- How to find the Process ID (PID) of a running terminal program?
- 11 Answers 11
- How do I Find Process ID in Ubuntu
- How to find process ID in Linux:
- How to find the process ID (PID) with the “pidof” command:
- How to Find Process ID (PID) with “pgrep” Command:
- How to find the process ID (PID) with the “lsof” command:
- How to find the process ID (PID) with the “ps” command:
- How to Find the Process ID (PID) with “pstree” Command:
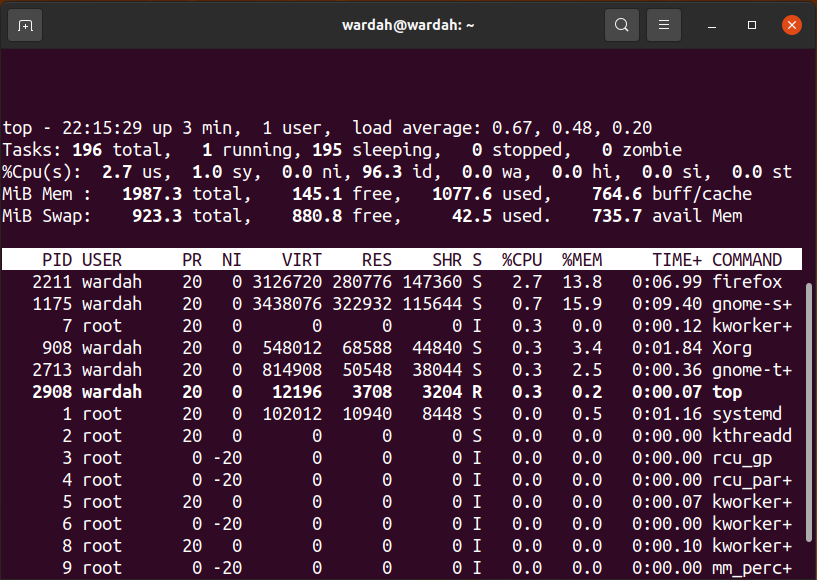
- How to find PIDs using the “top” Command:
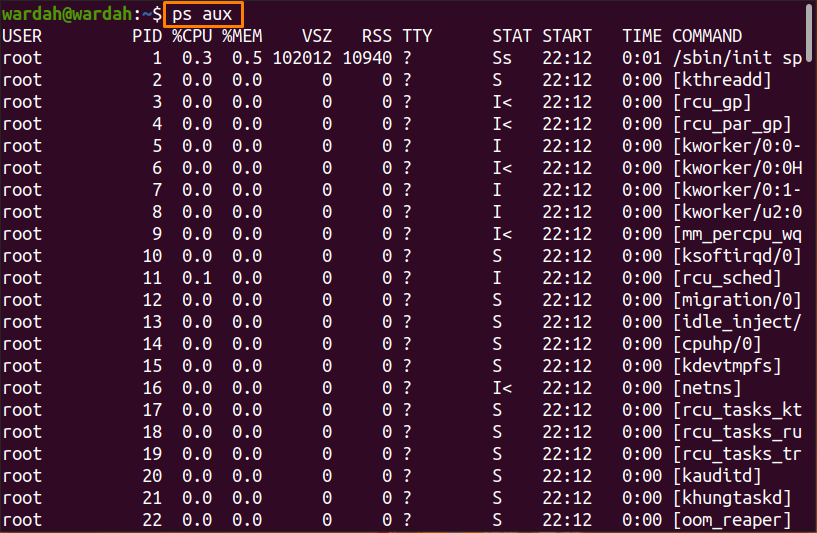
- How to find PIDs using the “ps aux” command:
- Conclusion:
- About the author
- Syeda Wardah Batool
- How to Find the Process ID of a Program and Kill it in Linux
- Method 1: Terminate a process using the kill command
- Step 1: Find the PID of a process
- Step 2: Kill the process using the PID
- Method 2: Kill a process using the top command
- Method 3: Killing a process in Linux via GUI
- What next?
How to find the Process ID (PID) of a running terminal program?
