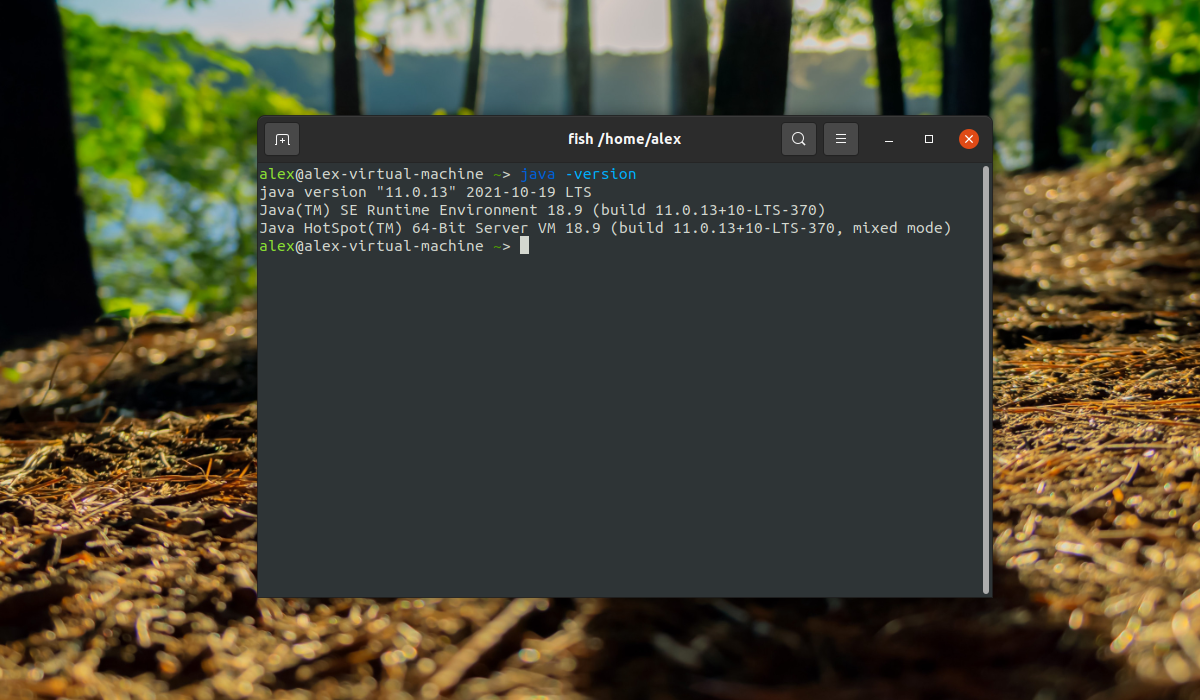
Before uninstalling java from your PC, it is essential to know which version of java you have got. To check it launch terminal by pressing “ctrl+alt+t” and type the below-mentioned command:
The above command will also indicate whether the version of java is “Open JDK” or “Oracle JDK.”
Standard output if the version is “OpenJDK”:
Standard output if the version is “Oracle Java”:
If you don’t have any version of java on your machine, the standard output will display it and provide some commands to install it.
How to switch versions of Java on Linux (Ubuntu):
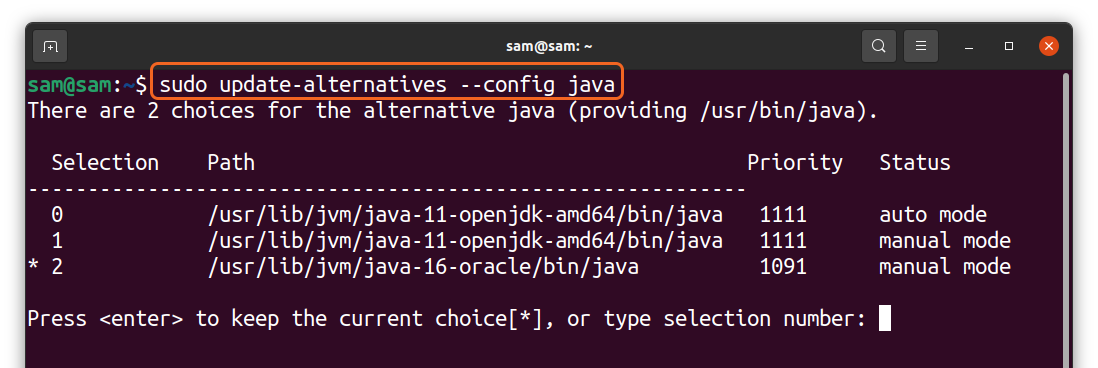
Interestingly, you can have more than one versions of java on your device, and you can check and switch any of them by using the command mentioned below:
The above command is displaying the different versions of java I have on my PC. To switch, simply type the number and press “Enter.”
