- ArchPKGs
- Guide on Install/Update/Remove nvidia on Arch Linux (Manjaro, Parabola)
- Table of Contents
- nvidia (Extra) link
- Install extra/nvidia link
- Update extra/nvidia link
- Remove extra/nvidia link
- nvidia (Testing) link
- Install testing/nvidia link
- Update testing/nvidia link
- Remove testing/nvidia link
- nvidia (extra-testing) link
- Install extra-testing/nvidia link
- Update extra-testing/nvidia link
- Remove extra-testing/nvidia link
- More Guides
- precompile-bits-stdc++.h Install/Update/Uninstall Guide on Arch Linux, Manjaro and Parabola
- How to Install perl-devel-ptkdb (Full Guide) on Arch Linux/Manjaro/Anarchy
- Full Tutorial on ndn-infoedit-git Installation on Arch Linux, Manjaro and Anarchy
- Quick Tutorial on Installing modrinth-cli-git on Arch-Based Linux (Manjaro/ArcoLinux)
- Installing thunderbird-extension-tbkeys (Step-by-Step Instructions) on Arch Linux (Manjaro/Parabola)
- A Straightforward Guide on Installing airdrop-tool-bin on Arch Linux (Manjaro/Parabola)
- How to install NVIDIA drivers, CUDA and Bumblebee on Arch Linux / BlackArch
- How to check whether an NVIDIA graphics card is active
- How to install NVIDIA video driver on Arch Linux or BlackArch
- How to install and use Bumblebee (how to enable NVIDIA Optimus on Arch Linux)
- System freezes after installing Bumblebee
- How to use Bumblebee / NVIDIA Optimus on Linux
- How to test Bumblebee / NVIDIA Optimus on Linux
- Related articles:
ArchPKGs
Guide on Install/Update/Remove nvidia on Arch Linux (Manjaro, Parabola)
There are 3 packages from Extra, Testing and extra-testing are named nvidia . We would recommend going with either the packages from the official repositories or an AUR package with a good reputation.
Table of Contents
nvidia (Extra) link
extra/nvidia is «NVIDIA drivers for linux» quoting from its gist. To install or remove extra/nvidia from Arch official repository (Extra) on Arch Linux and Arch-based distributions (e.g. Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Anarchy, RebornOS, Parabola) is rather uncomplicated. This guide will be covering how to install/update/uninstall the package with either the built-in package manager pacman or an AUR helper (e.g. yay ).
Install extra/nvidia link
Two typical methods are used to install extra/nvidia from Arch official repository (Extra). pacman is what you’re looking for if you’re an experienced Linux user and have the knowledge of how packages are built. Otherwise, yay is a popular alternative to install packages without the necessity to review PKGBUILD and build packages with makepkg on your own.
Using pacman link
sudo pacman -S extra/nvidia
Using yay link
yay -S --repo extra/nvidia
Update extra/nvidia link
Since Arch is a rolling-release Linux distribution, it is required to do a whole system upgrade before updating an official package due to safety reason.
Using pacman link
sudo pacman -Syu
Using yay link
Remove extra/nvidia link
Uninstalling packages is the simplest of these three,just choose whether to purge the unused dependencies and the configuration files used by the package.
Using pacman link
sudo pacman -R nvidia
sudo pacman -Rs nvidia
sudo pacman -Rns nvidia
Using yay link
yay -Rs nvidia
yay -Rns nvidia
nvidia (Testing) link
It might not be a good practice to install a developing package ( testing/nvidia ) unless you know what you’re doing.
«NVIDIA drivers for linux» is their definition of testing/nvidia . To install testing/nvidia from Arch official testing repository (Testing) on Arch Linux, Manjaro, EndeavourOS, BlackArch, Artix and Anarchy is relatively straightforward. This guide will taught you how to install/update/uninstall the package with either the default package manager pacman or an AUR helper like yay .
Install testing/nvidia link
To install packages from Testing, first you’ll need to uncomment [testing] section of /etc/pacman.conf , then use sudo pacman -Syu to update the packages list and upgrade your system.