I am running a program in the terminal that I can’t escape with Ctrl — C and that I want to kill. How can I find its PID?
This is a branch of What should I do when Ubuntu freezes? as a reference to prevent details in that question from becoming too technical.
11 Answers 11
Open another terminal and run ps ax | grep foo where foo is the name of the unresponsive program. This should return a line of output that looks something like this:
$ ps ax | grep firefox 2222 ? S 0:00 /bin/sh /usr/lib/firefox-3.6.9/firefox 2231 ? Sl 514:36 /usr/lib/firefox-3.6.9/firefox-bin 30290 pts/2 S+ 0:00 grep --color=auto firefox The first field of each line of output is a number which represents the Process ID of the program matched by grep (you can safely ignore the last one, which represents grep itself.
To halt the offending process, do: kill pid where pid is the Process ID of the program. You might have to use your judgment as to which of the matches needs to be kill ed, or you could use top instead. Using kill by itself sends SIGTERM, which you should try first as it allows the program to properly clean up after itself. If SIGTERM fails, try SIGHUP, which is stonger medicine: kill -HUP pid . If all else fails, send SIGKILL. But, you should only do so as a last resort, because SIGKILL causes the kernel to terminate the process immediately with no possibility for cleanup. This can at times result in data corruption or other problems. So again, only send SIGKILL as a last resort. To do so, do kill -KILL pid or kill -9 pid .
If you are running a graphical interface, of course, you don’t have to fool with this crazy command-line stuff to get the job done. Just open «System Monitor», navigate to the Processes tab, choose the process you want to halt (Hm, could it be the one using 90% CPU?) and right-click it. Since the process is already stopped, (that’s the problem, right?) choose End Process or Kill Process from the resulting menu.
How do I Find Process ID in Ubuntu
While working on an Operating System such as Linux distributions, the kernel creates a process when a program is launched. That process stores the program’s execution details in memory.
As we know that the Linux distributions are designed for multi-threaded purposes. Several processes run in the background simultaneously with the assigned unique identifiers. These identifiers are assigned automatically by the kernel and are known as Process Identifiers (PIDs).
While operating a system, sometimes we need to get details on how many processes are running and what the kernel gives PIDs.
Several reasons could be listed that why we need to know the PID of running the program. When multiple programs are executing, sometimes we want their PIDs for scheduling purposes, or when a program behaves abnormally, we need its PID to kill the associated program.
You can also find the PIDs through the Graphical User Interface (GUI), but you may not get the list of hidden running processes from GUI-based tools.
To get the PID of the running processes, a command-line interface is the most effective way.
How to find process ID in Linux:
There are different approaches to find PIDs; most of the simple and possible approaches are discussed below. Select the process you want to display the PID of and follow the approach according to choose.
For example, we will show the process ID of “VLC,” but you can select another process.
How to find the process ID (PID) with the “pidof” command:
To get the PID of the running process in a terminal with the help of the “pidof” command is the most common and simplest way.
Open the terminal and follow the given syntax of the “pidof” command to display process ID:
or to get the “VLC” PID, type:
How to Find Process ID (PID) with “pgrep” Command:
The “pgrep” command is another Linux utility that helps find the PID of a running program. To get PID of the “VLC” using the “pgrep” command utility, type:
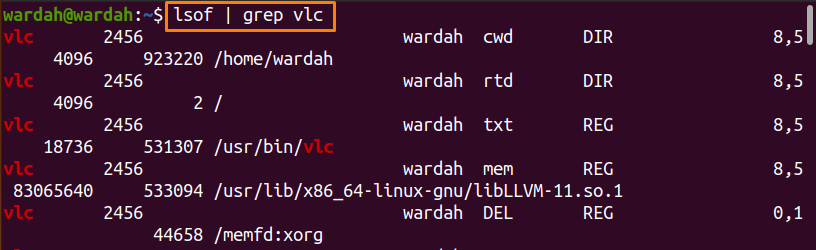
How to find the process ID (PID) with the “lsof” command:
The “lsof” command is an abbreviated form of “List Open Files.” It is used to fetch data about files opened by multiple processes.
