- Как установить пакеты DEB в Ubuntu и Linux Mint
- Установка пакетов DEB в Ubuntu и Linux Mint
- Метод I: Установка пакетов Debian через командную строку
- Метод 2: Установка пакетов Debian через графический интерфейс пользователя
- Установка пакета Debian с помощью Software Center
- Установка пакета Debian с помощью приложения GDebi
- 3 Command Line Tools to Install Deb Packages in Ubuntu
- 1. Install .deb Package Using dpkg Command
- Remove Deb Packages Using dpkg Command
- 2. Install .deb Package Using Apt Command
- Remove Deb Packages using apt Command
- 3. Install .deb Package Using Gdebi Command
- Install .deb Packages Using Gdebi GUI
- How to Install Deb Files in Ubuntu, Mint and Debian
- Installing Deb Package on Ubuntu, Mint, and Debian
- 1. Using the ‘dpkg’ Command
- 2. Using the apt Command
- 3. Using a Graphical Package Manager
- Remove Deb Packages in Ubuntu, Mint, and Debian
- Remove Deb File with Configuration Files
- Remove Deb File without Configuration Files
Как установить пакеты DEB в Ubuntu и Linux Mint
Если вы нашли установочный файл программного обеспечения, заканчивающийся форматом (.deb), это означает, что файл является пакетом Debian, разработанным специально для систем на базе Debian.
Если вы новичок в Linux, это может показаться немного раздражающим, потому что вам может понадобиться несколько дополнительных шагов для установки этих пакетов Debian. Но не волнуйтесь, мы здесь, чтобы помочь вам в этом.
Установка пакетов DEB в Ubuntu и Linux Mint
В этом руководстве мы собираемся показать вам шаг за шагом, как установить пакет Debian в Ubuntu. Мы рассмотрим два основных метода:
- Установка пакетов Debian через командную строку (терминал)
- Установка пакетов Debian через графический интерфейс пользователя (приложение Software Center и приложение GDebi).
Но прежде чем мы начнем наше руководство, давайте сначала убедимся, что у вас есть обновленная система Ubuntu, используя следующие две команды:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
Метод I: Установка пакетов Debian через командную строку
В методе командной строки мы будем использовать терминал для установки пакета Debian. В принципе, вы можете использовать терминал одним из двух методов:
В общем, если вы используете команду dpkg, вы можете использовать следующий формат команды:
sudo dpkg -i «пакет_debian.deb».
Где вам нужно заменить «пакет_debian.deb» на путь к вашему пакету Debian. Поэтому, например, для установки пакета ASC Music Debian вы используете команду, подобную следующей:
sudo dpkg -i Downloads/asc-music_1.3-4_all.deb
Наш второй метод работы с командной строкой — это использование команды GDebi. Если вы не установили GDebi в вашу систему, то используйте следующую команду для ее установки:
Далее, давайте воспользуемся командой GDebi для установки пакета Debian с помощью следующей команды:
sudo gdebi Downloads/asc-music_1.3-4_all.deb
Метод 2: Установка пакетов Debian через графический интерфейс пользователя
