- Installing and Using Homebrew Package Manager on Linux
- Why use Homebrew package manager on Linux when you have got apt, dnf, snap etc?
- Install Homebrew on Ubuntu and other Linux distributions
- Step 1: Install dependencies
- Step 2: Install Homebrew
- Step 3: Verify brew installation
- Using brew command for installing, removing and managing packages
- Removing Homebrew from Linux
- Conclusion
- How To Install and Use Homebrew on Linux Systems
- Why Homebrew Package Manager?
- Homebrew Installation on Linux Systems
- Step 1: Install Curl and Git Tools
- Step 2: Run Homebrew Installation Script
- Homebrew Usage in Linux
Installing and Using Homebrew Package Manager on Linux
Homebrew, also known as Brew, is a command line package manager primarily created for macOS.
Homebrew grew quite popular among macOS users as more developers created command line tools that could be easily installed with Homebrew.
This popularity resulted in the creation of Linuxbrew, a Linux port for Homebrew. Since it is primarily Git and Ruby, and Linux and macOS are both Unix-like systems, Brew works good on both kind of operating systems.
Linuxbrew project eventually merged with Homebrew project and now you just have one Brew project called Homebrew.
Why am I calling it brew, instead of Homebrew? Because the command starts with brew. You’ll see it in detail in a later section.
Why use Homebrew package manager on Linux when you have got apt, dnf, snap etc?
I know the feeling. You already have a good package manager provided by your distribution. In addition to that, you have Snap, Flatpak and other universal package system.
Do you really need Homebrew package manager on your Linux system? The answer depends on your requirement, really.
See, apart from the distribution’s package manager and universal packages, you’ll come across situations where you need other package managers like Pip (for Python applications) and Cargo (for Rust packages).
Imagine you came across a good command line utility and want to try it. It’s repository mentions that it can be installed using brew or source code only. In such a case, having brew on your system could be helpful. After all, installing from source code in the 2020s is not fashionable (and comfortable).
In other words, you’ll have an additional option in case you come across some interesting CLI tool that provides only brew installation option.
Install Homebrew on Ubuntu and other Linux distributions
The installation is quite easy. You just have to make sure that you have got all the dependencies.
Step 1: Install dependencies
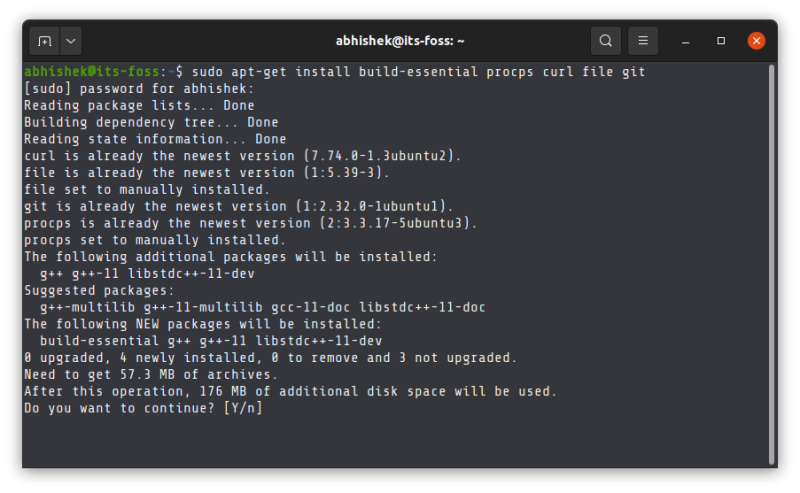
You need to have relatively newer version of gcc and glibc. You can install build-essential package on Ubuntu to get them. Apart from that, you also need to install Git, Curl and procps (used for monitoring system process).
You can install all of them together like this in Ubuntu and Debian based systems:
sudo apt-get install build-essential procps curl file gitFor other distributions, please use your package manager and install these dependencies.