Two well known ways are used to install the developing version of testing/nvidia from Arch official repository (Testing). pacman is the choice for you if you’re comfortable using Arch Linux and understand the concept of how packages are built. If not, yay is a common alternative to install packages without the hassle of reviewing PKGBUILD and build packages with makepkg yourself.
Using pacman link
sudo pacman -S testing/nvidia
Using yay link
yay -S --repo testing/nvidia
Update testing/nvidia link
Since Arch is a rolling-release Linux distribution, it is required to do a whole system upgrade before updating an official package due to safety reason.
Using pacman link
sudo pacman -Syu
Using yay link
Remove testing/nvidia link
Compared to installing and updating packages, removing is the most uncomplicated of these three,just choose whether to purge the dependencies that no longer required by other packages and the configuration files generated by the package.
Using pacman link
sudo pacman -R nvidia
sudo pacman -Rs nvidia
sudo pacman -Rns nvidia
Using yay link
yay -Rs nvidia
yay -Rns nvidia
nvidia (extra-testing) link
extra-testing/nvidia is «NVIDIA drivers for linux» according to its definition. To install this package ( extra-testing/nvidia ) from Arch official repository (extra-testing) on Arch Linux, Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Artix, RebornOS and Parabola is fairly simple. This guide will taught you how to install/update/uninstall the package with either the default package manager pacman or an AUR helper (e.g. yay ).
Install extra-testing/nvidia link
There are commonly two approaches to install extra-testing/nvidia from Arch official repository (extra-testing). pacman is what you’re looking for if you are a seasoned Linux user and know the concept of how packages are built. If not, yay is an acceptable alternative to install packages without the hassle of reviewing PKGBUILD and build packages with makepkg by yourself.
Using pacman link
sudo pacman -S extra-testing/nvidia
Using yay link
yay -S --repo extra-testing/nvidia
Update extra-testing/nvidia link
Since Arch is a rolling-release Linux distro, it is required to do a whole system upgrade before updating an official package due to safety reason.
Using pacman link
Request pacman to do a whole system upgrade which will update any packages you have installed before:
sudo pacman -Syu
Using yay link
Remove extra-testing/nvidia link
Compared to installing and updating packages, uninstalling is the easiest of these three,all you have to do is choose whether to keep the unused dependencies and the configuration files generated by the package.
Using pacman link
sudo pacman -R nvidia
sudo pacman -Rs nvidia
sudo pacman -Rns nvidia
Using yay link
yay -Rs nvidia
yay -Rns nvidia
More Guides
precompile-bits-stdc++.h Install/Update/Uninstall Guide on Arch Linux, Manjaro and Parabola
precompile-bits-stdc++.h is «Precompiles the bits/stdc++.h header file useful for competitive programming» according to its description. To get this package (precompile-bits-stdc++.h) from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux, Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Parabola, Anarchy and ArcoLinux is relatively simple. This tutorial will show you step-by-step how to install, update and uninstall the package with either the default package manager pacman or an AUR helper like yay.
How to Install perl-devel-ptkdb (Full Guide) on Arch Linux/Manjaro/Anarchy
Based on perl-devel-ptkdb’s gist, it is «Devel::ptkdb — Perl debugger using a Tk GUI». To install this package (perl-devel-ptkdb) from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux, Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Anarchy, Artix, BlackArch and Parabola is quite straightforward. This guide will show you step-by-step how to install, update and uninstall the package with either the built-in package manager pacman or an AUR helper (e.g. yay).
Full Tutorial on ndn-infoedit-git Installation on Arch Linux, Manjaro and Anarchy
ndn-infoedit-git is «Command Line Tools for Boost INFO Format» according to its own outline. To install or remove ndn-infoedit-git from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux and Arch-based Linux distros (e.g. Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Artix, Garuda, BlackArch, Anarchy) is rather uncomplicated. This guide will be covering how to install/update/remove the package with either the default package manager pacman or an AUR helper like yay.