Самый простой метод установки пакета Debian — это использование графического интерфейса пользователя. Опять же, вы можете выбрать один из двух методов:
Установка пакета Debian с помощью Software Center
В этом методе мы будем использовать Software Center по умолчанию, который поставляется с Ubuntu. К счастью, здесь не так много шагов, вы просто дважды щелкаете на пакете, который вам нужно установить. Затем установите его через приложение Software Center. Давайте подробнее рассмотрим следующие шаги:
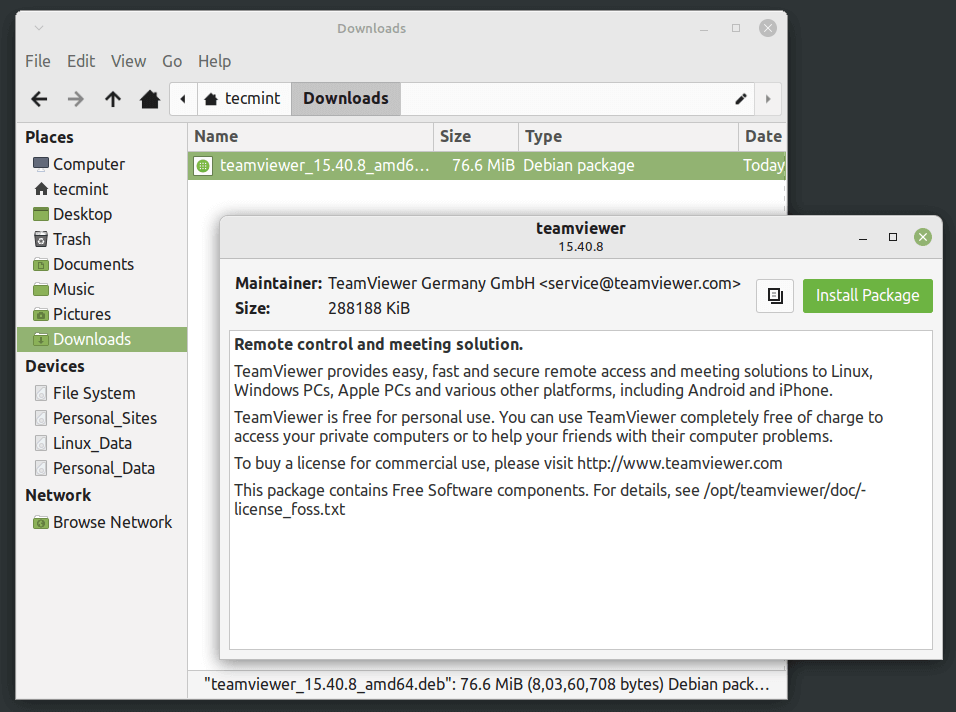
Шаг 1. Проверьте пакет Debian в каталоге Загрузки.
Дважды щелкните на пакете Debian.
Шаг 2. Как вы можете заметить, откроется Центр программного обеспечения. Теперь вы можете нажать кнопку Install, чтобы начать установку.
Шаг 3. Вам может потребоваться ввести пароль sudo для аутентификации. Как вы видите, установка пакета Debian продолжается.
После успешного завершения установки вы можете получить окно, как показано ниже, с кнопкой Remove. Кнопка Remove может быть использована для удаления пакета Debian из вашей системы.
Теперь вы должны были успешно установить пакет Debian.
Установка пакета Debian с помощью приложения GDebi
Во втором графическом методе мы можем использовать приложение GDebi. В этом методе у вас должен быть установлен пакет GDebi. Если он не установлен, вы можете использовать следующую команду для его установки:
Теперь давайте воспользуемся приложением GDebi.
Шаг 1. Сначала перейдите в каталог, где находится пакет Debian. Затем щелкните правой кнопкой мыши на пакете Debian и выберите «Открыть с помощью другого приложения».
Шаг 2. В меню рекомендуемых приложений выберите GDebi Package Installer. Затем нажмите кнопку «Выбрать».
Шаг 3. Приложение GDebi откроется и загрузит пакет Debian.
Шаг 4. После загрузки пакета Debian вы можете нажать кнопку Установить пакет, чтобы начать установку.
Шаг 5. Как вы можете заметить, панель установки находится внизу программы установки GDebi.
Шаг 6. После успешного завершения установки вы должны получить сообщение, как показано ниже.
Поздравляем, вы только что узнали несколько методов установки пакета Debian на вашу систему Ubuntu Linux. Это руководство должно работать на дистрибутивах Linux на базе Ubuntu, включая Linux Mint, elementary OS, Pop!_OS и других.
3 Command Line Tools to Install Deb Packages in Ubuntu
In this tutorial, you will learn how to install local software packages (.DEB) in Debian and its derivatives such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint using three different command line tools and they are dpkg, apt, and gdebi.
This is useful to those new users who have migrated from Windows to Ubuntu or Linux Mint. The very basic problem they face is installing local software on the system.
However, Ubuntu and Linux Mint have their own Graphical Software Center for easy software installation, but we will be looking forward to installing deb packages through the terminal way.