How to check the installation method of Java on Linux (Ubuntu):
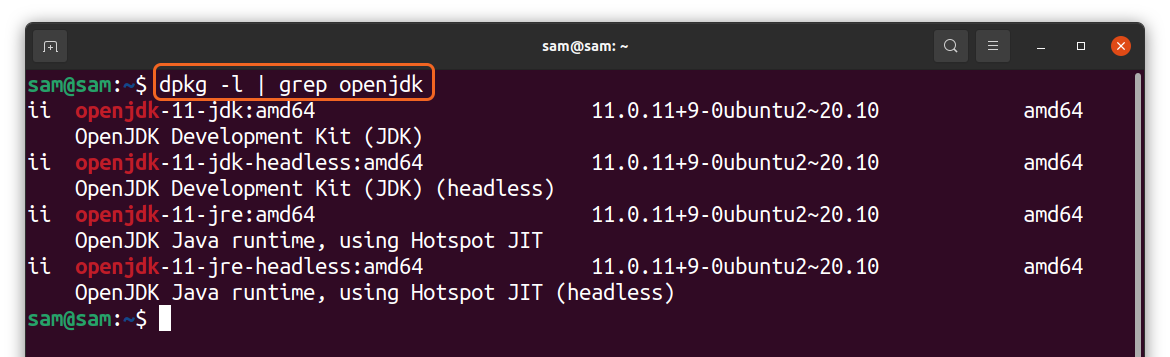
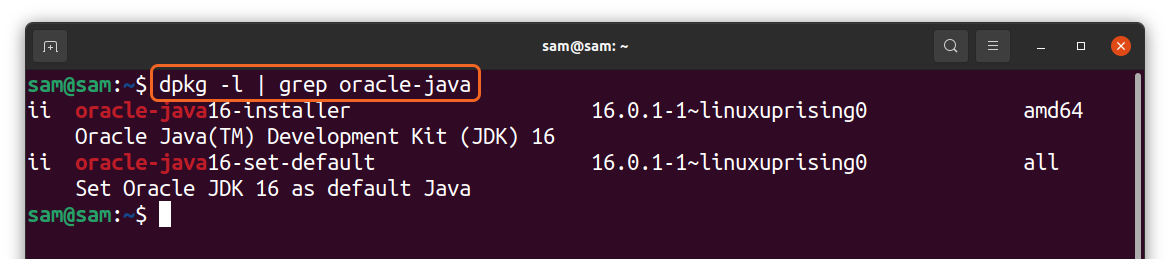
In some cases, it is crucial to identify the method of installation of java. To check it, use the command:
The above output will indicate whether the package is installed from an official repository or a third-party repository. The above screenshots are demonstrating that “Oracle Java” is installed using the third-party repository “Linux pricing,” whereas “OpenJDK” is installed using the official Ubuntu repository.
How to uninstall Java from Linux (Ubuntu):
In the above discussion, we learned that there are multiple versions of java; you can have all of them on your PC at a time and conveniently switch them. Various approaches can be used to delete java from ubuntu. To completely erase “OpenJDK,” use:
Как удалить Java в Ubuntu
Java — это очень популярный язык программирования, разработанный в компании Sun Microsystems, ныне принадлежащей корпорации Oracle. Существует две реализации Java открытая и свободная OpenJDK и проприетарная Oracle Java.
Если вы захотите установить одну из них, а другая уже установлена, то первую придется удалить. В этой статье будет рассмотрено удаление Java в Ubuntu 20.04, а также будет показано как определять тип и версию Java установленной на устройстве.
Как удалить Java в Ubuntu 20.04
1. Как узнать тип Java
Перед удалением Java с компьютера сначала необходимо узнать какой тип Java установлен в системе. Если Java ставилась только для запуска приложений, скорее всего это будет JRE (Java Runtime Environment — содержит только окружение для запуска программ). Если Java устанавливалась для разработки ПО, то в данном случае будет одна из следующих версий — Open JDK (полностью открытая версия) или Oracle Java (проприетарная версия от Oracle с дополнительными возможностями и поддержкой).
2. Как узнать версию Java
Чтобы узнать какая версия Java установлена в системе, а также узнать какой тип установлен необходимо выполнить команду в терминале:
В данном примере в системе установлена Java с типом JRE и версией 11.0.13.
3. Как узнать способ установки Java
Иногда требуется определить способ установки Java. Чтобы узнать это, необходимо выполнить команду:
Если команда ничего не вернула значит в система установлена Java от Oracle. Чтобы это проверить необходимо выполнить команду:
Также из вывода команды можно узнать, установлен ли пакет из официального репозитория или же из стороннего репозитория. На скриншоте выше можно увидеть, что Java в системе установлен при помощи стороннего репозитория под названием linuxprising. Если в выводе команды имя репозитория не отображается, значит Java была установлена при помощи официального репозитория Ubuntu.