Use it with the “grep” command to retrieve the “VLC” PID with the file data:
Keep in mind, most of the time, we use the “grep” command with multiple command-line tools. The purpose is that the “grep” command finds the file of a specified pattern of strings and displays it.
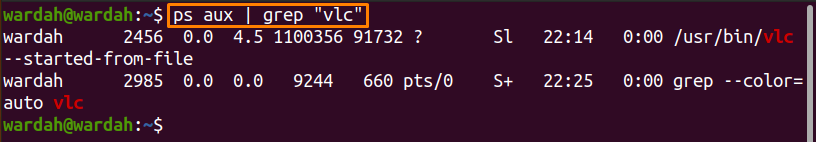
How to find the process ID (PID) with the “ps” command:
When we use the “ps” command, it lists the process ID of a running process and reads the related information from the “/proc” filesystem that contains the virtual files.
Type the given command to display PID of VLC:
(You might think why we used the “ps” command with the “aux” option. Keep that question in mind; we will use this command at the end of the article).
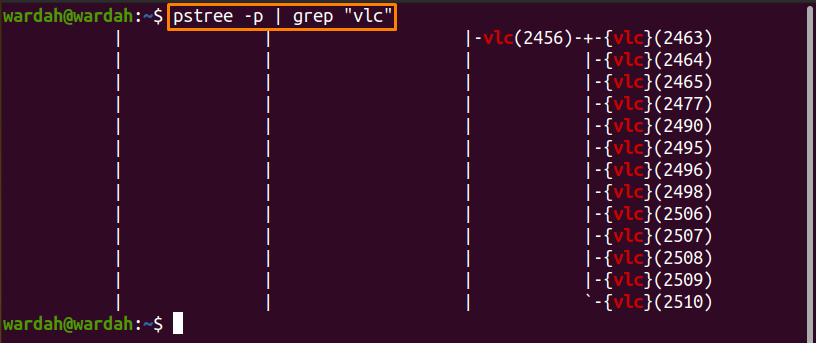
How to Find the Process ID (PID) with “pstree” Command:
The “pstree” command utility is an effective way to display the hierarchy of the running process in a tree format.
Type the “pstree” command to display a hierarchy of the VLC and get its PID as well:
The image has shown the parent process with its child processes.
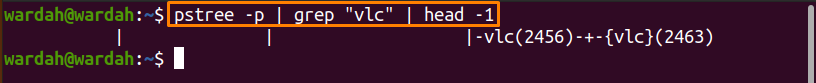
If you want to display only the parent process, use the mentioned command:
The approaches mentioned above are used to display the PID of a particular process.
If you want to display the list of all processes running in the background, use the “top” and “ps aux” command.
How to find PIDs using the “top” Command:
The “top” command displays the task manager, which contains the processing activity of all the running processes with their PIDs in the Linux system.
Type “top” in a terminal to get a list of processes:
How to find PIDs using the “ps aux” command:
We have already used the “ps aux” with the “grep” command above to display the “VLC” PID. That was for the particular process as we used it with the grep command.
If we talk about the “ps aux” command, it is an efficient command-line tool to monitor all the processes running in an operating system. You can manage process-related information once the list is displayed. It shows process names with their PIDs and memory usage.
Conclusion:
Linux is a multitasking operating system; multiple processes run simultaneously with unique identifiers called PIDs. From this write-up, you have learned how to find the PID of a particular process through different approaches. We have also checked how to get the list of all running processes using the “top” and “ps aux” command-line utilities.
About the author
Syeda Wardah Batool
I am a Software Engineer Graduate and Self Motivated Linux writer. I also love to read latest Linux books. Moreover, in my free time, i love to read books on Personal development.
How to Find the Process ID of a Program and Kill it in Linux
This tutorial teaches you to kill a process in Linux using both its process id and GUI method. This is particularly helpful in killing unresponsive programs.
You can easily stop a program in Linux terminal by pressing the Ctrl+C keys. But you often need to ‘kill’ an unresponsive program. In Windows, you have the task manager for this situation. In Linux, you can kill a process using the command line or GUI task managers. Using the command line is easier. All you have to do is:
- Finding the PID and killing a running process in the command line
- Using the top command to find and kill a process
- Using task managers in Linux desktop to terminate a running process
Let’s start with the command line first.