1. Install .deb Package Using dpkg Command
Dpkg is a package manager for Debian and its derivatives such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint. It is used to install, build, remove, and manage .deb packages. but unlike other Linux package management systems, it cannot automatically download and install packages with their dependencies.
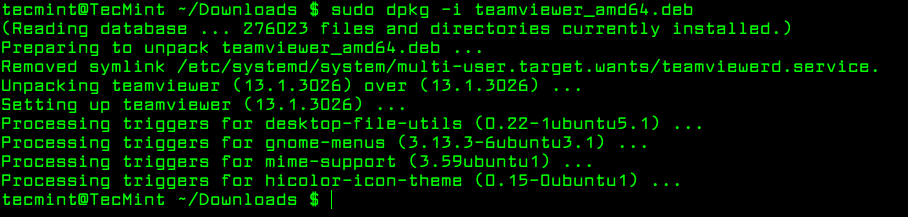
To install a .deb package, use the dpkg command with the -i flag along with the package name as shown.
$ sudo dpkg -i teamviewer_amd64.deb
If you get any dependency errors while installing or after installing and launching a program, you can use the following apt command to resolve and install dependencies using the -f flag, which tells the program to fix broken dependencies.
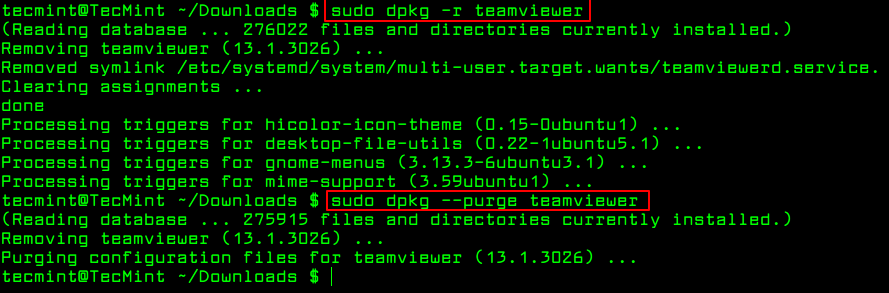
Remove Deb Packages Using dpkg Command
To remove a .deb package use the -r option or if you want to remove all its files including configuration files, you can purge it using the —purge option as shown.
$ sudo dpkg -r teamviewer [Remove Package] $ sudo dpkg --purge teamviewer [Remove Package with Configuration Files]
To know more about installed packages, read our article that shows how to list all files installed from a .deb package.
2. Install .deb Package Using Apt Command
The apt command is an advanced command-line tool, which offers new software package installation, existing software package upgradation, updating of the package list index, and even upgrading the whole Ubuntu or Linux Mint system.
It also offers apt-get and apt-cache command-line tools for managing packages more interactively on Debian and its derivatives such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint systems.
Essentially, apt-get or apt do not understand .deb files, they are designed to primarily handle package names (for example teamviewer, apache2, mariadb, etc..) and they retrieve and install .deb archives associated with a package name, from a source specified in the /etc/apt/sources.list file.