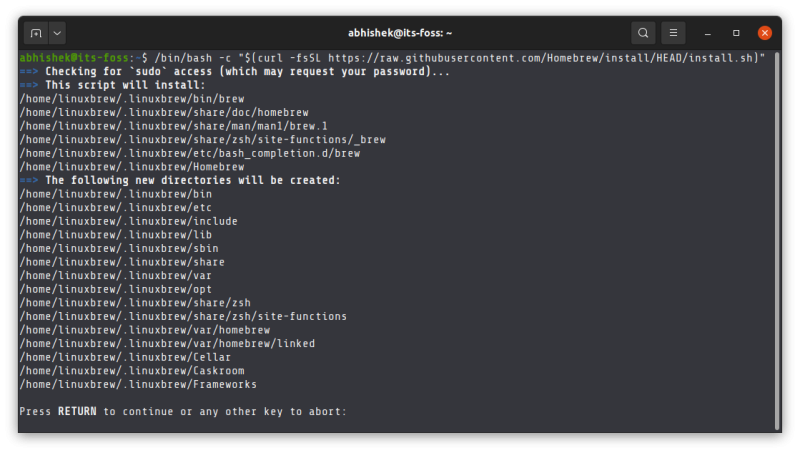
Step 2: Install Homebrew
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"When asked for RETURN key, press enter:
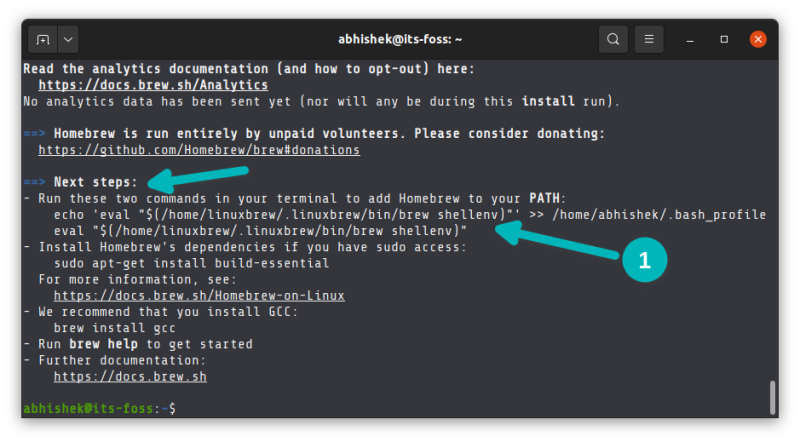
At the end of the script competition, it recommends to run a few commands to add it to the PATH variable. Homebrew is actually installed in your home directory and then soft linked to the /usr/local directory.
You can copy and paste in terminal easily. Just select the command it suggests and press Ctrl+Shift+C to copy and Ctrl+Shift+V to paste.
Alternatively, you can just copy paste this command:
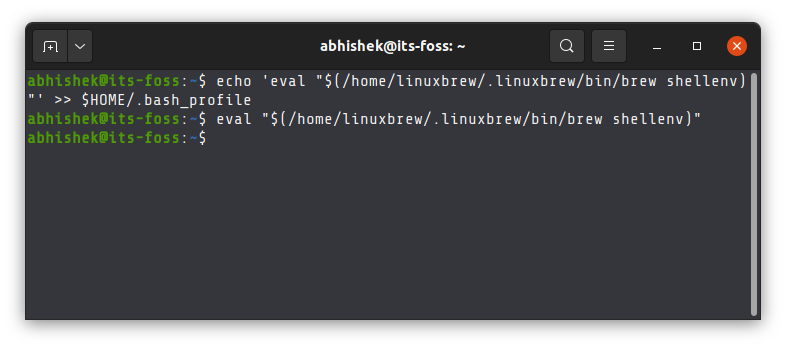
echo 'eval "$(/home/linuxbrew/.linuxbrew/bin/brew shellenv)"' >> $HOME/.bash_profileeval "$(/home/linuxbrew/.linuxbrew/bin/brew shellenv)"Step 3: Verify brew installation
You are almost done. Just verify that brew command is ready to run by using the brew doctor command:
The brew doctor command will tell you if there is any issue.
You may double verify by installing the sample hello project:
If you see no errors, you can enjoy the Homebrew package manager on Linux.
Using brew command for installing, removing and managing packages
Let me quickly tell you a few brew commands you can use for installing, removing and managing packages.
Since Homebrew is installed in your home directory, you do not need sudo to run it (just like Pip and Cargo).
To install a package with brew, use the install option:
brew install package_nameThere is no autocompletion for the package name here. You need to know the exact package name.
To remove a brew package, you can use either remove or uninstall option. Both works the same.