Method 1: Terminate a process using the kill command
To kill a process, you must know its process ID (PID). The following section tells you how to find the process ID of a program.
Step 1: Find the PID of a process
If you know the name of the process, you can use the command pidof in this fashion:
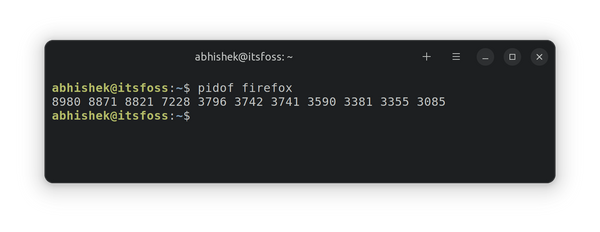
You can take the help of the tab completion to find the program’s name. The good thing about this command is that it will give the PIDs of all the processes initiated by the program. Here’s an example:
[email protected]:~$ pidof firefox 8980 8871 8821 7228 3796 3742 3741 3590 3381 3355 3085If the pidof command doesn’t result in anything, it could mean either there is no process running of that program or the program name you used is incorrect.
You can try the ps command if unaware of the exact program name. This ps command is used for seeing the running processes on the system. You can use the grep command with the program name (or whatever you remember about it).
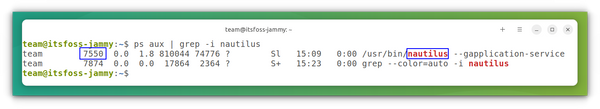
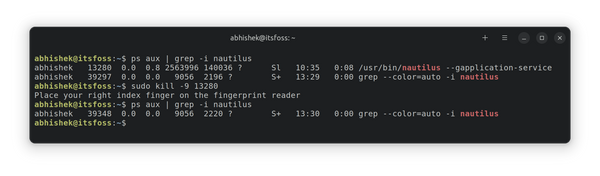
ps aux | grep -i “name of your desired program” The ps aux command returns all the running processes on the system. And the grep afterward shows the line which matches the program name. The output of the command will be like this:
As shown in the picture above, you can get the process ID of the program/process in the second column. Just ignore the line with “–color =auto”.
Step 2: Kill the process using the PID
Once you have the PID of the desired application, use the following command to kill the process immediately:
Here’s an example where I terminate a running instance of the Nautilus file manager. As you can see, Nautilus was no longer running after it was killed. The grep —color=auto -i nautilus is just the grep command running for nautilus search.
You can also use the kill command without option -9. Then it requests the process to terminate. With -9 option, it force kills the process immediately. Read more on sigterm and sigkill.
If you have more than one process id, you can kill them together by providing all the PIDs.
sudo kill -9 process_id_1 process_id_2 process_id_3You can also combine the kill command and the pidof command to kill all the processes of a program.
sudo kill -9 `pidof programe_name`Of course, you have to replace the program_name with the name of the program you want to kill.