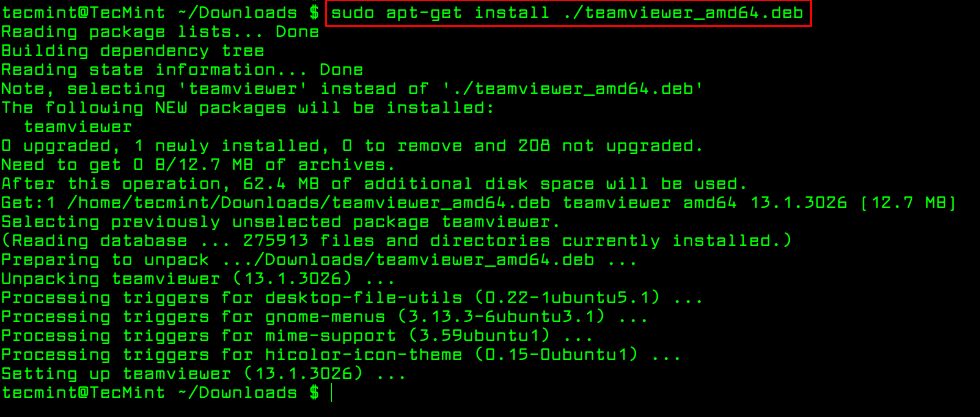
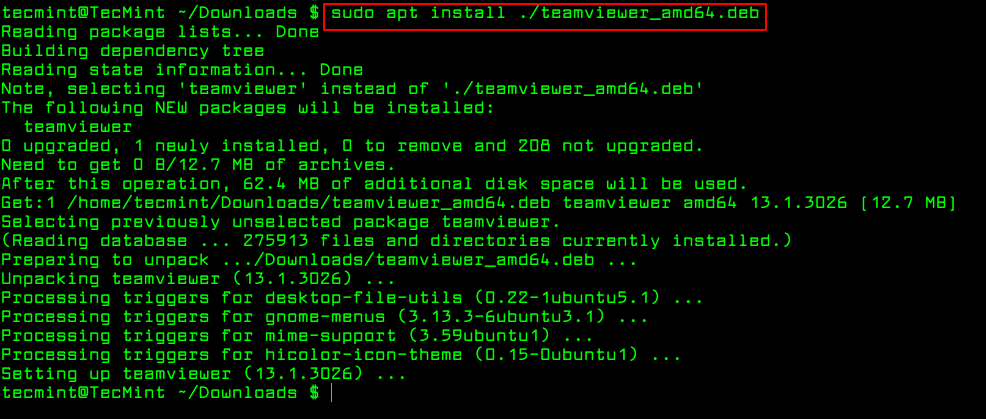
The only trick to installing a .deb Debian package using apt-get or apt is by specifying a local relative or absolute path ( ./ if in current dir) to the package, otherwise it will try to retrieve the package from remote sources and the operation will fail.
$ sudo apt install ./teamviewer_amd64.deb $ sudo apt-get install ./teamviewer_amd64.deb
Remove Deb Packages using apt Command
To remove a .deb package use the remove option or if you want to remove all its files including configuration files, you can purge it using the purge option as shown.
$ sudo apt-get remove teamviewer $ sudo apt-get purge teamviewer OR $ sudo apt remove teamviewer $ sudo apt purge teamviewer
3. Install .deb Package Using Gdebi Command
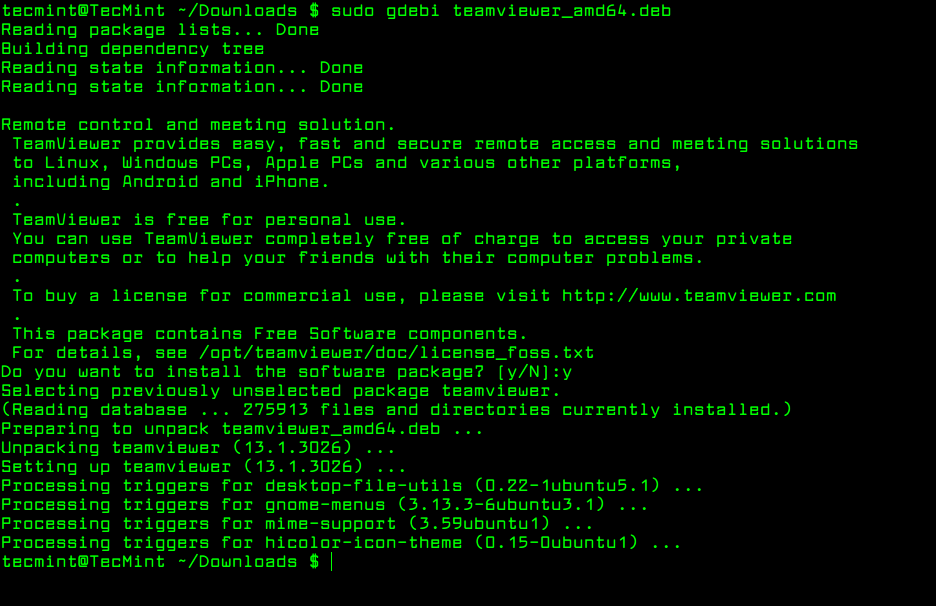
gdebi is a tiny command line and GUI tool for installing local deb packages. It resolves and installs package dependencies on the fly. To install a package, use the following command.