4. Удаление Java
Для удаления Java из Ubuntu необходимо использовать команду:
sudo apt purge oracle-java11*
Команда выше удалит версию Java от Oracle. Если в системе установлена бесплатная версия (OpenJDK) необходимо выполнить следующую команду:
Также вместо 11 версии необходимо подставить ту, которая установлена в системе.
Выводы
В этой статье было описано удаление Java в Ubuntu 20.04. Сама процедура удаления несложная и буквально выполняется при помощи одной команды. Надеюсь, информация из статьи была вам полезной.
Обнаружили ошибку в тексте? Сообщите мне об этом. Выделите текст с ошибкой и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.
How to completely uninstall Java?
How can I completely remove all traces of Java on my system? I already know how to install it in case I need it again.
9 Answers 9
dpkg-query -W -f='$\n' | grep -E -e '^(ia32-)?(sun|oracle)-java' -e '^openjdk-' -e '^icedtea' -e '^(default|gcj)-j(re|dk)' -e '^gcj-(.*)-j(re|dk)' -e '^java-common' | xargs sudo apt-get -y remove sudo apt-get -y autoremove dpkg -l | grep ^rc | awk '' | xargs sudo apt-get -y purge sudo bash -c 'ls -d /home/*/.java' | xargs sudo rm -rf for g in ControlPanel java java_vm javaws jcontrol jexec keytool mozilla-javaplugin.so orbd pack200 policytool rmid rmiregistry servertool tnameserv unpack200 appletviewer apt extcheck HtmlConverter idlj jar jarsigner javac javadoc javah javap jconsole jdb jhat jinfo jmap jps jrunscript jsadebugd jstack jstat jstatd native2ascii rmic schemagen serialver wsgen wsimport xjc xulrunner-1.9-javaplugin.so; do sudo update-alternatives --remove-all $g; done sudo updatedb sudo locate -b '\pack200' @JorgeCastro, absolutely. I built those commands one by one, then piped it all together and I ran all of them in different Java installation scenarios that I have for test purposes in some workstations at work. I really paid attention to the output of grep that is piped to apt-get remove , I think that it covers almost all possibilities regarding installation by deb packages.
Although the presented sequence of commands works on most cases, I think my answer needs some improvements. Everybody, please, feel free to suggest changes that can improve it, like better explanation of each command or pointing out a scenario not covered by them.
+1 for the answer. I recently found a scenario where removing openjdk causes installation of other java packages. A workaround for this problem is disabling all of the repository and then execute the removal command.
To completely remove OpenJDK on Ubuntu 11.10 (this may or may not be sufficient on other versions of Ubuntu), run:
sudo apt-get purge openjdk-\* icedtea-\* icedtea6-\* If you want instructions for removing the proprietary Oracle («Sun») version of Java, then you’ll have to specify how you installed it. (If you edit your question to indicate this and leave a comment to this answer, I’ll try to add information about how to remove that too.)
I tried the above, and it completed without error on Ubuntu 11, but after I can still run java -version and get back openjdk version «11.0.3» 2019-04-16
To uninstall Oracle Java 7, just press Ctrl + Alt + T on your keyboard to open Terminal. When it opens, run the command below.
sudo update-alternatives --display java To check the setup before uninstalling Java.
Next, remove symlinks
(replace the word (version)with your Java version. DO java -version to get yours. So if your version is 1.7.0_03, you would type sudo update-alternatives —remove «java» «/usr/lib/jvm/jdk1.7.0_03/bin/java» )
sudo update-alternatives --remove "java" "/usr/lib/jvm/jdk/bin/java" sudo update-alternatives --remove "javac" "/usr/lib/jvm/jdk/bin/javac" sudo update-alternatives --remove "javaws" "/usr/lib/jvm/jdk/bin/javaws" verify that the symlinks were removed
java -version javac -version which javaws The next 2 commands must be type excatly perfectly to avoid permanently destroying your system.
cd /usr/lib/jvm sudo rm -rf jdk
sudo update-alternatives --config java sudo update-alternatives --config javac sudo update-alternatives --config javaws Delete the line with JAVA_HOME 1
To uninstall OpenJDK (if installed). First check which OpenJDK packages are installed.
sudo dpkg --list | grep -i jdk sudo apt-get purge openjdk* Uninstall OpenJDK related packages.
sudo apt-get purge icedtea-* openjdk-* Check that all OpenJDK packages have been removed.
sudo dpkg --list | grep -i jdk