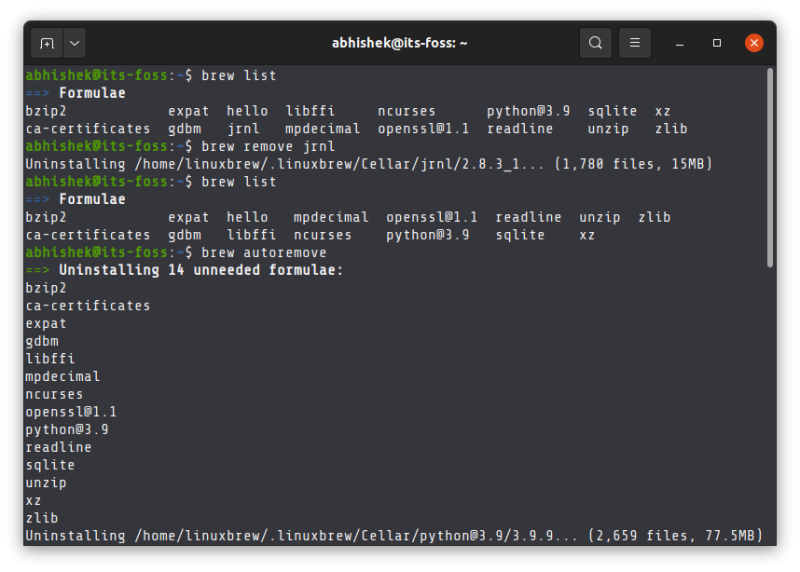
You can also list the installed brew packages with this command:
You can also remove the unneeded dependencies with the autoremove option:
In the next screenshot, I had only two packages installed with brew but it also shows the dependencies installed for those packages. Even after removing the package, dependencies remained. The autoremove finally removed them.
There are a lot more brew command options but that is out of scope for this tutorial. You can always go through their documentation and explore it further.
Removing Homebrew from Linux
This tutorial won’t complete without adding the steps for removing Homebrew from your Linux system.
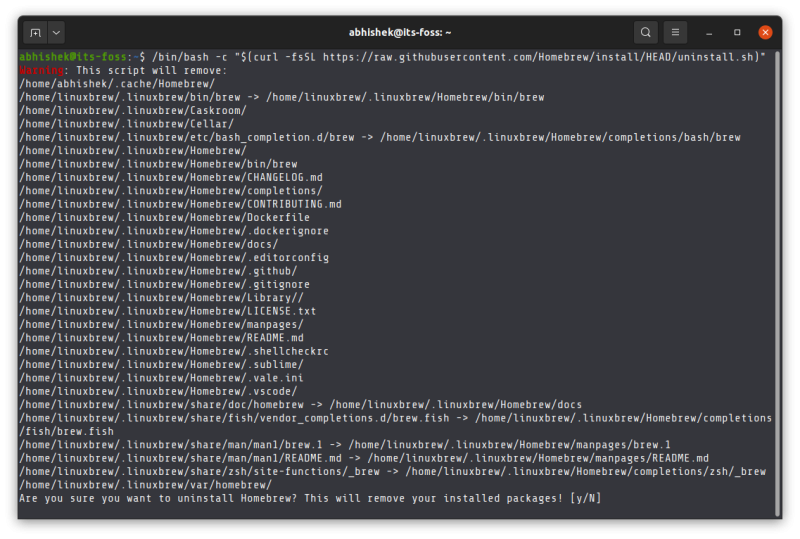
As per the steps mentioned on its GitHub repository, you have to download and run the uninstall script using this command:
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/uninstall.sh)"You’ll be asked to confirm the removal by entering the Y key.