$ sudo gdebi teamviewer_13.1.3026_amd64.deb
To remove a .deb package installed from gdebi, you can use apt, apt-get or dpkg commands using purge option as shown.
$ sudo apt purge teamviewer OR $ sudo apt-get purge teamviewer OR $ sudo dpkg --purge teamviewer
Install .deb Packages Using Gdebi GUI
The most recommended way for beginners to installing .deb files is through the Gdebi GUI installer. Simply, go to the directory where you have downloaded the file and double-click to install it as shown.
That’s It! In this tutorial, we have explained three different command line tools for installing or removing .deb Debian packages in Ubuntu and Linux Mint.
If you know any other way of installing local packages, do share with us using our comment section below.
How to Install Deb Files in Ubuntu, Mint and Debian
Before we look at the different approaches to installing deb files on Ubuntu or Debian-based Linux distributions, we first need to understand them.
Debian, Ubuntu, and Linux Mint distributions support the use of a package file with a ‘.deb’ file extension, which contains the needed metadata, scripts, and files that are crucial in the installation and management of targeted Linux-supported software packages.
The Debian Project developed the ‘.deb’ file format as a standard software package distribution format. By conceptualizing a ‘control file‘, the targeted software package is enriched with metadata info like name, version, dependencies, and installation scripts associated with the software package in question.
Installing Deb Package on Ubuntu, Mint, and Debian
There is more than one approach to installing ‘.deb’ files on Ubuntu and Debian-based Linux distributions as explained in the following steps.
1. Using the ‘dpkg’ Command
The dpkg command is used to install, manage, and remove ‘.deb’ software packages along with their dependencies if any as shown.
The -i flag in the command above triggers the installation of the google-chrome .deb file.
Once installed, you can confirm the installed version of the ‘.deb’ software package using the dpkg-query command.
$ sudo dpkg-query -l google-chrome-stable
2. Using the apt Command
The apt command is effective in managing packages (install, upgrade, and remove) since it is the default package manager. This approach of installing a ‘.deb’ file automatically caters to the download and installation of missing dependencies. Also, ‘.deb’ packages installed via this approach are automatically upgraded during the next system update.
To install a ‘.deb’ file using ‘apt’, implement the following command:
Once installed, you can confirm the installed version of the ‘.deb’ software package using the apt command.
$ sudo apt list -a google-chrome-stable
3. Using a Graphical Package Manager
A Graphical Package Manager is an ideal alternative to install Deb files on Ubuntu and Debian-based systems. Their user-friendly interface makes it easy to install, manage, and upgrade packages as shown.
To install Deb packages via the default Graphical Package Manager, consider the following installation steps:
Right-click on the targeted ‘.deb’ file.
Select the ‘Open With Other Application‘ option and choose the ‘Software Install‘ option.
Next, click on the ‘Select‘ button and wait for the application details to load. You should see an ‘install‘ button for installing the selected software package.
Click on it and provide a Sudoer user password for the installation to proceed.
After a while, the software package should be installed.
Remove Deb Packages in Ubuntu, Mint, and Debian
Before uninstalling a ‘.deb’ file, we need to be certain of its exact program name. For instance, for Google Chrome, we will run the following command:
From the above output, we can use the exact program name for Google Chrome (google-chrome-stable) software to uninstall it if necessary.
Remove Deb File with Configuration Files
Fully uninstall a Deb file together with its configuration files using the dpkg or apt command.
$ sudo dpkg -P google-chrome-stable OR $ sudo apt purge google-chrome-stable
Remove Deb File without Configuration Files
To uninstall a Deb file without removing configuration files, use the dpkg or apt command.
$ sudo dpkg -r google-chrome-stable OR $ sudo apt remove google-chrome-stable
Conclusion
The ‘.deb’ file format plays a crucial role in Debian-based distributions such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint. For instance, its existence makes it convenient and efficient to distribute and install targeted software packages on these systems.
If you have any questions on how to install and remove Deb files on Debian-based distributions, feel free to leave a comment.