Quick Tutorial on Installing modrinth-cli-git on Arch-Based Linux (Manjaro/ArcoLinux)
Based on modrinth-cli-git’s own definition, it’s «Official Modrinth CLI launcher. Open-source, built by the community, for the community.». To install this package (modrinth-cli-git) from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux and Arch-based Linux distributions (e.g. Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Parabola, Artix) is rather simple. This guide will be covering how to install/update/uninstall the package with either the default package manager pacman or an AUR helper (e.g. yay).
Installing thunderbird-extension-tbkeys (Step-by-Step Instructions) on Arch Linux (Manjaro/Parabola)
«Custom commands, functions, and keybindings for Thunderbird» is their outline of thunderbird-extension-tbkeys. To install or remove thunderbird-extension-tbkeys from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux, Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Parabola, BlackArch and Garuda is quite easy. This guide will show you step-by-step how to install, update and remove the package with either the default package manager pacman or an AUR helper (e.g. yay).
A Straightforward Guide on Installing airdrop-tool-bin on Arch Linux (Manjaro/Parabola)
airdrop-tool-bin is «Fetch & analyse blockchain tickets. View leaderboards and user tickets. Calculate and perform provably fair airdrops.» according to its own gist. To install and update this package (airdrop-tool-bin) from AUR (Arch User Repository) on Arch Linux and Arch-based Linux distros (e.g. Manjaro, EndeavourOS, Artix, Garuda, ArcoLinux) is fairly easy. This tutorial will show you step-by-step how to install/update/uninstall the package with either the built-in package manager pacman or an AUR helper (e.g. yay).
More guides… copyright 2023 ArchPKGs. All Rights Reserved.
How to install NVIDIA drivers, CUDA and Bumblebee on Arch Linux / BlackArch
There are several commands that will show which video card is used:
glxinfo|egrep "OpenGL vendor|OpenGL renderer"
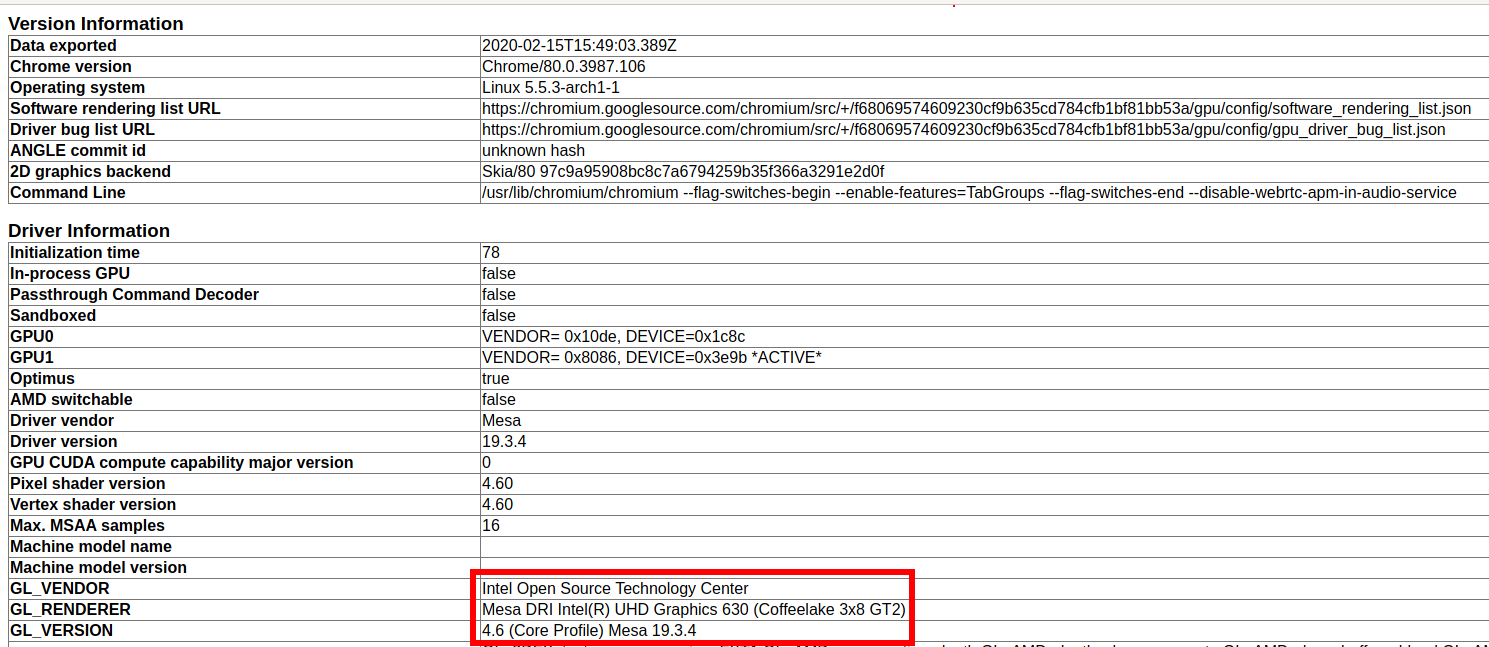