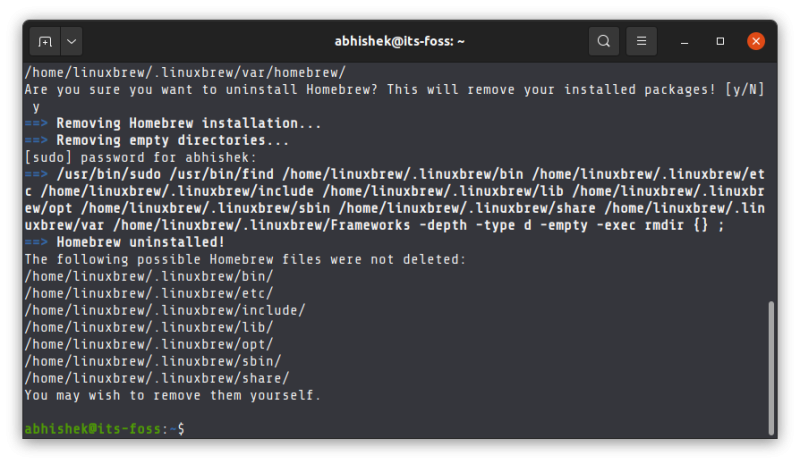
When the uninstallation of Homebrew completes, it lists the files and directories it has leftover:
I let you remove the files and directories on your own.
Conclusion
As I explained earlier, Homebrew provides an extension to what you have already got. If you stumble upon an application that has only brew as installation method, having Homebrew installed on your Linux system will come handy.
Anything you want to add to this topic or share your question or opinion? Please use the comment section.
How To Install and Use Homebrew on Linux Systems
macOS takes credit for the original development of the Homebrew package manager. With this package manager, Linux users are able to effortlessly install free and open-source software packages from their command-line environment.
You might think that the various popular Linux OS distributions are already equipped with their own package managers such as APT, DNF, YUM, PACMAN, and ZYPPER.
These default package managers are indeed sufficient when retrieving and installing tools and programs from maintained and trusted package repositories. However, these package managers are not always the go-to solution for all practical scenarios.
Why Homebrew Package Manager?
For instance, to use programming languages like Python and Node.js on a Linux environment, you will need to consider the use of their accustomed package managers like pip3 (for Python3) and npm (for Node.js). These software-based package managers make the installation of additional and mandatory libraries and scripts possible.
In comparison to the Linux-based repository packages, the equivalent of most of these packages are better maintained under the Homebrew package manager. Also, Homebrew packages attribute the provision of a per-user functionality making sure that there is no conflict between it and your default package manager like APT, DNF, etc.
This tutorial guide will walk us through the installation and usage of the Homebrew package manager on Linux.
Homebrew Installation on Linux Systems
The Homebrew package manager’s homepage provides an official installation script that works for all Linux operating system distributions. The installation procedure is associated with a preferred Homebrew prefix.
For instance, the preferred prefix for this package manager under Linux is /home/linuxbrew/.linuxbrew. This prefix disregards the necessity of using sudo when running the Homebrew package manager installation command (brew install).
This Homebrew installation script is user-interactive such that we will have to confirm every critical installation step prior to its execution.
Step 1: Install Curl and Git Tools
If they are not already installed on your machine, consider the following installation instructions:
$ sudo apt install curl git [On Debian, Ubuntu and Mint] $ sudo yum install curl git [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora and Rocky Linux/AlmaLinux] $ sudo pacman -S curl git [On Arch Linux] $ sudo zypper install curl git [On OpenSUSE]
Step 2: Run Homebrew Installation Script
Next, run the following script using the curl command, running this script will first ask you for the Sudoer user password of the Linux system.
$ /bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
Afterward, press [Enter] to confirm and continue the installation of Homebrew, its other associated packages, and the creation of needed directory paths.
The installation process should then take some time to complete, therefore, take a coffee break if need be. Once installed, consider executing the commands as advised on the final screen capture of Homebrew installation:
$ echo 'eval "$(/home/linuxbrew/.linuxbrew/bin/brew shellenv)"' >> /home/dnyce/.profile $ eval "$(/home/linuxbrew/.linuxbrew/bin/brew shellenv)" $ sudo apt-get install build-essential $ brew install gcc
On my end, a summary of executing the commands on the above screen capture is as follows:
Homebrew Usage in Linux
Open/start a new shell for this section. Verify that the installation of the Homebrew package manager is correctly done by running the command:
You should get an output similar to the following:
Let us for instance assume we are installing a Linux package called a tree.
$ brew search tree [Search a Package] $ brew install tree [Install a Package] $ brew upgrade tree [Upgrade a Package] $ brew uninstall tree [Remove a Package]
For more usage and example, read our guide on the homebrew commands cheat sheet.
You are now familiar with the installation and usage of Homebrew on Linux. Your comments and feedback are always appreciated!