Knowing the program’s name, you can use the magnificent killall command and kill all processes in one single command killall program_name
Method 2: Kill a process using the top command
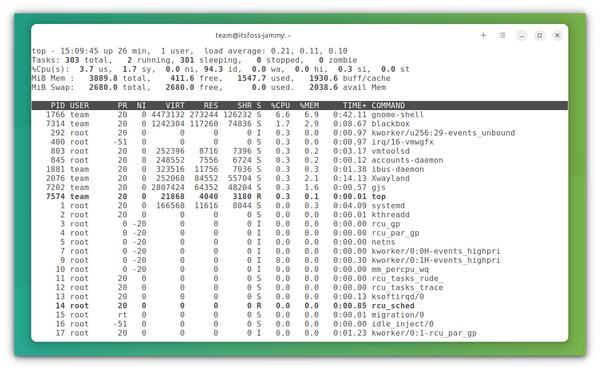
The top command is one of the popular commands, which is pre-installed on almost all Linux distributions. It is a powerful task management tool. To use it to kill a process, first open the top by entering:
This will open Top and list all the running processes:
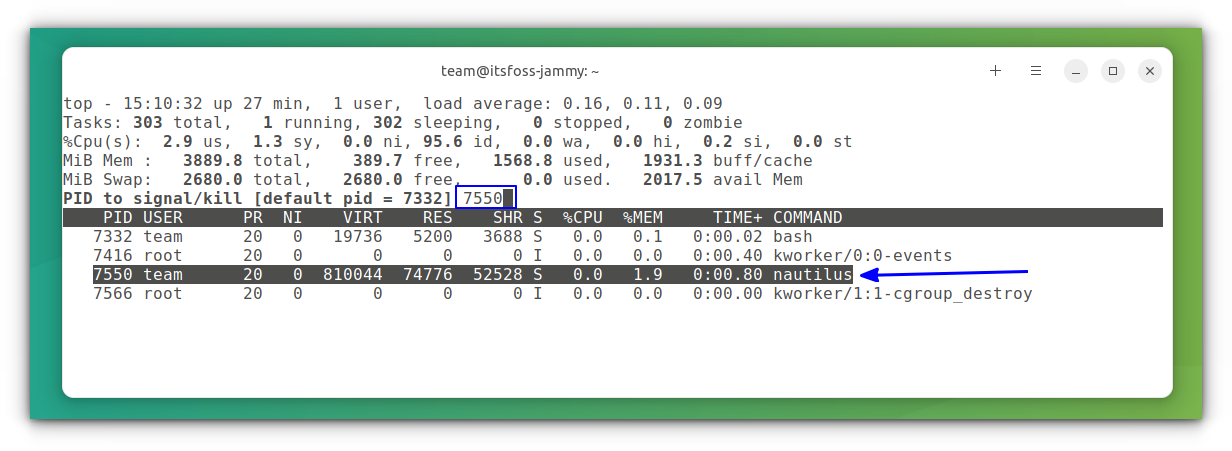
Inside the top command, press Shift+L. this will open a “Locate string” prompt, where we can search for the process by name. Once you have located the process that needs to be terminated, press the k key on the keyboard.
Now enter the process ID of the program.
This way, you can terminate any process using the top command. You can also use other system monitoring commands like htop for finding and terminating processes.
Method 3: Killing a process in Linux via GUI
If you are using a Linux desktop, you don’t necessarily have to use the terminal.
There is a task manager in every Linux distribution. It’s usually called a system monitor.
This system monitor is part of the desktop environment. GNOME, KDE, and Cinnamon, all of them have a system monitor. Just look for them in the system menu.
I’ll be demonstrating the GNOME system monitor here.
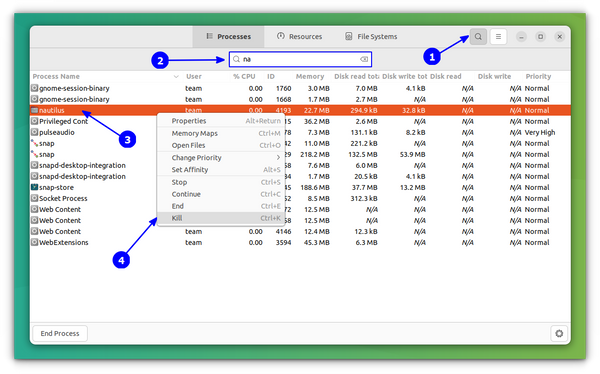
The default page lists all the running processes. You can kill a process by clicking on it and pressing the End Process button. Or you can right-click on the process and select Kill/End from the context menu.
Also, you can note that the process tab lists the process ID of the respective program.
You may also use various third-party tools like Stacer.
What next?
If you are interested in learning more about this topic, I suggest getting familiar with various termination signals.
The ps command is also quite versatile. Learning its usage will be helpful as well.
So, you learned the command line and GUI methods of terminating a running process in Linux.
The command line method is evergreen and you can use it on any Linux distribution, desktop, or server.
Now it’s your turn. Do you prefer the command line method or the GUI tools?