OpenGL vendor string: Intel Open Source Technology Center OpenGL renderer string: Mesa DRI Intel(R) UHD Graphics 630 (Coffeelake 3x8 GT2)
This is the same command, but launched via optirun from the Bumblebee package:
optirun glxinfo|egrep "OpenGL vendor|OpenGL renderer"
Sample output that shows that an NVIDIA graphics card is active:
OpenGL vendor string: NVIDIA Corporation OpenGL renderer string: GeForce GTX 1050 Ti/PCIe/SSE2
More about optirun and Bumblebee will come later a bit.
Another command that displays information about the active GPU (and a cool triangle as a bonus):
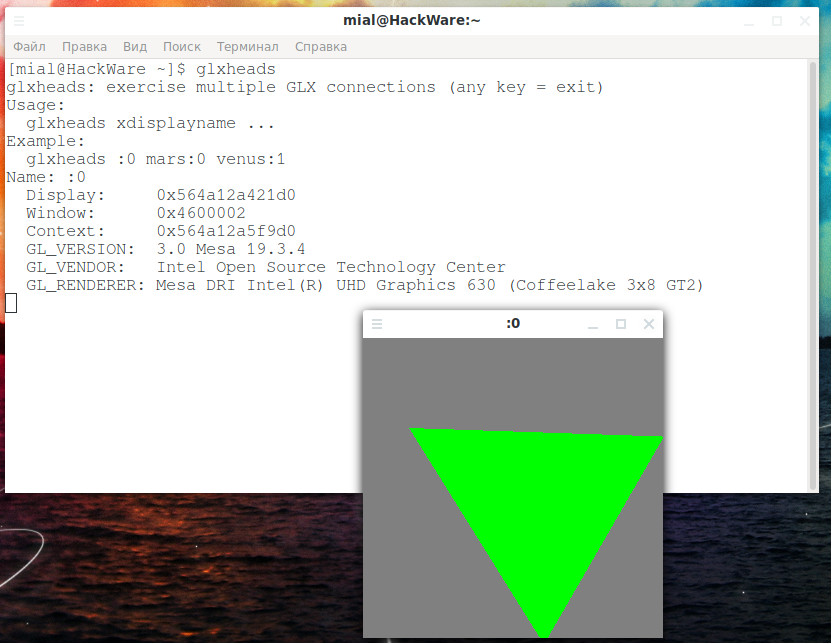
Using the lspci command with certain options, you can display information about the GPU. Any controller with [VGA controller] at the end is your currently active GPU. The others are switched off. Command to filter data:
lspci -vnnn | perl -lne 'print if /^\d+\:.+(\[\S+\:\S+\])/' | grep '\[VGA controller\]'
00:02.0 VGA compatible controller [0300]: Intel Corporation UHD Graphics 630 (Mobile) [8086:3e9b] (prog-if 00 [VGA controller])
How to check whether an NVIDIA graphics card is active
The following command will show the processes that the NVIDIA graphics card uses (if there are no processes, then the video adapter is not used):
Another command that shows the processes that consume the resources of an NVIDIA graphics card, as well as its load level, temperature and other metrics:
How to install NVIDIA video driver on Arch Linux or BlackArch
To install the NVidia driver in Arch Linux, BlackArch and their derivatives, run the command:
sudo pacman -S nvidia cuda nvidia-settings
How to install and use Bumblebee (how to enable NVIDIA Optimus on Arch Linux)
The Bumblebee package is needed to automatically switch between integrated and discrete graphics cards. Your card must support NVidia Optimus technology, a list of supporting cards can be found on this page: https://www.geforce.com/hardware/technology/optimus/supported-gpus
If your card is there, then proceed to the following commands. You must already have the NVIDIA proprietary driver installed, as shown above.
On Arch Linux, BlackArch, and their derivatives, run:
sudo pacman -S bumblebee virtualgl bbswitch acpid mesa sudo systemctl enable bumblebeed.service sudo systemctl enable acpid.service sudo usermod -a -G bumblebee $USER
System freezes after installing Bumblebee
I ran into a problem that Bumblebee works, but when using some commands that use CUDA or access kernel modules, the system freezes. To check if you have this problem, run the lspci command, for example:
If the system freezes completely, reboot and remove the bbswitch package.
How to use Bumblebee / NVIDIA Optimus on Linux
Now any program that should use the NVIDIA graphics card can be launched with a command of the form:
When optirun is not used, the NVIDIA card must be in the off state, which should save electricity.
How to test Bumblebee / NVIDIA Optimus on Linux
Run the GPU performance test with the usual command:
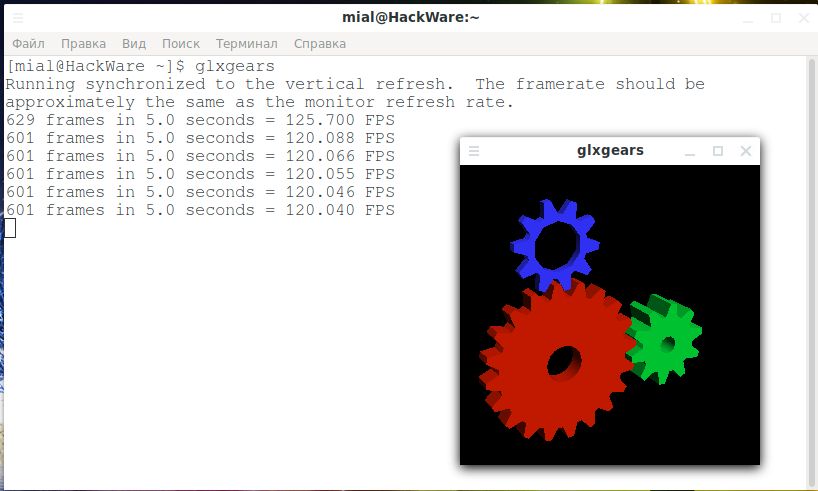
And also with optirun:

Note that FPS has grown approximately 20 times.
Another option for a video card test:
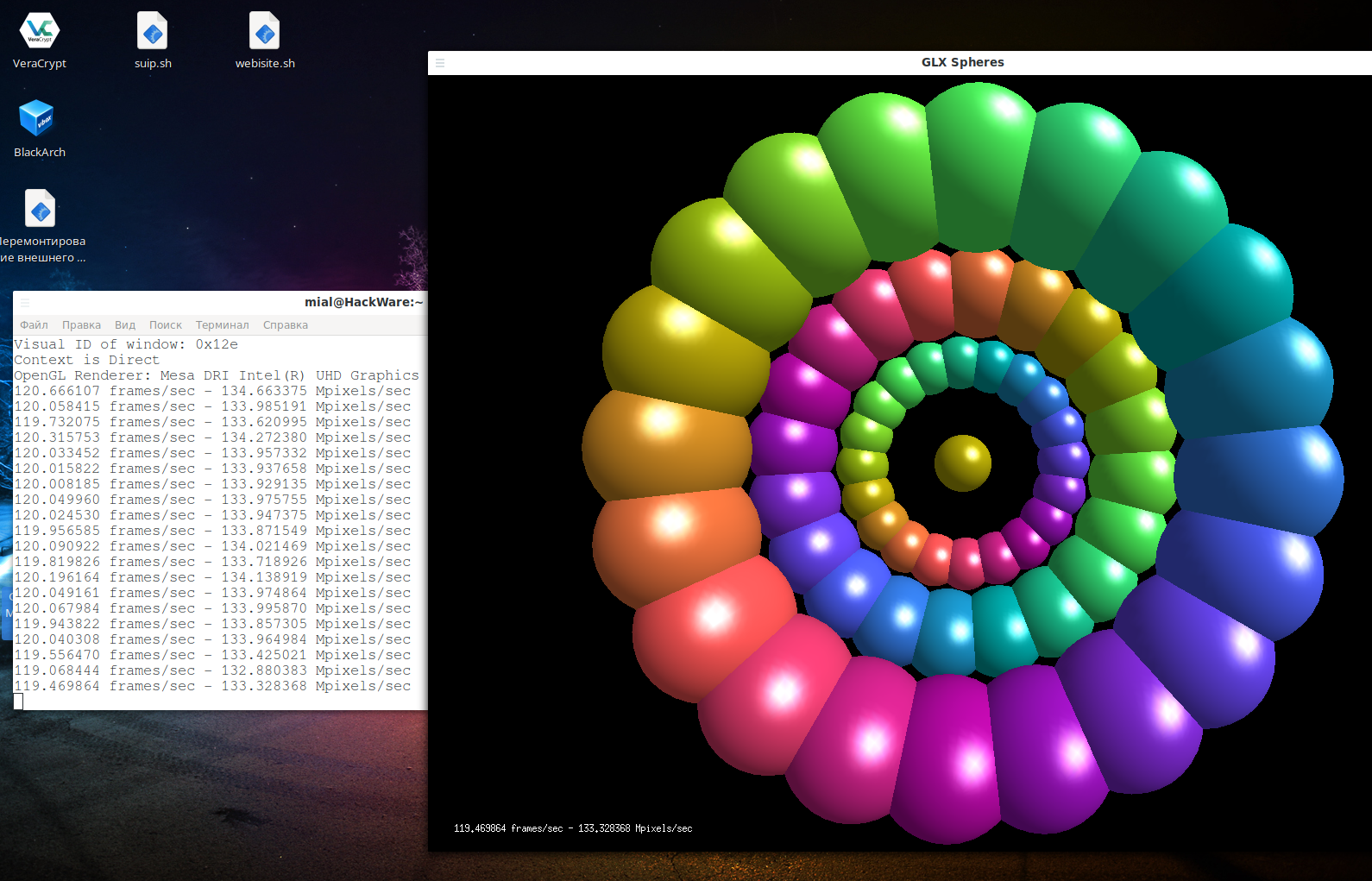
And also with optirun:
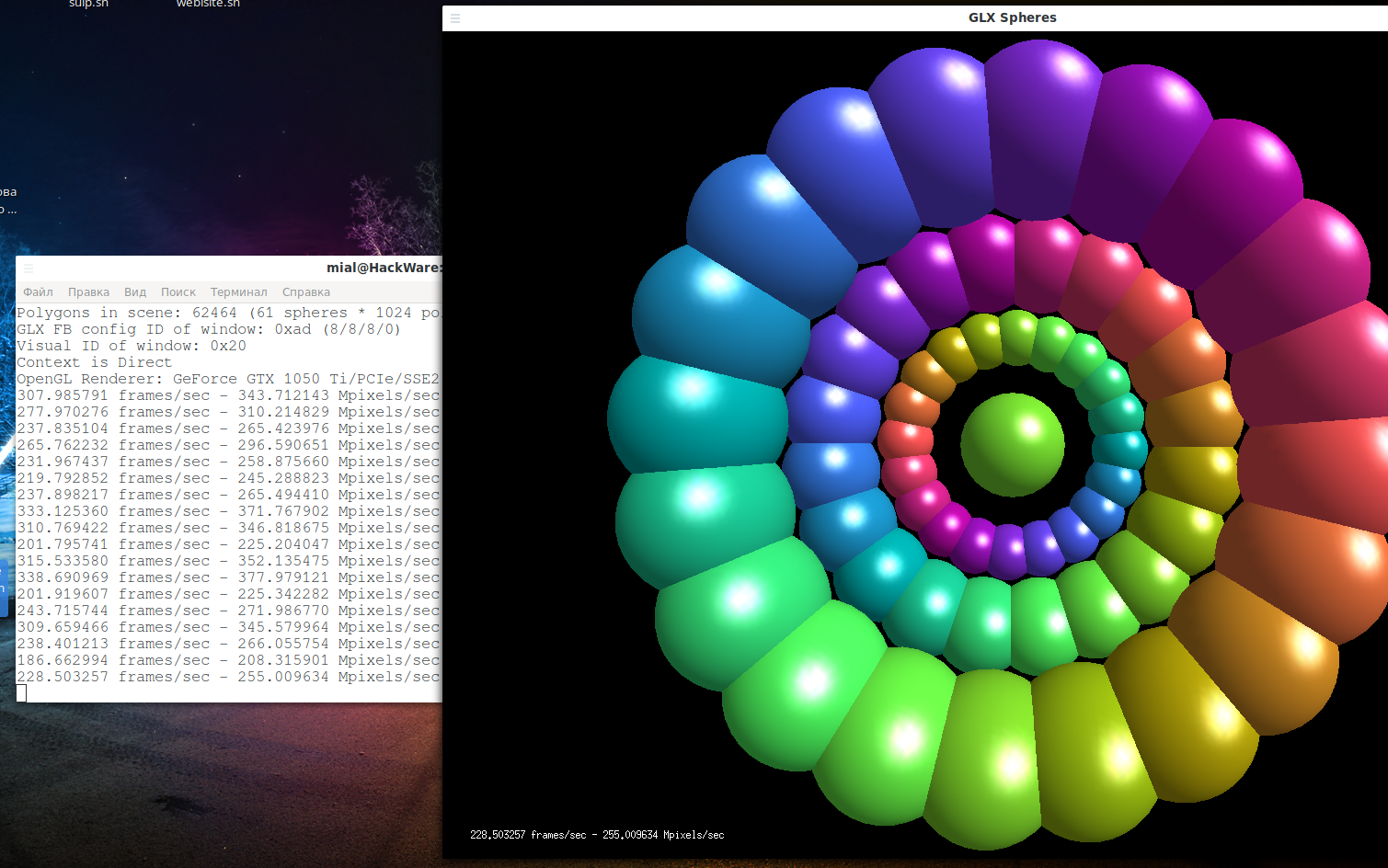
You should see a performance boost when using optirun.
While these tests are running, run the command:
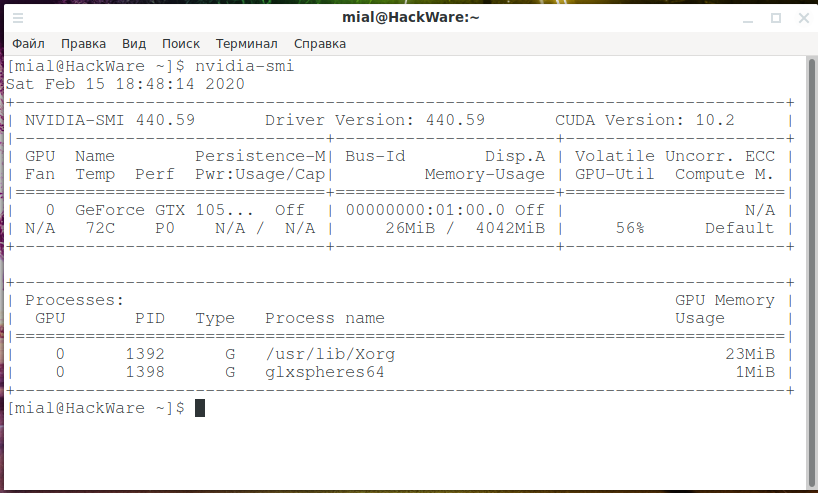
You should see processes that use a discrete graphics card.
If you have the Chromium web browser installed, then launch it in two ways:
chromium optirun chromium
In both cases, open the tab:
There you will see information about the active graphics chip: